Слайд 111-
Lecture 1
The Strategy of International Business
Слайд 211-
Learning Objectives
To evaluate industry structure, firm strategy, and value creation
To
profile the features and functions of the value chain
To assess
how managers configure and coordinate a value chain
To explain global integration and local responsiveness
To profile the types of strategies firms use in international business
Слайд 3Why Internationalize?
Potential new opportunities
Apply innovations in domestic market to
foreign markets
Extend product life cycle
Pressure for global integration and
globally branded products
Global economies of scale
High potential demand for products and services
Currency fluctuations and tariffs
Capitalize on core competencies
Growth
11-
Слайд 4What are Strategies?
Strategies are the plans that help business achieve
their aims and objectives,
which
- take into account financial, operational
and human resource requirements;
- are delivered through a series of shorter term tactics;
- can be developed for different levels within an organisation.
11-
Слайд 5An International Strategy
is a strategy through which the firm sells
its goods or services outside its domestic market.
A growth strategy
Also
referred to as geographic diversification
11-
Слайд 6
Levels and Types of GD
Level is a number of
countries
markets
or regions
Types are
Multidomestic
Global
Transnational
11-
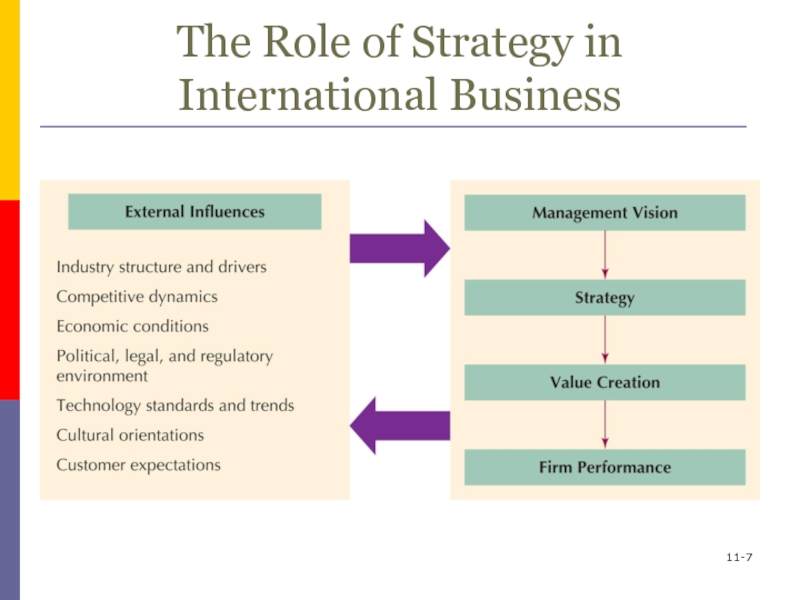
Слайд 711-
The Role of Strategy in International Business
Слайд 8Internal Drivers for IS
Influenced by prevailing mind-set in the company:
Ethnocentrism
– home country orientation
Polycentrism – host country orientation with low
involvement
Regiocentrism – regional orientation
Geocentrism – global orientation, looking at best practices
11-
Слайд 94 Primary Benefits of IS
Increased market share
Can expand size of
potential market
Domestic market may have limited growth opportunities
Larger markets offer
higher potential returns and pose less risk for a firm’s investments
11-
Слайд 104 Primary Benefits of IS
Greater return on investment (ROI)
Larger markets
are more attractive
To generate above average returns on investments
11-
Слайд 114 Primary Benefits of IS
Greater economies of Scale, Scope, or
Learning
Expanding size or scope of markets can help firms achieve
economies of scale in manufacturing, marketing, R&D, distribution, and service activities
Can exploit core competencies in international markets through resource and knowledge sharing across borders
11-
Слайд 124 Primary Benefits of IS
Competitive advantages through location
Can help the
firm reduce costs
Access to lower-cost labor, energy, and other natural
resources
Access to critical supplies and to customers
11-
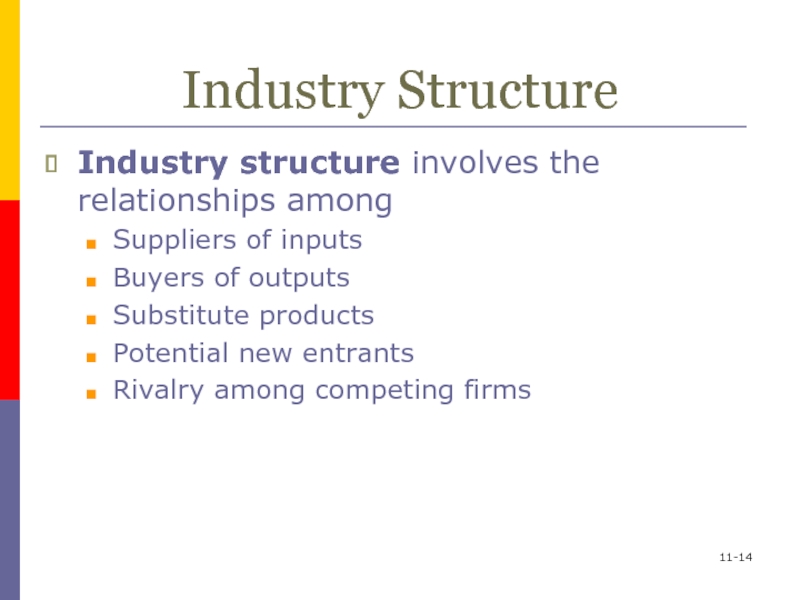
Слайд 1311-
Industry Structure
Learning Objective 1:
To evaluate industry structure, firm strategy,
and value creation
Слайд 1411-
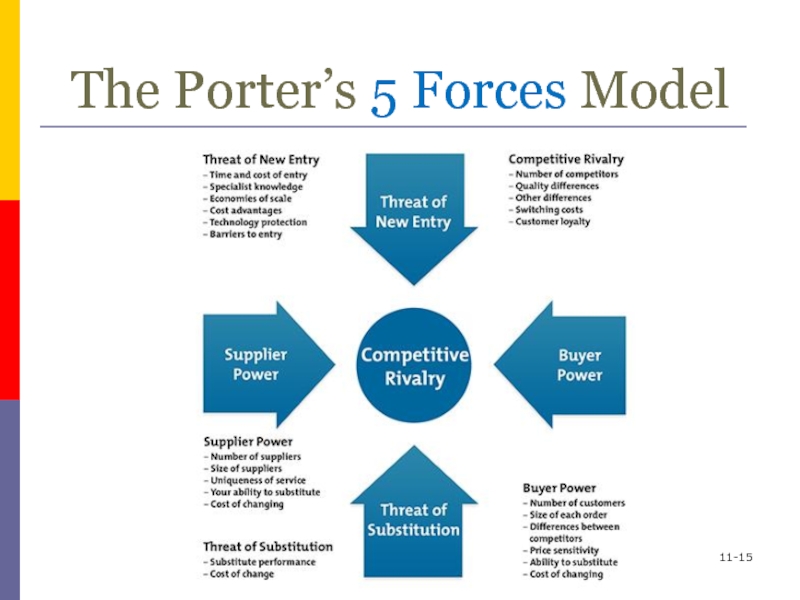
Industry Structure
Industry structure involves the relationships among
Suppliers of inputs
Buyers of
outputs
Substitute products
Potential new entrants
Rivalry among competing firms
Слайд 1611-
Industry Change
Industry structure changes because of
Competitor moves
Government policies
Shifting preferences
Technological developments
Слайд 1711-
Creating Value
Value
the measure of a firm’s capability of selling
what it makes for more than the costs incurred to
make it
Create value using
A cost leadership strategy
make products for a lower cost than competitors
A differentiation strategy
make products for which consumers are willing to pay a premium price
Слайд 1811-
The Firm as a Value Chain
Learning Objective 2:
To profile
the features and functions of the value chain
Слайд 1911-
The Firm as a Value Chain
The value chain
the set
of linked activities the company performs to design, produce, market,
distribute, and support a product
The value chain consists of
Primary activities
design, make, sell, and deliver the product
Support activities
implement primary activities
Слайд 2011-
The Firm as a Value Chain
Primary and Support Activities
Слайд 21International Strategy and Value Chain
International strategy development helps achieving certain
global synergies:
Localizing operations globally
Localizing core competencies globally
Economies of scale
Economies of
scope
International growth
11-
Слайд 22A Core Competency
is a set of a company’s unique skills
and/or knowledge that is better than its competitors and is
essential for its competitiveness.
Product development
Employee productivity
Manufacturing experience
Marketing imagination
Executive leadership
11-
Слайд 2311-
Managing the Value Chain
Learning Objective 3:
To assess how managers
configure and coordinate a value chain
Слайд 2411-
Managing the Value Chain
Configuration
distributing value chain activities around the
world
concentrated
putting all value chain activities in one location
dispersed
performing
different value chain activities in different locations
location economies
Слайд 2511-
Managing the Value Chain
When configuring the value, consider
The business environment
Innovation
context
Resource costs
Logistics
Digitization
Scale economies
Cluster effects
Customer needs
Слайд 2611-
Managing the Value Chain
Coordination
linking the value chain activities
Factors that
influence coordination
Operational obstacles
National cultures
Core competencies (Learning Effects & Experience Curve)
special outlook, skill, capability, or technology that runs through the firm’s operations, threading disconnected activities into an integrated value chain
Subsidiary networks
social networks
Слайд 2711-
Change and the Value Chain
The configuration and coordination of a
value chain responds to changes in customers, competitors, industries, and
environments
Even a well configured and coordinated value chain can become obsolete
So, designing and delivering a strategy should be an ongoing process
Слайд 2811-
Global Integration vs.
Local Responsiveness
Learning Objective 4:
To explain global
integration and local responsiveness
Слайд 2911-
Global Integration vs.
Local Responsiveness
Firms face two conflicting pressures:
Pressures
for global integration
the process of combining differentiated parts into
a standardized whole
maximize efficiency
Pressures for local responsiveness
the process of disaggregating a standardized whole into differentiated parts
optimize effectiveness
Слайд 3011-
Pressures for Global Integration
Drivers of global integration
The globalization of markets
Technology
helps standardize consumer preferences
Global products have become popular
allows for
standardization of product design
The efficiency gains of standardization
Location, scale, and learning effects
WTO supports global standards
Слайд 3111-
Pressures for Local Responsiveness
Pressure for local responsiveness is driven by
Consumer
divergence
cultural predisposition
historical legacy
nationalism
Host government policies
fiscal, monetary, and business regulations
Слайд 3211-
When Pressures Interact
Integration/Responsiveness (I/R) Grid
Слайд 3311-
Types of Strategy
Learning Objective 5:
To profile the types of
strategies firms use in international business
Слайд 3511-
International Strategy
International strategy
leverage a company’s core competencies into foreign
markets
critical elements of the value chain are centralized at headquarters
The
strategy works well when
the firm has core competencies that foreign rivals lack
there is low pressure for global integration
there is low pressure for local responsiveness
Слайд 3611-
Multidomestic Strategy
Multidomestic strategy
emphasizes responsiveness to the unique circumstances that
prevail in a country’s market
value added activities are adapted to
local markets
The strategy works well when
there is high pressure for local responsiveness
there is low pressure for global integration
Слайд 3711-
Transnational Strategy
Transnational strategy simultaneously leverages core competencies worldwide, reduces costs
by exploiting location economics, and adapts to local conditions
The strategy
works well when
global learning and knowledge flows are emphasized
there is high pressure for local responsiveness
there is high pressure for global integration
Слайд 3811-
Global Strategy
Global strategy
make standardized products that are marketed with
little adaptation to local conditions
exploit location economies and capture scale
economies
The strategy works well when
the MNE is the cost leader
there is low pressure for local responsiveness
there is high pressure for global integration
Слайд 39Market Entry Strategies
Exports
Joint ventures and alliances
Licensing
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
11-
Слайд 40How to Manage Strategy?
Market based view on strategy requires:
Strategic leadership
Strategic
planning
11-
Слайд 41Key Drivers of Strategizing
Logical incrementalism
Resource allocation
Organizational policies
Organizational culture
11-
Слайд 42Systematic Process to Adopt IS
Proper analysis with...
Identification of potential economies
Identification
of other internationalization benefits
Develop managers’capacities for international business
Adapt performance and
reward systems
Balance analysis with vision
11-
Слайд 43The two phases of an IBP
Analytical phase:
Internal analysis
External analysis
SWOT analysis
for an international market
Risk assessment
Planning phase:
International business strategy
International marketing
plan
International business action plan
Costs and benefits estimate
11-