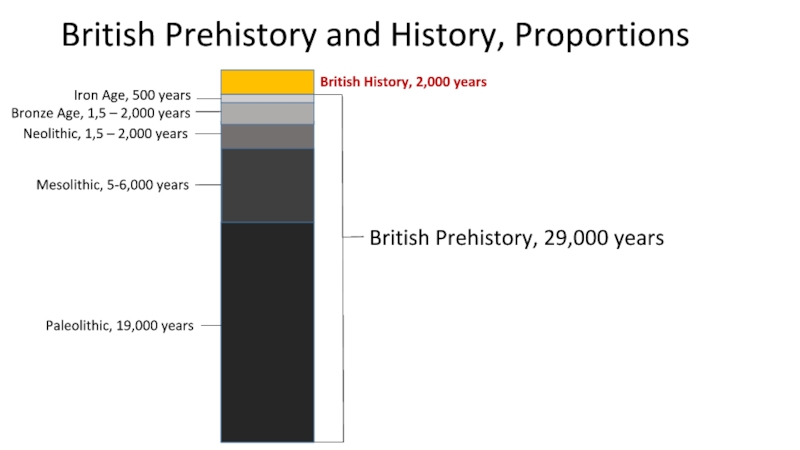
years
Paleolithic, 19,000 years
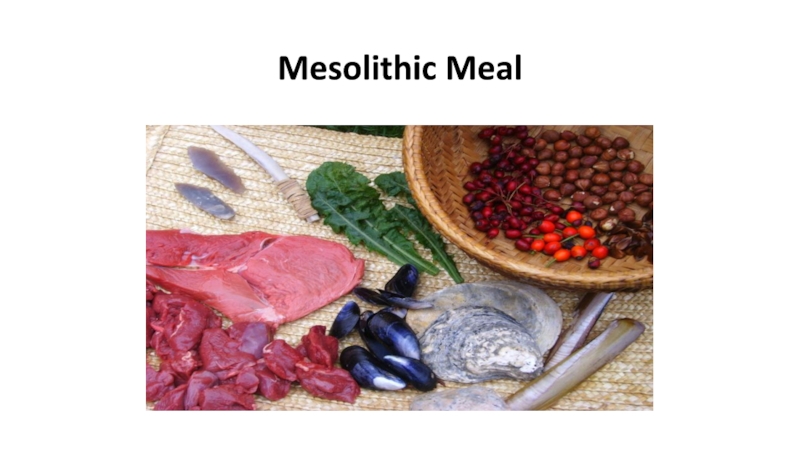
Mesolithic, 5-6,000 years
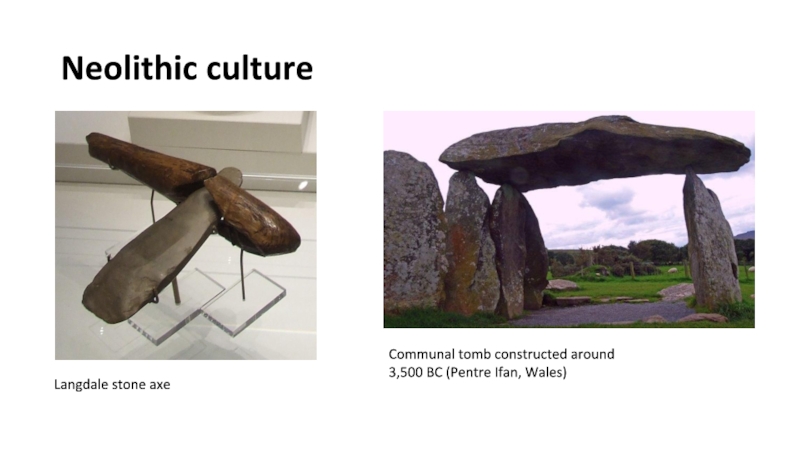
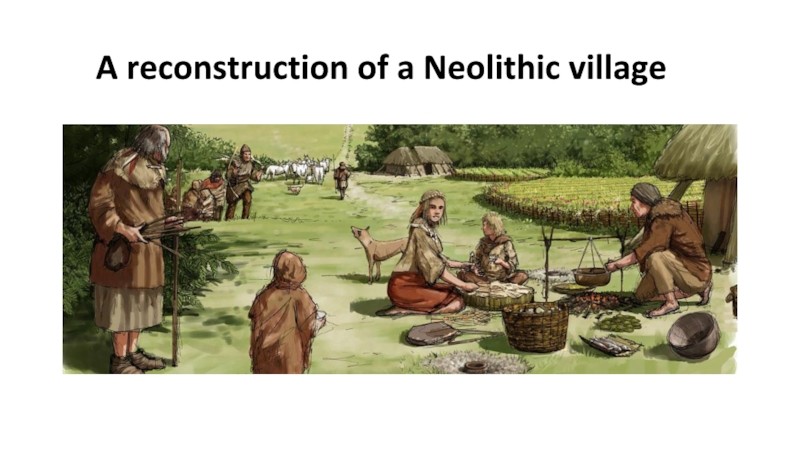
Neolithic, 1,5 – 2,000 years
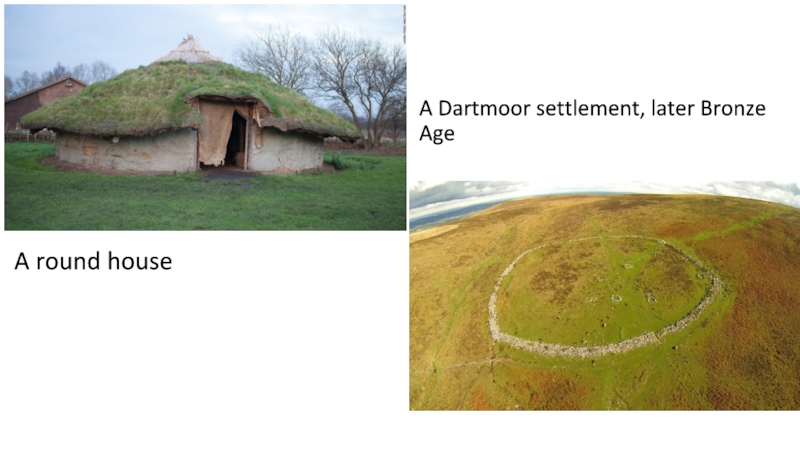
Bronze Age,
1,5 – 2,000 yearsIron Age, 500 years