Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Grade 11 1 quarter
Содержание
- 1. Grade 11 1 quarter
- 2. UNIT 11.1A COMPUTER SYSTEMS UNIT 11.1B PROGRAMMING PARADIGMS UNIT 11.1C SYSTEMS LIFECYCLE
- 3. Unit 11.1A Computer Systems11.3.1.1 justify the choice
- 4. 11.3.1.1 justify the choice of software and
- 5. Questions
- 6. AnswersSystem software Q1 Disk formatter is part
- 7. 11.3.1.3 describe the purpose and basic functions
- 8. 11.3.2.1. describe the interaction of the central
- 9. Describe the Fetch Execute Cycle using registers?Program counterMemory Address RegisterMemory Data RegisterInstruction registerAccumulator
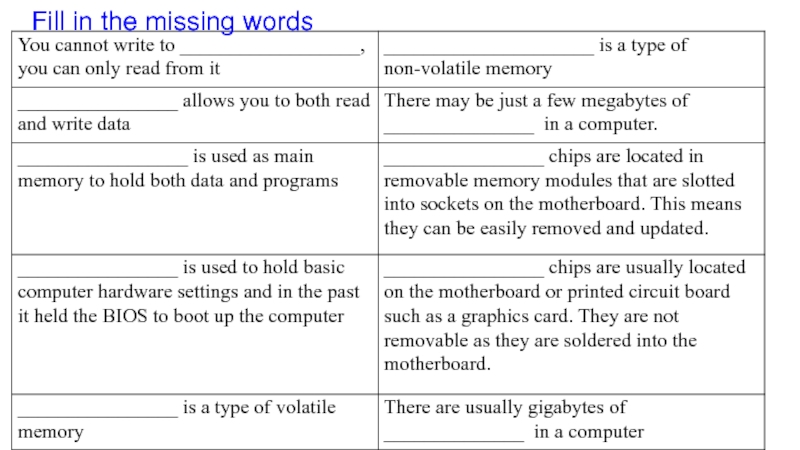
- 10. 11.3.4.1 explain the differences between RAM and
- 11. Fill in the missing words
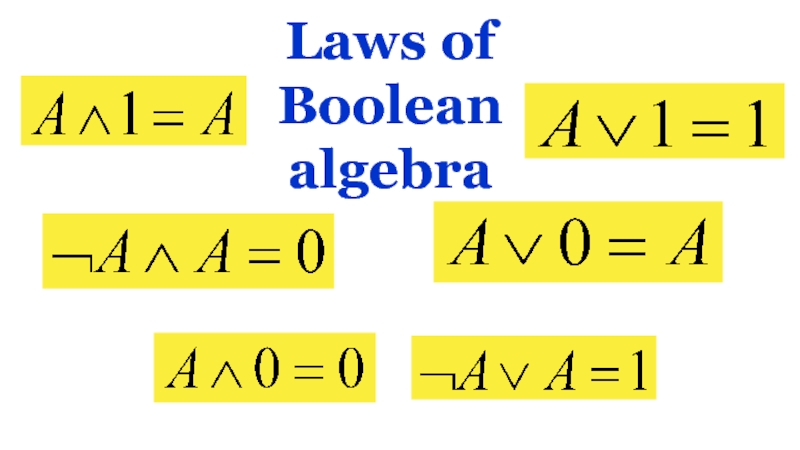
- 12. 11.3.3.1 to distinguish the laws of Boolean
- 13. Laws of Boolean algebra
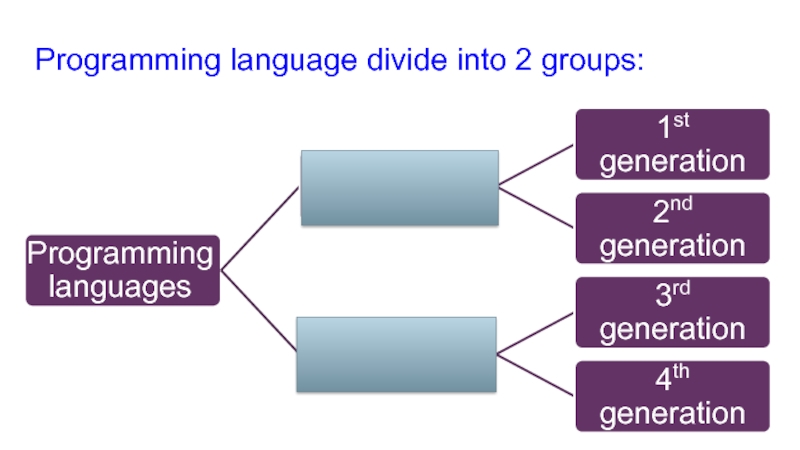
- 14. Unit 11.1B Programming Paradigms11.5.1.1 to distinguish between
- 15. Programming language divide into 2 groups:
- 16. Compare two programming languages, and solve this task with Java program language.
- 17. Программа сложения двух чиселC#include int
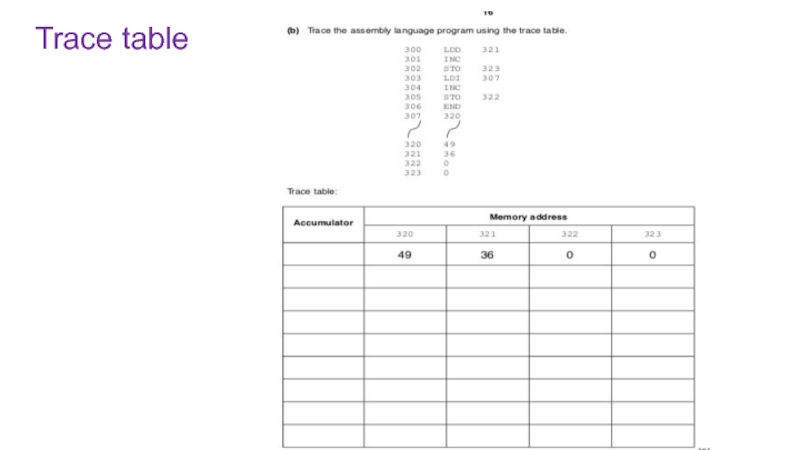
- 18. Trace table
- 19. Trace table
- 20. TranslatorsName types of translatorsWhat their roles are, and what are the differences between compilers and interpreters.
- 21. Unit 11.1C Systems Lifecycle11.2.1.8 develop requirements for
- 22. What is a System Lifecycle? Name the type of models SLC?
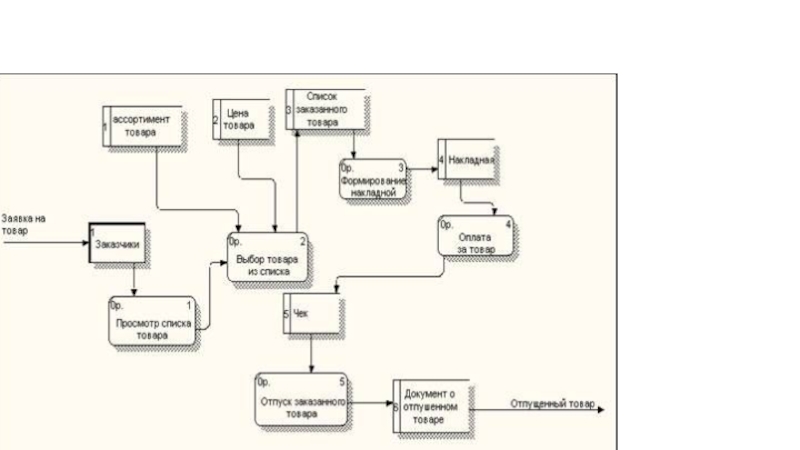
- 23. Where we can use DFD? Based on the example make DFD pizza order
- 24. Слайд 24
- 25. Слайд 25
- 26. Слайд 26
- 27. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
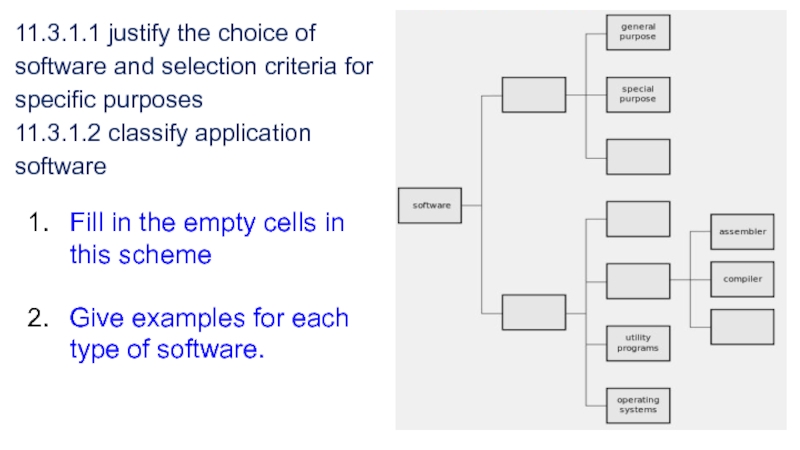
Слайд 411.3.1.1 justify the choice of software and selection criteria for
specific purposes 11.3.1.2 classify
application softwareFill in the empty cells in this scheme
Give examples for each type of software.
Слайд 6Answers
System software
Q1 Disk formatter is part of system software.
Q2 Types
of language translators: assembler, interpreter, compiler. Q3 An assembler is used
to translate assembly code into machine code. Q4 C# is translated using a compiler. Q5 The compiler reads source code and produces object code.Application software Q6 Both types of software cost the same amount of money to develop. Bespoke software is paid for wholly by the client that requires this software. The development cost of off-the-shelf software is spread over a wide customer base, so is cheaper for an individual customer. Q7 General purpose software: spreadsheet. Special purpose software: accounting package, photo editor, presentation package. Q8 Application software is a program or series of programs that allows a user to perform non- computer tasks.
Generations of programming languages Q9 First and second generation languages are classed as low level as the instruction sets they use reflect the processor architecture. Q10 There are many types of problems to be solved by computer and different languages were developed to make it easier to solve these problems. Q11 One high-level language statement will generally be translated into several low-level language statements.
Слайд 711.3.1.3 describe the purpose and basic functions of operating systems 11.3.1.4
compare single-user and multi-user operating systems 11.3.1.5 compare single-tasking and multitasking
operating systemsWhat is an operating system?
What is the basic functions OS?
Name of types OS?
Describe and give examples for each type of OS?
What is GUI and CLI? Where their could use?
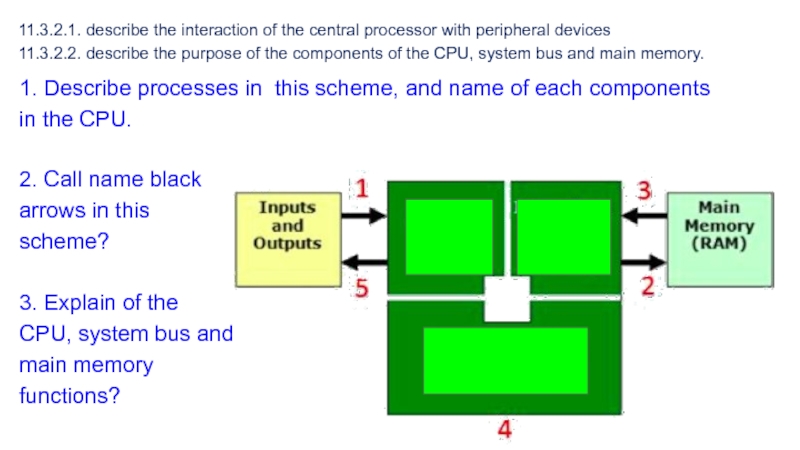
Слайд 811.3.2.1. describe the interaction of the central processor with peripheral
devices 11.3.2.2. describe the purpose of the components of the CPU,
system bus and main memory.2. Call name black arrows in this scheme?
3. Explain of the CPU, system bus and main memory functions?
1. Describe processes in this scheme, and name of each components in the CPU.
Слайд 9Describe the Fetch Execute Cycle using registers?
Program counter
Memory Address Register
Memory
Data Register
Instruction register
Accumulator
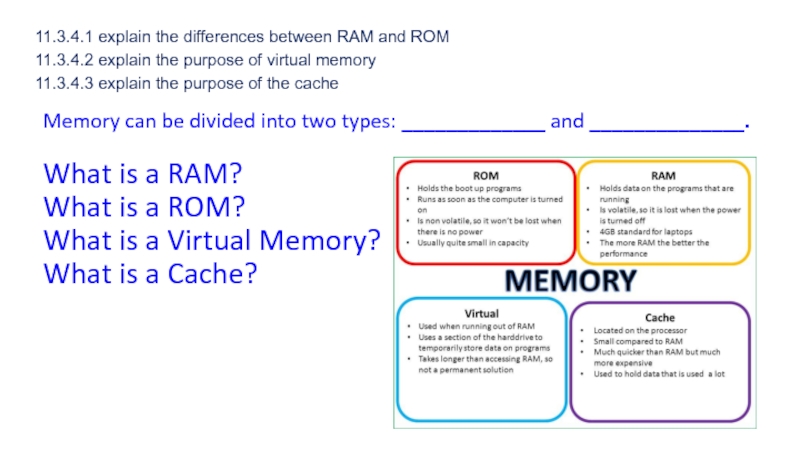
Слайд 1011.3.4.1 explain the differences between RAM and ROM 11.3.4.2 explain the
purpose of virtual memory
11.3.4.3 explain the purpose of the cache
Memory
can be divided into two types: _____________ and ______________.
What is a RAM?
What is a ROM?
What is a Virtual Memory?
What is a Cache?
Слайд 1211.3.3.1 to distinguish the laws of Boolean algebra 11.3.3.2 simplify logical
expressions using the laws of Boolean algebra 11.3.3.3 build truth tables
AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, XORAND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, XOR
Слайд 14Unit 11.1B Programming Paradigms
11.5.1.1 to distinguish between the generations of
programming languages
11.5.1.2 classify low and high level programming languages
11.5.1.3 to
analyze a simple program in assembler language11.5.1.4 use trace tables to find and validate the algorithm
Слайд 17Программа сложения двух чисел
C
#include
int main(void) {
int a,
b; scanf("%d", &a); scanf("%d", &b); printf("%d\n", a
+ b); return 0; }C++ Pascal Java Pyton begin end input a,b output (a+b)
#include
var a, b: longint;
begin
readln(a, b);
writeln(a + b);
end.
import java.util.Scanner;
class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(s.nextInt() + s.nextInt());
}
}
from string import split
a,b=map(int,split(raw_input()))
print a+b
Слайд 20Translators
Name types of translators
What their roles are, and what are
the differences between compilers and interpreters.
Слайд 21Unit 11.1C Systems Lifecycle
11.2.1.8 develop requirements for the new system
based on the information collected
11.2.1.7 use flowcharts to represent input,
processing, storage and output in computing systems11.2.1.6 use data flow diagrams (DFD-1 level) to represent input, processing, storage and output in computing systems