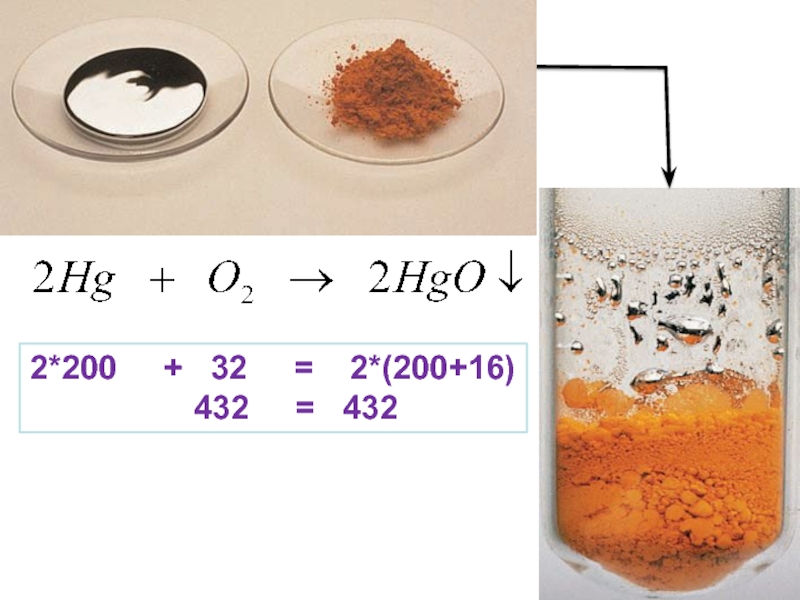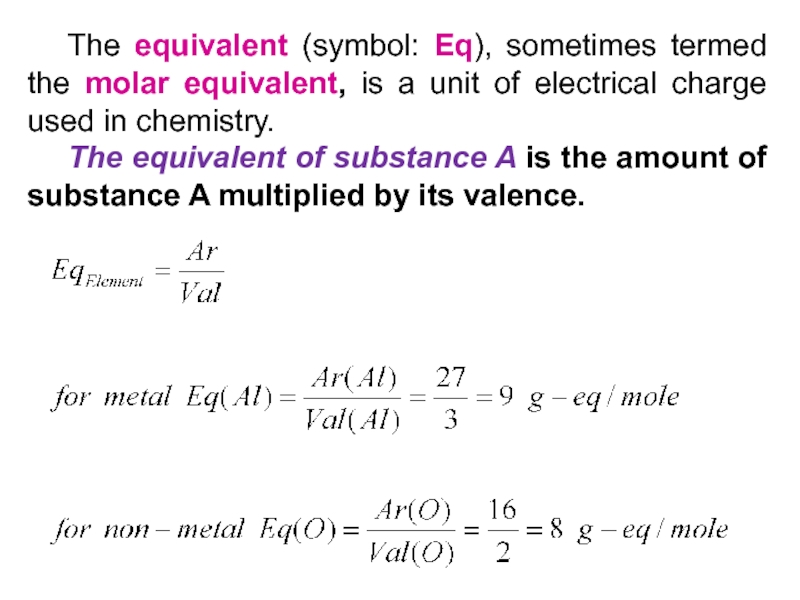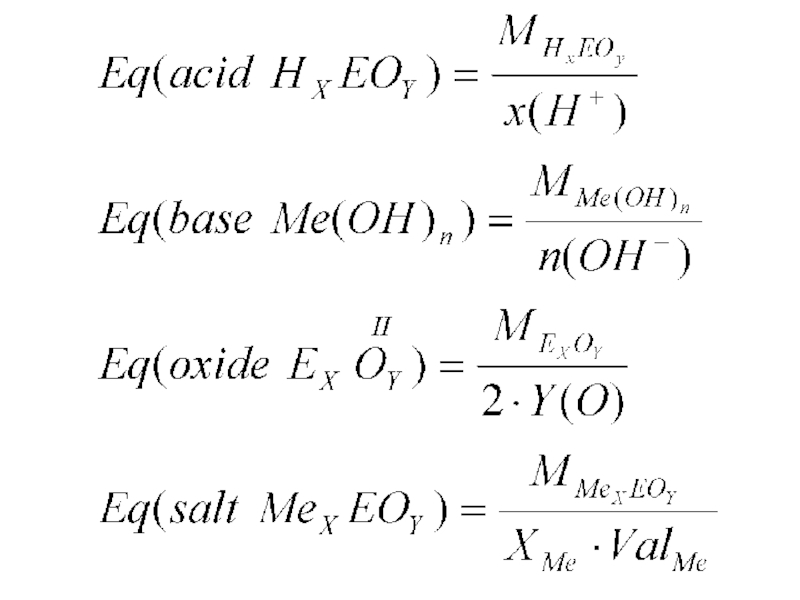Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
LECTURE №1 Basic concepts and laws of chemistry 18.01.2016
Содержание
- 1. LECTURE №1 Basic concepts and laws of chemistry 18.01.2016
- 2. QUIZ ME1. What is Chemistry?is studies the
- 3. WHAT IS CHEMISTRY? Chemistry is the study of matter,
- 4. The universe is composed of matter and
- 5. HeO2 H2ONaCl
- 6. QUIZ ME2. A pure substance can only
- 7. A MIXTURE is any physical material that
- 8. QUIZ ME3. Which one of the following
- 9. INORGANIC COMPOUNDSMineralacidsBasesAnd AlkalisOxidesSalts
- 10. Solid the form of matter characterized by
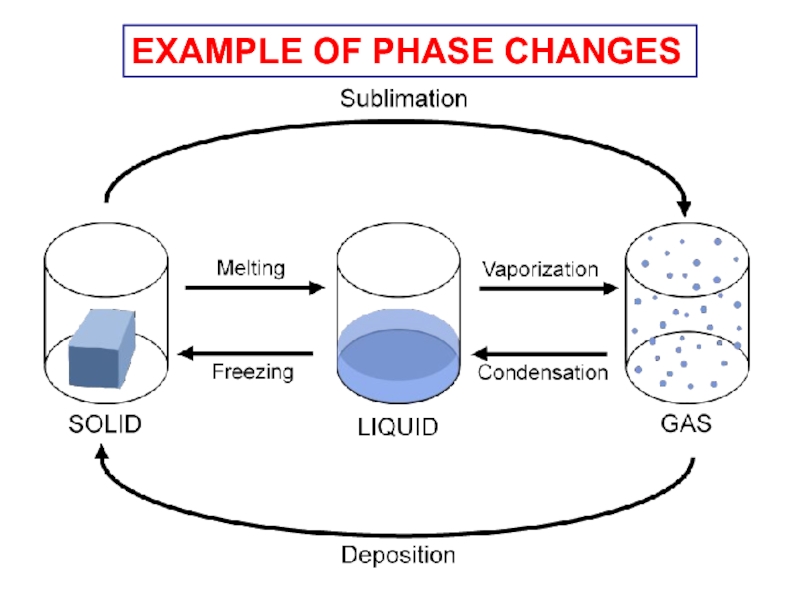
- 11. EXAMPLE OF PHASE CHANGES
- 12. Слайд 12
- 13. An atom is the basic unit of a chemical
- 14. A chemical reaction is the change that
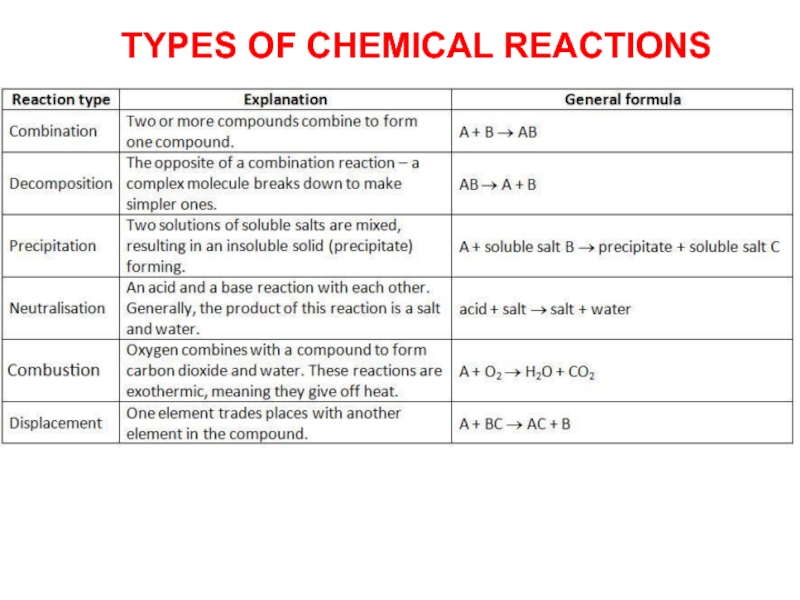
- 15. TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS
- 16. Слайд 16
- 17. QUIZ ME4. The father of modern chemistry is:DaltonLavoisierMendeleeff NEXTProust
- 18. Chemical reactions are governed by certain laws,
- 19. Antoine Lavoisier (1743–1794), a French chemist, was
- 20. 2*200 + 32
- 21. The Proust's law of definite proportions states
- 22. DALTON'S ATOMIC THEORY John Dalton (1808) used
- 23. An atom is the smallest unit of
- 24. RELATIVE ATOMIC MASS OF AN ELEMENT For example,
- 25. Слайд 25
- 26. C12,011 ATOMIC WEIGHTMass number =
- 27. Слайд 27
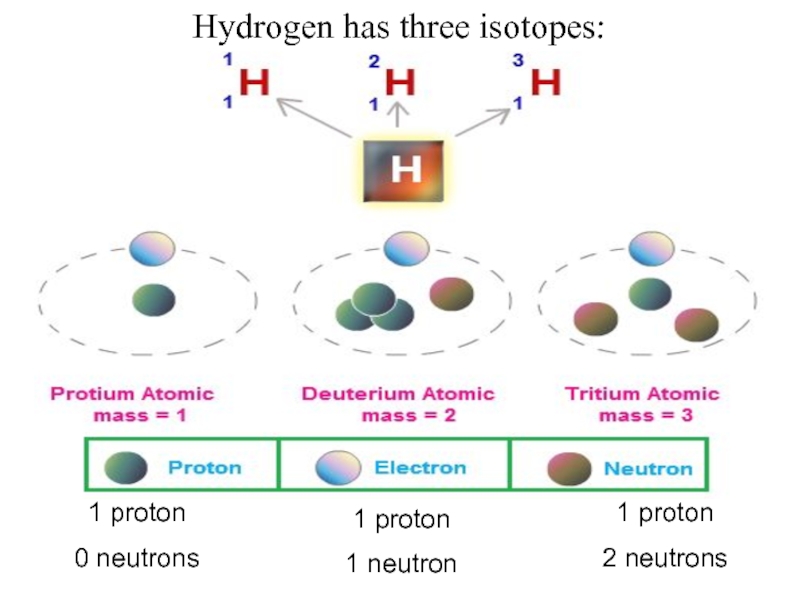
- 28. Hydrogen has three isotopes:1 proton0 neutrons1 proton1 neutron1 proton2 neutrons
- 29. Слайд 29
- 30. CHEMICAL BOND The sharing or transfer of electrons
- 31. The amount of a substance is the
- 32. Relative molecular mass (Mr) or molecular weight
- 33. Even before the creation of the doctrine
- 34. The equivalent (symbol: Eq), sometimes termed the
- 35. The equivalent could be also formally defined
- 36. Слайд 36
- 37. Law of Equivalents: the mass ratio of
- 38. Avogadro's Law Amedeo Avogadro introduced the term "molecule" and distinguished
- 39. BOYLE’S LAW According to Boyle’s Law
- 40. CHARLES’ LAW According
- 41. GAY-LUSSAC'S LAW Gay Lussac's Law
- 42. Partial Pressure Pressure each gas in a mixture
- 43. Dalton’s Law of Partial PressuresPtotal = PА + PВPВPАV=constV=constV=const
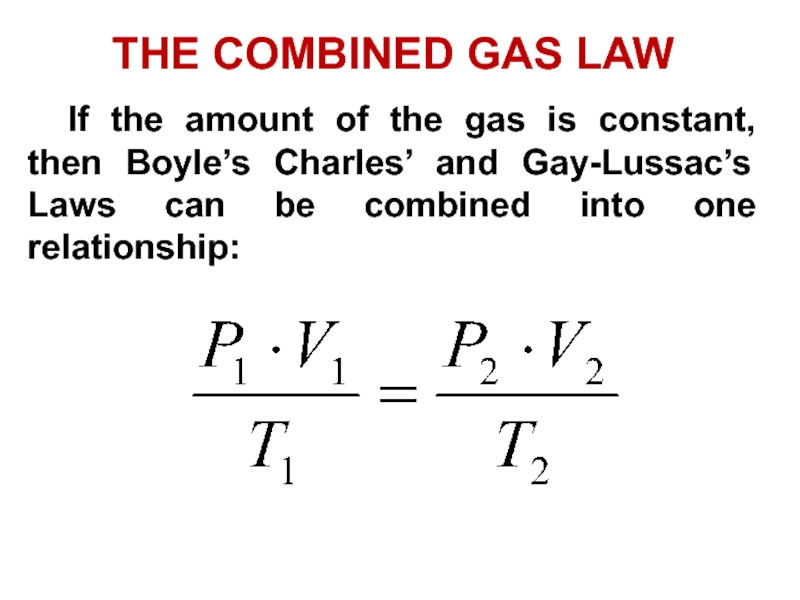
- 44. THE COMBINED GAS LAW If the amount of
- 45. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2QUIZ ME
1. What is Chemistry?
is studies the physical properties and
chemical change of matter
is studies the composition, structure, properties and
change of matter and energyis studies the physical properties and chemical change of compounds
NEXT
Слайд 3WHAT IS CHEMISTRY?
Chemistry is the study of matter, including its composition,
properties, and structure, how it changes, and how it interacts
with energy.Matter is pretty important because it's anything that has mass and takes up space - basically, all of the 'stuff' that makes up our world! Chemists study atoms, which are the basic building blocks of matter, as well interactions between atoms.
We also study subatomic particles, which are smaller than atoms, and these include things like protons, neutrons, and electrons. Since everything on Earth is made of matter, and matter is made of atoms, you can see how this creates the overlap between chemistry and other sciences.
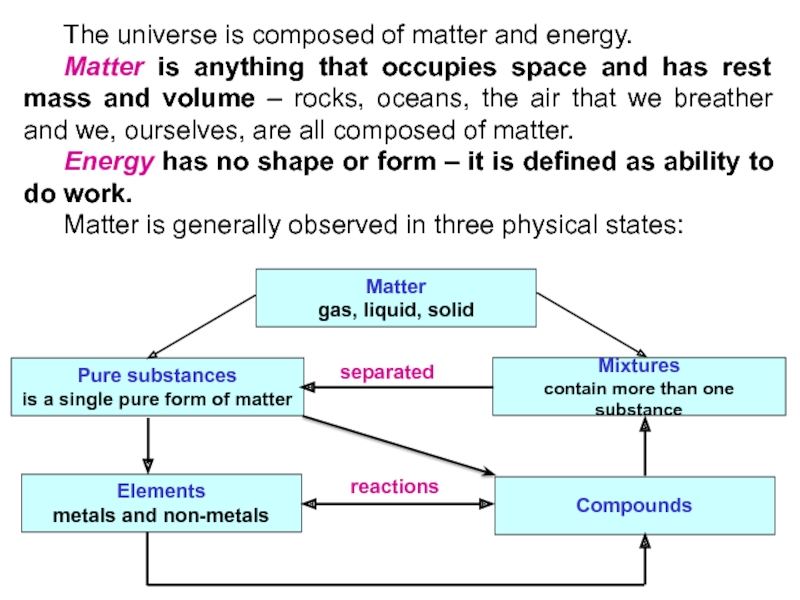
Слайд 4 The universe is composed of matter and energy.
Matter is
anything that occupies space and has rest mass and volume
– rocks, oceans, the air that we breather and we, ourselves, are all composed of matter.Energy has no shape or form – it is defined as ability to do work.
Matter is generally observed in three physical states:
Matter
gas, liquid, solid
Pure substances
is a single pure form of matter
Mixtures
contain more than one substance
Elements
metals and non-metals
Compounds
separated
reactions
Слайд 6QUIZ ME
2. A pure substance can only be:
a heterogeneous mixture
an
element or a compound
an element
compound
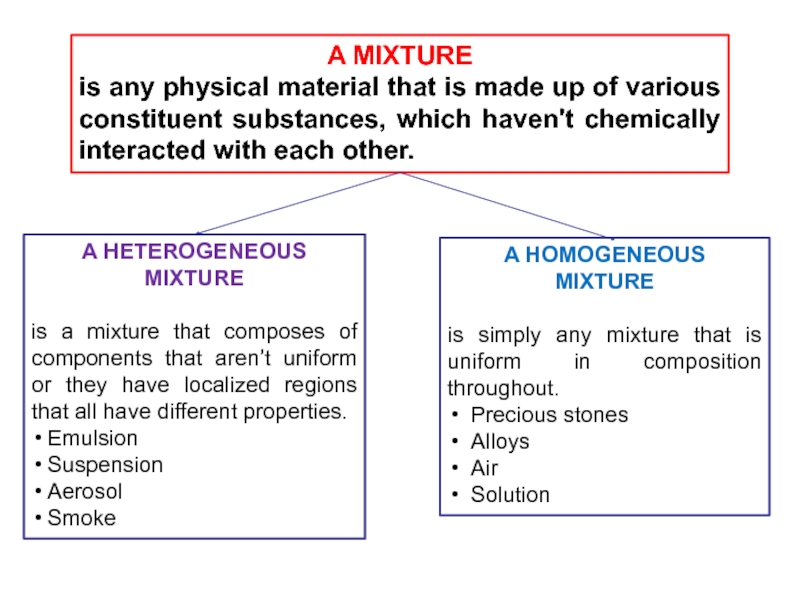
Слайд 7A MIXTURE
is any physical material that is made up
of various constituent substances, which haven't chemically interacted with each
other.A HETEROGENEOUS MIXTURE
is a mixture that composes of components that aren’t uniform or they have localized regions that all have different properties.
Emulsion
Suspension
Aerosol
Smoke
A HOMOGENEOUS
MIXTURE
is simply any mixture that is uniform in composition throughout.
Precious stones
Alloys
Air
Solution
Слайд 8QUIZ ME
3. Which one of the following mixture is homogeneous?
starch
and sugar
ethanol and water
graphite and charcoal
calcium carbonate and
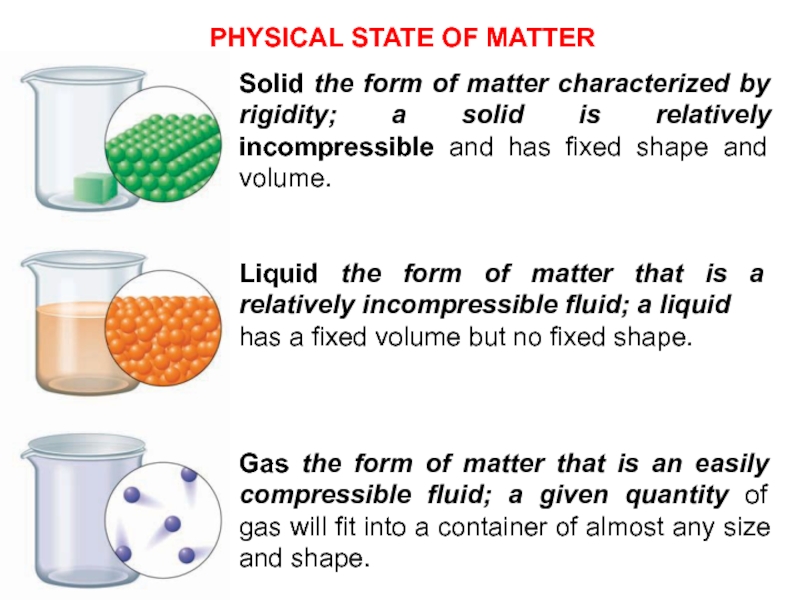
calcium bicarbonateСлайд 10Solid the form of matter characterized by rigidity; a solid
is relatively incompressible and has fixed shape and volume.
Liquid the
form of matter that is a relatively incompressible fluid; a liquidhas a fixed volume but no fixed shape.
Gas the form of matter that is an easily compressible fluid; a given quantity of gas will fit into a container of almost any size and shape.
PHYSICAL STATE OF MATTER
Слайд 13 An atom is the basic unit of a chemical element. Everything in
the world is made out of atoms.
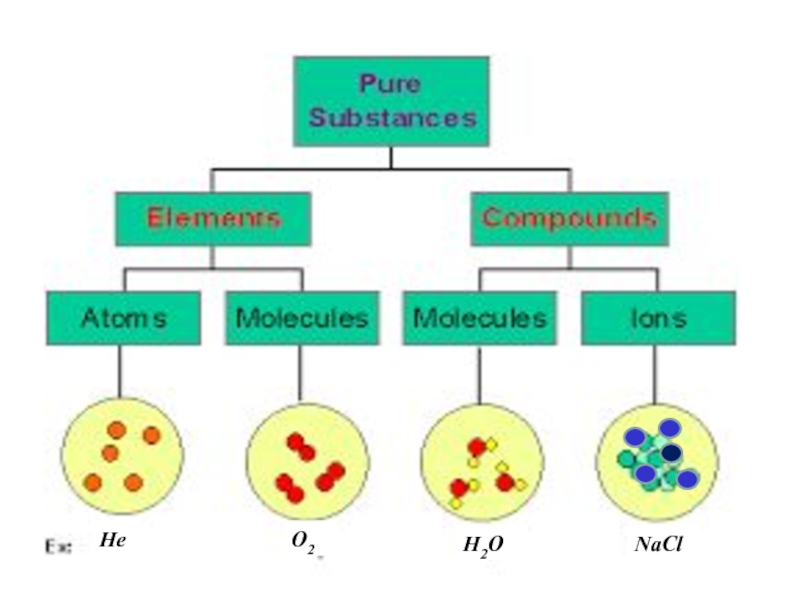
An element is a pure substance
that cannot be broken down by chemical methods into simpler components.Combinations of atoms are called molecules. A molecule is a part of matter that is made up of more than one atom. Molecules may contain one kind of atom or more than one kind of atom.
A compound is a pure substance that consists of two or more elements chemically combined in a fixed proportion. All compounds are molecules, but not all molecules are compounds.
An ion is an atom or group of atoms in which the number of electron s is different from the number of protons. Atoms may lose electrons to form cations, or gain electrons to form anions.
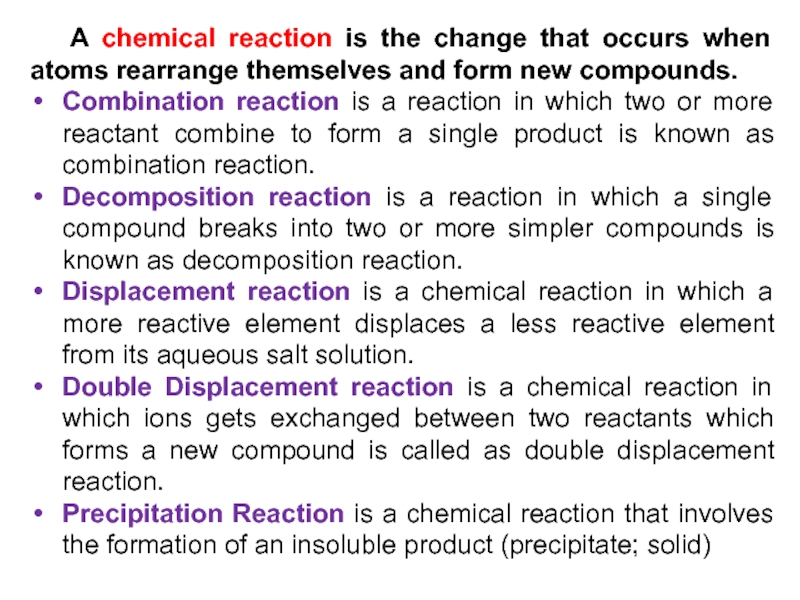
Слайд 14 A chemical reaction is the change that occurs when atoms
rearrange themselves and form new compounds.
Combination reaction is a reaction
in which two or more reactant combine to form a single product is known as combination reaction.Decomposition reaction is a reaction in which a single compound breaks into two or more simpler compounds is known as decomposition reaction.
Displacement reaction is a chemical reaction in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its aqueous salt solution.
Double Displacement reaction is a chemical reaction in which ions gets exchanged between two reactants which forms a new compound is called as double displacement reaction.
Precipitation Reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the formation of an insoluble product (precipitate; solid)
Слайд 18 Chemical reactions are governed by certain laws, which have become
fundamental concepts in chemistry. Some of them are:
Law of conservation
of energy leads to the important concepts of equilibrium, thermodynamics and kinetics.Law of conservation of mass continues to be conserved in isolated systems, even in modern physics.
Law of multiple proportions
Law of definite composition, although in many systems (notably biomacromolecules and minerals) the ratios tend to require large numbers, and are frequently represented as a fraction.
Fick's laws of diffusion
Le Chatelier's principle
Gas Laws:
Avogadro's law
Boyle's law (1662, relating pressure and volume)
Charles's law (1787, relating volume and temperature)
Gay-Lussac's law (1809, relating pressure and temperature)
Henry's law
Слайд 19 Antoine Lavoisier (1743–1794), a French chemist, was one of the
first to insist on the use of the balance in
chemical research. By weighing substances before and after chemical change, he demonstrated the law of conservation of mass, which states that the total mass remains constant during a chemical change (chemical reaction):Matter can be neither created nor destroyed, though it can be rearranged. Mass remains constant in an ordinary chemical change.
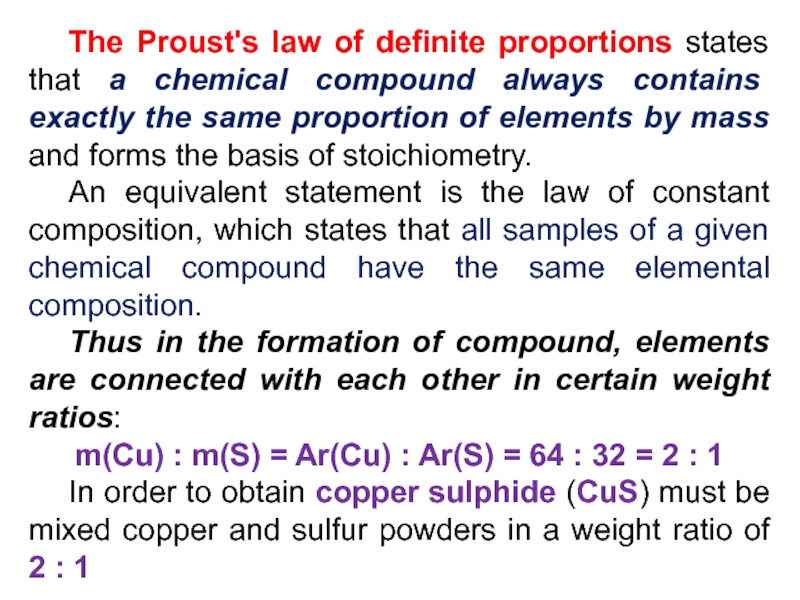
Слайд 21 The Proust's law of definite proportions states that a chemical
compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by
mass and forms the basis of stoichiometry.An equivalent statement is the law of constant composition, which states that all samples of a given chemical compound have the same elemental composition.
Thus in the formation of compound, elements are connected with each other in certain weight ratios:
m(Cu) : m(S) = Ar(Cu) : Ar(S) = 64 : 32 = 2 : 1
In order to obtain copper sulphide (CuS) must be mixed copper and sulfur powders in a weight ratio of 2 : 1
Слайд 22DALTON'S ATOMIC THEORY
John Dalton (1808) used the Greek concept
of an atom and the laws of definite proportions, conservation
of mass and multiple proportions to give the atomic theory on scientific basis. Dalton proposed that the properties of elements differ from one another because their atoms differ. He also recognized that even though they may share the same atoms, compounds have properties that bear no relationship to those elements of which they are composed. Dalton’s atomic theory stated that:
1) All matter is made of atoms. Atoms are indivisible and indestructible.
2) All atoms of a given element are identical in mass and properties
3) Compounds are formed by a combination of two or more different kinds of atoms.
4) A chemical reaction is a rearrangement of atoms.
John Dalton (1766 - 1844)
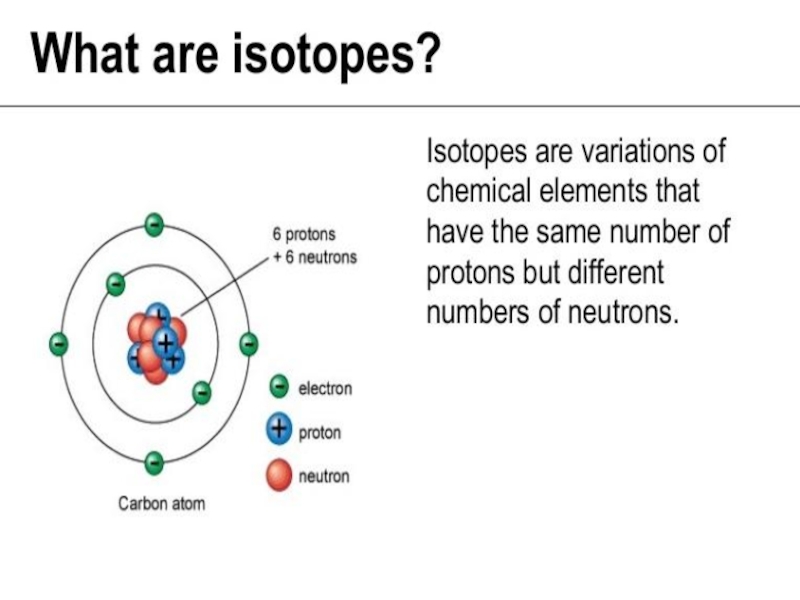
Слайд 23 An atom is the smallest unit of matter that defines
the chemical elements. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is
made up of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are very small: the size of atoms is measured in picometers - trillionths (10−12) of a meter.The atomic mass (ma) is the mass of an atomic particle, sub-atomic particle, or molecule. The protons and neutrons account for almost all of the mass of an atom. By international agreement, 1 unified atomic mass unit is defined as 1/12 of the mass of a single carbon-12 atom (at rest):
The mass number should also not be confused with the relative atomic mass (also called atomic weight) of an element, which is the ratio of the average atomic mass of the different isotopes of that element (weighted by abundance) to the unified atomic mass unit. This weighted average can be quite different from the near-integer values for individual isotopic masses.
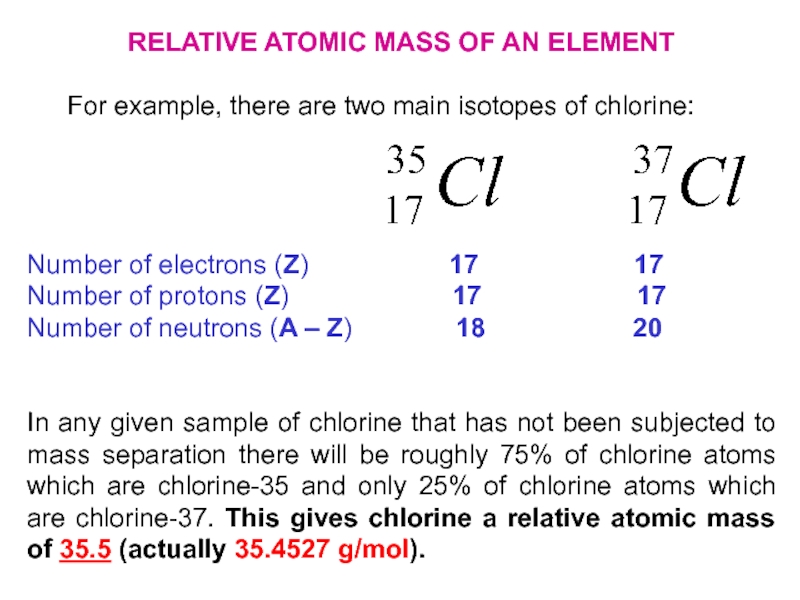
Слайд 24RELATIVE ATOMIC MASS OF AN ELEMENT
For example, there are two
main isotopes of chlorine:
Number of electrons (Z)
17 17Number of protons (Z) 17 17
Number of neutrons (A – Z) 18 20
In any given sample of chlorine that has not been subjected to mass separation there will be roughly 75% of chlorine atoms which are chlorine-35 and only 25% of chlorine atoms which are chlorine-37. This gives chlorine a relative atomic mass of 35.5 (actually 35.4527 g/mol).
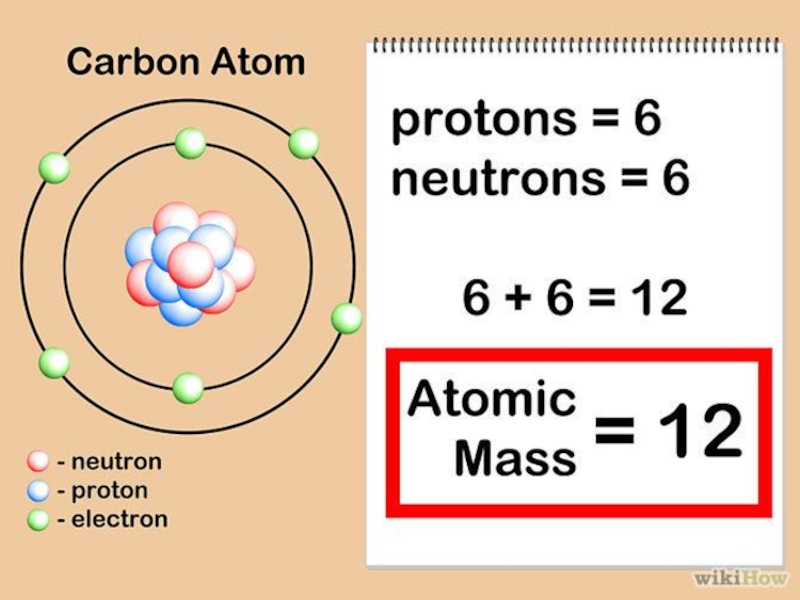
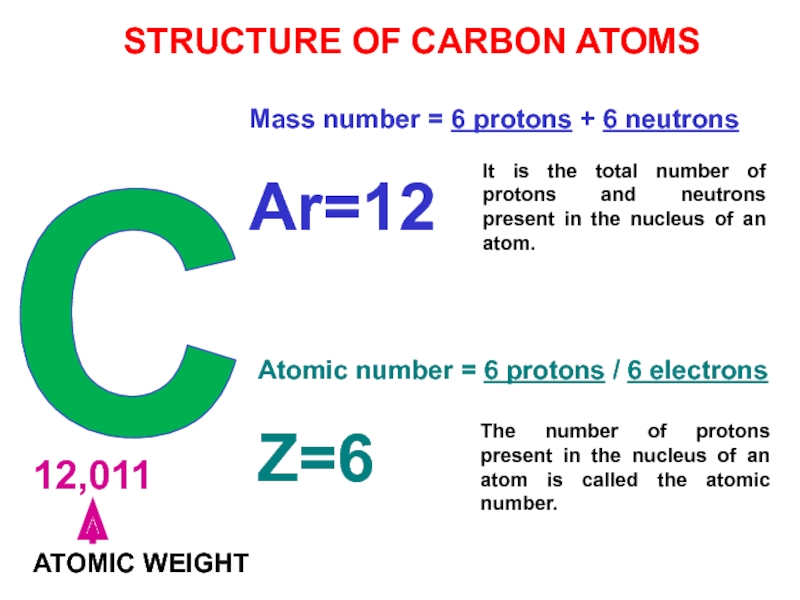
Слайд 26C
12,011
ATOMIC WEIGHT
Mass number = 6 protons +
6 neutrons
Ar=12
Atomic number = 6 protons / 6 electrons
Z=6
STRUCTURE OF
CARBON ATOMSThe number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom is called the atomic number.
It is the total number of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom.
Слайд 30CHEMICAL BOND
The sharing or transfer of electrons creates some attraction
force between elements that is called as chemical bond.
Types of Chemical
Bonding:As a matter of convenience we usually divide chemical bonds into different types. There are two major classes of bonding:
Ionic bonding which results from electrostatic interaction among ions; and can be formed by the transfer of one or more electrons from one atom or group of atoms to another.
Covalent bonding which results from sharing one or more electron pairs between two atoms.
These represent two extremes and all bonds have at least some degree of both ionic and covalent character. Compounds in which the bonding is predominantly ionic are called ionic compounds, and those in which the bonding is predominantly covalent are called covalent compounds.
Bonding between metal ions is known as metallic bonding.
A hydrogen bond is an interaction that directs the association of the covalently bounded hydrogen atom with one or more other atoms, group of atoms or molecules into an aggregate structure that is sufficiently stable to make it convenient for the chemist to consider it as an independent chemical species.
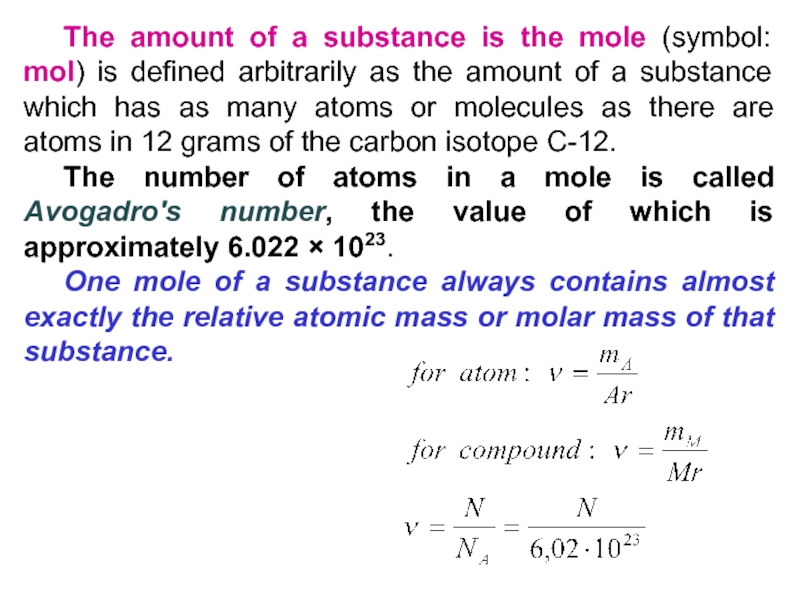
Слайд 31 The amount of a substance is the mole (symbol: mol)
is defined arbitrarily as the amount of a substance which
has as many atoms or molecules as there are atoms in 12 grams of the carbon isotope C-12.The number of atoms in a mole is called Avogadro's number, the value of which is approximately 6.022 × 1023.
One mole of a substance always contains almost exactly the relative atomic mass or molar mass of that substance.
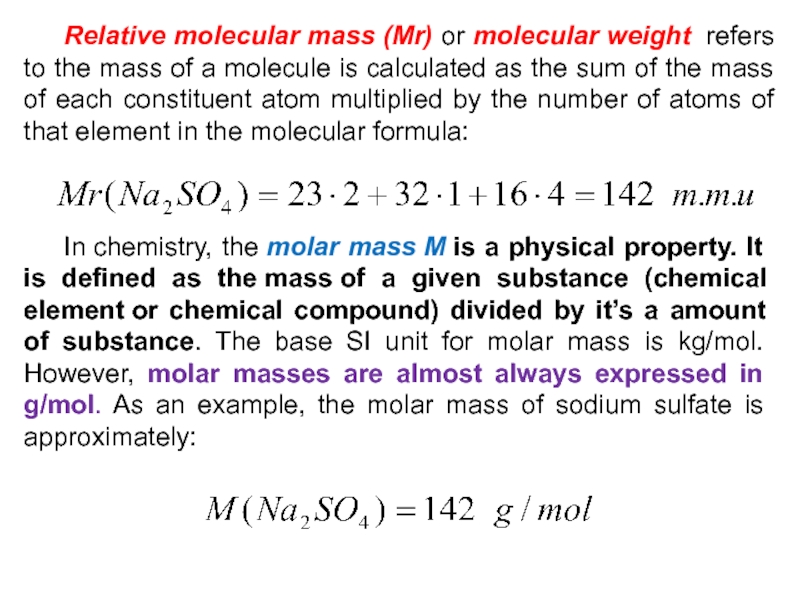
Слайд 32 Relative molecular mass (Mr) or molecular weight refers to the
mass of a molecule is calculated as the sum of
the mass of each constituent atom multiplied by the number of atoms of that element in the molecular formula: In chemistry, the molar mass M is a physical property. It is defined as the mass of a given substance (chemical element or chemical compound) divided by it’s a amount of substance. The base SI unit for molar mass is kg/mol. However, molar masses are almost always expressed in g/mol. As an example, the molar mass of sodium sulfate is approximately:
Слайд 33 Even before the creation of the doctrine of atom and
molecula it was found that simple and complex chemical substances
react in the reaction mass in strictly defined ratios.Law of equivalents: All substances react and form in equivalent proportions.
The equivalent ratio is the same number of moles of equivalents. Thus the law of equivalents can be formulated differently: the number of mole equivalents for all substances involved in the reaction is the same.
Слайд 34 The equivalent (symbol: Eq), sometimes termed the molar equivalent, is
a unit of electrical charge used in chemistry.
The equivalent of
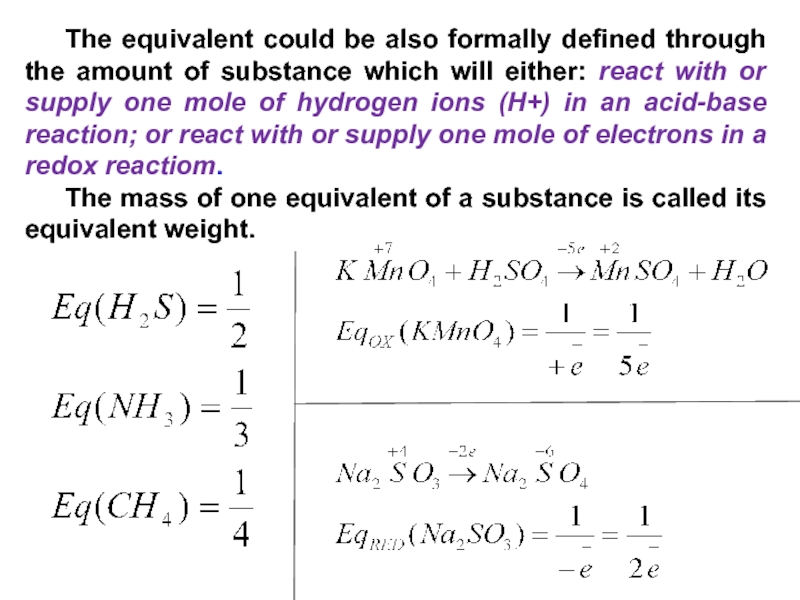
substance A is the amount of substance A multiplied by its valence.Слайд 35 The equivalent could be also formally defined through the amount
of substance which will either: react with or supply one
mole of hydrogen ions (H+) in an acid-base reaction; or react with or supply one mole of electrons in a redox reactiom.The mass of one equivalent of a substance is called its equivalent weight.
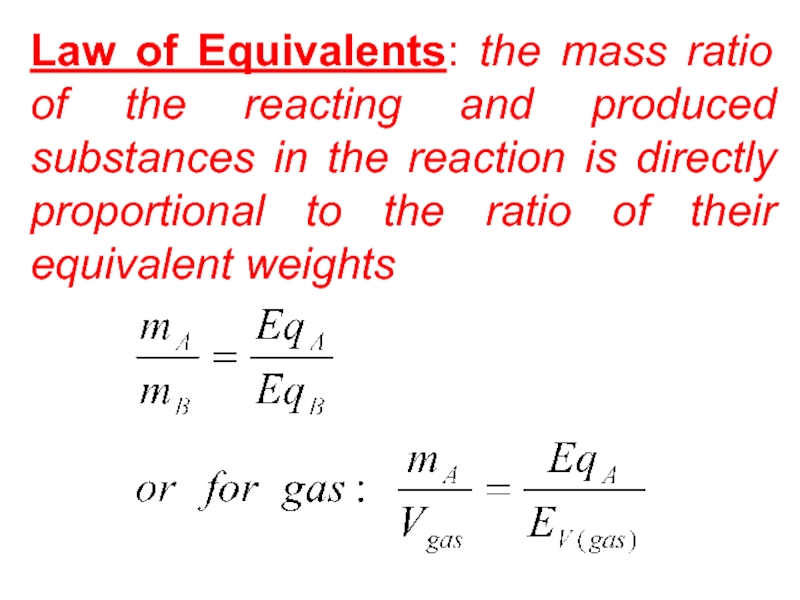
Слайд 37Law of Equivalents: the mass ratio of the reacting and
produced substances in the reaction is directly proportional to the
ratio of their equivalent weightsСлайд 38Avogadro's Law
Amedeo Avogadro introduced the term "molecule" and distinguished it from 'atom'. According
to Avogadro, particles in the gaseous state do not exist
as atoms but as molecules. In 1811 he proposed his famous hypothesis, now known as 'Avogadro's Law'. The Law states that "Equal volume of all the gases at same temperature and pressure, contains equal number of molecules."
Standard temperature and pressure is called as STP. For gases, the term STP is often used. STP means the temperature of the gas is 273K and the pressure of the gas is 1 atm. Avogadro said that 1 mole of any gas at STP occupies 22.4L of volume.
Avogadro also expressed the number of atoms present in the mole of a gas. He stated that 6.022 x 1023 particles are present in the 1 mole of a gas.
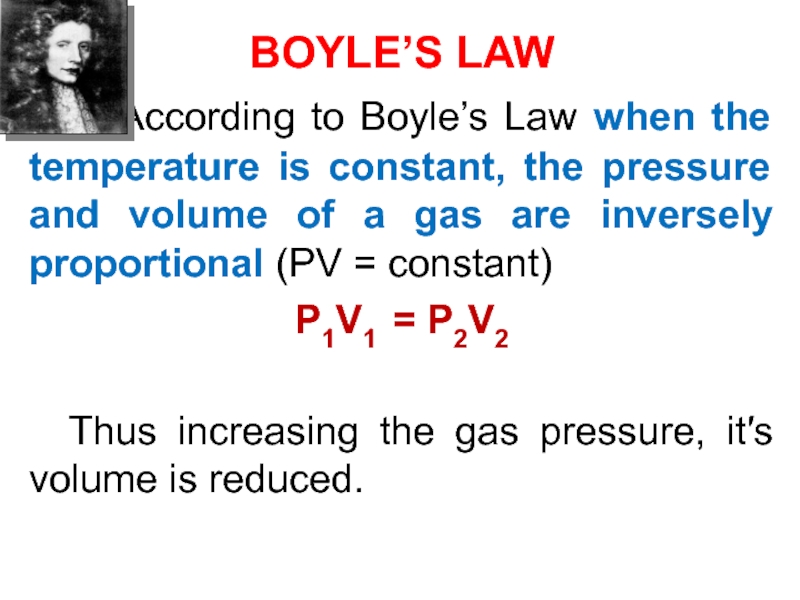
Слайд 39BOYLE’S LAW
According to Boyle’s Law when the temperature
is constant, the pressure and volume of a gas are
inversely proportional (PV = constant)P1V1 = P2V2
Thus increasing the gas pressure, its volume is reduced.
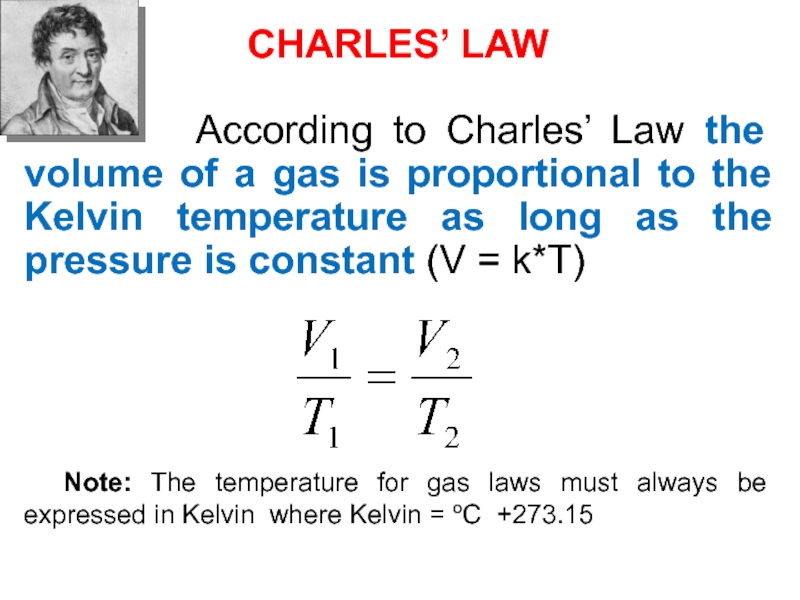
Слайд 40CHARLES’ LAW
According to Charles’ Law
the volume of a gas is proportional to the Kelvin
temperature as long as the pressure is constant (V = k*T)Note: The temperature for gas laws must always be expressed in Kelvin where Kelvin = oC +273.15
Слайд 41GAY-LUSSAC'S LAW
Gay Lussac's Law of pressure and temperature
describes the direct relationship between pressure and temperature, if mass
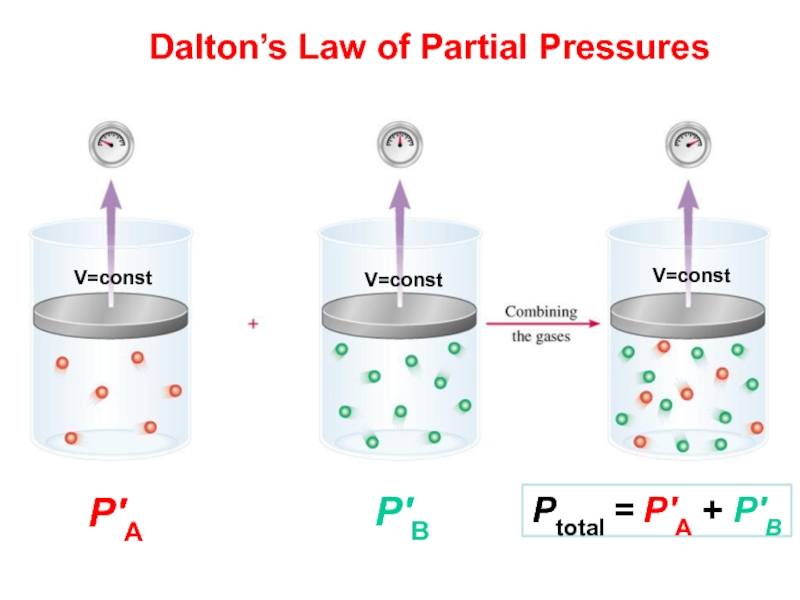
and volume of gas are fixed. If the absolute temperature of a fixed gas volume is increased, then the pressure will be increases proportionally (P=k*T):Слайд 42Partial Pressure
Pressure each gas in a mixture would exert if
it were the only gas in the container:
Dalton's Law of
Partial Pressures (1801) The total pressure exerted by a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures (Pn) of the gases in that mixture:
PTotal = P1 + P2 + P3 + .....