Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Global Economic Environment
Содержание
- 1. Global Economic Environment
- 2. The World Economy (an overview)a. Which historical
- 3. answersa. World War IIb. before 10% , now 50%c. cars
- 4. In the last 20 years the global
- 5. answersa. Cereal farmingb. Leaders and policy makers
- 6. Economic systemsTraditional approach:Based on resource allocation (market
- 7. Modern approach:Based on a more descriptive criteria.Type
- 8. Advanced Industry State Emerging Economy Type of Economy Transition
- 9. Complete free trade Incomplete free trade Trade and
- 10. -Pensions, health care and education providedServices
- 11. Free markets with high risk/ high reward
- 12. Stages of Market DevelopmentLow income countries: Gross
- 13. Stages of Market DevelopmentLow income countries: less
- 14. anwers:a. There are low wagesIndustry is promoted
- 15. c. InfosysMahindra and MahindraTataWiprod. Huge population
- 16. Lower middle income countries: GNI per capita
- 17. answersa. Mature, standirized labor intense industries such
- 18. Upper middle income countries: GNI per capita
- 19. Exercise:a. Name some advantageous characteristics of Brazil?b.
- 20. Answersa. is the largest in South America
- 21. Balance of PaymentsRecord of all economic transsactions
- 22. A country accumulates reserves when the net
- 23. Overview of International Finance- spot market vs
- 24. Слайд 24
- 25. Скачать презентанцию
The World Economy (an overview)a. Which historical event marks the emergence of global markets?b. What was the percentage of economic integration at the beginning of the 20th century and what is
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Global Economic Environment
-THE WORLD ECONOMY (AN OVERVIEW)
-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
-STAGES OF MARKET
DEVELOPMENT
Слайд 2The World Economy (an overview)
a. Which historical event marks the
emergence of global markets?
b. What was the percentage of economic
integration at the beginning of the 20th century and what is the precentage now?c. Which product can be use as an example to show such market integration?
Слайд 4In the last 20 years the global market has change
shaping a number of new realites to be taken into
acount:Capital movements replace trade as the driving force of economy
Production is uncoupled from employment
a. which economic activity in USA is a clear example of this disparity?
Countrys' economies are subordinate to global economy
b. What is the secret of the succes of Japanese and German companies?
Pure socialism prove to be inefficient as economic system
c. How socialist countries adapted to new global market conditions?
e-commerce has diminished the importance of national barriers
d. which two inventions made possible the informatic era?
Слайд 5answers
a. Cereal farming
b. Leaders and policy makers focus on world
market and the competition in each country
c. by mix approach
with capitalism d. PC's and the Internet
Слайд 6Economic systems
Traditional approach:
Based on resource allocation (market vs command) and
ownership
(Private vs State)
Market Capitalism
Centrally Planned Socialism
Centrally Planned Capitalism
Market Socialism
Слайд 7Modern approach:
Based on a more descriptive criteria.
Type of Economy
Type of
government
Trade and Capital Flows
The commanding Heights
Services provided by the state
and funded through taxesInstitutions
Markets
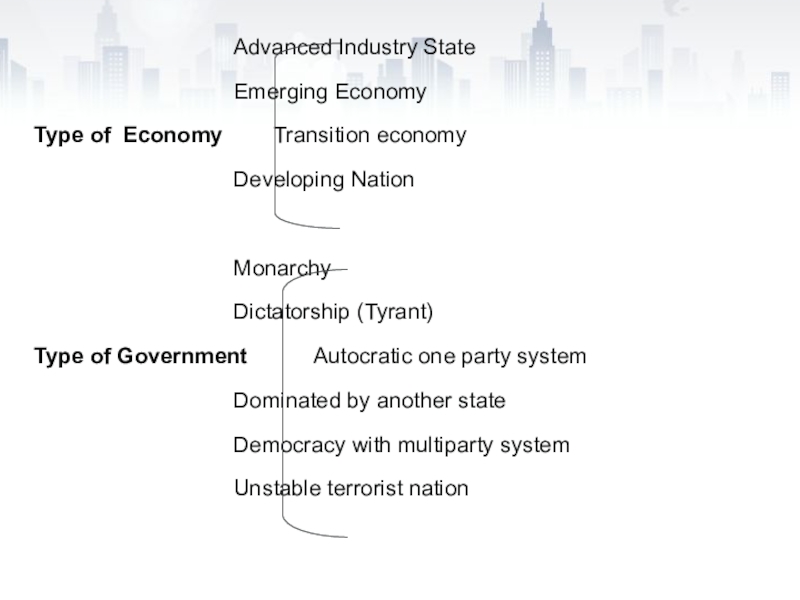
Слайд 8 Advanced Industry State
Emerging Economy
Type of Economy Transition economy
Developing Nation
Monarchy
Dictatorship (Tyrant)
Type
of Government Autocratic one party system
Dominated by another state
Democracy with
multiparty systemUnstable terrorist nation
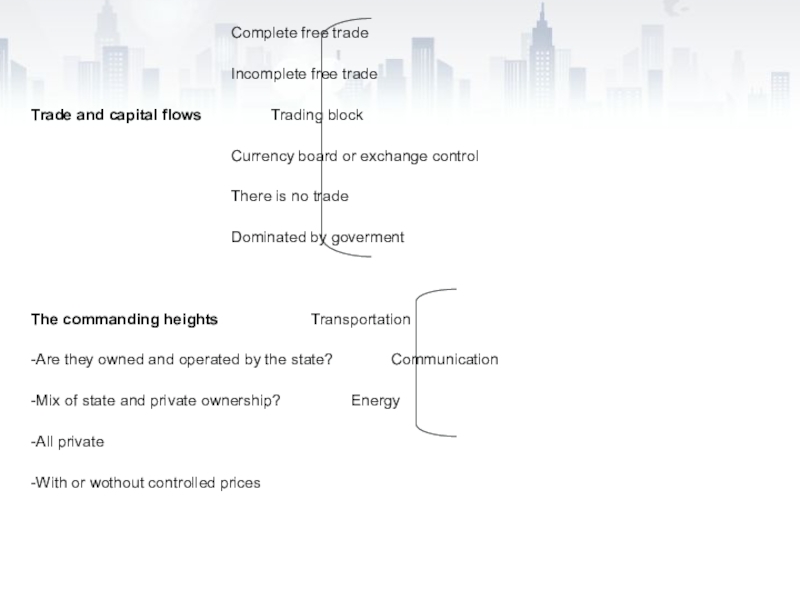
Слайд 9 Complete free trade
Incomplete free trade
Trade and capital flows Trading block
Currency
board or exchange control
There is no trade
Dominated by goverment
The commanding
heights Transportation -Are they owned and operated by the state? Communication
-Mix of state and private ownership? Energy
-All private
-With or wothout controlled prices
Слайд 10 -Pensions, health care and education provided
Services provided by the
state -Pensions and education and funded through taxes
(no health care)-Privatized systems dominate
Transparency
Standards
Institutions No corruption
Free press
Strong court
Слайд 11 Free markets with high risk/ high reward entrepreneurial dynamism
Free market
dominated by monopolies, cartels, and concentrated industries
Markets Socialized market with cooperation
between business, government and labor (little entrepreneurial support)Planning includes price and wage control and it is dominated by the center
Слайд 12Stages of Market Development
Low income countries: Gross Net Income per
capita less than $ 936
Lower middle income countries: GNI
per capita from $936 to $3705 Upper middle income countries: GNI per capita from $3706 to $11455
High income countries: GNI per capita over $11455
Слайд 13Stages of Market Development
Low income countries: less than $ 936
-Little industrialization, high agriculture (peasants farming)
-Low literacy rates
-Reliance on foreign
aid-Political inestability / unrest
Exercise:
a. Why is Bangladesh genuine market opportunity?
b. Which measures were taken by india to promote market development?
c. Which are some of indias world class companies?
d. Which characteristic makes India a good place to sell products and services?
Слайд 14anwers:
a. There are low wages
Industry is promoted by the goverment
It
is favored by a trade agreement (MFA) -Mul-Fiber Arrangement-
It sells
in places others can't (like USA where chinese products are restricted)b. Eliminating import license requirements
Reducing tariffs
Easing restrictions on Foreign Investment
Liberalizing the rupee
Слайд 16Lower middle income countries: GNI per capita from $936 to
$3705
-Rapid expansion
-Labor forces target foreign markets
(Russia, China)
Exercise:
a. What
is their competitive advantage?b. Why is the Chinese market attrative for other countries?
c. How is China supporting its export led economic transformation?
Слайд 17answers
a. Mature, standirized labor intense industries such as toy makers
and textiles.
b. becouse of its vast size and market potential.
c.
Infrastructure projects (airports, cargo ports, railroads, etc)Слайд 18Upper middle income countries: GNI per capita from $3706 to
$11455
AKA industrialized or developing countries.
-Low percentage of people involved in
agriculture- Increased degree of urbanization
- High literacy rates
- Wages growth
(Russia, Brazil)
Слайд 19Exercise:
a. Name some advantageous characteristics of Brazil?
b. Which kind of
contrasting situations can be found in Brazilian economy?
c. Are there
any similar contrasts in China?Слайд 20Answers
a. is the largest in South America in terms of
economy, population, territory, and natural resources
b. while distribution services are
computarized, horse drawn carts are a common way to deliver goods.c. your opinion
Слайд 21Balance of Payments
Record of all economic transsactions between residents of
a country and the rest of the world.
It can be
measured by analysing the Current accounts, and the Capital AccountsThe current account: is a broad measure that includes:
-merchandise trade -Service trade and
-Some financial transfers (humanitarian aid)
A country with negative current account balance has trade deficit when the flow of money exceeds the inflow of money for sales exports. (it is buying more than it sells). On the other hand, positive current account balance translates in trade surplus.
Capital account: is a record of all long term direct ivestment, portafolio investment, and other short and long term capital flows.
Слайд 22A country accumulates reserves when the net of current and
capital account transactions show surplus. In contrast, it gives up
reserves when the net shows a deficit.Exercise:
a. Why USA shows a growing trade deficit?
-increased imports from china
-insatiable demand for imported products
-the cost of military operations in middle east
(USA balances the situation with a continuos and growing surplus on services)
Слайд 23Overview of International Finance
- spot market vs forward market
-central bank
role: buys and sells currency to influence exchange rates
-currency speculators
-currency
conversion issue for companiesPurchasing power parity
Economic exposure
Managing exchange rate exposure