Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
lnternational Marketing Chapter 9 Global Price Decision
Содержание
- 1. lnternational Marketing Chapter 9 Global Price Decision
- 2. Global pricingGlobal pricing strategies Global pricing decisions
- 3. A. Global PricingWhat is price?The amount
- 4. Global pricing is one of the most
- 5. CASE
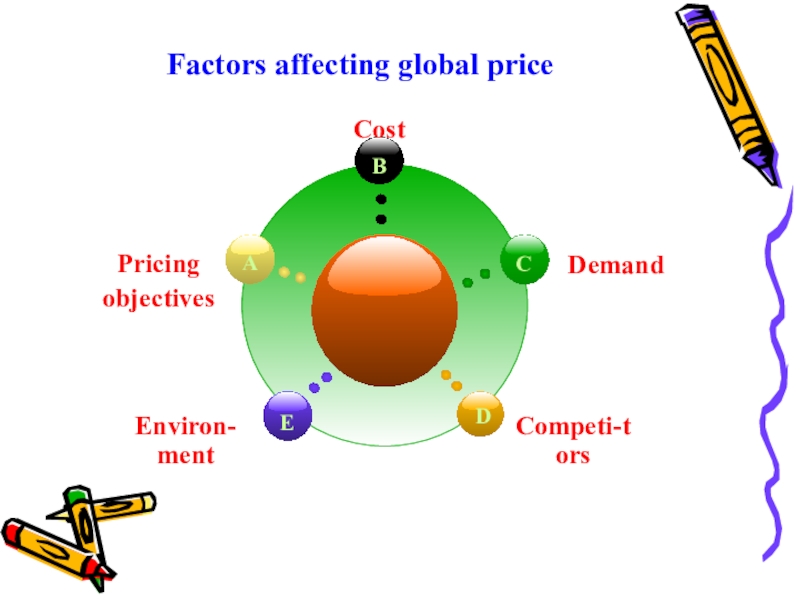
- 6. Factors affecting global price
- 7. 1.Pricing objectivesPricing objectives give direction to the
- 8. enhance the image of the firm, brand,
- 9. 2. Cost Include fix and viriable costs
- 10. 3.Demand Demand is a important element of
- 11. CASE
- 12. 4. CompetitorsPricing decisions are also bounded by
- 13. 5. EnvironmentCurrency fluctuations (exchange rate)InflationGovernment policy (tariff )
- 14. When currency fluctuation occurs, there are two
- 15. Inflation is a worldwide phenomenon. Inflation requires
- 16. TariffA tariff is a tax placed on
- 17. It is also used to raise
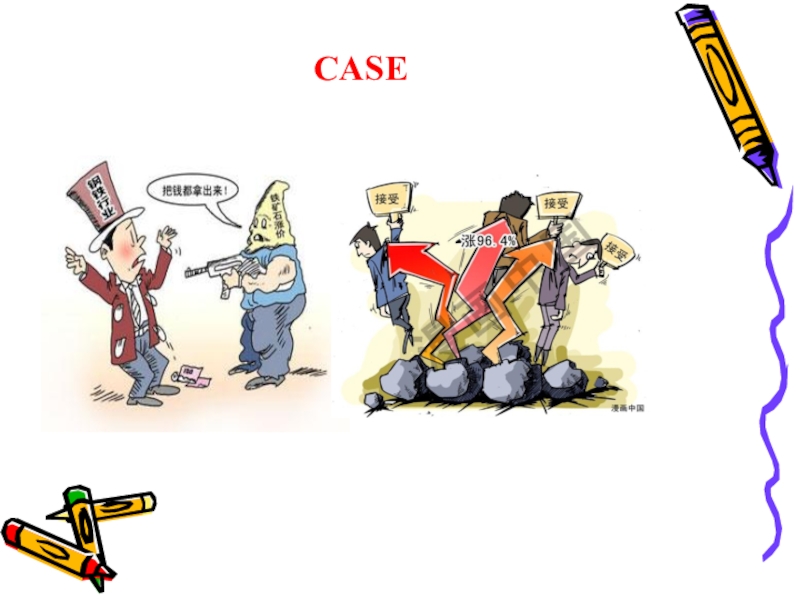
- 18. CASE
- 19. CASE 1 175+ 10% tariff+ 30%Consumption tax tax+ others=275275+ 5%Operation tax+17%Value added tax+others=540
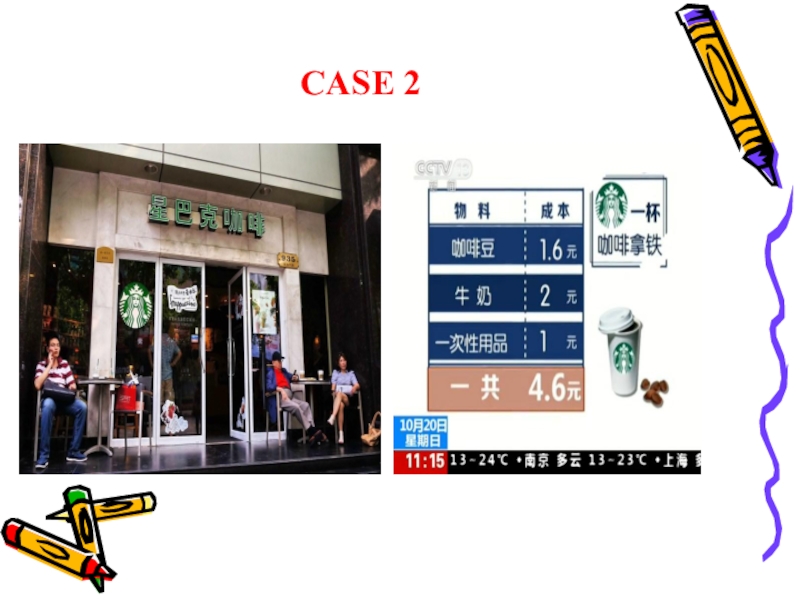
- 20. CASE 2
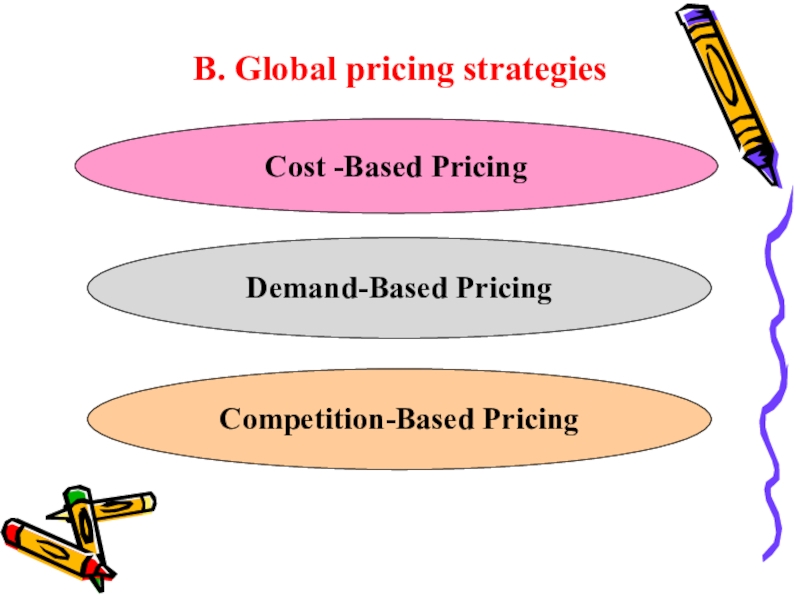
- 21. B. Global pricing strategiesCost -Based PricingDemand-Based PricingCompetition-Based Pricing
- 22. 1. Cost -Based PricingCost – plus pricingFirst
- 23. If a business sells a microwave that
- 24. Dumping Dumping is the act of
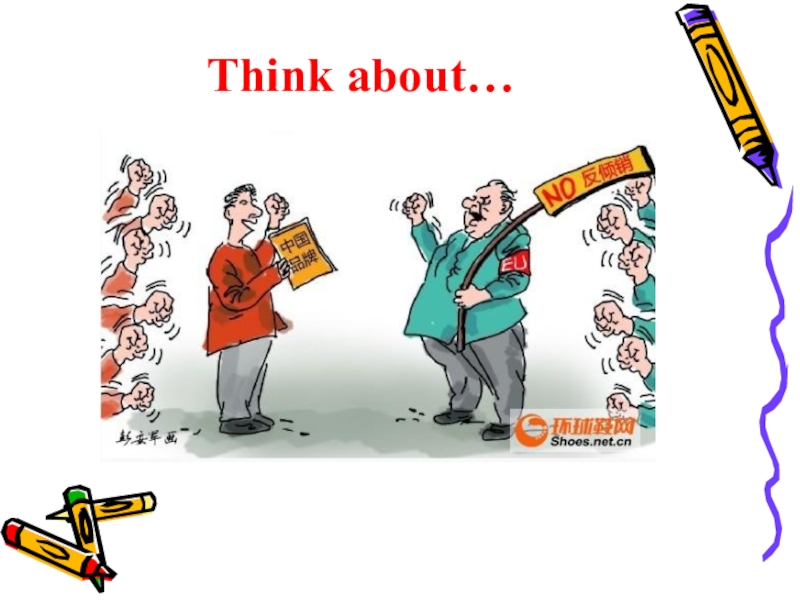
- 25. Think about…
- 26. B. Demand based pricing1.Value- Based Pricing
- 27. Слайд 27
- 28. CASE
- 29. Discriminating pricingTime
- 30. PlaceSupermarketRestaurant PUB,KTV
- 31. C. Competition -Based PricingGoing-ratepricingSealed-bidpricing
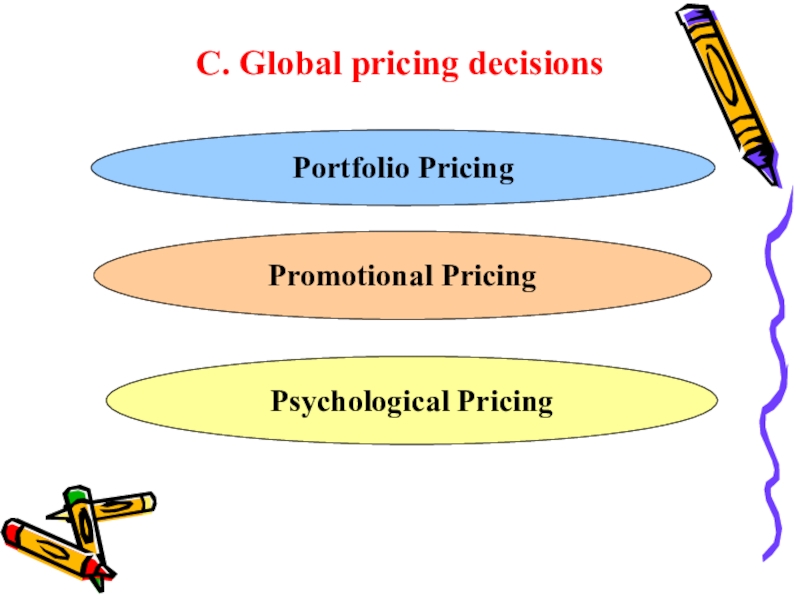
- 32. C. Global pricing decisionsPortfolio PricingPromotional Pricing Psychological Pricing
- 33. 1.Portfolio Pricing The term portfolio
- 34. CASE 1
- 35. CASE 2
- 36. CASE 3
- 37. CASE 4
- 38. 2. Promotional Pricing Buy one , Get one free
- 39. SPRING SALESUMMER SALEAUTUMN SALEYEAR END SALECHRISTMAS SALEEASTER SALE
- 40. 3. Psychological Pricing 4.99 VS 52400 VS 2399.95
- 41. Transfer pricing Transfer pricing refers to
- 42. Multinational enterprises are growing in number
- 43. SummaryGlobal pricingGlobal pricing strategies Global pricing decisionsTransfer pricing
- 44. Referencehttp://www.fao.org/docrep/w5973e/w5973e0d.htm国际税收
- 45. Слайд 45
- 46. Скачать презентанцию
Global pricingGlobal pricing strategies Global pricing decisions
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 4Global pricing is one of the most critical and
complex issues that a global firms face.
Price is the only
marketing mix instrument that creates revenues. All other elements entail costs.A company’s global pricing policy may make or break its overseas expansion efforts.Multinationals also face the challenge of how to coordinate their pricing policy across different countries.
Слайд 71.Pricing objectives
Pricing objectives give direction to the whole pricing process.
Determining what your objectives are is the first step in
pricing.When deciding on pricing objectives you must consider: the overall financial, marketing, and strategic objectives of the company; the objectives of your product or brand; consumer price elasticity and price points; and the resources you have available.
Слайд 8enhance the image of the firm, brand, or product
maximize
short-run profit
increase sales volume (quantity)
increase market share
company
growth maintain price leadership
desensitize customers to price
discourage new entrants into the industry
Слайд 92. Cost
Include fix and viriable costs associated with the product.
Exporting
involves more steps and substantially higher risks than domestic marketing.
To cover the incremental costs (shipping, insurance, labor,promotion etc), the final foreign retailprice will often be much higher than the domestic retail price.Слайд 103.Demand
Demand is a important element of global pricing
If demand of the host country is strong. The price
of product might be higher in that country.Слайд 124. Competitors
Pricing decisions are also bounded by competitive action. If
competitors are manufacturing or sourcing in a lower costs country,
it may be necessary to cut prices to stay competitive.Слайд 14When currency fluctuation occurs, there are two options for pricing:
one is to fix the price of products in country
target market. In this case, any appreciation or depreciation of the value of the currency in the country of production will lead to gain or losses for the seller.The other option is to fix the price of products in home country currency. If it is done, any appreciation or depreciation of the home country currency will result in price increases or decreases for customers and no immediate consequences for the seller.
Слайд 15Inflation is a worldwide phenomenon. Inflation requires periodic adjustments. These
adjustments are caused by rising costs that must be covered
by increased selling prices.An essential requirement when pricing in an inflationary environment is the maintenance of operating profit margins.
Слайд 16Tariff
A tariff is a tax placed on imported goods. Each
country has separate tariff regulations. WHY?
Tariff increases government funds. For
example, countries that do not grow bananas may create a tariff on importing bananas. The government would then make money from businesses that import bananas. Слайд 17 It is also used to raise the price of
imported goods .
A higher tariff allows a local
company to compete with foreign competition.When no tariff or other restrictions are placed on imported goods, it is called free trade.
Слайд 19CASE 1
175+ 10% tariff+ 30%Consumption tax tax+ others=275
275+ 5%Operation
tax+17%Value added tax+others=540
Слайд 21B. Global pricing strategies
Cost -Based Pricing
Demand-Based Pricing
Competition-Based Pricing
Слайд 221. Cost -Based Pricing
Cost – plus pricing
First calculates the cost
of the product, then includes an
additional amount to represent profit.
(average variable cost + allocation of
fixed costs)*(1+ markup%).
Слайд 23If a business sells a microwave that has a variable
cost of $15.00, a fixed cost allocation of $5, and
a desired markup of 30%The price of the microwave using this method would be ($15 + $5)*(1+0.30), or $26.
Слайд 24Dumping
Dumping is the act of charging a lower
price for a good in a foreign market than one
charges for the same good in a domestic market. This is often referred to as selling at less than "fair value".Anti dumping is a measure to rectify the situation arising out of the dumping of goods and its trade distortive effect. Thus, the purpose of anti dumping duty is to rectify the trade distortive effect of dumping and re-establish fair trade.
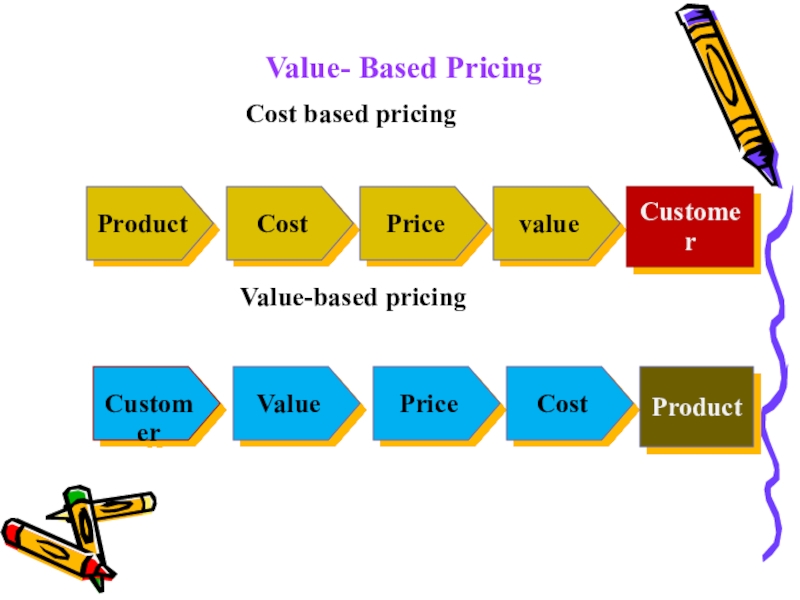
Слайд 26B. Demand based pricing
1.Value- Based Pricing
It sets selling
prices on the perceived value to the customer, rather than
on the actual cost of the product, the market price, competitors prices, or the historical price.2.discriminating pricing
Слайд 27
Value- Based Pricing
Cost based pricingValue-based pricing
Product
Cost
Price
value
Customer
Value
Price
Cost
Customer
Product