Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Germanic languages - копия
Содержание
- 1. Germanic languages - копия
- 2. The Germanic languages branch Indo-European family. Distributed
- 3. HISTORYThe history of the development of the
- 4. WRITINGThe most ancient monuments of German literature
- 5. Слайд 5
- 6. LITERATUREAdmoni V. G., Yartsev V. N. Historical
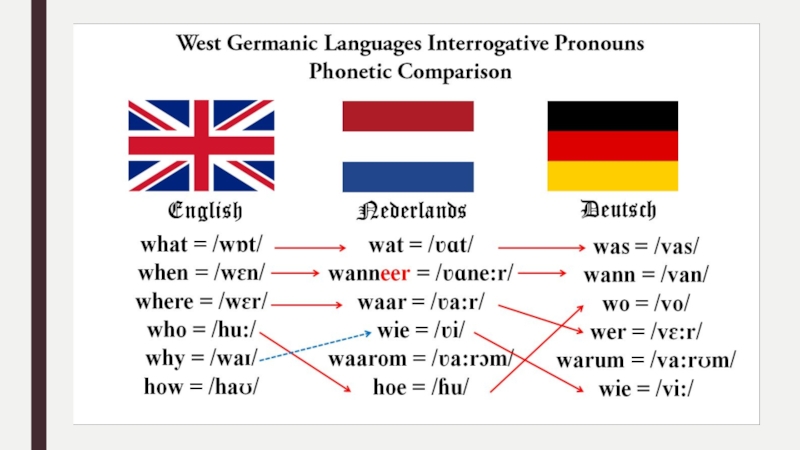
- 7. Among Indo-European languagesDistinctive features of the Germanic
- 8. The largest Germanic languagesSpeaking of Germanic languages,
- 9. THANKS FOR ATTENTION НАЗАРЛАРЫҢЫЗҒА РАХМЕТ
- 10. Скачать презентанцию
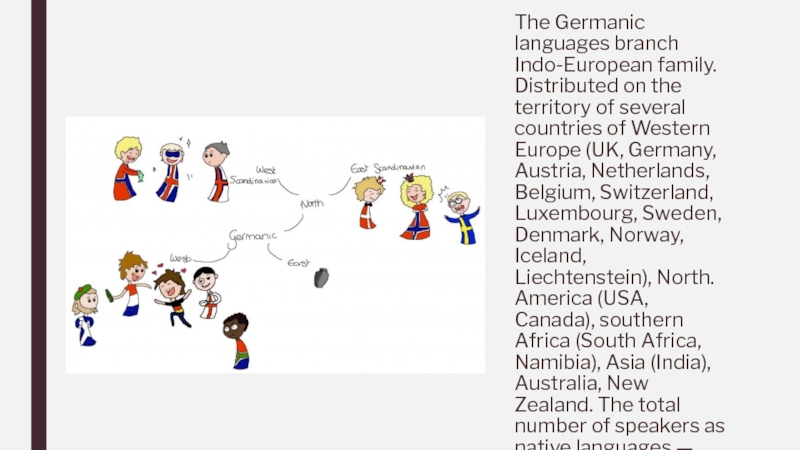
The Germanic languages branch Indo-European family. Distributed on the territory of several countries of Western Europe (UK, Germany, Austria, Netherlands, Belgium, Switzerland, Luxembourg, Sweden, Denmark, Norway, Iceland, Liechtenstein), North. America (USA,