Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Introduction to databases
Содержание
- 1. Introduction to databases
- 2. OverviewWhat a database isHow it fits into
- 3. What is a database? A database is a storage space for content / information (data)
- 4. But what is data? And where is
- 5. What does “managing information” mean?Making information work
- 6. Managing as re-organising We often need to access
- 7. Managing as re-processing The processing power of a database allows it to:SortMatchLinkAggregateSkip fieldsCalculateArrange
- 8. Databases everywhere! Because of the versatility of databases,
- 9. Exercise 1: Understanding data and data-gatheringThink of
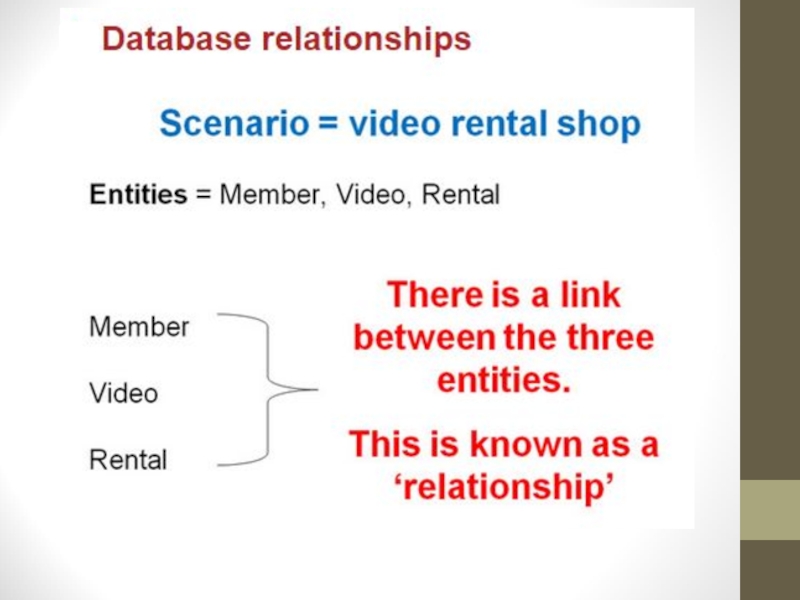
- 10. Different parts of a databaseFieldsRecordsEntityAttributesQueriesReports
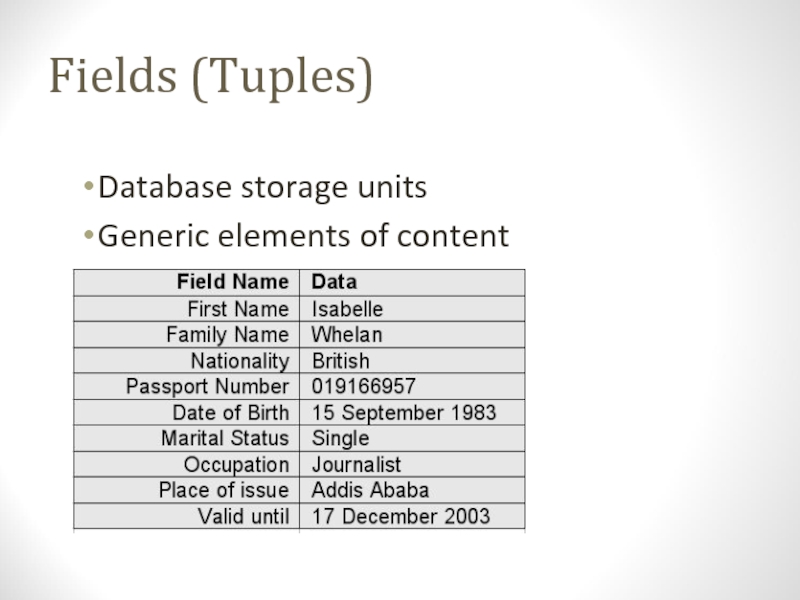
- 11. Fields (Tuples)Database storage unitsGeneric elements of content
- 12. Exercise 2: Breaking down content into fields
- 13. Records and TablesA simple table showing fields
- 14. Слайд 14
- 15. Слайд 15
- 16. Слайд 16
- 17. Time to thinkHow do you think table are sorted?
- 18. KeysSort key also known as the primary
- 19. Exercise 3: Entities, Attributes and TuplesThink of
- 20. Слайд 20
- 21. Слайд 21
- 22. Слайд 22
- 23. Слайд 23
- 24. One to One RelationshipsOccur when each entry
- 25. One to Many RelationshipsMost common type of
- 26. Слайд 26
- 27. QueriesQueries are the information retrieval requests you
- 28. ReportsIf the query is a question... ...then
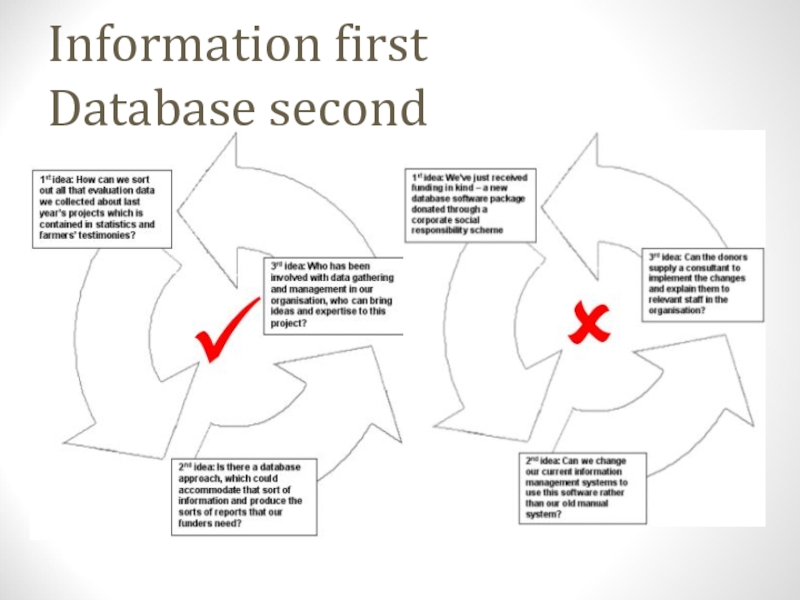
- 29. Information first Database second
- 30. Exercise 4Think of school student management system.Create
- 31. Conclusion: Database - the information toolA powerful tool for managing informationInformation first - database second
- 32. Скачать презентанцию
OverviewWhat a database isHow it fits into the broader information management pictureWhat the different parts of a database are
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 4But what is data? And where is it now?
Data is
factual information about objects and concepts, such as:
measurements
statistics
You can find it in:
spreadsheets
folders
lists
piles of papers on your desk
Слайд 5What does “managing information” mean?
Making information work for us
Making
information useful
Making information easily accessible and integrated with the rest
of our workСлайд 6Managing as re-organising
We often need to access and re-sort data
for various uses. These may include:
Creating mailing lists
Writing management reports
Generating
lists of selected news storiesIdentifying various client needs
Can you add to the list?
Слайд 7Managing as re-processing
The processing power of a database allows it
to:
Sort
Match
Link
Aggregate
Skip fields
Calculate
Arrange
Слайд 8Databases everywhere!
Because of the versatility of databases, we find them
powering all sorts of projects:
A web site that is capturing
registered usersA client tracking application for social service organisations
A medical record system for a health care facility
Your personal address book in your e-mail client
A collection of word processed documents
A system that issues airline reservations
Слайд 9Exercise 1: Understanding data and data-gathering
Think of Facebook
What data does
it gather?
What do you think it does with the data
it gathersСлайд 12Exercise 2: Breaking down content into fields and field types
Thinking
of Facebook again. List the field names and then think
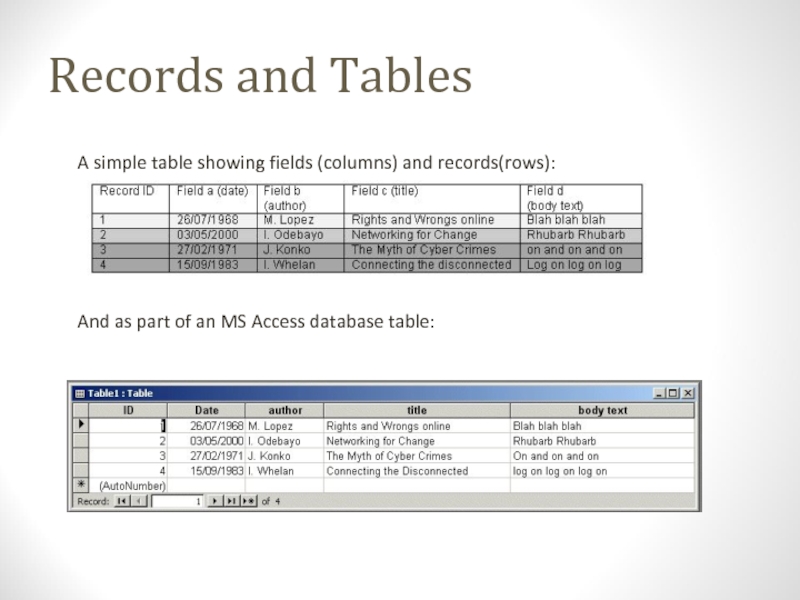
about what field type it may be. E.g. integer, string, etcСлайд 13Records and Tables
A simple table showing fields (columns) and records(rows):
And
as part of an MS Access database table:
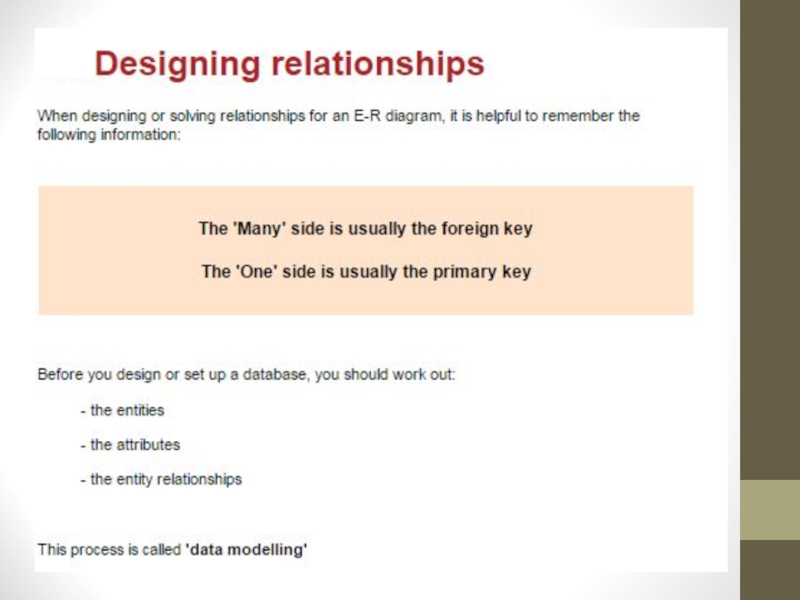
Слайд 18Keys
Sort key also known as the primary key
If two tables
are connected they must be connected through a key, known
as a foreign key.Слайд 19Exercise 3: Entities, Attributes and Tuples
Think of a hospital, can
you think of what tables (Entities) it may contain?
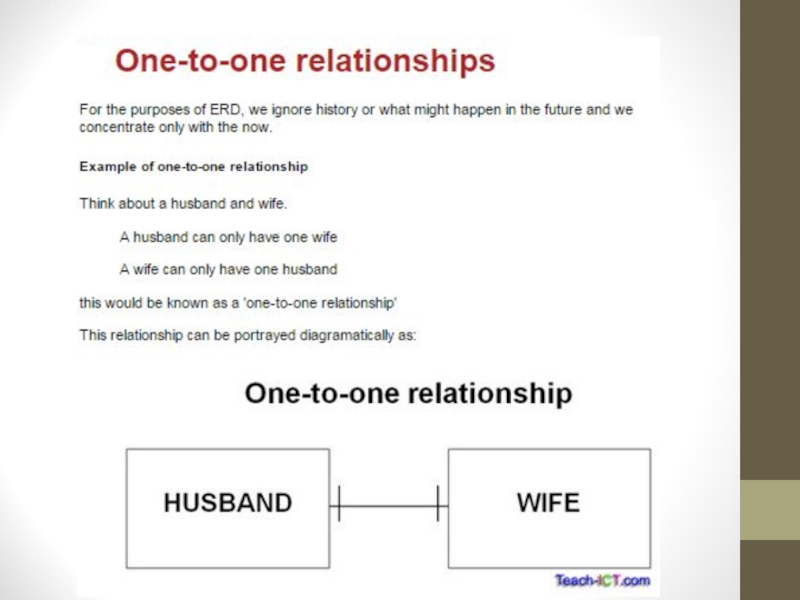
Слайд 24One to One Relationships
Occur when each entry in the first
table has one, and only one, counterpart in the second
table.One-to-one relationships are rarely used because it is often more efficient to simply put all of the information in a single table.
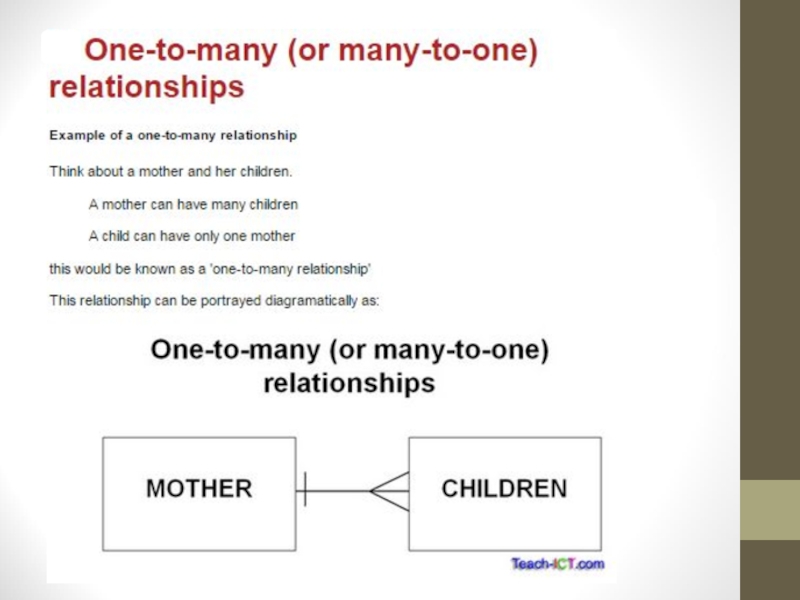
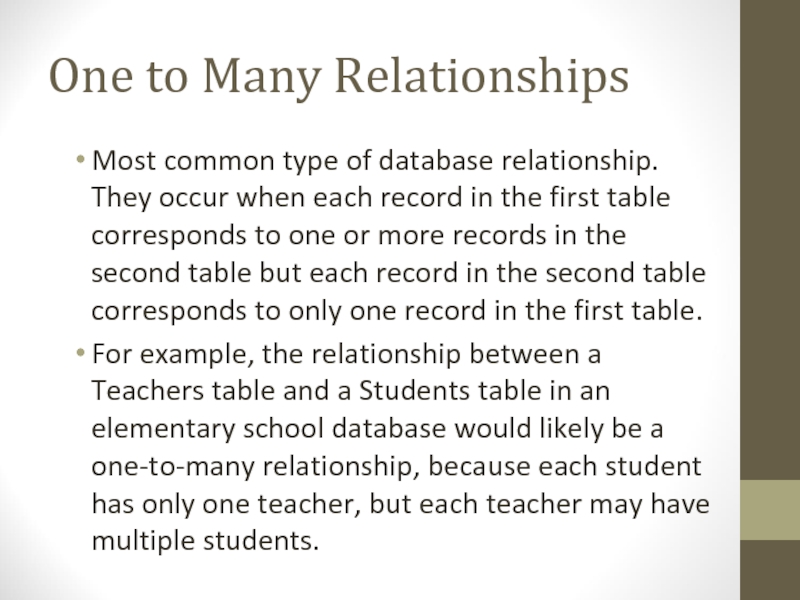
Слайд 25One to Many Relationships
Most common type of database relationship. They
occur when each record in the first table corresponds to
one or more records in the second table but each record in the second table corresponds to only one record in the first table.For example, the relationship between a Teachers table and a Students table in an elementary school database would likely be a one-to-many relationship, because each student has only one teacher, but each teacher may have multiple students.
Слайд 27Queries
Queries are the information retrieval requests you make to the
database
Your queries are all about the information you are
trying to gather Слайд 28Reports
If the query is a question...
...then the report is
its answer
Reports can be tailored to the needs of
the data-user, making the information they extract much more usefulСлайд 30Exercise 4
Think of school student management system.
Create a two tables
within that system (Students and Courses) showing the fields and
field types they would containHow would you link the tables?





































![ДИФФЕРЕНЦИАЦИЯ
ЗВУКОВ [ Л ] – [ Р ]
В СЛОВОСОЧЕТАНИЯХ,
ПРЕДЛОЖЕНИЯХ](/img/tmb/7/638811/01f33de5038c0fd4eacd0ea3d9bda242-800x.jpg)

