Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Jsc astana medical university department of inner diseases iws chronic
Содержание
- 1. Jsc astana medical university department of inner diseases iws chronic
- 2. Chronic gastritis
- 3. EtiologyHelicobacter pylori is the main reason of development of the chronic gastritis
- 4. Virulence
- 5. Pathogenicity of helicobacter pylori
- 6. Autoimmune atrophic gastritisis a chronic inflammatory disease
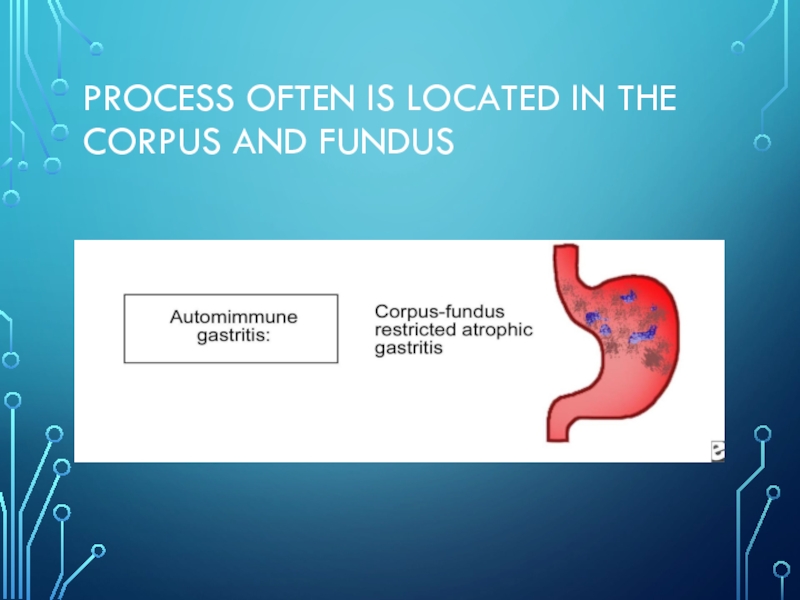
- 7. Process often is located in the corpus and fundus
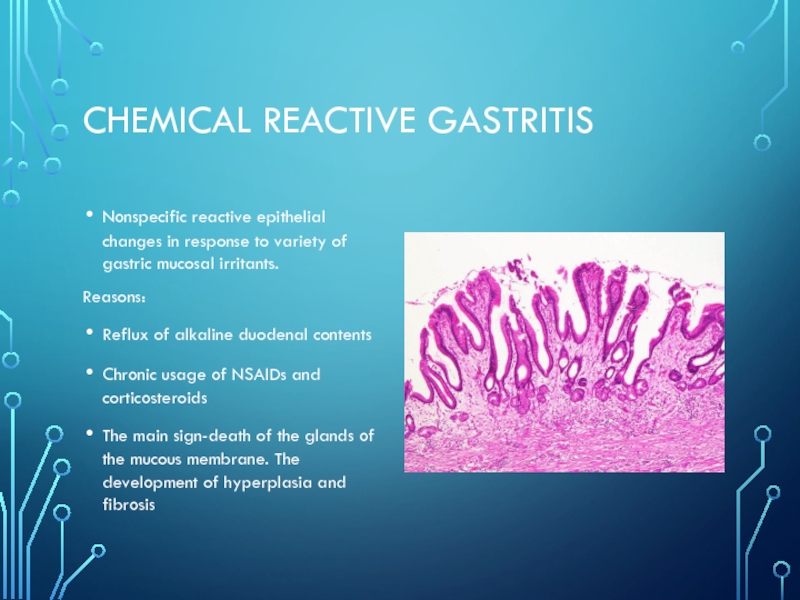
- 8. Chemical reactive gastritisNonspecific reactive epithelial changes in
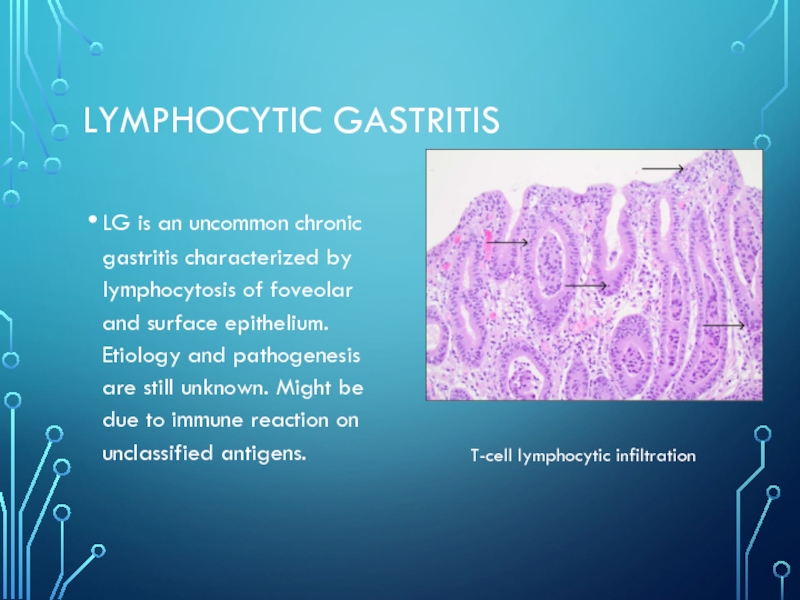
- 9. Lymphocytic gastritisLG is an uncommon chronic gastritis
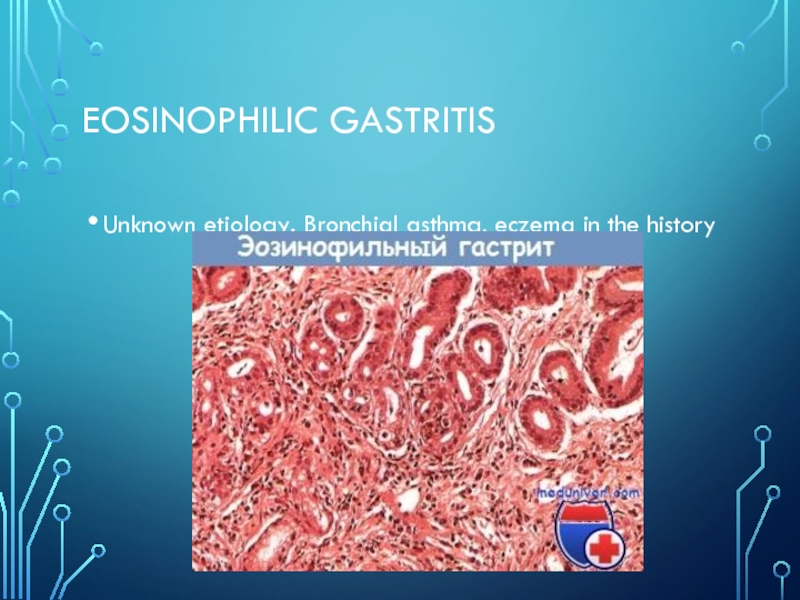
- 10. eosinophilic gastritisUnknown etiology. Bronchial asthma, eczema in the history
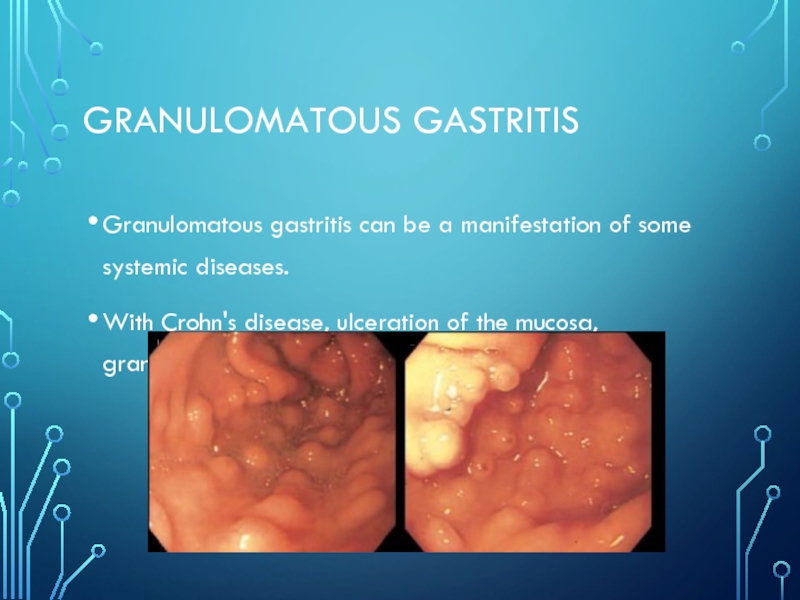
- 11. granulomatous gastritisGranulomatous gastritis can be a manifestation
- 12. giant hypertrophic gastritisEtiology and pathogenesis are unknownGiant
- 13. clinical pictureChronic non-atrophic gastritis1. Pain syndromePain in
- 14. Atrophic gastritis+ vitamin B12 deficiencyheaviness in the epigastric
- 15. Chemical gastritistriad of symptoms:pain vomiting weight loss
- 16. giant hypertrophic gastritispain in the epigastric region,often
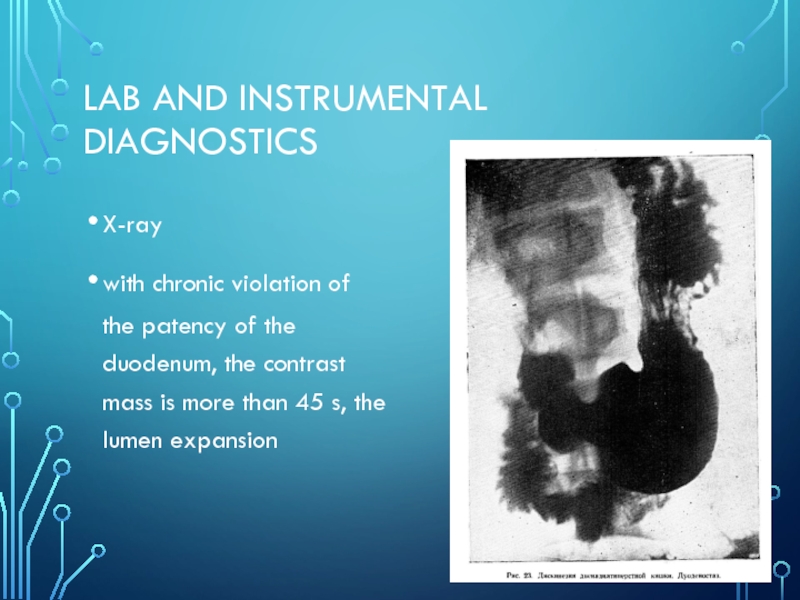
- 17. Lab and instrumental diagnostics X-raywith chronic violation
- 18. localization in the body with a very
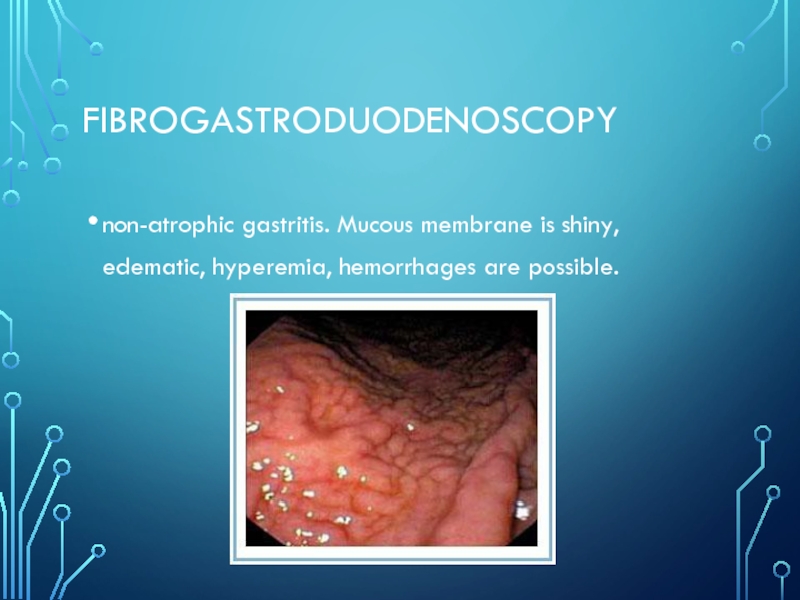
- 19. fibrogastroduodenoscopynon-atrophic gastritis. Mucous membrane is shiny, edematic, hyperemia, hemorrhages are possible.
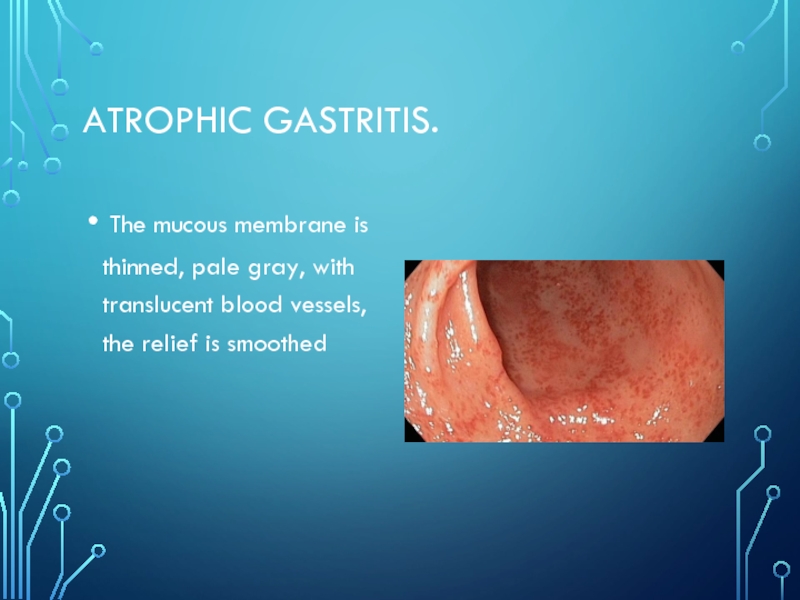
- 20. atrophic gastritis. The mucous membrane is thinned,
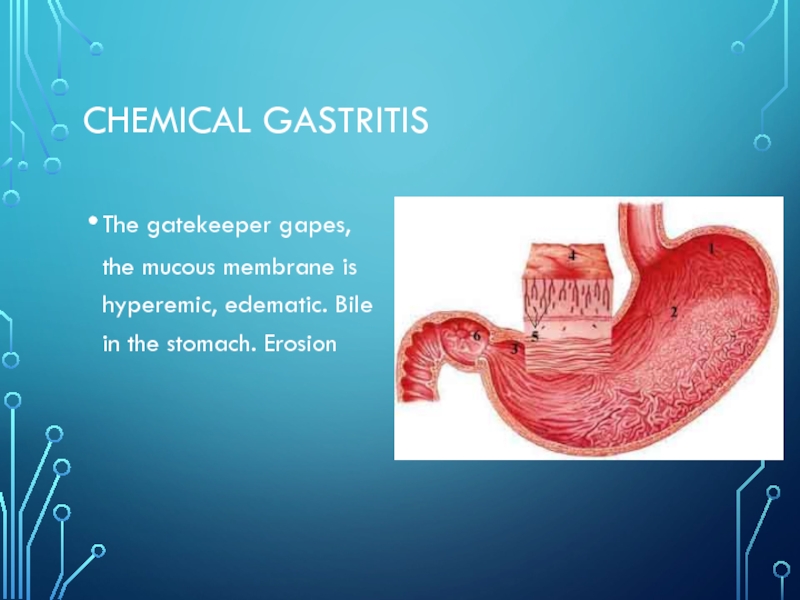
- 21. Chemical gastritisThe gatekeeper gapes, the mucous membrane is hyperemic, edematic. Bile in the stomach. Erosion
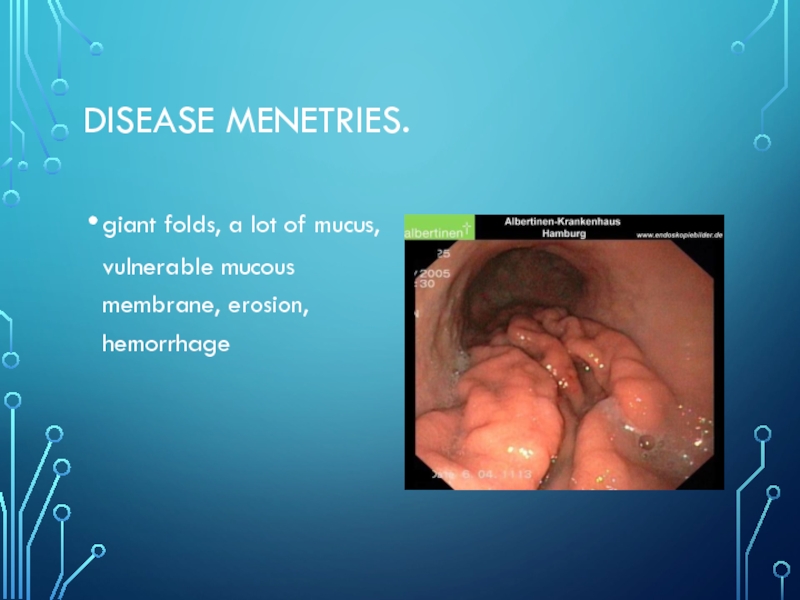
- 22. Disease Menetries. giant folds, a lot of mucus, vulnerable mucous membrane, erosion, hemorrhage
- 23. study of secretory function of the stomach
- 24. revealing Helicobacter pylori
- 25. Differential diagnosticsChronic multifocal atrophic gastritisChronic autoimmune atrophic gastritisStomach ulcerGastric adenocarcinoma
- 26. treatment
- 27. Слайд 27
- 28. Thanks for attention
- 29. Скачать презентанцию
Chronic gastritis
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Jsc «astana medical university»
department of inner diseases
iws
«chronic gastritis»
Done by: antikeyeva
Aliya
Слайд 6Autoimmune atrophic gastritis
is a chronic inflammatory disease in which the immune
system mistakenly destroys a special type of cell (parietal cells) in the stomach. Parietal
cells make stomach acid (gastric acid) and a substance our body needs to help absorb vitamin B12 (called intrinsic factor). The progressive loss of parietal cells may lead to iron deficiency and finally vitamin B12 deficiency.Слайд 8Chemical reactive gastritis
Nonspecific reactive epithelial changes in response to variety
of gastric mucosal irritants.
Reasons:
Reflux of alkaline duodenal contents
Chronic usage of
NSAIDs and corticosteroidsThe main sign-death of the glands of the mucous membrane. The development of hyperplasia and fibrosis
Слайд 9Lymphocytic gastritis
LG is an uncommon chronic gastritis characterized by lymphocytosis
of foveolar and surface epithelium. Etiology and pathogenesis are still
unknown. Might be due to immune reaction on unclassified antigens.T-cell lymphocytic infiltration
Слайд 11granulomatous gastritis
Granulomatous gastritis can be a manifestation of some systemic
diseases.
With Crohn's disease, ulceration of the mucosa, granulomas and scar
strictures are observed.Слайд 12giant hypertrophic gastritis
Etiology and pathogenesis are unknown
Giant hypertrophic gastritis (GHG)
is a general term for inflammation of the stomach due
to the accumulation of inflammatory cells in the inner wall (mucosa) of the stomach resulting in abnormally large, coiled ridges or folds that resemble polyps in the inner wall of the stomach (hypertrophic gastric folds).Слайд 13clinical picture
Chronic non-atrophic gastritis
1. Pain syndrome
Pain in the epigastric area
and on an empty stomach
2. Dyspeptic syndrome
heartburn, sour eructations,
nausea, vomiting with gastric acidic reaction contentСлайд 14Atrophic gastritis
+ vitamin B12 deficiency
heaviness in the epigastric area, a feeling
of overeating, stomach overflow, burping food and air, an unpleasant
aftertaste in the mouth, a decrease in appetite, flatulence, unstable stoolsСлайд 16giant hypertrophic gastritis
pain in the epigastric region,often aching
Occur after
eating, a feeling of heaviness in the stomach.
Vomiting and
diarrhea are possible. Decreased appetite.
Losing weight.
Peripheral edema.