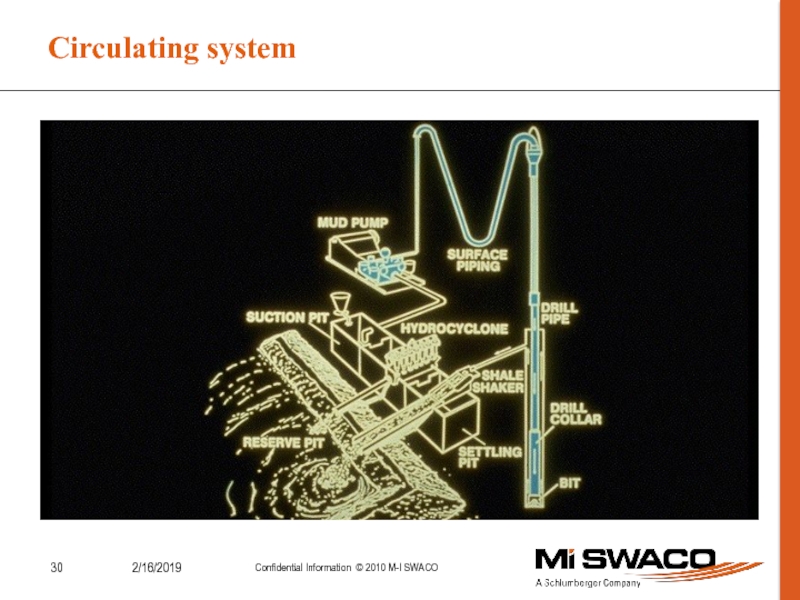
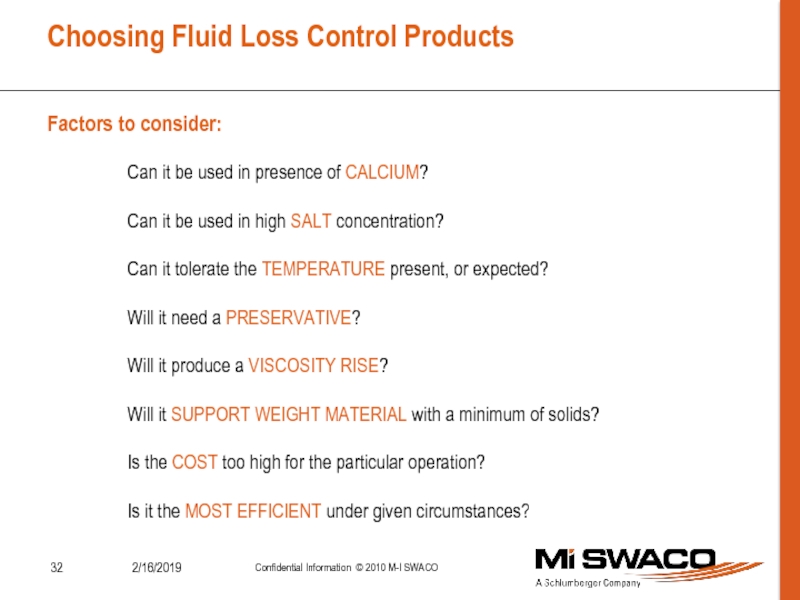
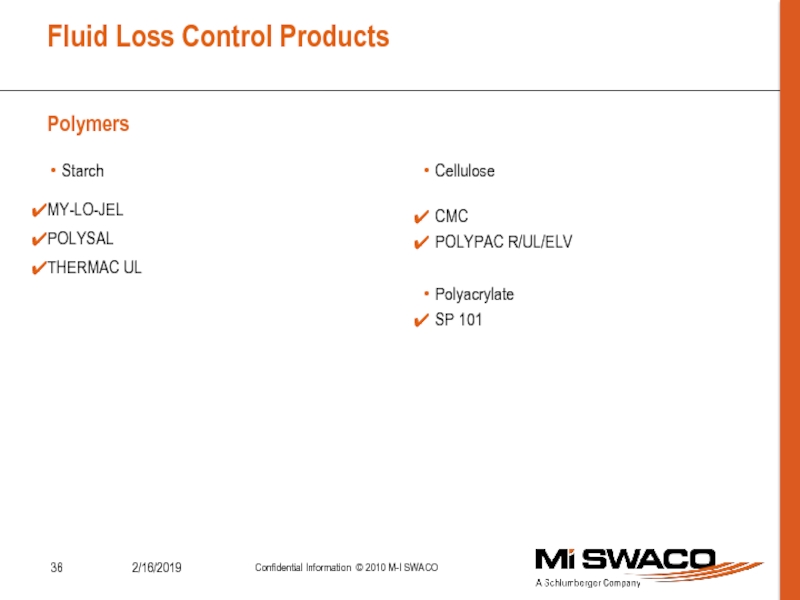
Control Formation Pressure.
3. Suspend And Release Cuttings.
4. SEAL PERMEABLE FORMATIONS.5. MAINTAIN WELLBORE STABILITY.
6. MINIMIZE RESERVOIR DAMAGE.
7. Cool, Lubricate And Support The Bit And Drilling Assembly.
8. Transmit Hydraulic Energy To Tools And Bit.
9. ENSURE ADEQUATE FORMATION EVALUATION.
10. Control Corrosion.
11. FACILITATE CEMENTING AND COMPLETION.
12. Minimize Impact On Environment.
13. Prevent Gas Hydrate Formation.
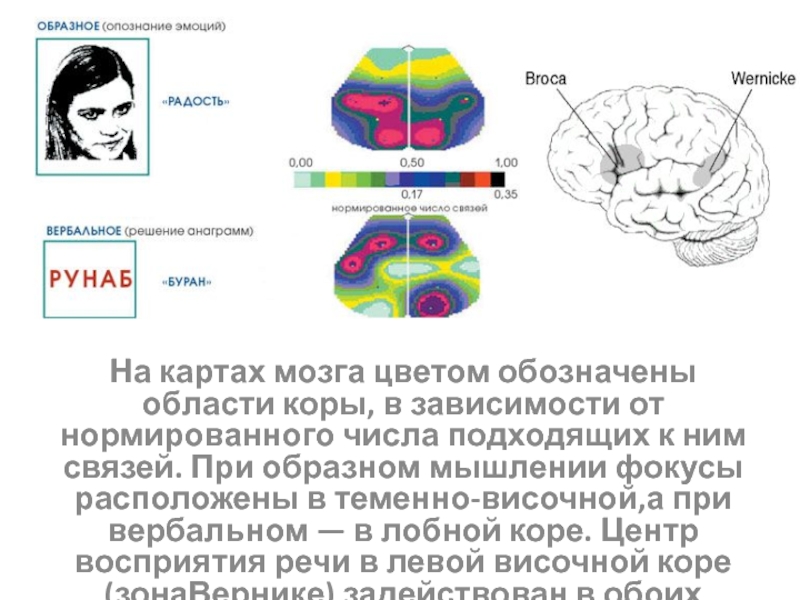
The functions of drilling fluids