Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
MAN Diesel PrimeServ Academy ME Concept
Содержание
- 1. MAN Diesel PrimeServ Academy ME Concept
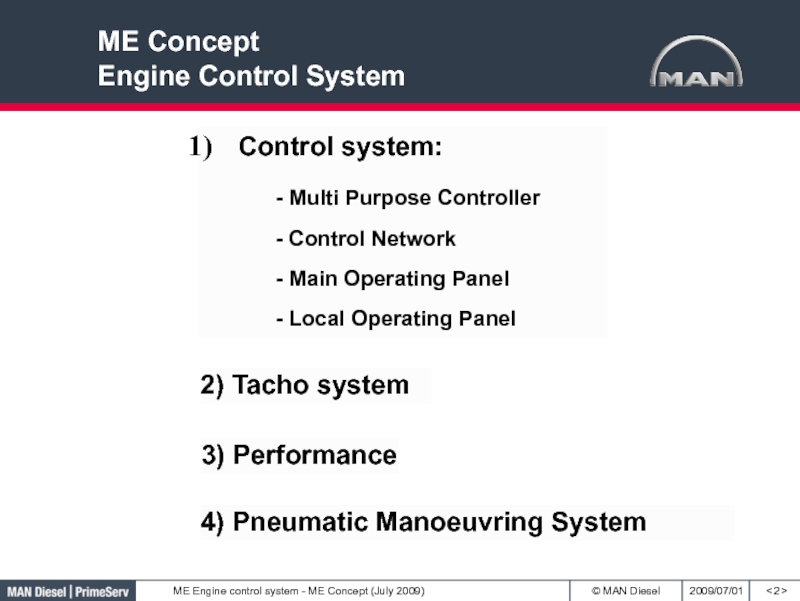
- 2. < >Control system: - Multi Purpose Controller - Control
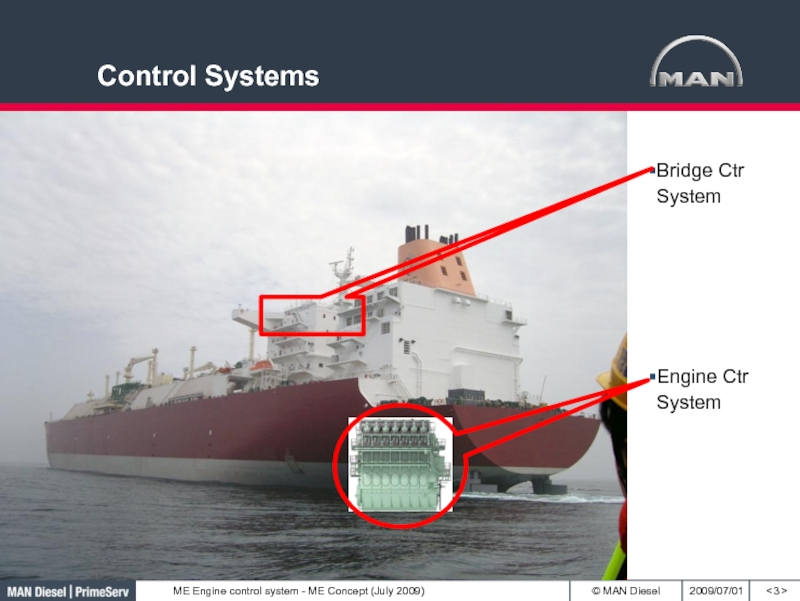
- 3. Control Systems< >Bridge Ctr SystemEngine Ctr System
- 4. Engine Control System MPC & Control Network<
- 5. Multi Purpose Controller, MPC< > 24 VDC,
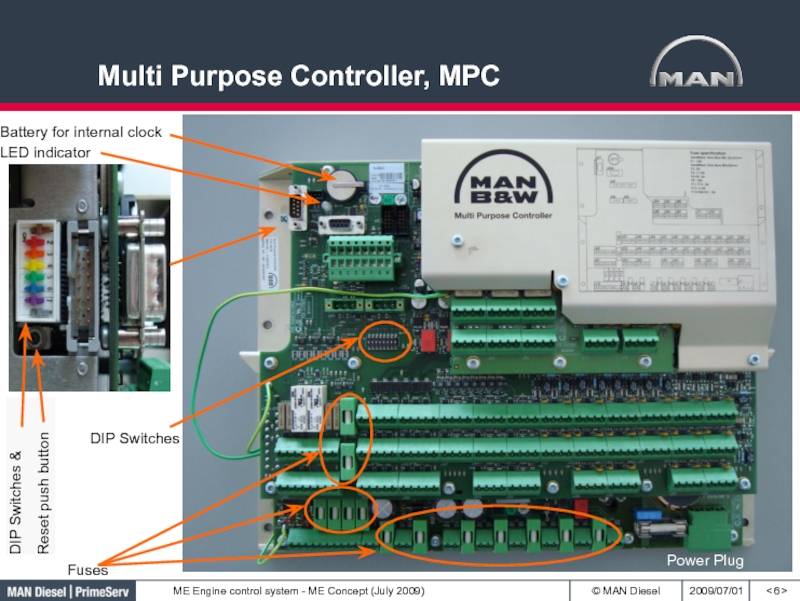
- 6. Multi Purpose Controller, MPC< >DIP SwitchesDIP Switches &Reset push buttonPower Plug
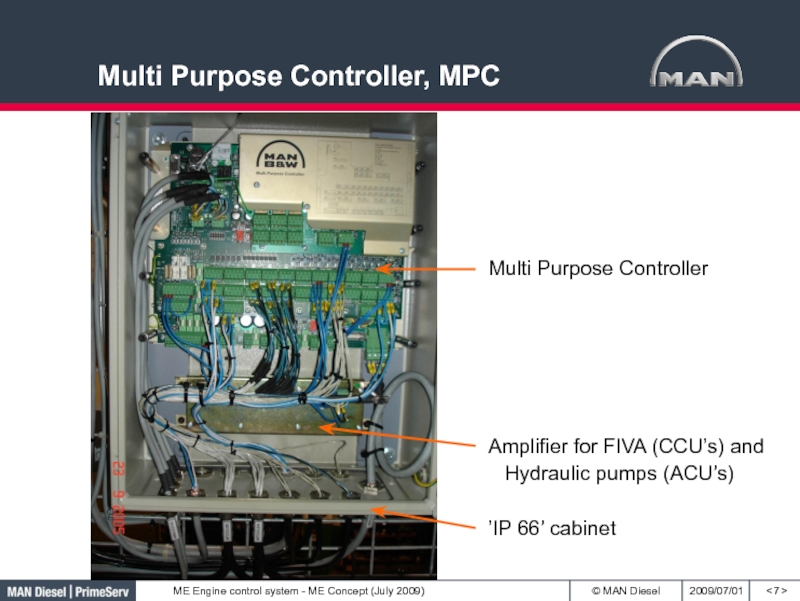
- 7. Multi Purpose Controller, MPC< >Amplifier for FIVA (CCU’s) and Hydraulic pumps (ACU’s)Multi Purpose Controller’IP 66’ cabinet
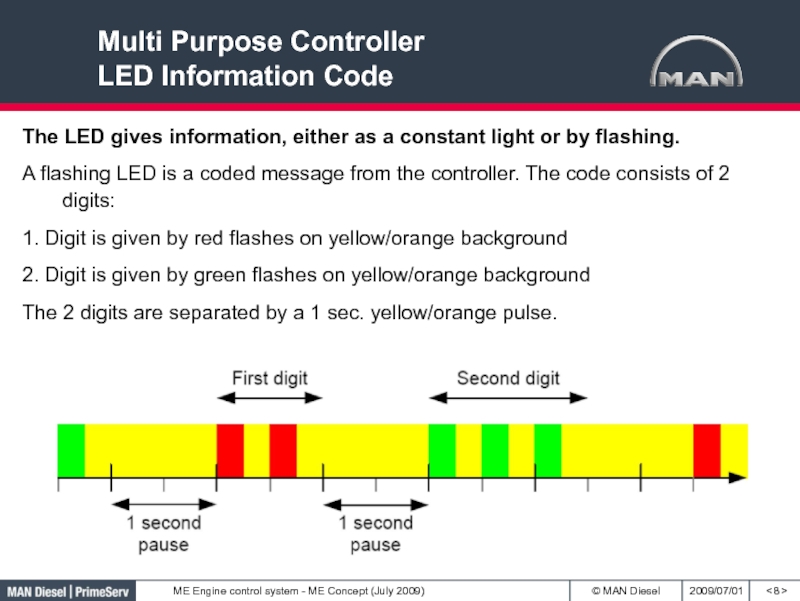
- 8. Multi Purpose Controller LED Information Code<
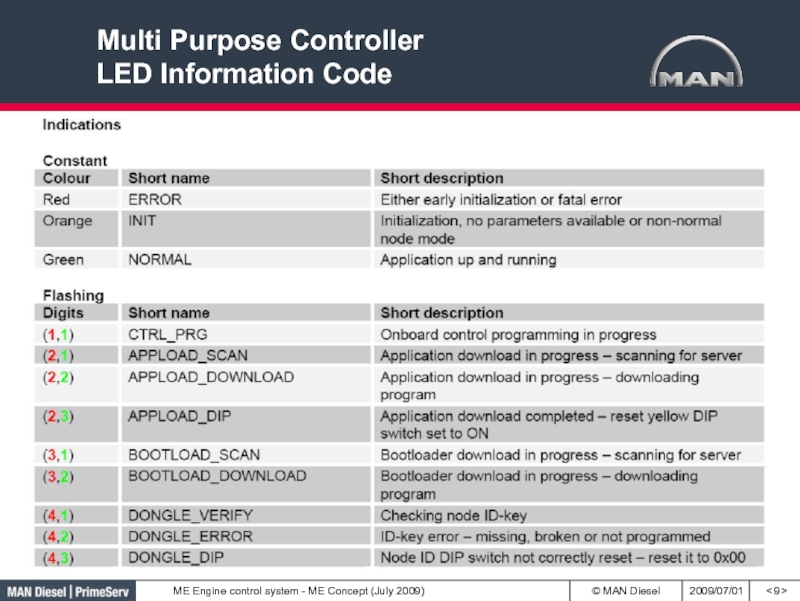
- 9. Multi Purpose Controller LED Information Code< >
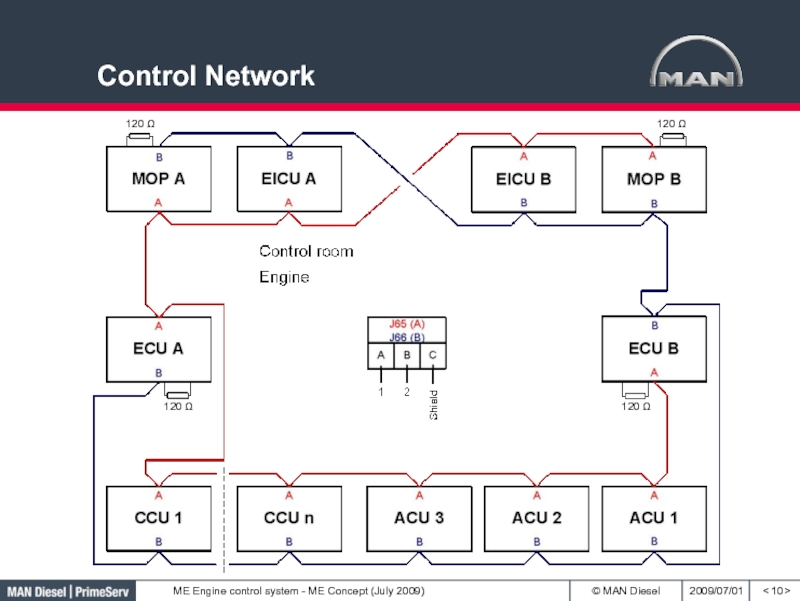
- 10. Control Network< >120 Ω120 Ω120 Ω120 Ω
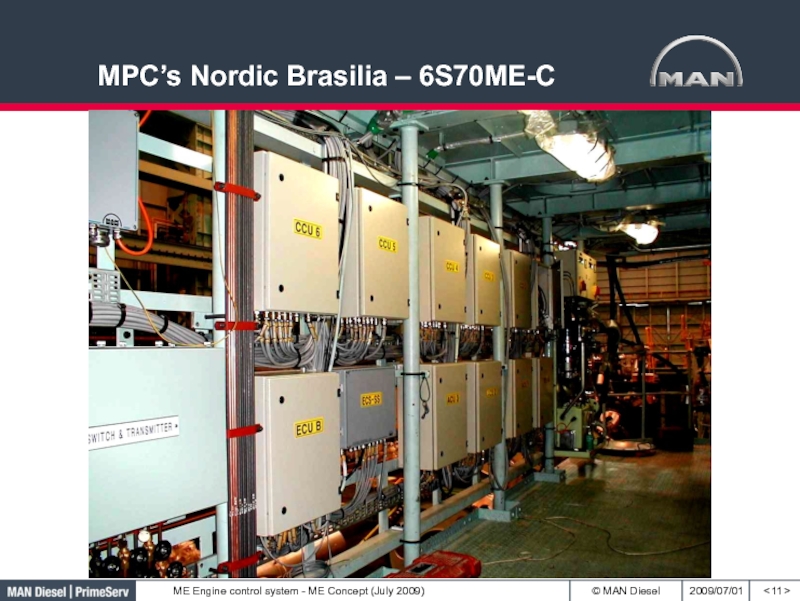
- 11. MPC’s Nordic Brasilia – 6S70ME-C< >
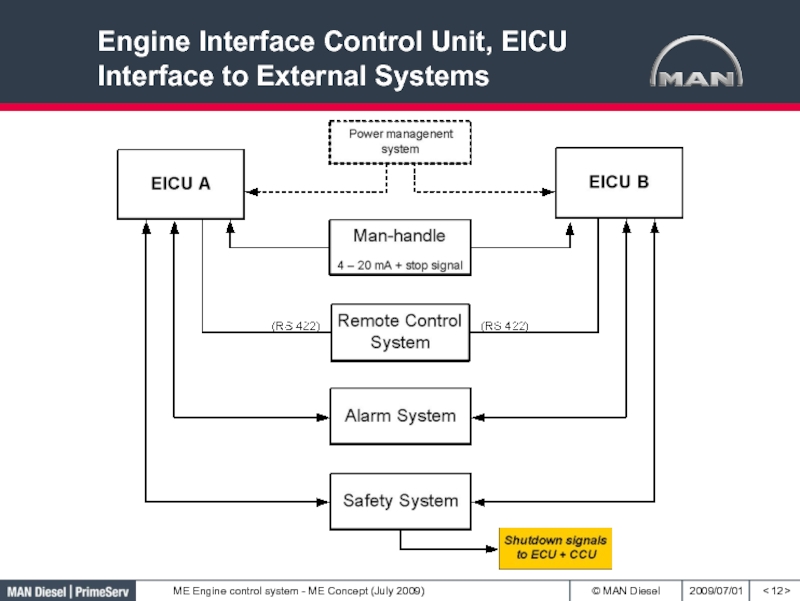
- 12. Engine Interface Control Unit, EICU Interface to External Systems< >
- 13. Engine Interface Control Unit, EICU Speed Setpoint<
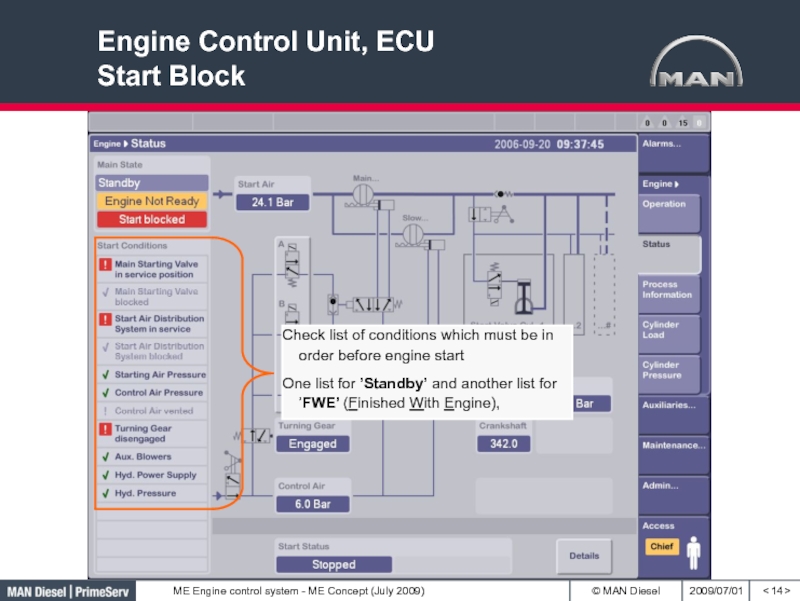
- 14. Engine Control Unit, ECU Start Block< >
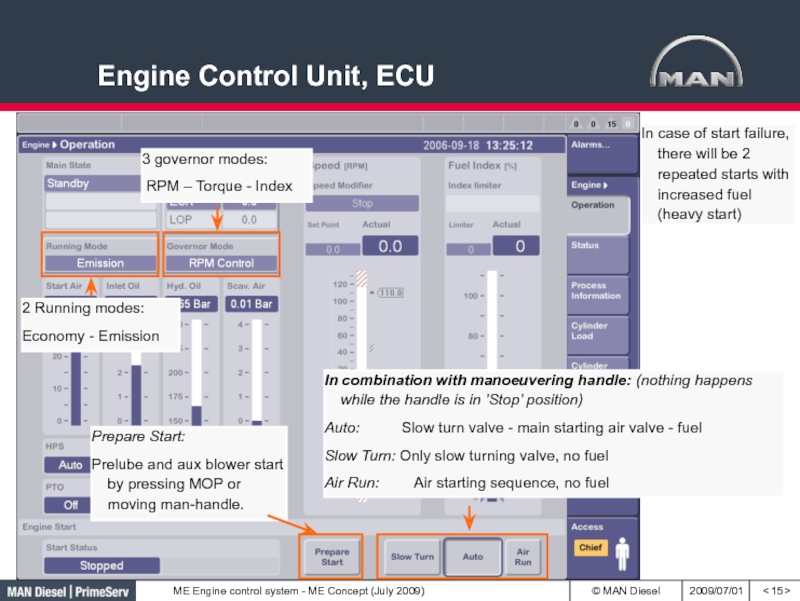
- 15. Engine Control Unit, ECU< >3 governor modes:
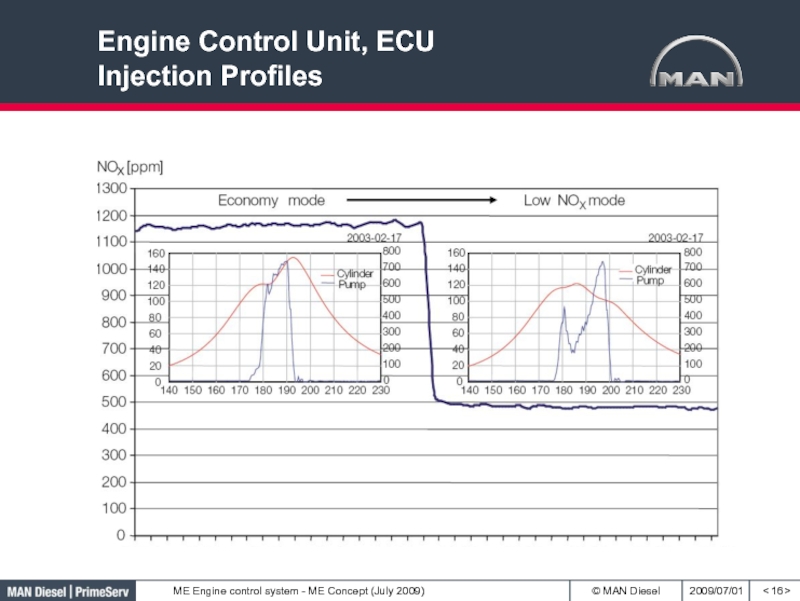
- 16. Engine Control Unit, ECU Injection Profiles< >
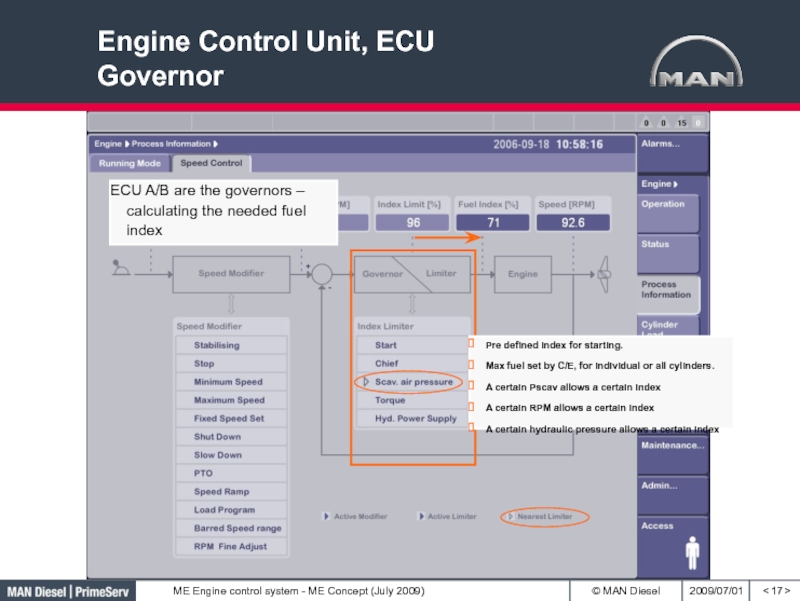
- 17. Engine Control Unit, ECU Governor< >Pre
- 18. Cylinder Control Unit, CCU< >Fuel plunger position
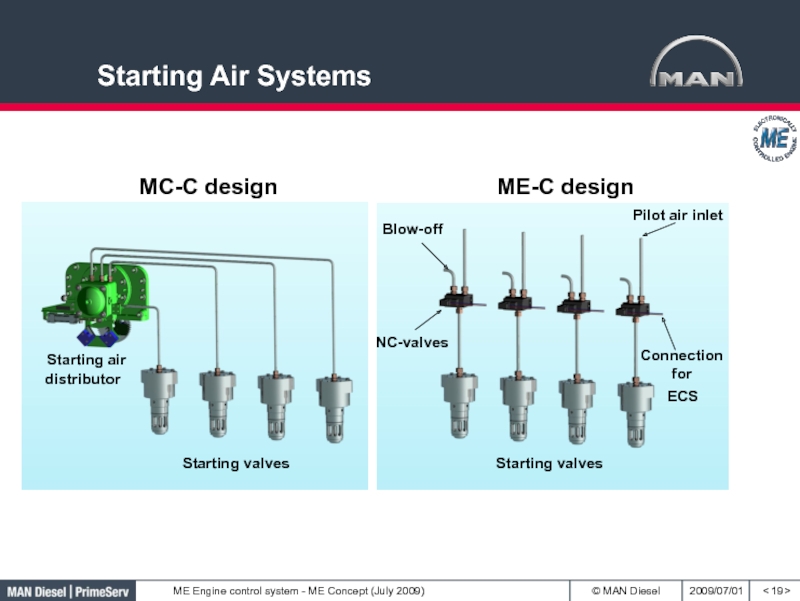
- 19. Starting Air Systems< >
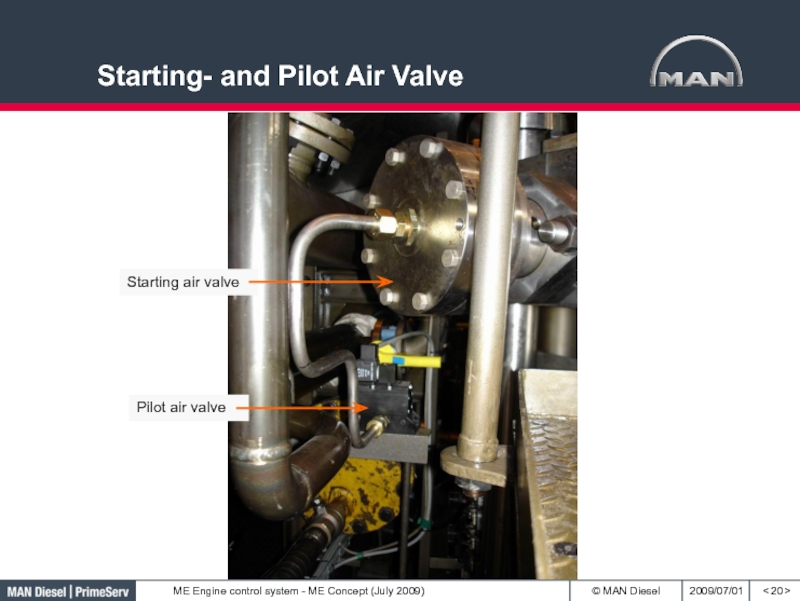
- 20. Starting- and Pilot Air Valve< >
- 21. Auxiliary Control Unit, ACU Blower Control< >The
- 22. Auxiliary Control Unit, ACU Pump Control< >Electrically
- 23. Multi Purpose Controller, MPC Summary< >The MPC’s
- 24. Engine Control System Control Panels< >Bridge Control
- 25. Main Operating Panel, MOP< >
- 26. Local Operating Panel (LOP) FPP< >
- 27. Local Operating Panel (LOP) CPP< >
- 28. Engine Control System Tacho System< >There are
- 29. Tacho System< >
- 30. Tacho System Angle Encoders< >90 deg ATDCAngle encoder AAngle encoder B
- 31. Tacho system Angle encoder A + B<
- 32. Tacho System, Angle Encoders< >
- 33. Tacho System Amplifier Boxes, TSA< >
- 34. Tacho System, Semicircular Ring< >
- 35. Tacho System, Master Slave A, MSA, on AFT end of Engine< >
- 36. Tacho System Trigger Rings + Sensors (option)<
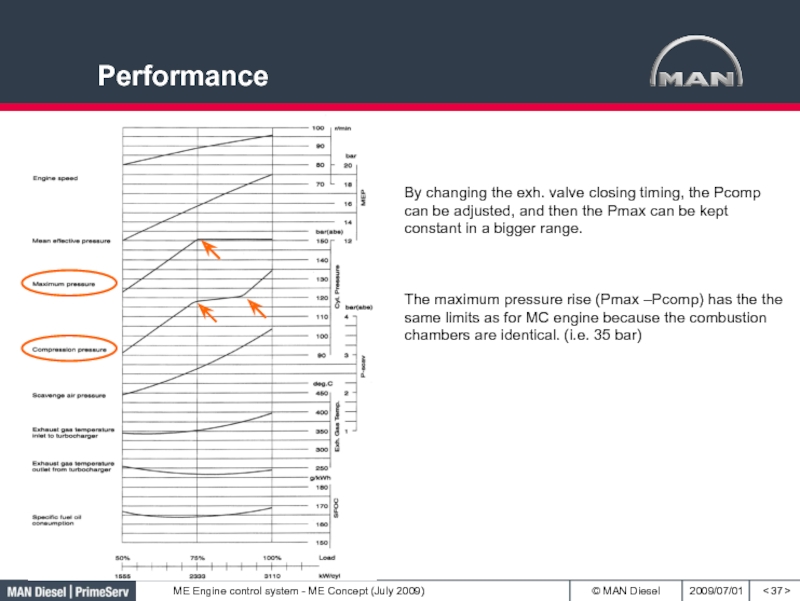
- 37. Performance< >By changing the exh. valve closing
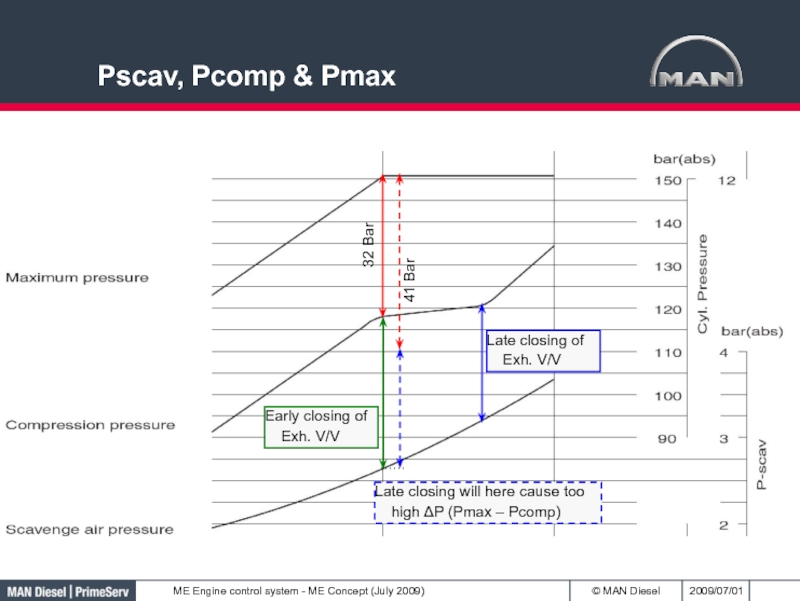
- 38. Pscav, Pcomp & Pmax
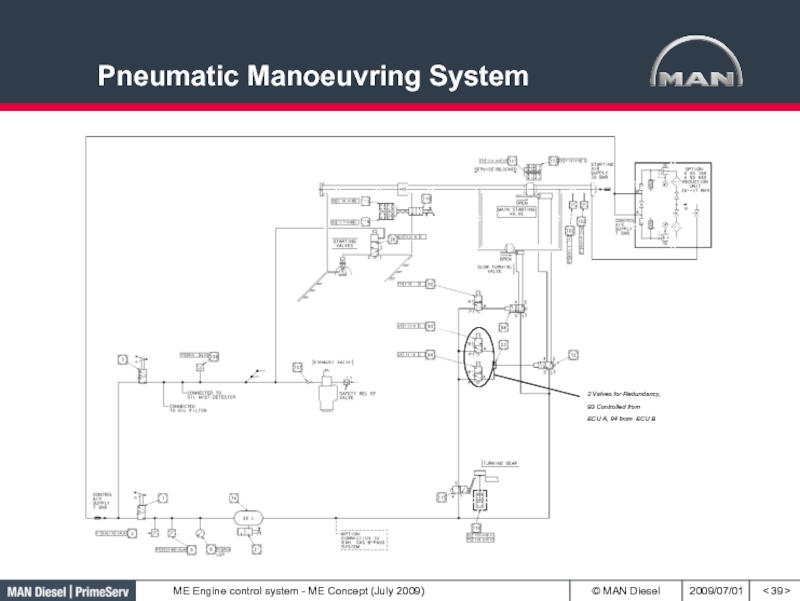
- 39. Pneumatic Manoeuvring System< >2 Valves for Redundancy,93 Controlled fromECU A, 94 from ECU B
- 40. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2< >
Control system:
- Multi Purpose Controller
- Control Network
- Main Operating
Panel
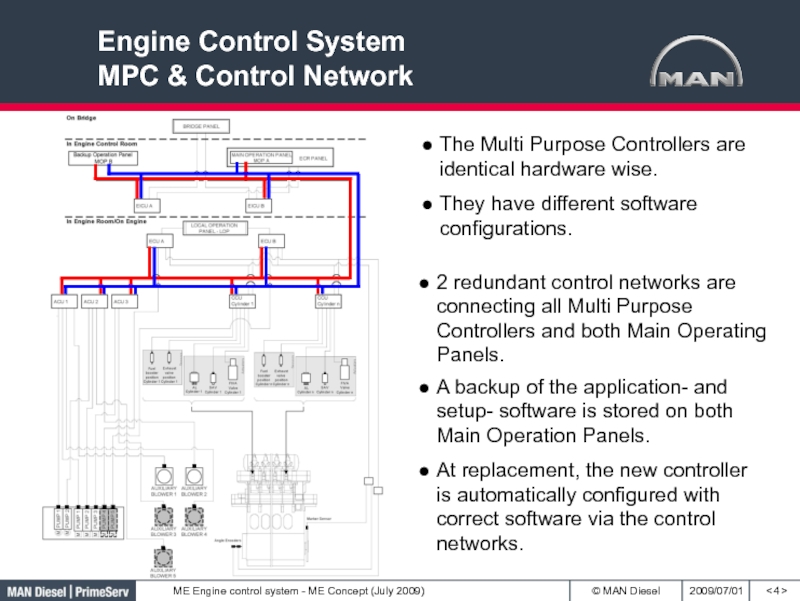
Concept Engine Control SystemСлайд 4Engine Control System
MPC & Control Network
< >
2 redundant control networks
are connecting all Multi Purpose Controllers and both Main Operating
Panels.A backup of the application- and setup- software is stored on both Main Operation Panels.
At replacement, the new controller is automatically configured with correct software via the control networks.
The Multi Purpose Controllers are identical hardware wise.
They have different software configurations.
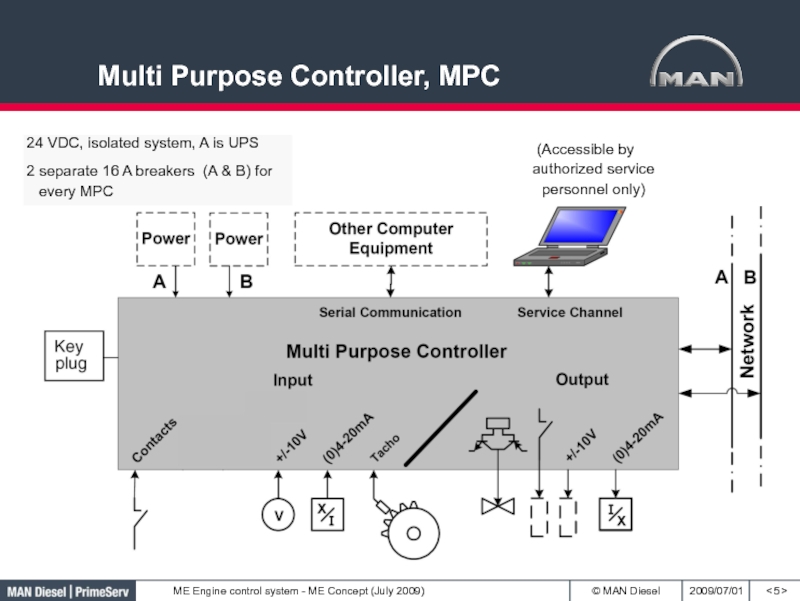
Слайд 5Multi Purpose Controller, MPC
< >
24 VDC, isolated system, A
is UPS
2 separate 16 A breakers (A & B)
for every MPC(Accessible by authorized service personnel only)
Слайд 7Multi Purpose Controller, MPC
< >
Amplifier for FIVA (CCU’s) and Hydraulic
pumps (ACU’s)
Multi Purpose Controller
’IP 66’ cabinet
Слайд 8Multi Purpose Controller
LED Information Code
< >
The LED gives information,
either as a constant light or by flashing.
A flashing LED
is a coded message from the controller. The code consists of 2 digits:1. Digit is given by red flashes on yellow/orange background
2. Digit is given by green flashes on yellow/orange background
The 2 digits are separated by a 1 sec. yellow/orange pulse.
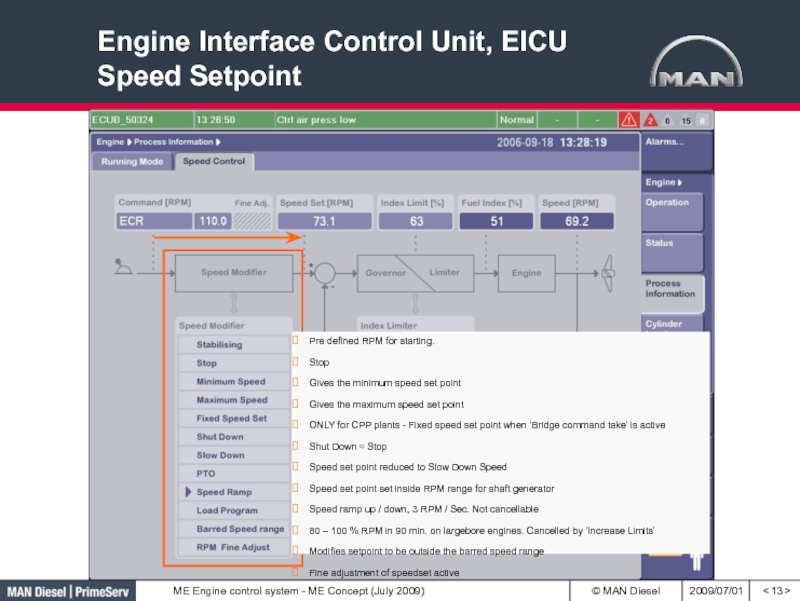
Слайд 13Engine Interface Control Unit, EICU Speed Setpoint
< >
Pre defined RPM
for starting.
Stop
Gives the minimum speed set point
Gives the maximum speed
set pointONLY for CPP plants - Fixed speed set point when ’Bridge command take’ is active
Shut Down Stop
Speed set point reduced to Slow Down Speed
Speed set point set inside RPM range for shaft generator
Speed ramp up / down, 3 RPM / Sec. Not cancellable
80 – 100 % RPM in 90 min. on largebore engines. Cancelled by ’Increase Limits’
Modifies setpoint to be outside the barred speed range
Fine adjustment of speedset active
Слайд 15Engine Control Unit, ECU
< >
3 governor modes:
RPM – Torque
- Index
2 Running modes:
Economy - Emission
In combination with manoeuvering handle:
(nothing happens while the handle is in ’Stop’ position)Auto: Slow turn valve - main starting air valve - fuel
Slow Turn: Only slow turning valve, no fuel
Air Run: Air starting sequence, no fuel
Prepare Start:
Prelube and aux blower start by pressing MOP or moving man-handle.
In case of start failure, there will be 2 repeated starts with increased fuel (heavy start)
Слайд 17
Engine Control Unit, ECU
Governor
< >
Pre defined index for starting.
Max fuel
set by C/E, for individual or all cylinders.
A certain Pscav
allows a certain indexA certain RPM allows a certain index
A certain hydraulic pressure allows a certain index
ECU A/B are the governors – calculating the needed fuel index
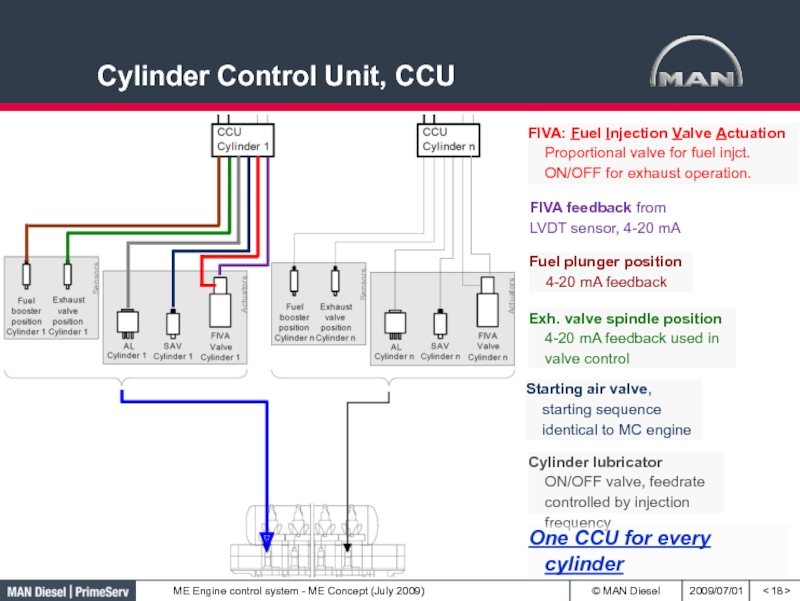
Слайд 18Cylinder Control Unit, CCU
< >
Fuel plunger position 4-20 mA feedback
Exh. valve spindle position 4-20 mA feedback used in valve
controlOne CCU for every cylinder
FIVA feedback from LVDT sensor, 4-20 mA
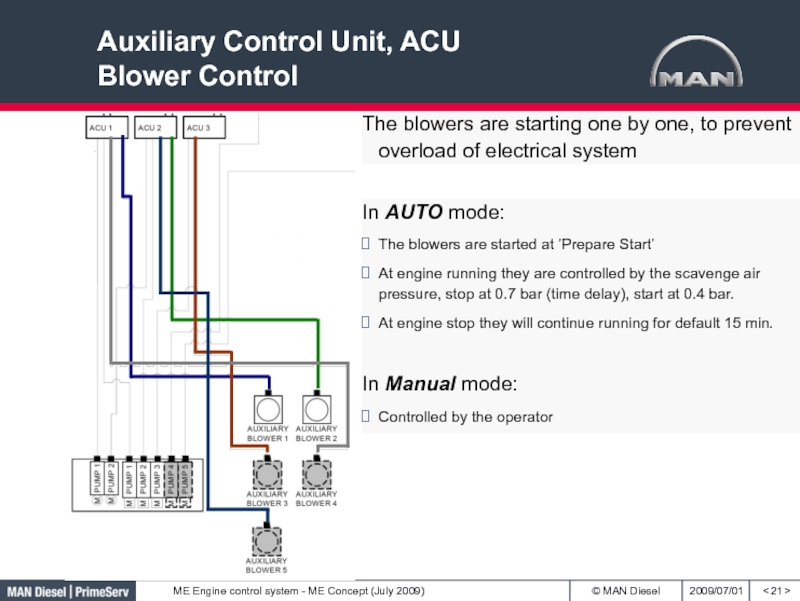
Слайд 21Auxiliary Control Unit, ACU
Blower Control
< >
The blowers are starting one
by one, to prevent overload of electrical system
In AUTO mode:
The
blowers are started at ’Prepare Start’ At engine running they are controlled by the scavenge air pressure, stop at 0.7 bar (time delay), start at 0.4 bar.
At engine stop they will continue running for default 15 min.
In Manual mode:
Controlled by the operator
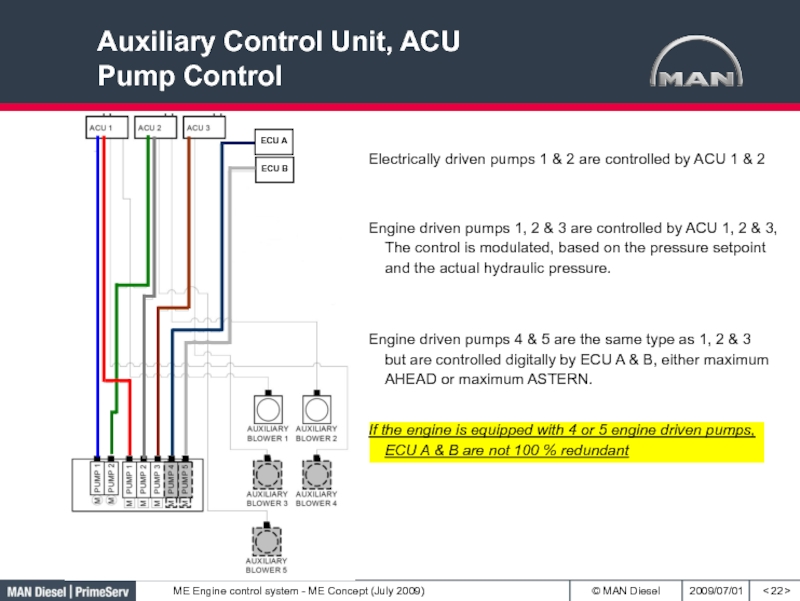
Слайд 22Auxiliary Control Unit, ACU
Pump Control
< >
Electrically driven pumps 1 &
2 are controlled by ACU 1 & 2
Engine driven pumps
1, 2 & 3 are controlled by ACU 1, 2 & 3, The control is modulated, based on the pressure setpoint and the actual hydraulic pressure.Engine driven pumps 4 & 5 are the same type as 1, 2 & 3 but are controlled digitally by ECU A & B, either maximum AHEAD or maximum ASTERN.
If the engine is equipped with 4 or 5 engine driven pumps, ECU A & B are not 100 % redundant
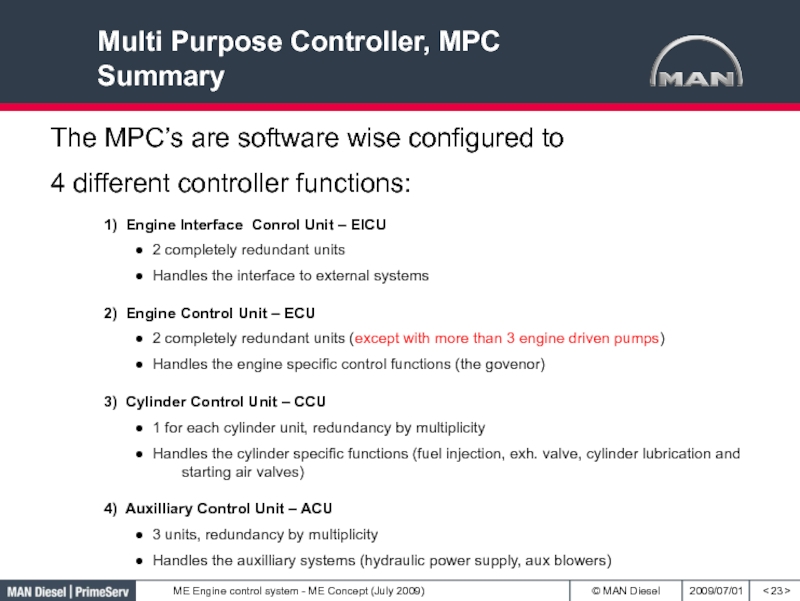
Слайд 23Multi Purpose Controller, MPC
Summary
< >
The MPC’s are software wise configured
to
4 different controller functions:
1) Engine Interface Conrol Unit – EICU
2 completely redundant unitsHandles the interface to external systems
2) Engine Control Unit – ECU
2 completely redundant units (except with more than 3 engine driven pumps)
Handles the engine specific control functions (the govenor)
3) Cylinder Control Unit – CCU
1 for each cylinder unit, redundancy by multiplicity
Handles the cylinder specific functions (fuel injection, exh. valve, cylinder lubrication and starting air valves)
4) Auxilliary Control Unit – ACU
3 units, redundancy by multiplicity
Handles the auxilliary systems (hydraulic power supply, aux blowers)
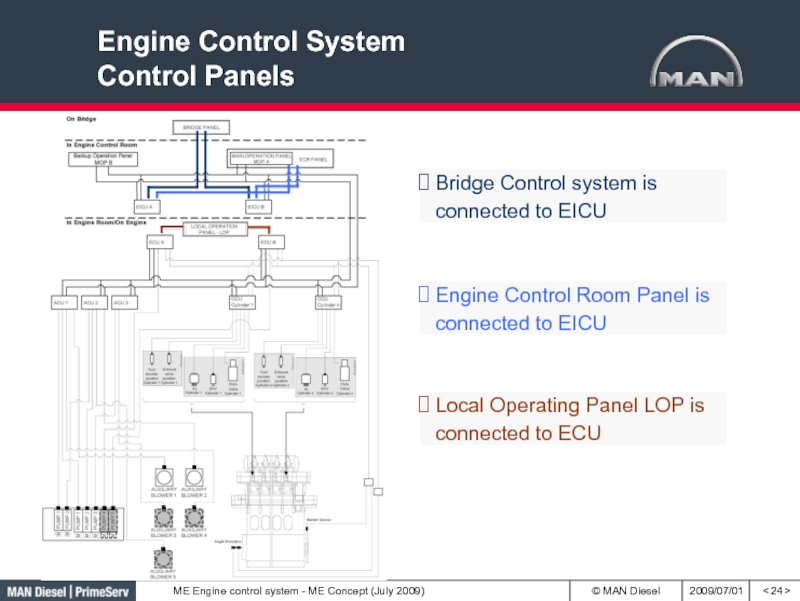
Слайд 24Engine Control System
Control Panels
< >
Bridge Control system is connected to
EICU
Engine Control Room Panel is connected to EICU
Local Operating Panel
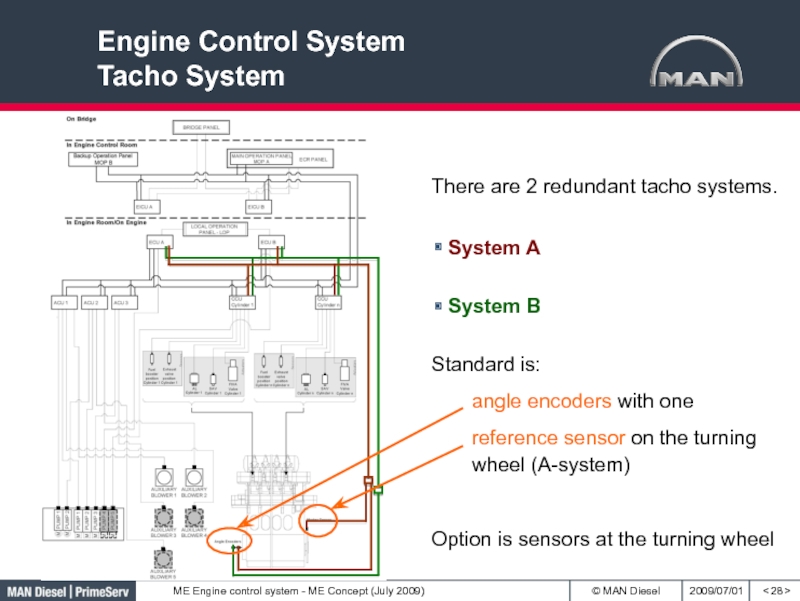
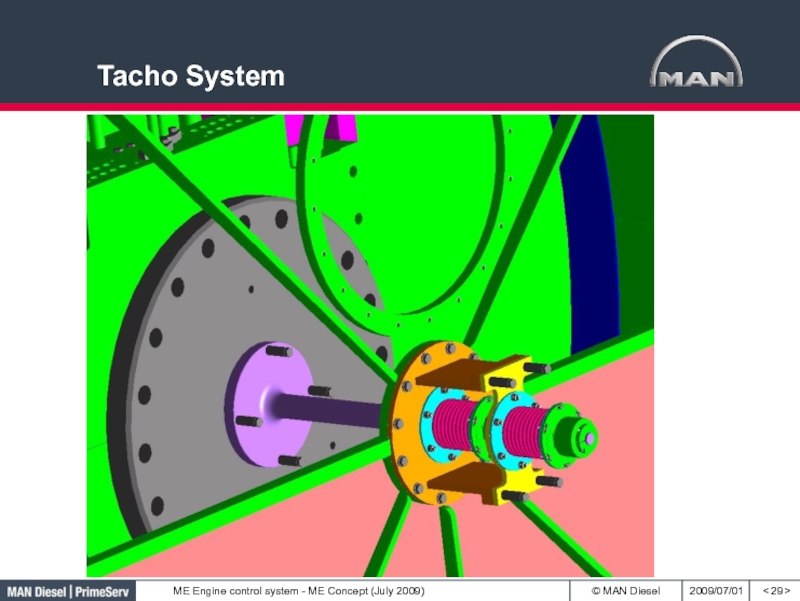
LOP is connected to ECUСлайд 28Engine Control System
Tacho System
< >
There are 2 redundant tacho systems.
System
B
System A
Standard is:
angle encoders with one
reference sensor on
the turning wheel (A-system)Option is sensors at the turning wheel
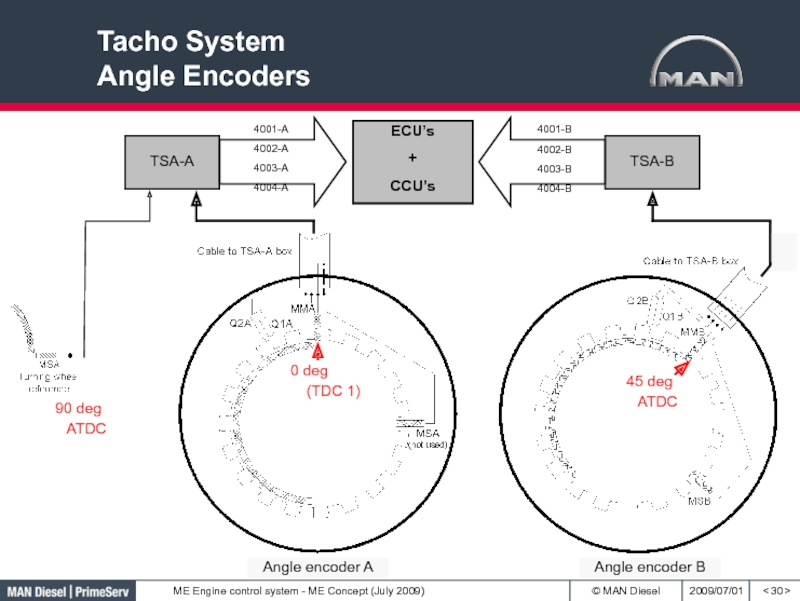
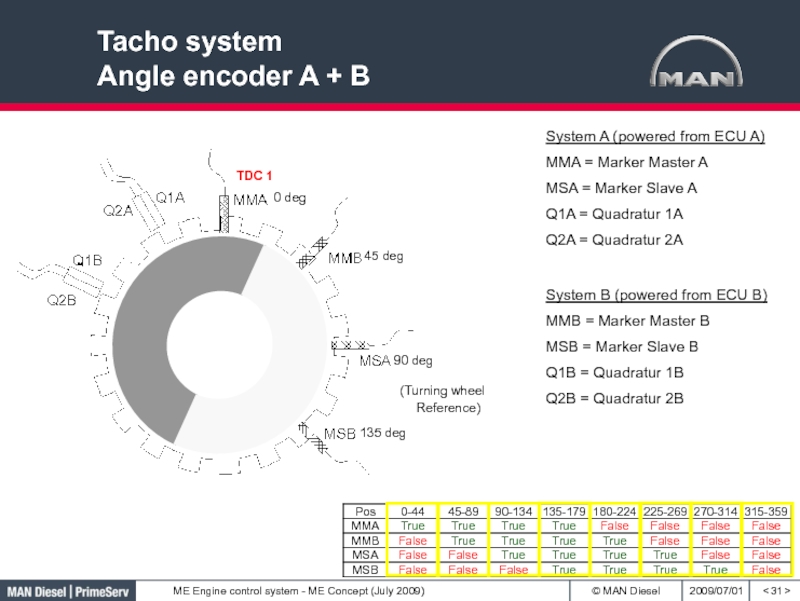
Слайд 31Tacho system
Angle encoder A + B
< >
System A (powered from
ECU A)
MMA = Marker Master A
MSA = Marker Slave A
Q1A
= Quadratur 1AQ2A = Quadratur 2A
System B (powered from ECU B)
MMB = Marker Master B
MSB = Marker Slave B
Q1B = Quadratur 1B
Q2B = Quadratur 2B
(Turning wheel Reference)
0 deg
45 deg
90 deg
135 deg
TDC 1
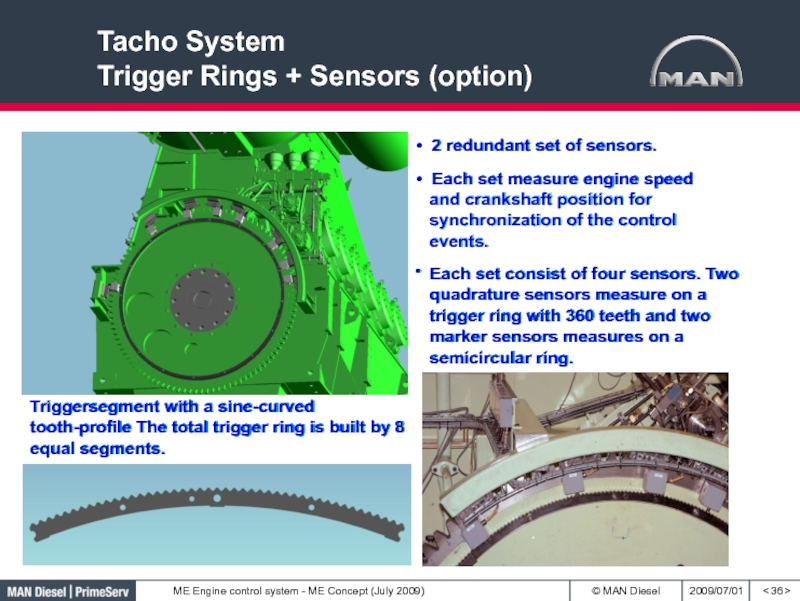
Слайд 36Tacho System
Trigger Rings + Sensors (option)
< >
Triggersegment with a sine-curved
tooth-profile The total trigger ring is built by 8 equal
segments.• 2 redundant set of sensors.
Each set consist of four sensors. Two quadrature sensors measure on a trigger ring with 360 teeth and two marker sensors measures on a semicircular ring.
• Each set measure engine speed
•
and crankshaft position for synchronization of the control events.
Слайд 37Performance
< >
By changing the exh. valve closing timing, the Pcomp
can be adjusted, and then the Pmax can be kept
constant in a bigger range.The maximum pressure rise (Pmax –Pcomp) has the the same limits as for MC engine because the combustion chambers are identical. (i.e. 35 bar)