Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
MAJOR Sources of energy
Содержание
- 1. MAJOR Sources of energy
- 2. COALCoal – is a readily combustible black
- 3. About 300 million years
- 4. CLASSIFICATION As geological processes apply
- 5. Subbituminous coal – this is
- 6. EXTRACTING Coal mining has had
- 7. PETROLEUM Petroleum or crude oil
- 8. FORMATION Petroleum is formed by
- 9. CLASSIFICATION Petroleum is usually classified
- 10. USES OF PETROLEUM Here are
- 11. NATURAL GAS Natural gas is
- 12. FORMATION Most natural gas was
- 13. Слайд 13
- 14. Before natural gas can
- 15. USES OF NATURAL GAS Natural
- 16. QUESTIONS1. Give the definition of coal.2. What
- 17. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1MAJOR
Sources of energy
Underground Mining Department
National Mining University
Dnipropetrovsk
UKRAINE
Слайд 3 About 300 million years ago, the Earth
had dense forests in low-lying wetland areas. Due to natural
processes such as flooding, these forests were buried under the soil. As more and more soil deposited over them, they were compressed. The temperature also rose as they sank deeper and deeper.For the process to continue, the plant matter was protected from biodegradation and oxidization, usually by mud or acidic water. This trapped the carbon in immense peat bogs that were eventually covered and deeply buried by sediments. Under high pressure and high temperature dead vegetation were slowly converted to coal. As coal contains mainly carbon, the conversion of dead vegetation into coal is called carbonization.
FORMATION
Слайд 4CLASSIFICATION
As geological processes apply pressure to dead
biotic material over time, under suitable conditions it is transformed
successively into:Peat – considered as a precursor of coal, has industrial importance as a fuel in some countries. In its dehydrated form, peat is a
Lignite – this is a brownish-black coal with high moisture and ash content, which has the lowest heating value of the all types of coal. It is considered an “immature” coal that is still soft. It is used for generating electricity.
highly effective absorbent for fuel and oil spills on land and water. It is also used as a conditioner for soil to make it more able to retain and slowly release water.
Слайд 5 Subbituminous coal – this is a black coal
with a higher heating value than lignite, and is used
principally for electricity and space heating. Hard coal or Bituminous coal – it is the most commonly used type of coal for electric power generation. It is a dark coal that has a higher heating value than lignite and subbituminous coal, but a lower heating value than anthracite.
Anthracite – this is coal that was formed from bituminous coal under increased pres-sures in rock strata during the creation of mountain ranges. This type of coal is the most compact and therefore, has the highest energy content of the all levels of coal. It is used for space heating and generating electricity.
Слайд 6EXTRACTING
Coal mining has had a lot of
developments over the recent years, from the early days of
men tunneling, digging and manually extrac-ting the coal on carts to large open cuts and long walls mines.Mining at this scale requires the use of draglines, trucks, conve-yors, jacks and shearers. Coal mining can have a large environmen-tal impact and needs to be managed. Many mines are required by government to rehabilitate the area that was mined. Coal is extrac-ted from the ground by underground mining either surface mining.
USES OF COAL
Coal is used primarily as an energy source, either for heat or electricity. It was once heavily used to heat homes and power loco-motives and factories. Bituminous coal is also used to produce coke for making steel and other industrial process heating.
Coal gasification and coal liquefaction (coal-to-liquids) are also possible uses of coal for producing synthetic fuel.
Слайд 7PETROLEUM
Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally
occurring liquid found in formations in the Earth consisting of
a complex mixture of hydrocarbons (mostly alkanes) of various lengths. Petroleum literally means «rock oil»; oil that comes from rock. Oil is a hydrocarbon-based liquid which is sometimes present in porous rocks beneath the earth’s surface.Слайд 8FORMATION
Petroleum is formed by the slow alteration
of organic remains over time. It consists of a mixture
of liquid hydrocarbon compounds and varies widely in composition, color, density and viscosity. From this liquid after distillation yields a range of combustible fuels, petrochemi-cals, and lubricants.Compounds and mixtures of compounds separated from crude petroleum by distillation include gasoline, diesel fuel, kerosene, fuel oil, some types of alcohol, benzene, different grades of lubricating oils.
Слайд 9CLASSIFICATION
Petroleum is usually classified according to the
predominance of paraffin or asphal-ted compounds and accordingly is said
to
have a paraffin base, an intermedia-te base, or an asphalt base.
Oil wells are drilled as deep as ten kilometers into the Earth to search for petroleum. These wells can cost millions of dollars to
EXTRACTING
drill, drilling is done because petroleum is a valuable natural resource. Although the major use of petroleum is as a fuel (it often use to generate electricity), there are many other uses as well.
Слайд 10USES OF PETROLEUM
Here are some of the
ways petroleum is used in our everyday life. All plastic
is made from petroleum and plastic is used almost everywhere, in cars, houses, toys, computers and clothing. Asphalt used in road construction is a petroleum product as is the synthetic rubber in the tires. Wax paraffin comes from petroleum, as do fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides, detergents, phonograph records, photog-raphic film, furniture, packaging mate-rials, surfboards, paints and artificial fibers used in clothing, upholstery, and carpets.
Petroleum is used principally as a source of fuel and lubrica-ting oils. Only when these reserves of oil are restricted or threate-ned does the average person begin to realize their importance.
Слайд 11NATURAL GAS
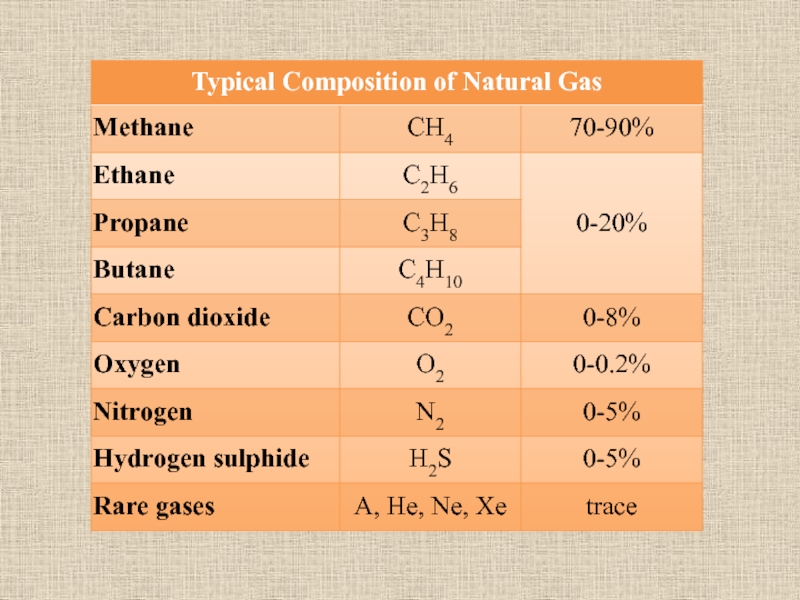
Natural gas is a naturally occurring
hydrocarbon gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, with up to
20% of other hydrocarbons as well as impurities in varying amounts such as carbon dioxide.Слайд 12FORMATION
Most natural gas was created over time
by two mechanisms: biogenic and thermo-genic. Biogenic gas is created
by methano-gens in bogs and sediments. Deeper in the earth, at greater temperature and pressure, thermogenic gas is created from buried organic material. Natural gas is found in deep un-derground natural rock formations or associated with other hydrocar-bon reservoirs, in coal beds, and as methane clathrates (or methane hydrate). Often petroleum is also found near natural gas deposits.
Слайд 14 Before natural gas can be used as
a fuel, it must undergo processing to clean the gas
and remove impurities including water in order to meet the specifications of marke-table natural gas.EXTRACTING
The by-products of processing include ethane, propane, butanes, pentanes, and higher molecular weight hydrocarbons, hydrogen sulphide (which may be converted into pure sulfur), carbon
dioxide, water vapor, and sometimes helium and nitrogen.
Natural gas is often informally called to simply as gas, especially when compared to other energy sources such as oil or coal.
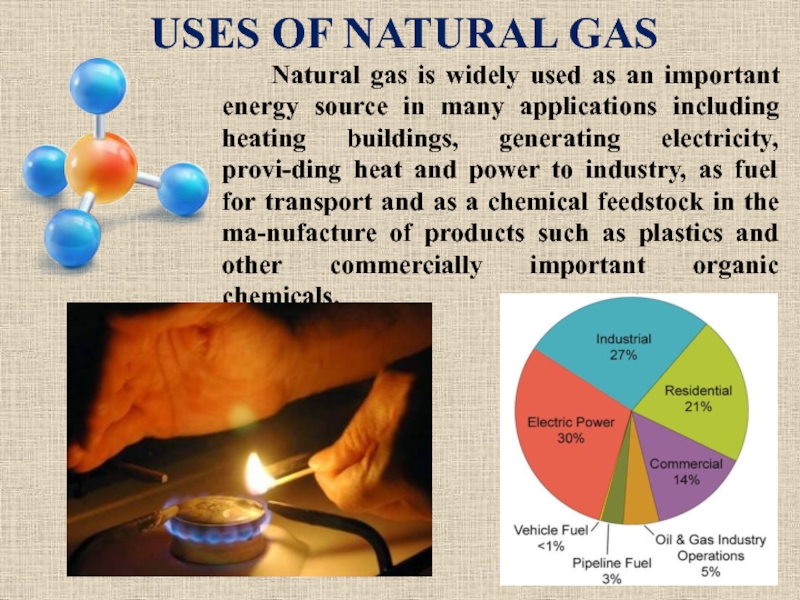
Слайд 15USES OF NATURAL GAS
Natural gas is widely
used as an important energy source in many applications including
heating buildings, generating electricity, provi-ding heat and power to industry, as fuel for transport and as a chemical feedstock in the ma-nufacture of products such as plastics and other commercially important organic chemicals.Слайд 16QUESTIONS
1. Give the definition of coal.
2. What main variations of
coal do you know?
3. What is a petroleum?
4. How oil
is formed?5. In what ways petroleum is used?
6. Typical composition of natural gas.