Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
lnternational Marketing Chapter1 Introduction
Содержание
- 1. lnternational Marketing Chapter1 Introduction
- 2. What is marketing?What is global marketing? Why it is important?What is meant by global localization?
- 3. MarketingWhat is a Market?A market is all
- 4. Analyzing the needs of the peopleTrying to
- 5. …. AndFigure out the best price to
- 6. The idea that you must satisfy the
- 7. The Marketing Mix is comprised of four basic marketing strategies, collectively known as the“Four P’s.”
- 8. Product StrategyWhat product to makeHow to package
- 9. Place StrategiesHow and where a product will
- 10. When you buy a product - the
- 11. The marketing functionsBuying Selling TransportationStorageStandardizationFinancing Risk Taking Information Collection
- 12. B.Global marketing• Exporting: Marketing domestically produced
- 13. The main difference is the scope of
- 14. Unstable governmentsForeign-exchange problemsDifferent culture Legal systemForeign entry
- 15. Increases in new products, product extensions, high
- 16. Decisions to make:Deciding to go abroadDeciding which
- 17. Слайд 17
- 18. CASE In Hong Kong, a German
- 19. When he gets home, sitting on an
- 20. Reasons for Global MarketingA. To Survive and
- 21. B. To Diversify Product and Market Portfolios
- 22. C. To Operate Within a Global MarketplaceGoods,
- 23. For US-based companies, 75% of sales potential
- 24. CASE
- 25. Toyota's history dates back to 1897, In
- 26. In June 1995, Toyota announced the 'New
- 27. In April 2002, Toyota announced another corporate
- 28. One of its strongest markets was the
- 29. In January 2004, leading global automobile company
- 30. Toyota has been badly hit by the
- 31. Toyota came back in 2012 with full
- 32. Analysts felt that the following factors were
- 33. D. Globalization Globalization is the process
- 34. CASE 1
- 35. Boeing is actively pursuing a strategy for
- 36. As Boeing produces globally, it also is
- 37. The recent establishment of a new Phantom
- 38. The series of Boeing-sponsored International Technology Summits
- 39. Jeppesen Sanderson Inc., a Boeing subsidiary since
- 40. CASE 2
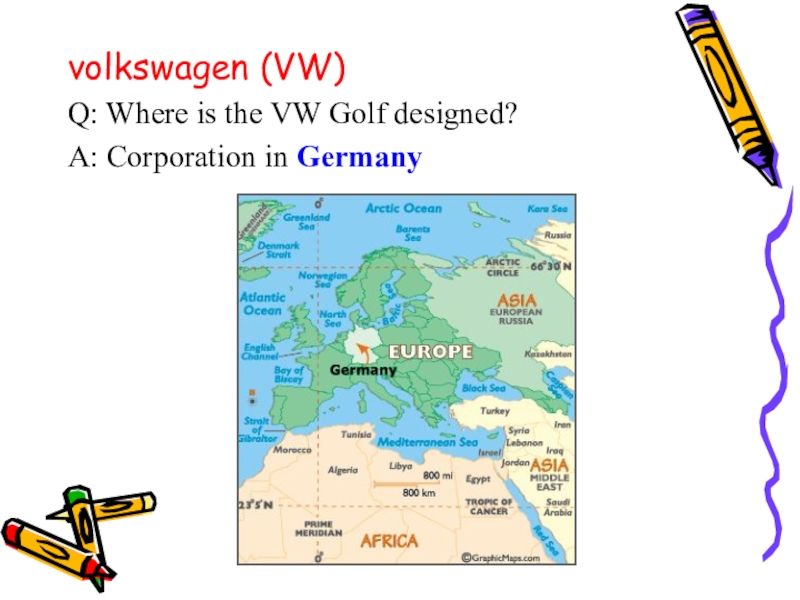
- 41. volkswagen (VW)Q: Where is the VW Golf designed?A: Corporation in Germany
- 42. Q: Where might the parts originate for the U.S. Model?A: Japan; Mexico, China…
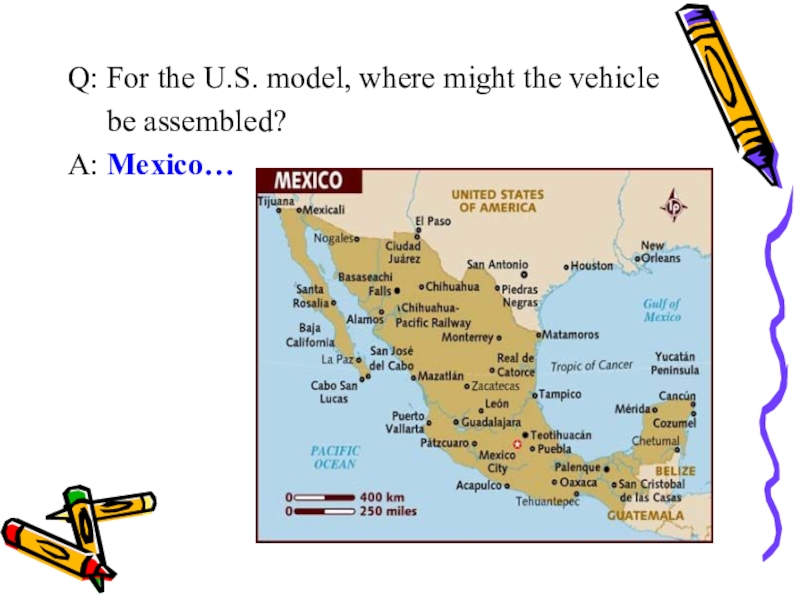
- 43. Q: For the U.S. model, where might the vehicle be assembled?A: Mexico…
- 44. Q: For the U.S. model, where might the steel come from for the parts?A: South Korea…
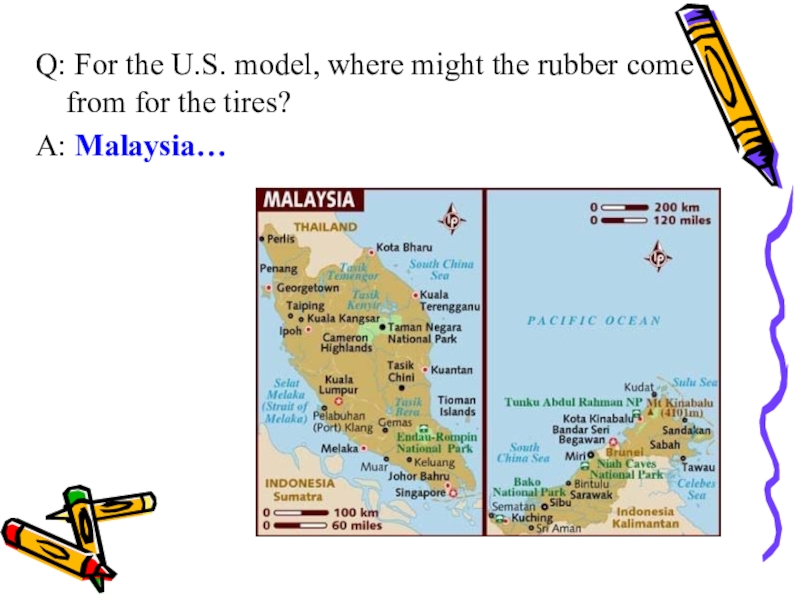
- 45. Q: For the U.S. model, where might the rubber come from for the tires?A: Malaysia…
- 46. Q: For the U.S. model, where might
- 47. Слайд 47
- 48. Every American household is full of goods
- 49. C. Global localizationIt means a successful global
- 50. Case McDonald’s Global MarketingMarketing Mix
- 51. Summary Marketing is the process used to
- 52. Reference市场营销学 陆娟 南京大学出版社市场营销学 胡正明 山东人民出版社国际市场营销学 闫国庆 清华大学出版社
- 53. Слайд 53
- 54. Скачать презентанцию
What is marketing?What is global marketing? Why it is important?What is meant by global localization?
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2What is marketing?
What is global marketing?
Why it is important?
What
is meant by global localization?
Слайд 3Marketing
What is a Market?
A market is all potential customers who
share
common needs and wants and who have the ability
and
willingness to buy the product.What is Marketing?
The process used to determine the customers’
needs. satisfy the customers’ needs and in
order to make a profit.
Слайд 4
Analyzing the needs of the people
Trying to guess what types
of products they want
Estimate how much they will buy
Predict when
they will want to buyDetermine where they go to buy the stuff
Слайд 5…. And
Figure out the best price to sell it at
- and can you still make a profit selling it
at that priceDecide on promotional things to create awareness about the product
Look at the competition to see what they are doing with pricing, features etc.
Слайд 6The idea that you must satisfy the customers’
needs and wants in order to make a profit.
Businesses must
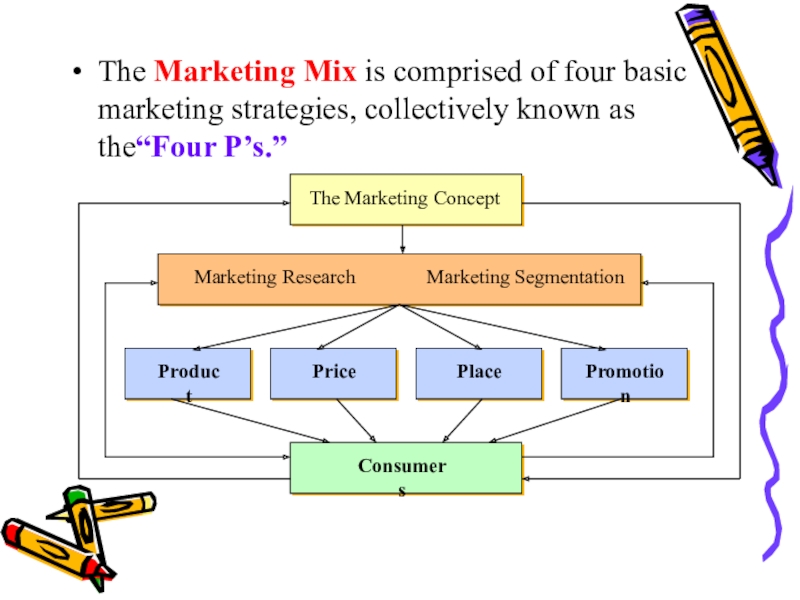
have the right goods and services at the right time, at the right price and at the right place. Plus they must communicate this to their customersСлайд 7The Marketing Mix is comprised of four basic marketing strategies,
collectively known as the“Four P’s.”
Слайд 8Product Strategy
What product to make
How to package it
What brand name
to use
What image to project
Price Strategies
Reflects what the customers are
willing andable to pay.
Слайд 9Place Strategies
How and where a product will be distributed
Promotion Strategies
How
will the customer be told about the product
What will the
message beWhen and where will it be delivered
With what media
Слайд 10When you buy a product - the cost of marketing
amounts to 40 ~ 60% of the total
eg.
If we buy shoes for $70, $35 of that 70 has been spent on marketing (including advertising, market research, development etc.)Слайд 11The marketing functions
Buying
Selling
Transportation
Storage
Standardization
Financing
Risk Taking
Information
Collection
Слайд 12B.Global marketing
• Exporting: Marketing domestically produced
goods and services in foreign countries.
• Importing: Purchasing foreign goods and services.
Global Marketing: Focuses resources on global
market opportunities and threats
Слайд 13The main difference is the scope of activities
because global
marketing occurs in markets
outside the organization’s home country.
Marketing has become more complex.Any Risk?
Слайд 14
Unstable governments
Foreign-exchange problems
Different culture
Legal system
Foreign entry and government bureaucracy
Tariffs
and other trade barriers
High cost of product and communication adaptations
Слайд 15Increases in new products, product extensions, high cost of distribution
and shelf space.
Expansion of retailer control and power, changing
media habits.Ultimate goal of programs
Timing goals
Global compepitors
Company needs a larger customer base for economies of scale.
Слайд 16Decisions to make:
Deciding to go abroad
Deciding which markets
Deciding how to
enter markets
Deciding on marketing programs
Deciding on marketing organization
Слайд 18CASE
In Hong Kong, a German businessperson is
driving a Lexus; he’s wearing Bruno Magli shoes, Irish cashmere
socks, Calvin Klein underwear, an Armani suit, with a Gucci belt.He has a Mont Blanc pen, in his Italian shirt. He’s going to meet an American investor at a KFC restaurant, for a Coke.
Слайд 19When he gets home, sitting on an ottoman, he has
an Absolut vodka nightcap, while listening to
American country western
music. Слайд 20Reasons for Global Marketing
A. To Survive and Growth
1. Access to
new markets and resources
2. Manage marketing tasks more efficiently and
effectively3. Expand customer base to include developed and developing nations
4. Against competitors with lower costs (due to increased access to resources)
Слайд 21B. To Diversify Product and Market Portfolios
and Improve
competitiveness
Effects of seasonal and cyclical fluctuations in one market offset
by othersDiversification increases market size and enhances economies of scale
Слайд 22C. To Operate Within a Global Marketplace
Goods, services, capital, technology,
and labour are going global
Reduced government restrictions are affecting global
marketingBilateral and multilateral negotiations are reducing restrictions
Слайд 23For US-based companies, 75% of sales potential is outside the
US.
About 90% of Coca-Cola’s operating income is generated outside the
US.For Japanese companies, 85% of potential is outside Japan.
For German and other EU companies, 94% of potential is outside Germany.
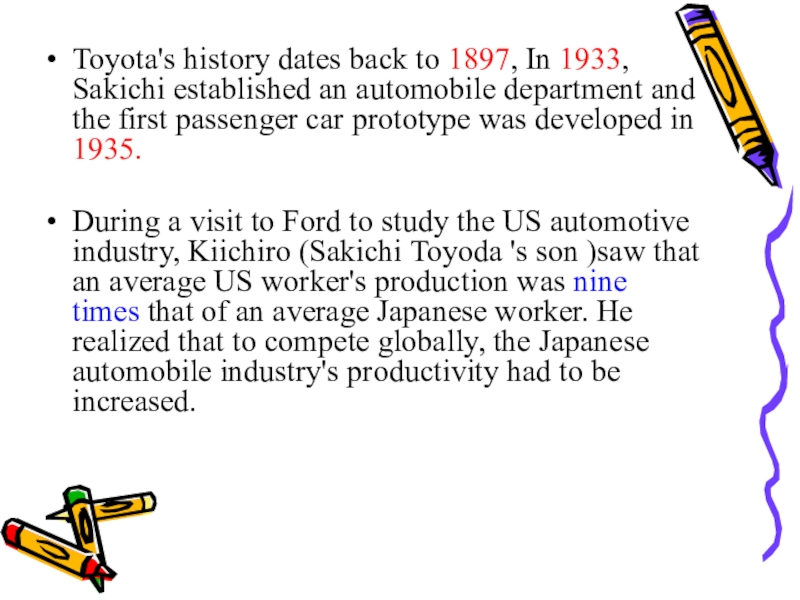
Слайд 25Toyota's history dates back to 1897, In 1933, Sakichi established
an automobile department and the first passenger car prototype was
developed in 1935.During a visit to Ford to study the US automotive industry, Kiichiro (Sakichi Toyoda 's son )saw that an average US worker's production was nine times that of an average Japanese worker. He realized that to compete globally, the Japanese automobile industry's productivity had to be increased.
Слайд 26In June 1995, Toyota announced the 'New Global Business Plan,'
aimed at advancing localization and increasing imports over a three
year period.A major objective of this plan was to increase Toyota's offshore production capacity to 2 million units by 1998.
Apart from this short-term global business plan, Toyota also came up with a long-term global business vision in June 1996, named the 'Global Vision 2005.
Слайд 27In April 2002, Toyota announced another corporate strategy to boost
its globalization efforts. the '2010 Global Vision' was aimed at
achieving a 15% market share of the global automobile market by early 2010.By mid-2003, Toyota was present in almost all the major segments of the automobile market that included small cars, luxury se, pickup trucks, SUVs, small trucks and cvehicles. Toyota had 45 manufacturing plants in 26 countries and regions by this time, and sold vehicles in 160 countries.
Слайд 28One of its strongest markets was the US, the world's
largest automobile market. Toyota had emerged as a strong foreign
player in Europe as well, with a 4.4% market share. In China, it had a 1.5% market share.The other major markets in which the company was fast strengthening its presence were South America, Southwest Asia, Southeast Asia and Africa. Back home in Japan, it enjoyed a market share of over 43%.
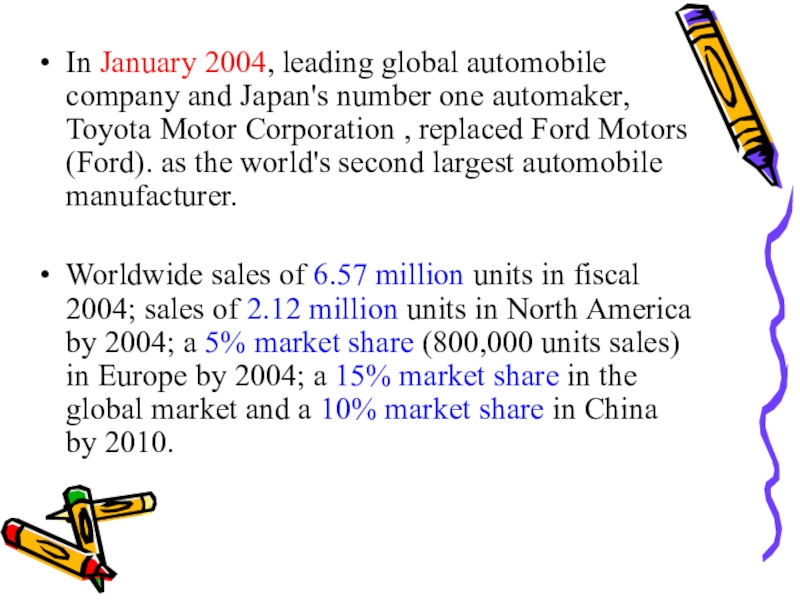
Слайд 29In January 2004, leading global automobile company and Japan's number
one automaker, Toyota Motor Corporation , replaced Ford Motors (Ford).
as the world's second largest automobile manufacturer.Worldwide sales of 6.57 million units in fiscal 2004; sales of 2.12 million units in North America by 2004; a 5% market share (800,000 units sales) in Europe by 2004; a 15% market share in the global market and a 10% market share in China by 2010.
Слайд 30Toyota has been badly hit by the global economic crisis
in 2008 and said its global sales were down 4
% in 2008, but GM witnessed sales fall 10.8 % in the same period.In 2008.Toyota has overtaken General Motors as the largest car maker in the world in terms of sales volume. Toyota sold 8.97 million vehicles , beating the 8.35 million sold by the Detroit auto giant and ending GM's 77-year reign at the top. And held the position for three years.
Слайд 31
Toyota came back in 2012 with full production and higher
discounts in a bid to gain market share. Toyota sold
9.75 million vehicles , compared with 9.29 million for GM. And it was boosted by a 27% sales increase in the U.S .The Japanese giant sold 2.43 million vehicles globally in the first three months of 2013, fending off strong competition from both Volkswagen and General Motors, which sold 2.27 million and 2.36 million respectively.
Слайд 32Analysts felt that the following factors were helping the company
in its quest to become a truly global automobile major:
Strong financial condition
Globally efficient production system
Unique corporate culture
The ability to develop a product range that met the unique needs and desires of customers in different regions
Слайд 33D. Globalization
Globalization is the process of international integration
arising from the interchange of world views, products, ideas, and
other aspects of culture.A shirt could have very well been made with Chinese cotton sewed by Thai hands, shipped across the Pacific on a French freighter crewed by Spanish to a Los Angeles harbor.
Слайд 35Boeing is actively pursuing a strategy for globalization and global
value creation through new partnerships, joint ventures, mergers and acquisitions,
supplier relationships and a greatly expanded international presence.Their customers are in more than 90 countries around the world, and they have employees in about 70 countries. About 3% employees of Boeing are based outside the US including approximately 3,000 in Australia with hundreds more in Britain, Germany and Russia.
Слайд 36As Boeing produces globally, it also is sourcing globally.
Almost
400 Russian engineers work for Boeing in Moscow, and are
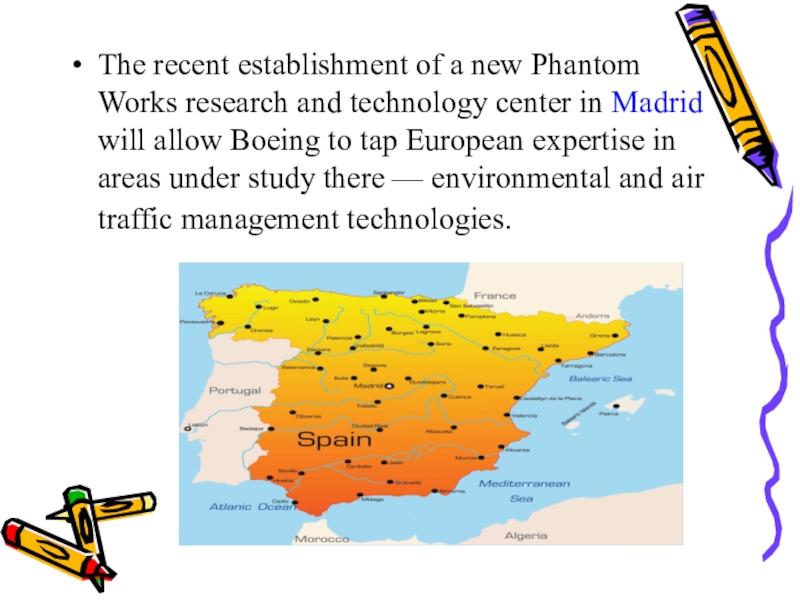
linked electronically to a design team in Seattle.Слайд 37The recent establishment of a new Phantom Works research and
technology center in Madrid will allow Boeing to tap European
expertise in areas under study there — environmental and air traffic management technologies.Слайд 38The series of Boeing-sponsored International Technology Summits that have been
held in Tokyo, London, Paris and Madrid. More are scheduled
for Berlin, Seoul, and other locations.These events bring together decision makers from important regions to discuss key topics such as air traffic management, aerospace and the environment, international co-operation in defense, future aircraft concepts, advanced manufacturing and more.
Слайд 39Jeppesen Sanderson Inc., a Boeing subsidiary since October 2000, is
the world's leading supplier of flight information, flight planning services,
aviation weather services, maintenance information and aviation training systems.It has an 85 percent global airline market share for its core navigation services such as aeronautical charts and electronic navigation data. Jeppesen products are a key component of Boeing's growing customer information services business. Jeppesen has offices in the US, UK, Germany, Australia, China and Russia.
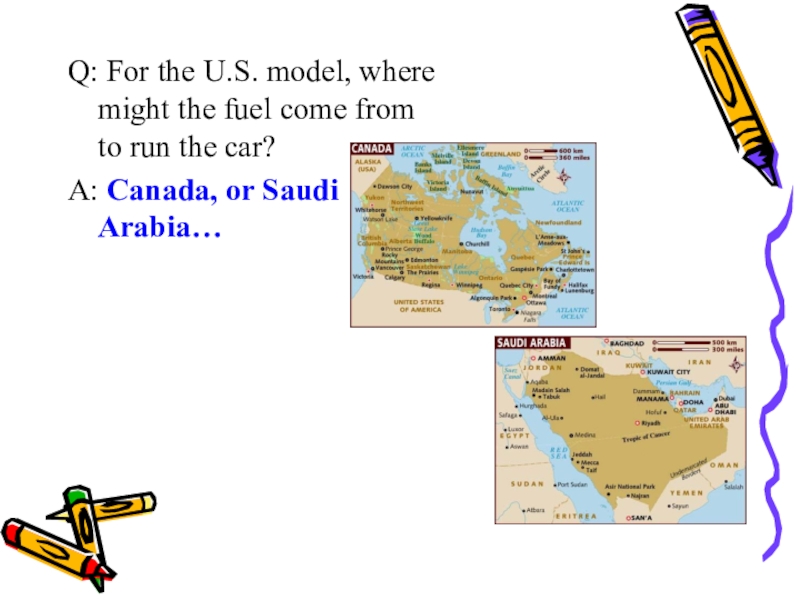
Слайд 46Q: For the U.S. model, where might the fuel come
from to run the car?
A: Canada, or Saudi Arabia…
Слайд 48Every American household is full of goods made in China.
Whether it’s clothes, toys, or increasingly technology, Made in China
is hard to miss. Yet, those goods are not China brands. They’re Nike. They’re Hasbro. They’re Ralph Lauren.Слайд 49C. Global localization
It means a successful global marketer must have
the ability to “ think globally and act locally”.
A central
issue in global marketing is how to tailor the global marketing concept to fit a particular product or businessСлайд 50Case
McDonald’s Global Marketing
Marketing Mix Element Standardization Localized
Product
Promotion
Place
Price
Big Mac
Brand name
Advertising
slogan “I’m Loving It”
Free-standing
Big Mac is $3.10 in U.S. and
TurkeyMcAloo Tikka potato burger (India)
Slang ’Macca’s (Australia)
MakDo (Philippines)
McJoy magazine, “Hawaii Surfing Hula” promotion (Japan)
Home delivery (India)
Swiss rail system dining cars
$5.21 (Switzerland)
Слайд 51Summary
Marketing is the process used to determine the customers’
needs. satisfy the customers’ needs and in order to make
a profit.4Ps: Product. Price. Place. Promotion
Doing global marketing is risky. But there are still many reasons for that.
Do Remember: Think globally and act locally.