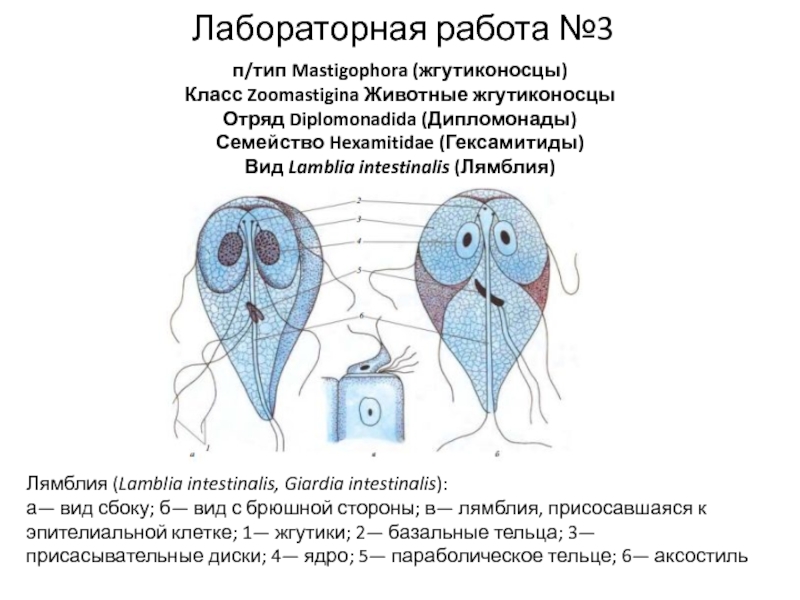
Слайд 1G11.4B – Evolution I Antibiotic Resistance
Evidence for change within populations
Learning
Objectives
11.2.6.1 Analyze the evidence for evolution
Success Criteria
1. Name
and describe three examples of evidence of evolution.
2. Explain how to test for antibiotic resistance.
3. Explain results of antibiotic resistance test.
CIE Biology Jones
p402 to 418
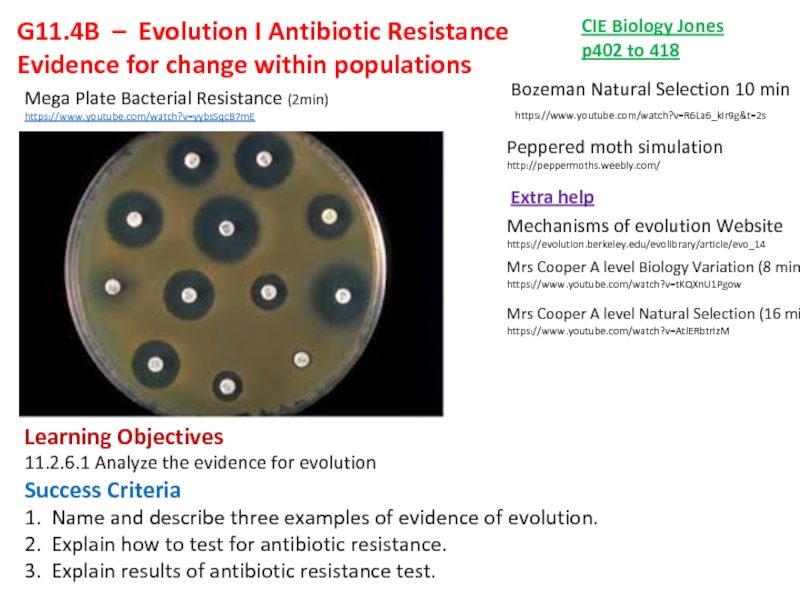
Mega Plate Bacterial Resistance (2min)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yybsSqcB7mE
Mrs Cooper A level Biology Variation (8 min) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tKQXnU1Pgow
Mrs Cooper A level Natural Selection (16 min )
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AtlERbtrIzM
Peppered moth simulation
http://peppermoths.weebly.com/
Bozeman Natural Selection 10 min
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R6La6_kIr9g&t=2s
Mechanisms of evolution Website https://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/evo_14
Extra help
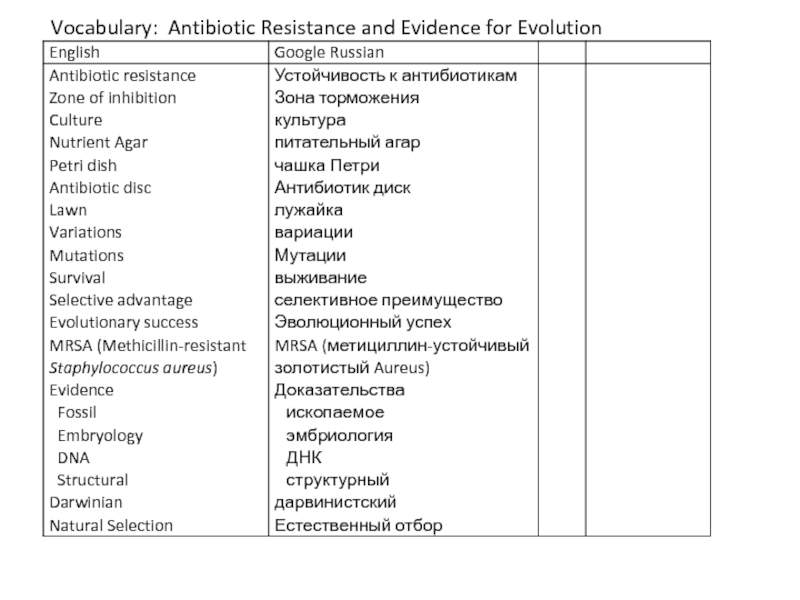
Слайд 3Vocabulary: Antibiotic Resistance and Evidence for Evolution
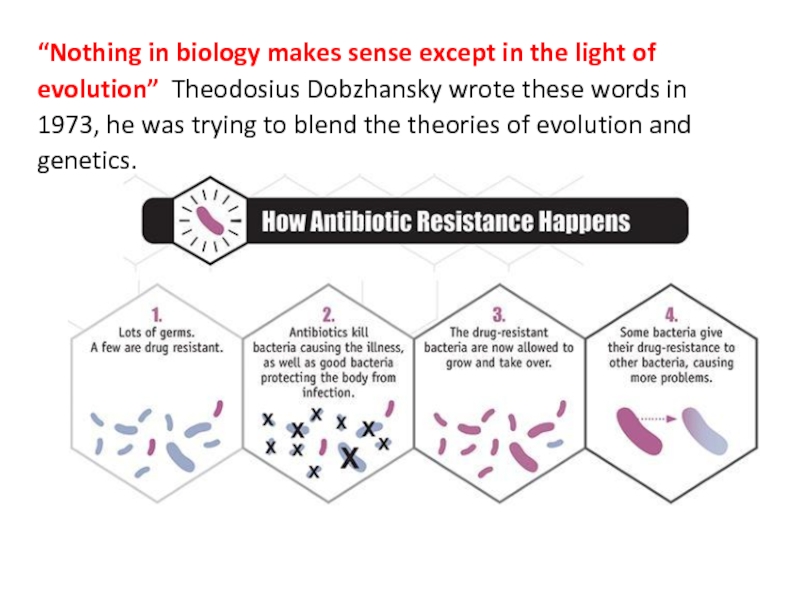
Слайд 4“Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of
evolution” Theodosius Dobzhansky wrote these words in 1973, he was
trying to blend the theories of evolution and genetics.
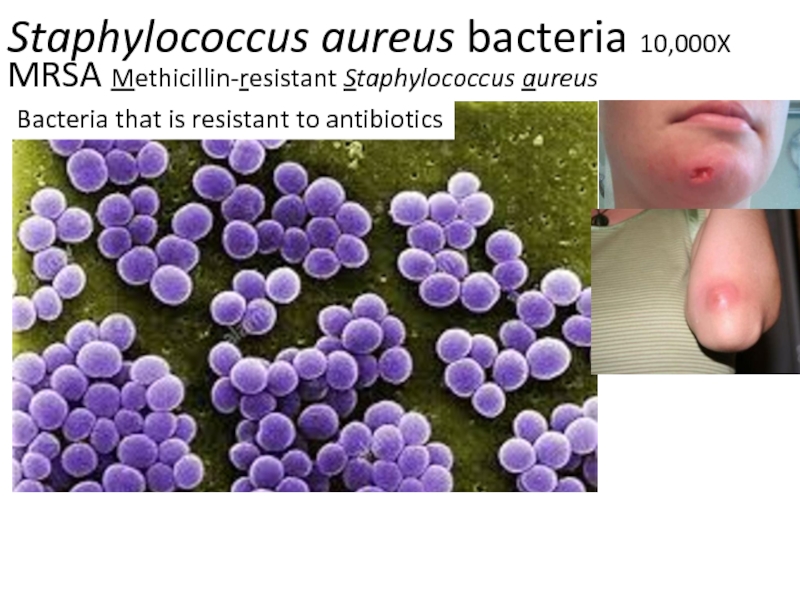
Слайд 5Staphylococcus aureus bacteria 10,000X
MRSA Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Bacteria that is resistant
to antibiotics
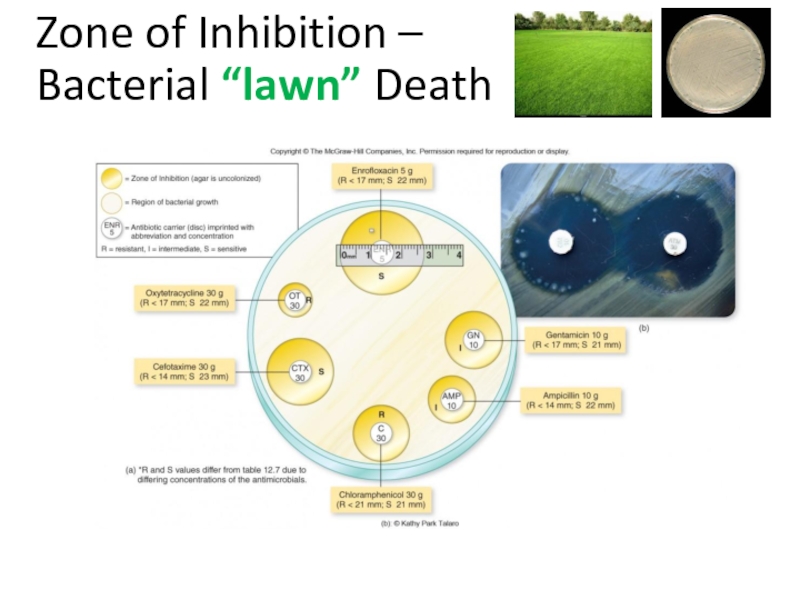
Слайд 6Zone of Inhibition –
Bacterial “lawn” Death
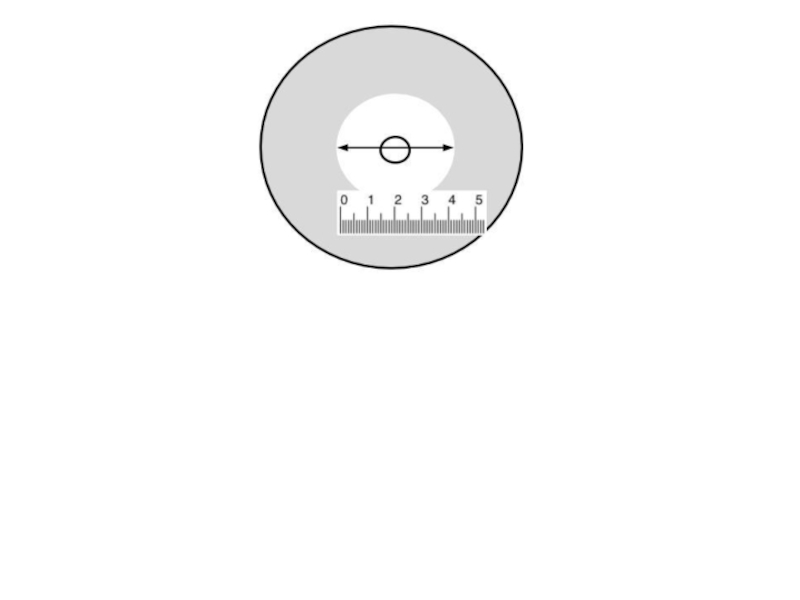
Слайд 7Kirby Bauer Assay
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BXr_kcki4Ag
Time Lapse 1 min
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-L4MeZBtvXM
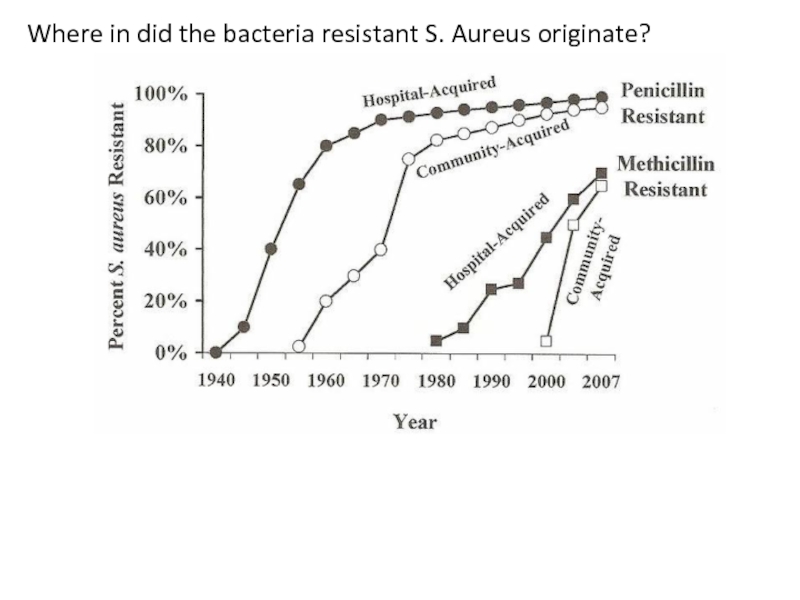
Слайд 8Where in did the bacteria resistant S. Aureus originate?
Слайд 11Explain two examples of evolution in response to environmental change.
Ask yourself “What is the…”
Example 1: Staphylococcus aureus (associated with a
variety of conditions, including skin and lung infections)
Variation: Antibiotic resistance (some strains have a drug-resistant gene ; other strains do not)
Environmental change: Exposure to antibiotic (methicillin)
Response: Methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA) die, whereas methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) survive and can pass ontheir genes
Evolution: Over time, the frequency of antibiotic resistance in the population increases (drug-resistant gene can also be transferred by conjugation)
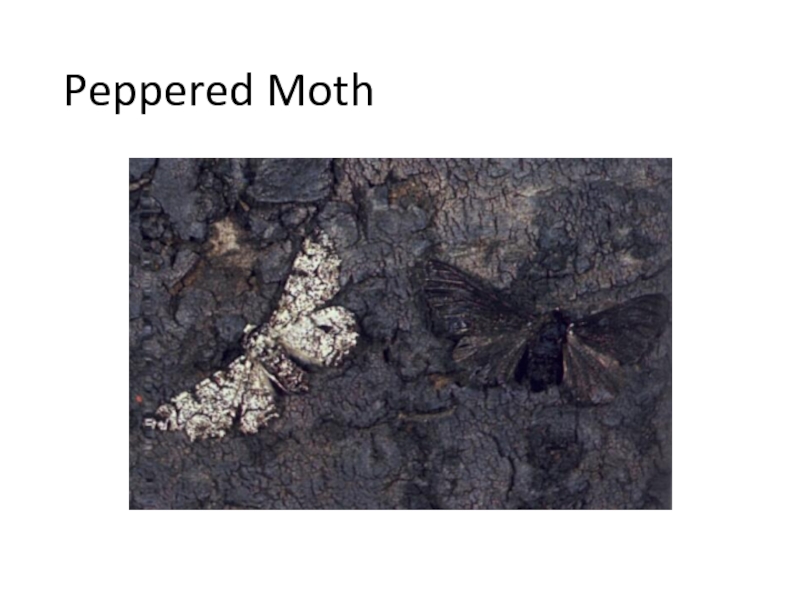
Example 2: Peppered Moth (Biston betularia)
Variation: Colouration (some moth have a light colour, while others are a darker melanic colour)
Environmental change: Pollution from industrial activities caused trees to blacken with soot during the Industrial Revolution
Response: Light coloured moths died from predation, whereas melanic moths were camouflaged and survived to pass on their genes
Evolution: Over time, the frequency of the melanic form increased (with improved industrial practices, the lighter variant has become more common)

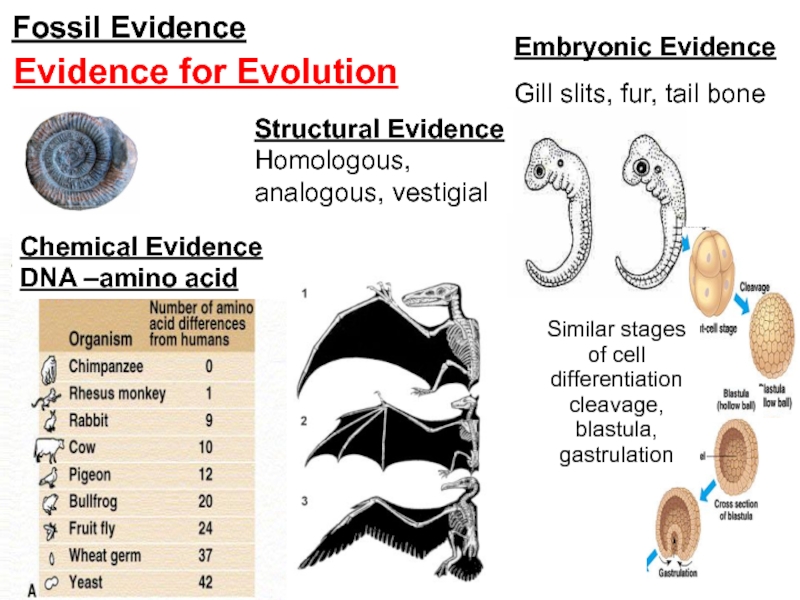
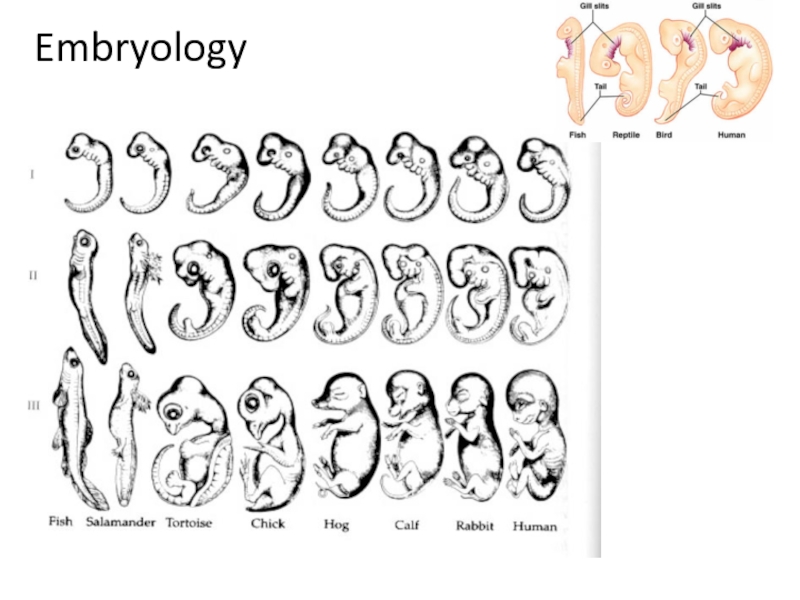
Слайд 14Fossil Evidence
Embryonic Evidence
Gill slits, fur, tail bone
Similar stages of cell
differentiation cleavage, blastula, gastrulation
Evidence for Evolution
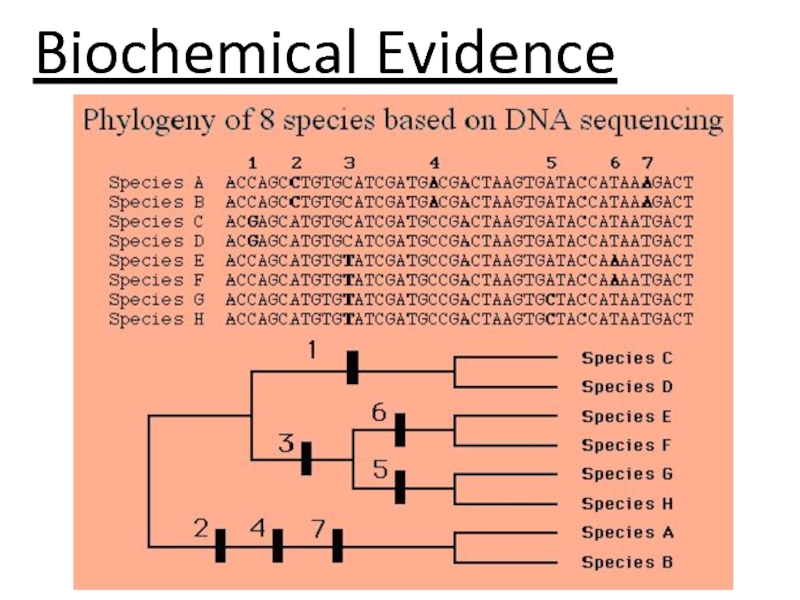
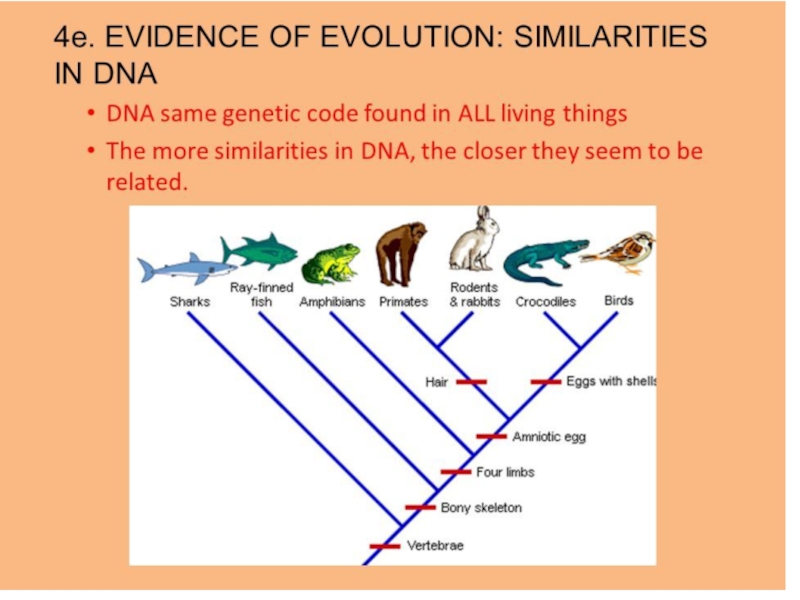
DNA evidence
Chemical Evidence
DNA –amino acid
Structural
Evidence
Homologous, analogous, vestigial
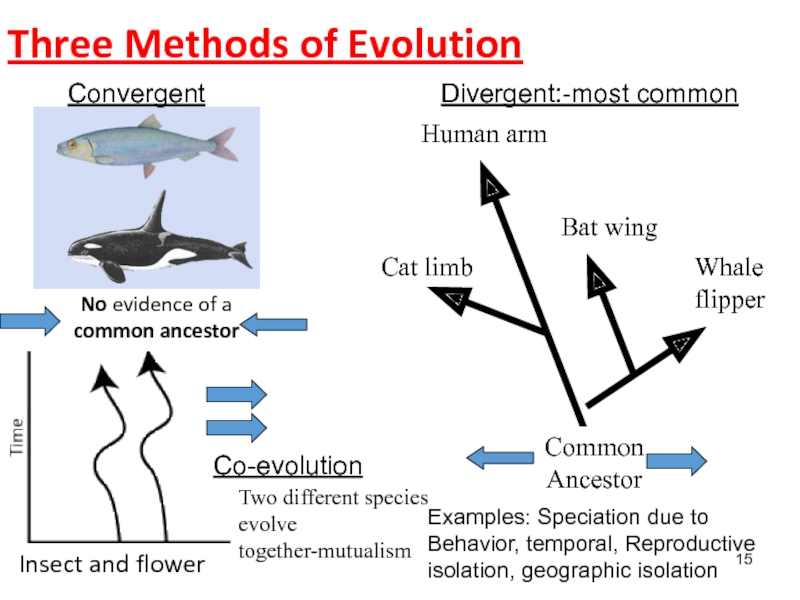
Слайд 15Three Methods of Evolution
Common
Ancestor
Whale flipper
Human arm
Bat wing
Cat limb
Divergent:-most common
Convergent
No evidence of a
common ancestor
Co-evolution
Two different species evolve together-mutualism
Examples:
Speciation due to
Behavior, temporal, Reproductive isolation, geographic isolation
Insect and flower
Слайд 16Fossils
Are the preserved remains or traces of animals, plants, and other organisms
from the remote past.
ammonite
Priscacara liops;
Green River, WY
Mermaid Fossil
Types
of Fossils
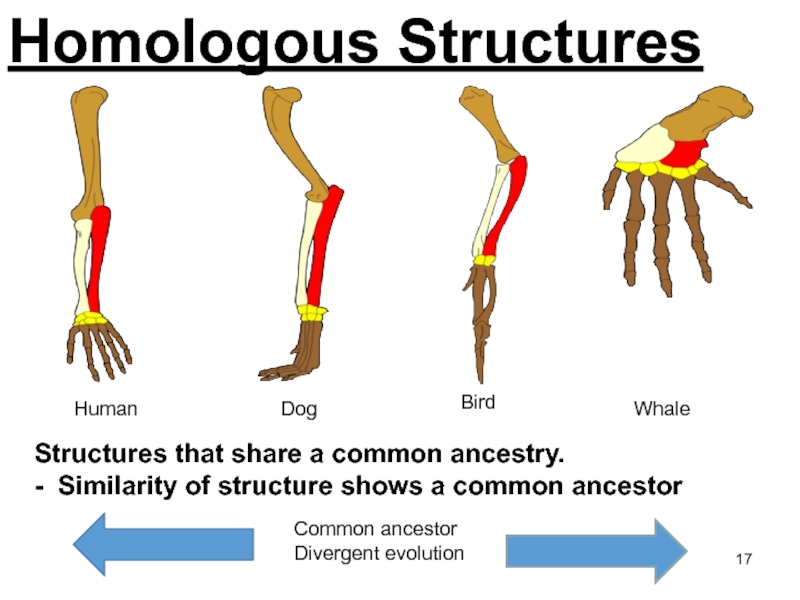
Слайд 17Homologous Structures
Structures that share a common ancestry.
- Similarity of
structure shows a common ancestor
Common ancestor
Divergent evolution
Human
Dog
Bird
Whale
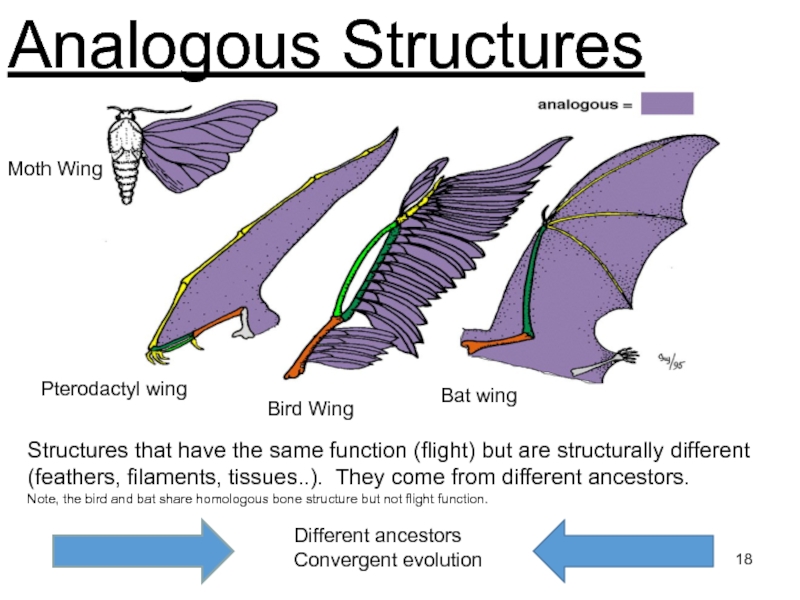
Слайд 18Analogous Structures
Structures that have the same function (flight) but are
structurally different (feathers, filaments, tissues..). They come from different ancestors.
Note, the bird and bat share homologous bone structure but not flight function.
Moth Wing
Bird Wing
Pterodactyl wing
Bat wing
Different ancestors
Convergent evolution
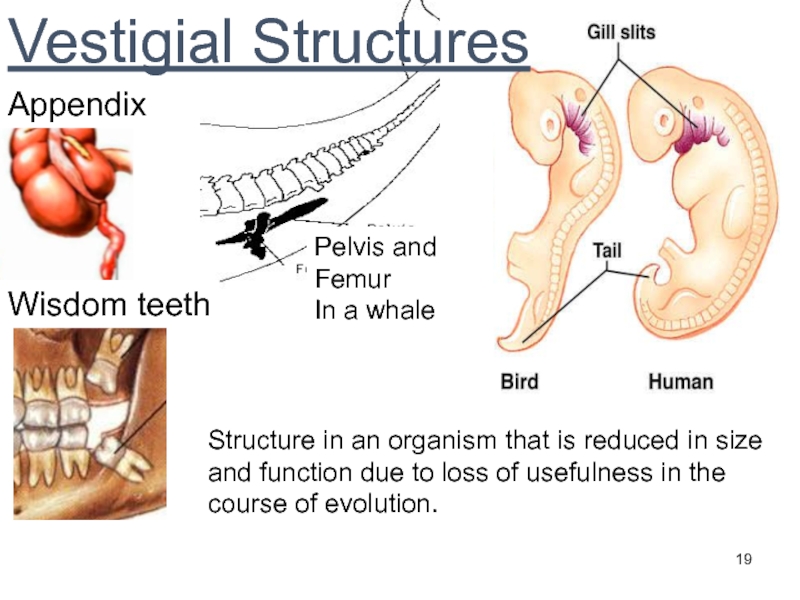
Слайд 19Wisdom teeth
Appendix
Vestigial Structures
Structure in an organism that is reduced in
size and function due to loss of usefulness in the
course of evolution.
Pelvis and
Femur
In a whale
Слайд 23Evolution II
Learning Objectives
Explain the relationship between genetic variability and
evolution
Classify the main mechanisms of speciation
Know the factors affecting the
frequency of alleles
Слайд 24Evolution
Learning Objectives
Explain the relationship between genetic variability and evolution
-To
study the inheritance of a trait, we study and individual.
-To
study the genetic frequency of alleles, we study a population.
-This study of a population is called the measurement of variability.
-A population with high genetic variability has more evolutionary success, where as a population with low genetic diversity has a low evolutionary success and could quickly reach extinction if there is a change in the environmental condtions.
Classify the main mechanisms of speciation
Know the factors affecting the frequency of alleles
Слайд 25Species
A single group of organisms that are closely related and
can mate to reproduce fertile offspring.
Barn Owls
Geese
Swans
Turtle Doves
Sea Horses
All examples
show are species that have the same mate for life.
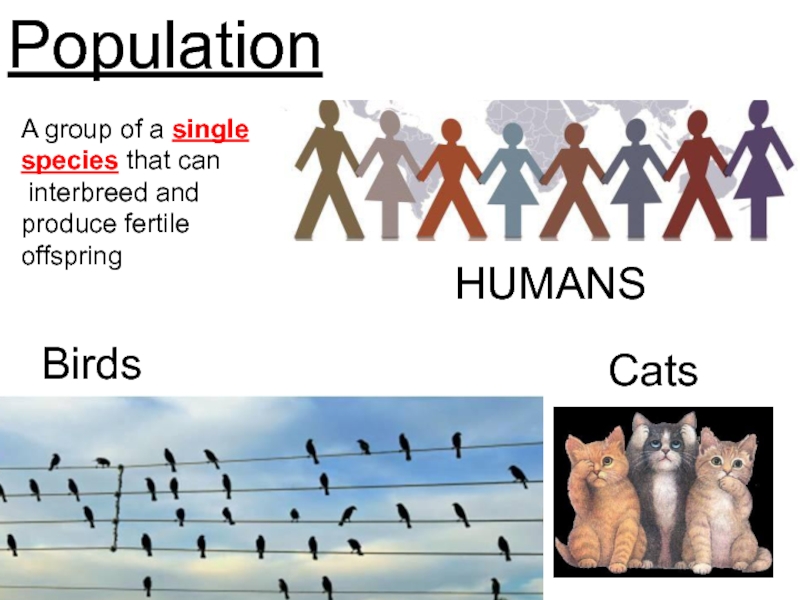
Слайд 26Population
HUMANS
A group of a single
species that can
interbreed and
produce fertile
offspring
Birds
Cats
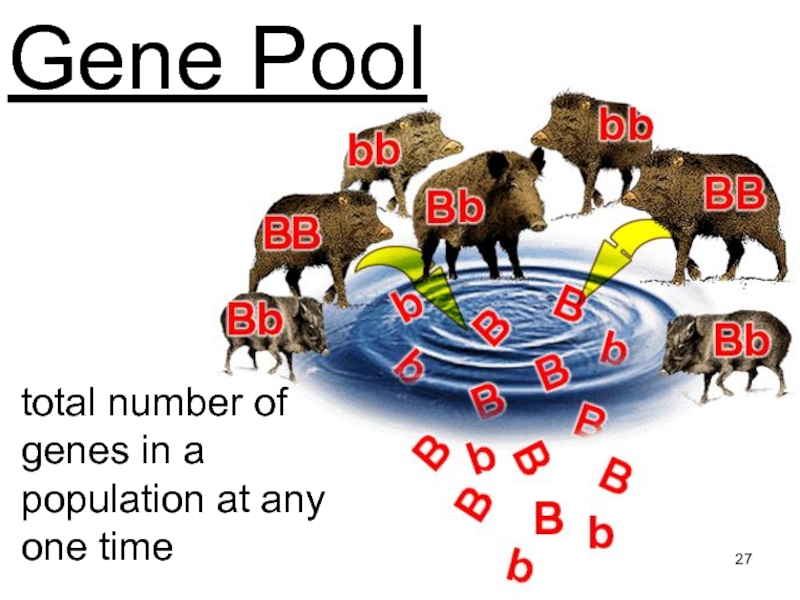
Слайд 27Gene Pool
total number of genes in a population at any
one time
Слайд 28Vocabulary: Variation, speciation, frequency
Explain the relationship between genetic variability
and evolution
Слайд 29What is Natural Selection?
1. Revise natural selection and variation,
how it leads to adaptations, and to how it leads
to changes in allelic frequency and finally speciation. Hardy Weinburg introduced
What is natural selection?
What is variation?
How does variation lead to adaptations?
How does it lead to variation in allelic frequency.
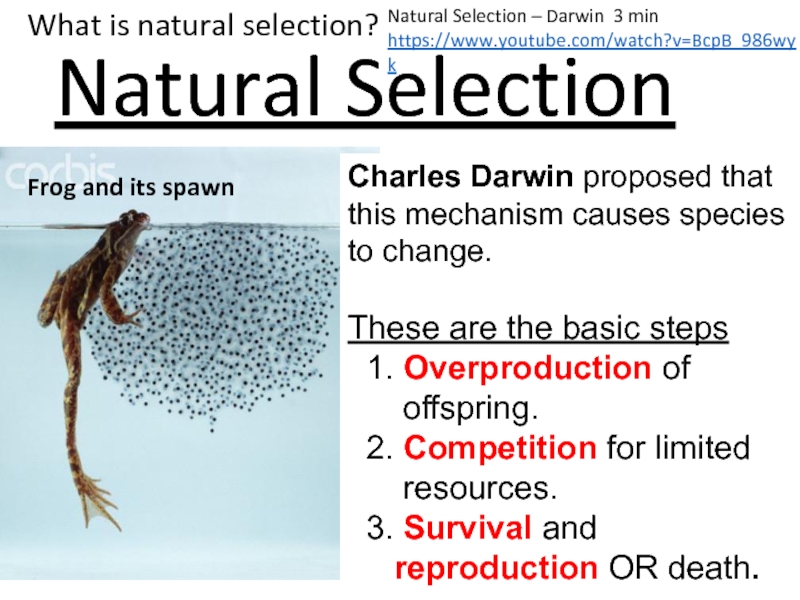
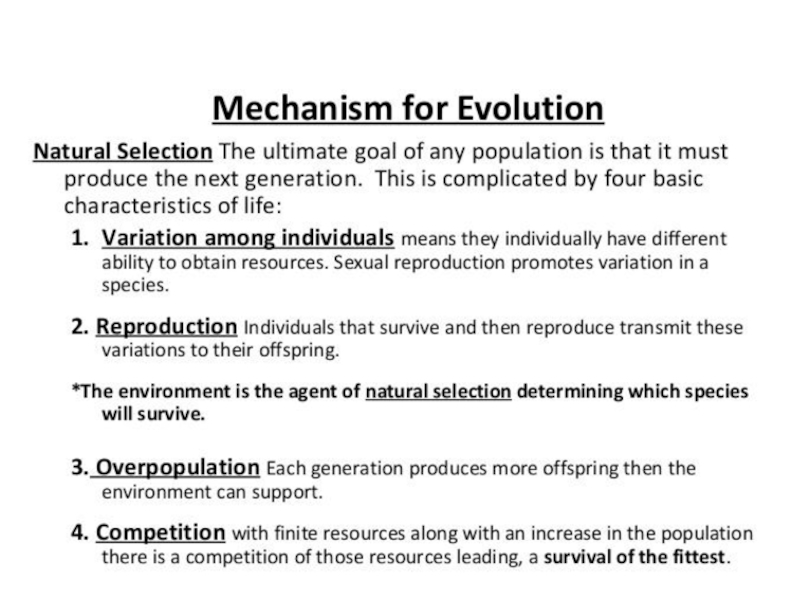
Слайд 30Natural Selection
Frog and its spawn
Charles Darwin proposed that this mechanism
causes species to change.
These are the basic steps
1.
Overproduction of
offspring.
2. Competition for limited
resources.
3. Survival and
reproduction OR death.
What is natural selection?
Natural Selection – Darwin 3 min https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BcpB_986wyk
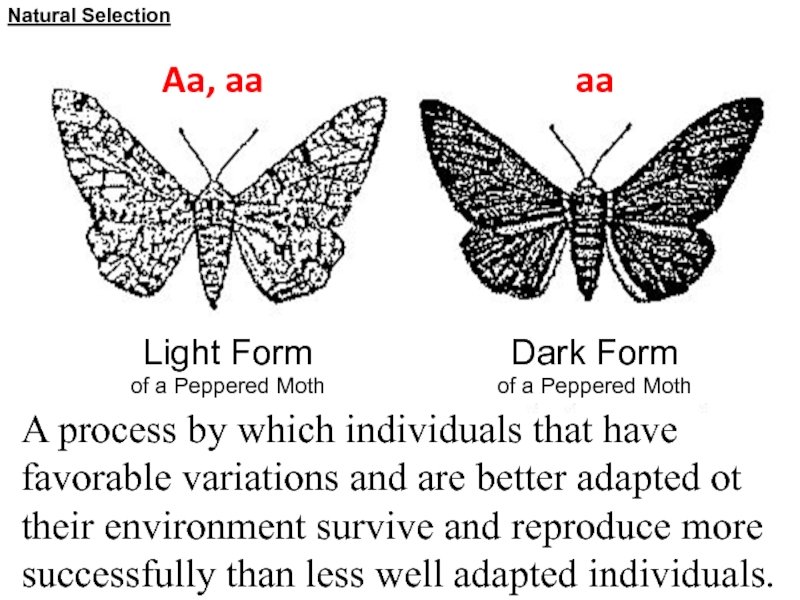
Слайд 31Natural Selection
A process by which individuals that have favorable variations
and are better adapted ot their environment survive and reproduce
more successfully than less well adapted individuals.
Light Form
of a Peppered Moth
Dark Form
of a Peppered Moth
Aa, aa
aa
Слайд 32Diversity
The number of different variations one species in a found
in community.
Tree frog diversity within the species Philautus found in
Western Ghats, India
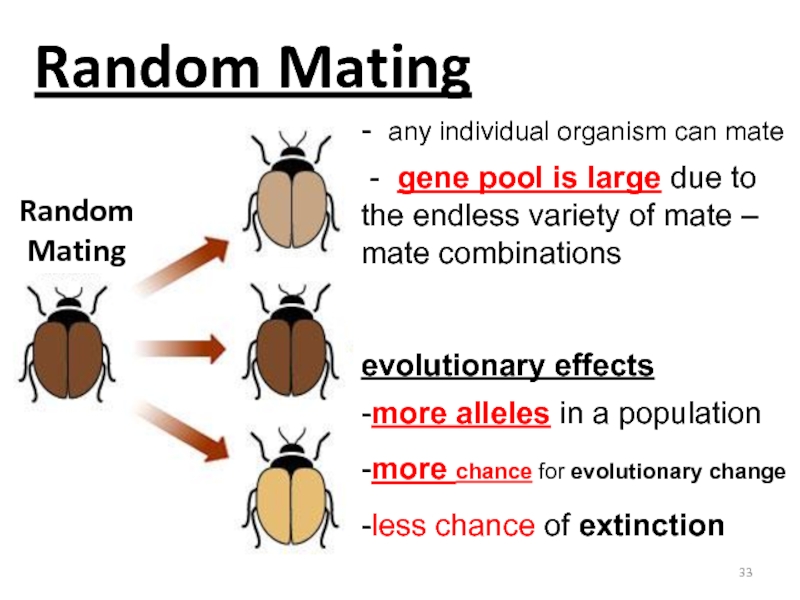
Слайд 33Random Mating
Random
Mating
Non- Random
Mating
- any individual organism can mate
- gene pool is large due to the
endless variety of mate – mate combinations
evolutionary effects
-more alleles in a population
-more chance for evolutionary change
-less chance of extinction
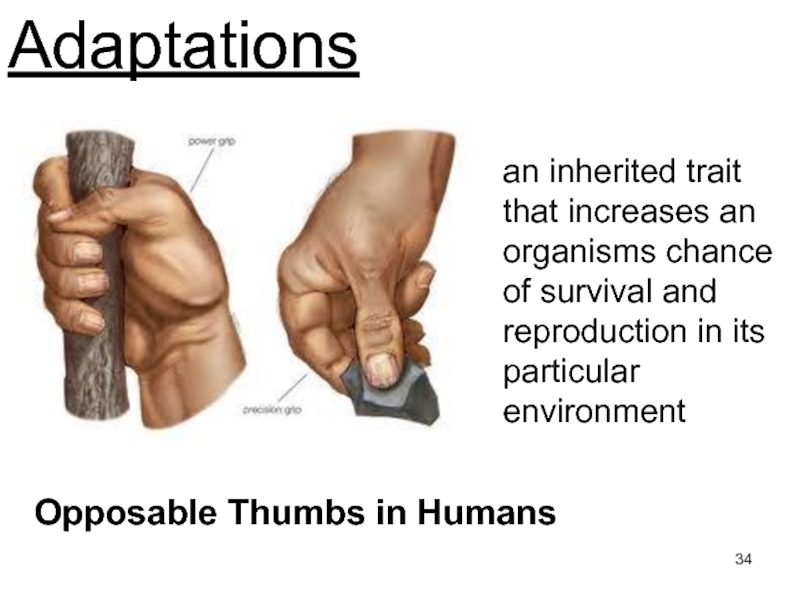
Слайд 34Adaptations
Opposable Thumbs in Humans
an inherited trait that increases an organisms
chance of survival and reproduction in its particular environment
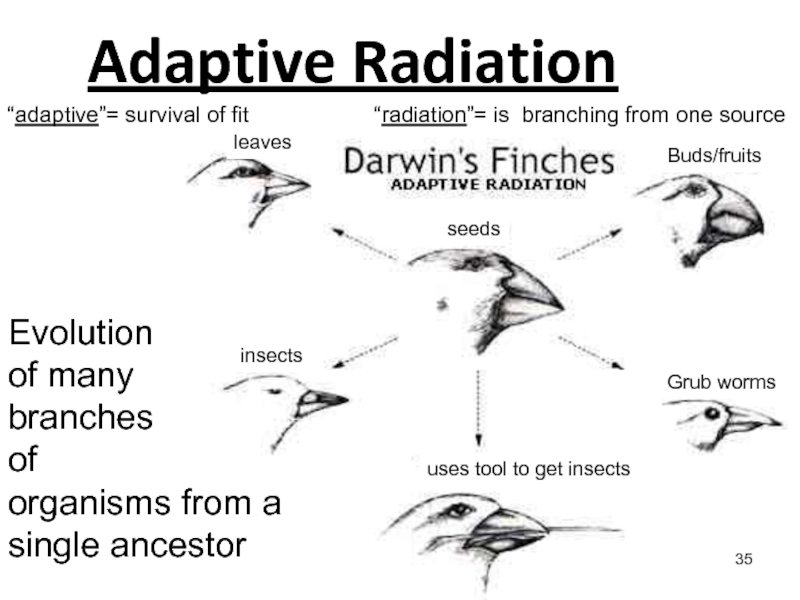
Слайд 35Adaptive Radiation
“radiation”= is branching from one source
“adaptive”= survival of
fit
leaves
seeds
Buds/fruits
Grub worms
uses tool to get insects
insects
Evolution
of many
branches
of
organisms from a
single ancestor
Слайд 361 - What are sources of variation?
-How does it lead
to adaptations?
-What is survival of the fittest? Give some examples.
-What
are the properties of Natural Selection?
How does it influence variation?
How does it influence allelic frequency
-What are the links between genetic variability and evolution?
-What are the types of speciation?
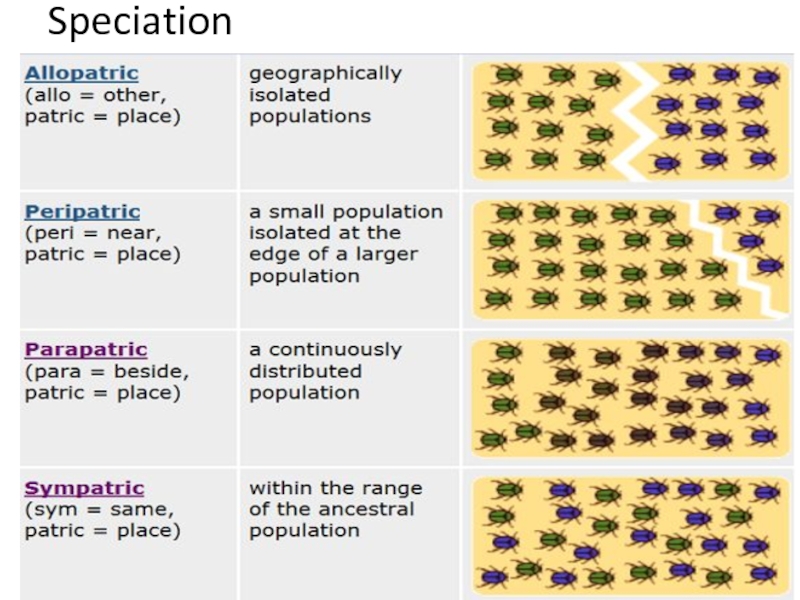
Слайд 372-What are the types of speciation?
Sympatric speciation
Allopatric speciation
Peripatric speciation
Parapatric speciation
Слайд 38Species
A group of organisms that are closely related and can
mate to reproduce fertile offspring.
Barn Owls
Geese
Swans
Turtle Doves
Sea Horses
All examples show
are species that have the same mate for life.
Слайд 39Horse X Zebra = Zorse
Hybrid
The offspring of two animals or
plants of different breeds, varieties, or species.
Usually infertile, sterile.
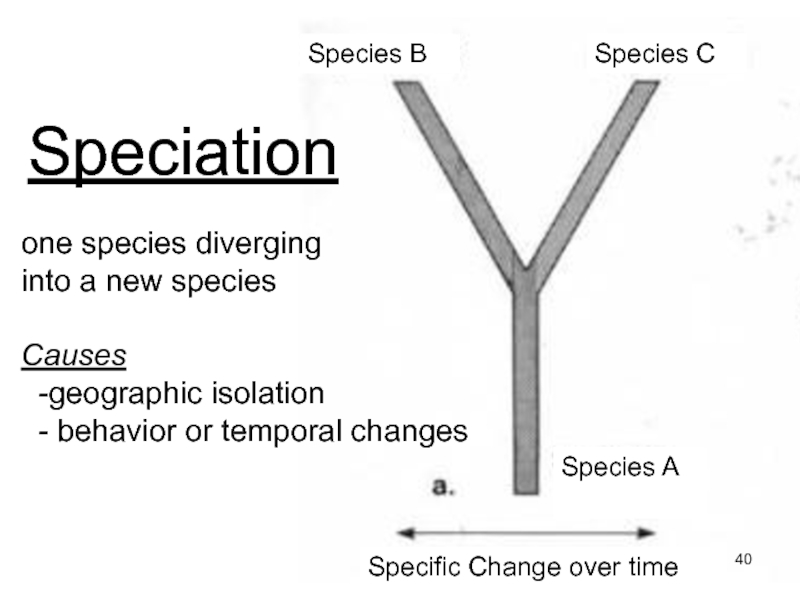
Слайд 40Speciation
one species diverging
into a new species
Causes
-geographic isolation
- behavior or temporal changes
Species B
Species C
Species A
Specific Change over
time
Слайд 41Speciation
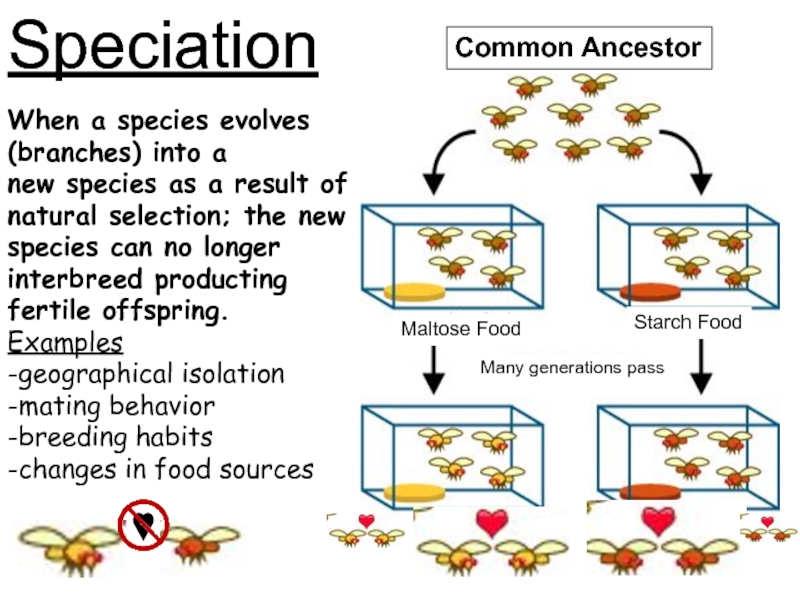
Common Ancestor
When a species evolves
(branches) into a
new species as a
result of natural selection; the new species can no longer
interbreed producting fertile offspring.
Examples
-geographical isolation
-mating behavior
-breeding habits
-changes in food sources
Maltose Food
Starch Food
Many generations pass
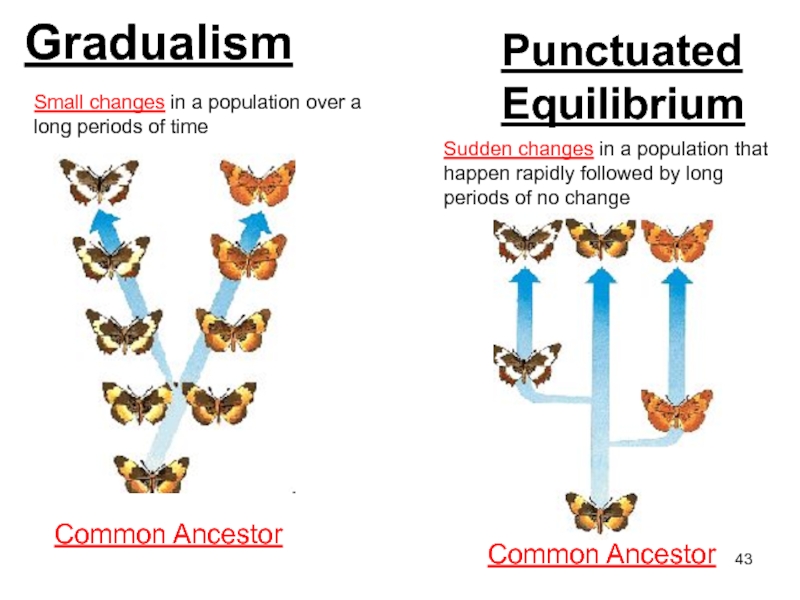
Слайд 43Gradualism
Common Ancestor
Small changes in a population over a long
periods of time
Punctuated
Equilibrium
Sudden changes in a population that happen
rapidly followed by long periods of no change
Common Ancestor
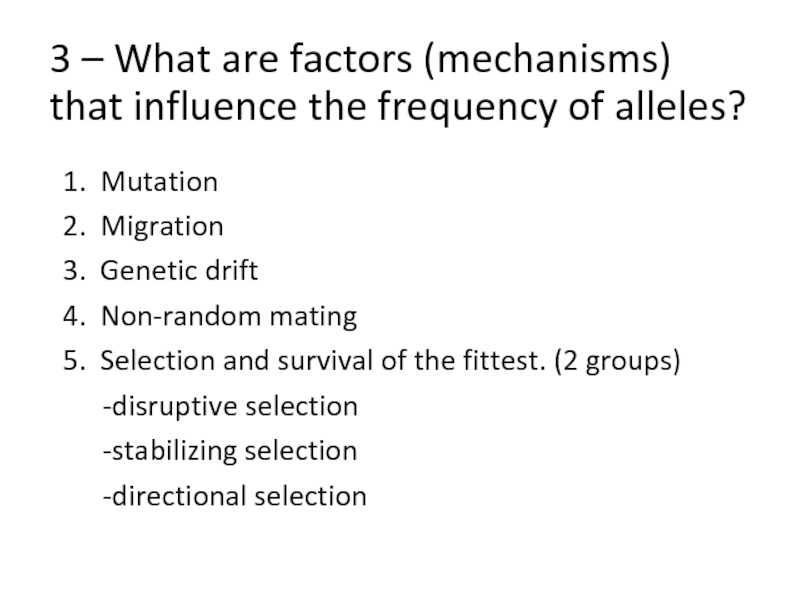
Слайд 443 – What are factors (mechanisms) that influence the frequency
of alleles?
1. Mutation
2. Migration
3. Genetic drift
4. Non-random mating
5. Selection
and survival of the fittest. (2 groups)
-disruptive selection
-stabilizing selection
-directional selection
Слайд 453 - Investigate one factor affecting the frequency of alleles
Criteria
Clear use of terminology
Mechanism explained in your own words
Example
of the factor
Picture of the factor
Слайд 46Gene Mutation
A change in the DNA. This can cause VARIATIONS
in individuals which can be passed to their offspring. Over
time mutations can change a population
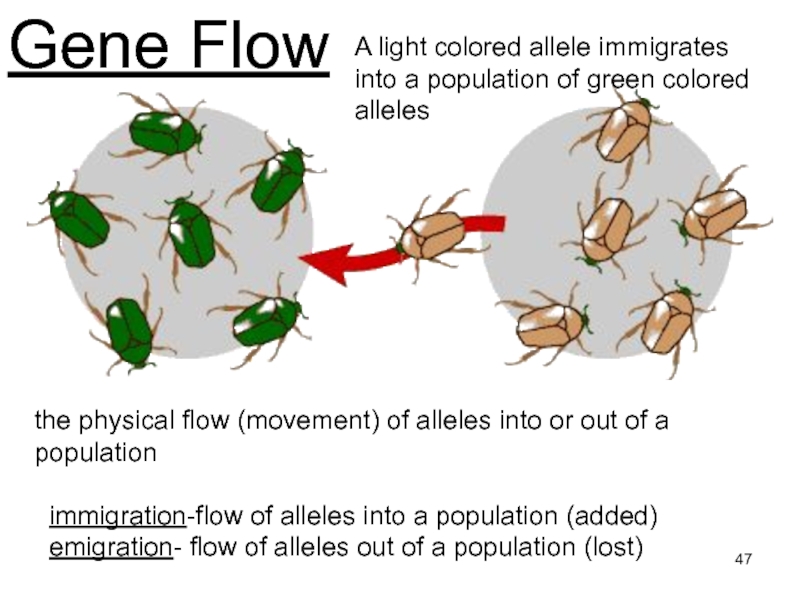
Слайд 47Gene Flow
A light colored allele immigrates into a population of
green colored alleles
the physical flow (movement) of alleles into or
out of a population
immigration-flow of alleles into a population (added)
emigration- flow of alleles out of a population (lost)
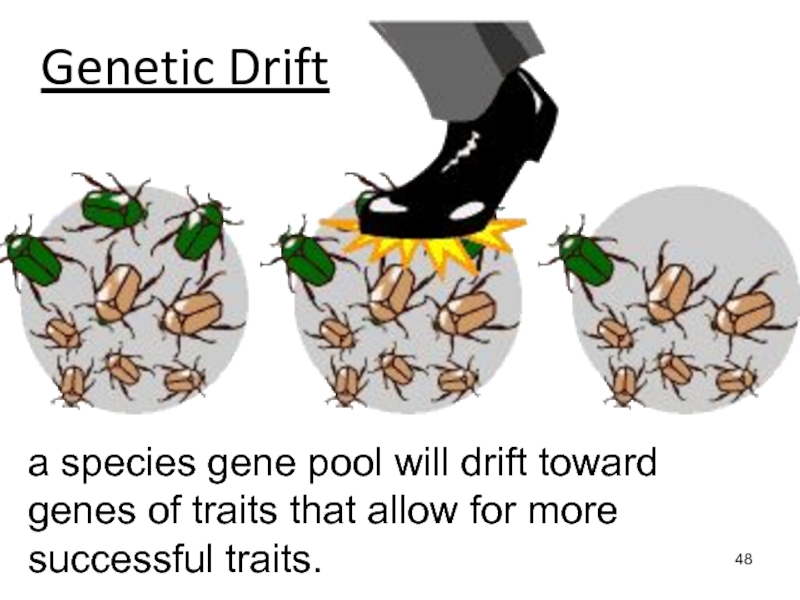
Слайд 48Genetic Drift
a species gene pool will drift toward genes of
traits that allow for more successful traits.
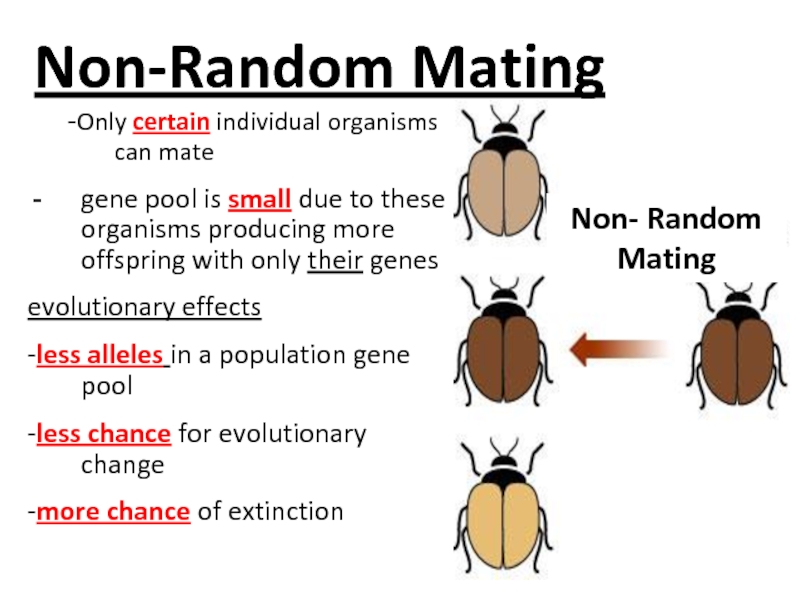
Слайд 49Non-Random Mating
Random
Mating
Non- Random
Mating
-Only certain individual organisms can mate
gene
pool is small due to these organisms producing more offspring
with only their genes
evolutionary effects
-less alleles in a population gene pool
-less chance for evolutionary change
-more chance of extinction
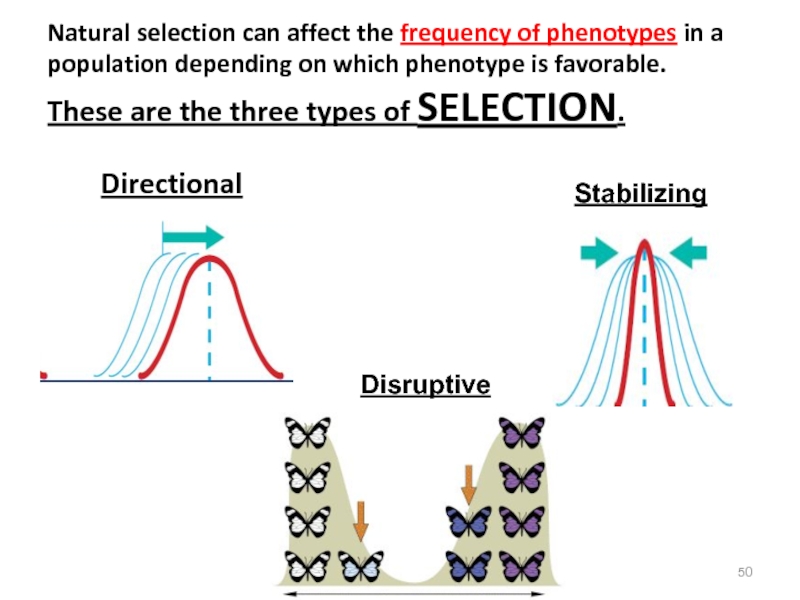
Слайд 50Directional
Stabilizing
Disruptive
Natural selection can affect the frequency of phenotypes in a
population depending on which phenotype is favorable.
These are the
three types of SELECTION.
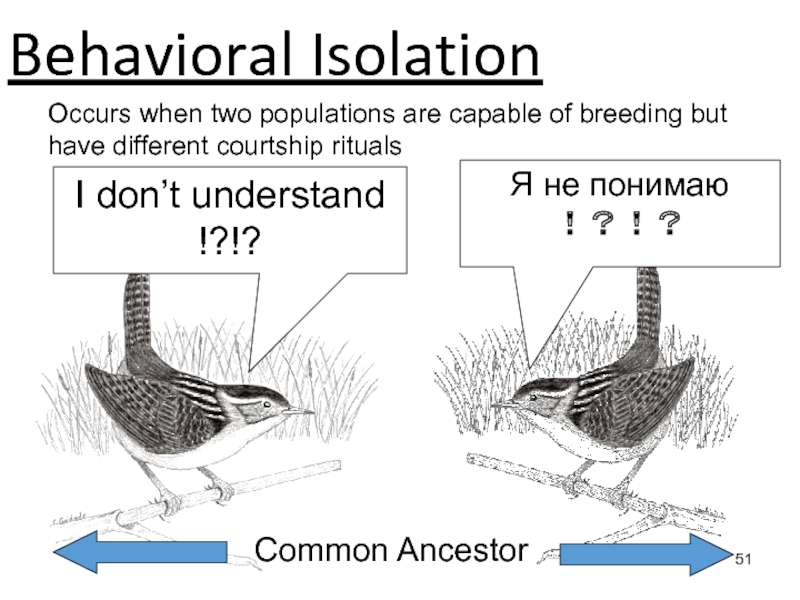
Слайд 51Behavioral Isolation
I don’t understand
!?!?
Я не понимаю
!?!?
Occurs when two populations are
capable of breeding but have different courtship rituals
Common Ancestor
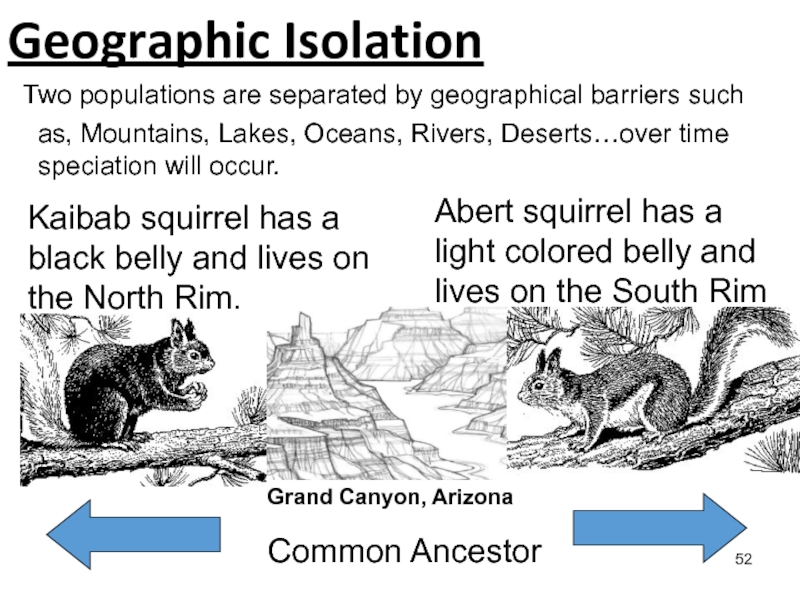
Слайд 52 Two populations are separated by geographical barriers such as,
Mountains, Lakes, Oceans, Rivers, Deserts…over time speciation will occur.
Geographic Isolation
Kaibab
squirrel has a black belly and lives on the North Rim.
Abert squirrel has a light colored belly and lives on the South Rim
Grand Canyon, Arizona
Common Ancestor
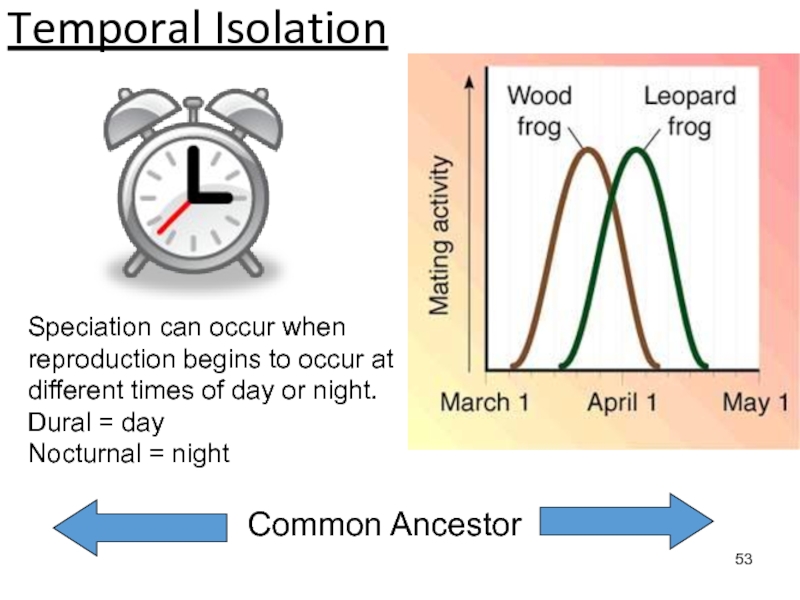
Слайд 53Temporal Isolation
Speciation can occur when reproduction begins to occur at
different times of day or night.
Dural = day
Nocturnal =
night
Common Ancestor
Слайд 54Sexual Selection
Peacock feathers
rituals…
Traits which attract mates. Include behavioral, structural and
physiological
Examples
Attractive coloring of fur, feathers, scents, mating calls, or
rituals.
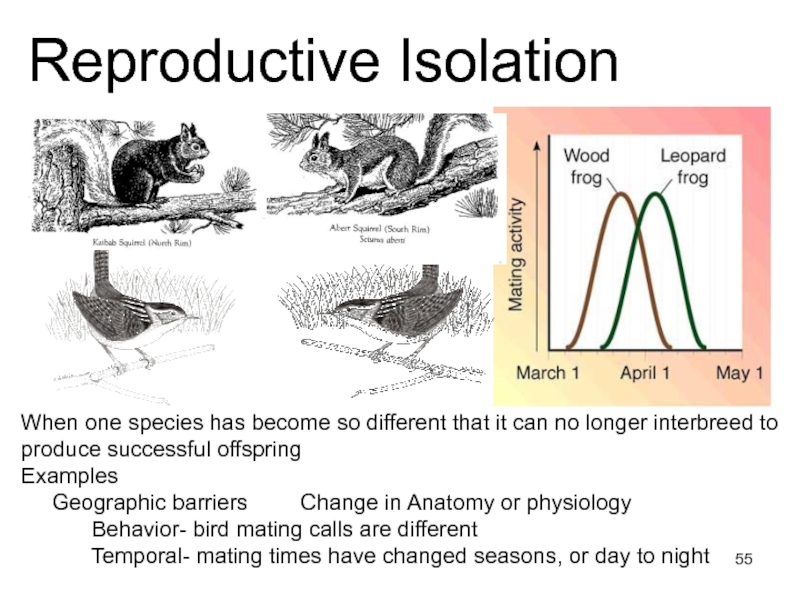
Слайд 55Reproductive Isolation
When one species has become so different that it
can no longer interbreed to produce successful offspring
Examples
Geographic barriers Change in Anatomy or physiology
Behavior- bird mating calls are different
Temporal- mating times have changed seasons, or day to night
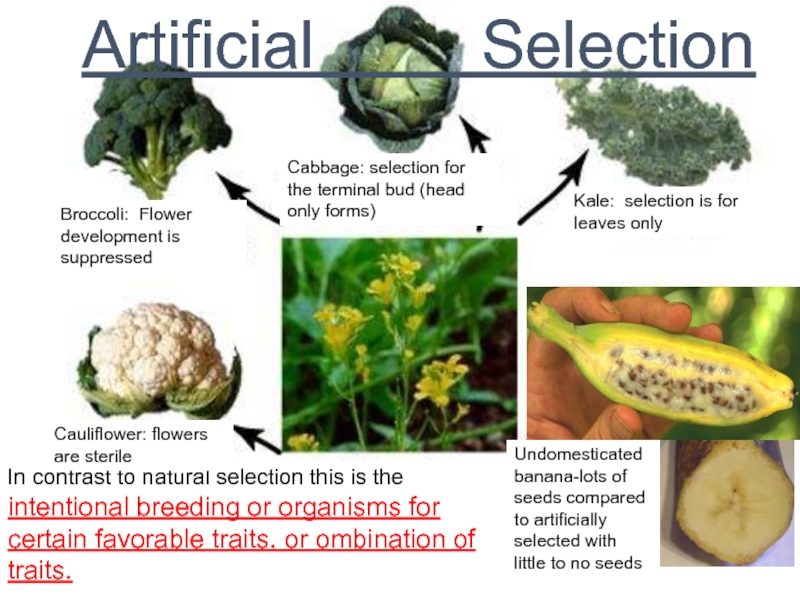
Слайд 56 Artificial Selection
In contrast to
natural selection this is the
intentional breeding or organisms for
certain favorable traits, or ombination of traits.
Broccoli: Flower development is suppressed
Cauliflower: flowers are sterile
Cabbage: selection for the terminal bud (head only forms)
Kale: selection is for leaves only
Undomesticated
banana-lots of seeds compared
to artificially
selected with little to no seeds