Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Modern Strategic Analysis
Содержание
- 1. Modern Strategic Analysis
- 2. Theme 2. Strategy definition, strategy pyramid. Corporate strategy. Dr. Prof. Aleksandr Kozlov27/09/2016
- 3. Strategy definition (1)„..the determination of the long-run
- 4. Strategy definition (2)STRATEGY is the direction an
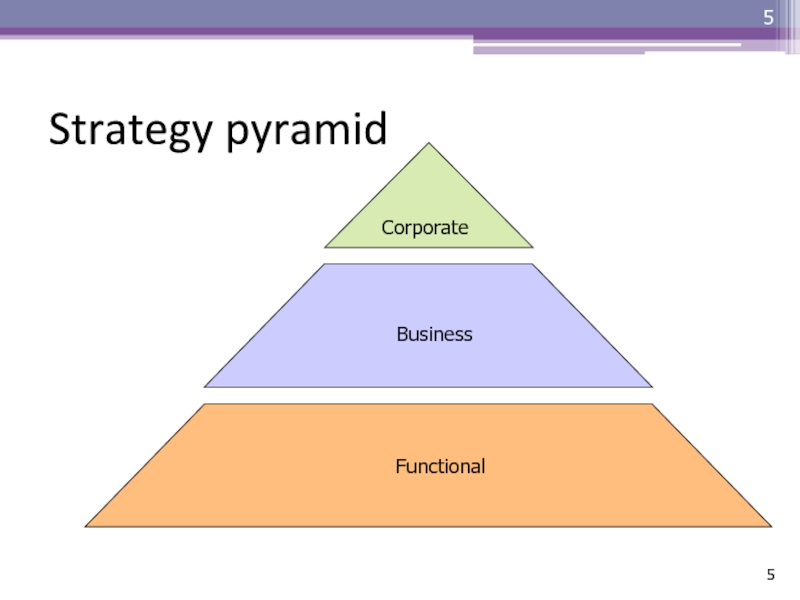
- 5. Strategy pyramidCorporate BusinessFunctional
- 6. Corporate strategy is a proprietary set of
- 7. For corporate strategy the fundamental task is to
- 8. Corporate Strategy. Tools for analysis of
- 9. Corporate Strategy. Boston Consulting Group matrix
- 10. Cash CowsThese units generate cash in excess
- 11. DogsLow market share in a mature, slow-growing
- 12. Question marks They are a starting point
- 13. Stars Stars are successful question marks and
- 14. Tools for analysis of Strategic Business
- 15. Business Strength Characteristics
- 16. Business Attractiveness Characteristics
- 17. General Electric matrixBusiness attractivenessBusiness strengthstrongmediumweaklowMediumhighmediumlowmediummedium highmedium highmedium
- 18. General Electric matrixBusiness attractivenessBusiness strengthstrongmediumweaklowMediumhighmediumlowmediummedium highmedium highmedium
- 19. General Electric matrixBusiness attractivenessBusiness strengthstrongmediumweaklowMediumhighmediumlowmediummedium highmedium highmedium
- 20. Shortcomings of the GE matrixNo generic or
- 21. Скачать презентанцию
Theme 2. Strategy definition, strategy pyramid. Corporate strategy. Dr. Prof. Aleksandr Kozlov27/09/2016
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Theme 2.
Strategy definition, strategy pyramid. Corporate strategy.
Dr. Prof.
Aleksandr Kozlov
Слайд 3Strategy definition (1)
„..the determination of the long-run goals and objectives
of an enterprise and the adoption of courses of action
and the allocation of resource necessary for carrying out these goals‟ Alfred Chandler„Competitive strategy is about being different. It means deliberately choosing a different set of activities to deliver a unique mix of value‟ Michael Porter
Sources: A.D. Chandler, Strategy and Structure: Chapters in the History of American Enterprise, MIT Press, 1963, p. 13
M.E. Porter, „What is strategy?‟, Harvard Business Review, 1996, November–December, p. 60
Слайд 4Strategy definition (2)
STRATEGY is the direction an organization takes with
the objective of achieving business success in the long term.
Слайд 6Corporate strategy is a proprietary set of actions that enables
a company to be successful in its multimarket activities in
the long term.The process of corporate strategy formulation includes setting priorities for development of company’s business units operating in a different markets and decision making about investment, keeping the status quo or withdrawal
Corporate strategy
Слайд 7For corporate strategy
the fundamental task is to develop a balanced
portfolio of businesses which will achieve the goals of the
corporation and satisfy its stakeholders.Corporate strategy
Слайд 8Corporate Strategy.
Tools for analysis of
Strategic Business Unit (SBU)
Boston
Consulting Group matrix
General Electric matrix
Слайд 9Corporate Strategy.
Boston Consulting Group matrix
High
Low
Relative position
(Market share)
Business Growth rate
High
Low
?
Слайд 10Cash Cows
These units generate cash in excess of the amount
of cash needed to maintain the business.
Typically belonging to
a "mature" market, and every corporation would be thrilled to own as many as possible. They are to be "milked" continuously with as little investment as possible, since such investment would be wasted in an industry with low growth.
Слайд 11Dogs
Low market share in a mature, slow-growing industry.
From an
accounting point of view such a unit is worthless, not
generating cash for the company.They depress a profitable company's return of assets ratio.
They should be sold off.
Слайд 12Question marks
They are a starting point for most businesses.
Question marks have a potential to gain market share and
become stars, and eventually cash cows when market growth slows.If question marks do not succeed in becoming a market leader, they will degenerate into dogs when market growth declines.
Question marks must be analyzed carefully in order to determine whether they are worth the investment required to grow market share.
Слайд 13Stars
Stars are successful question marks and become a market
leader in a high growth sector. .
Require high funding
to fight competitions and maintain a growth rate. When growth slows, if they have been able to maintain their category leadership stars become cash cows, else they become dogs due to low relative market share.
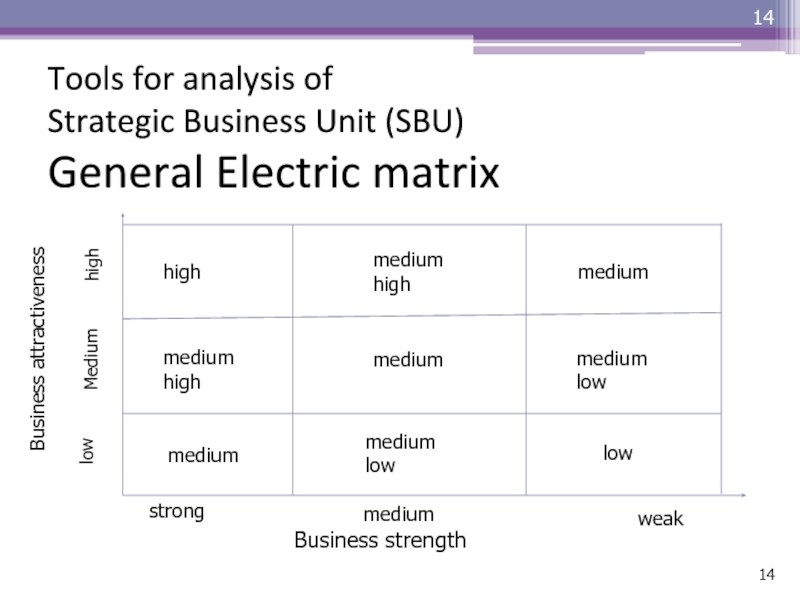
Слайд 14Tools for analysis of Strategic Business Unit (SBU) General Electric
matrix
Business attractiveness
Business strength
strong
medium
weak
low
Medium
high
medium
low
medium
medium high
medium high
medium low
medium low
high
medium
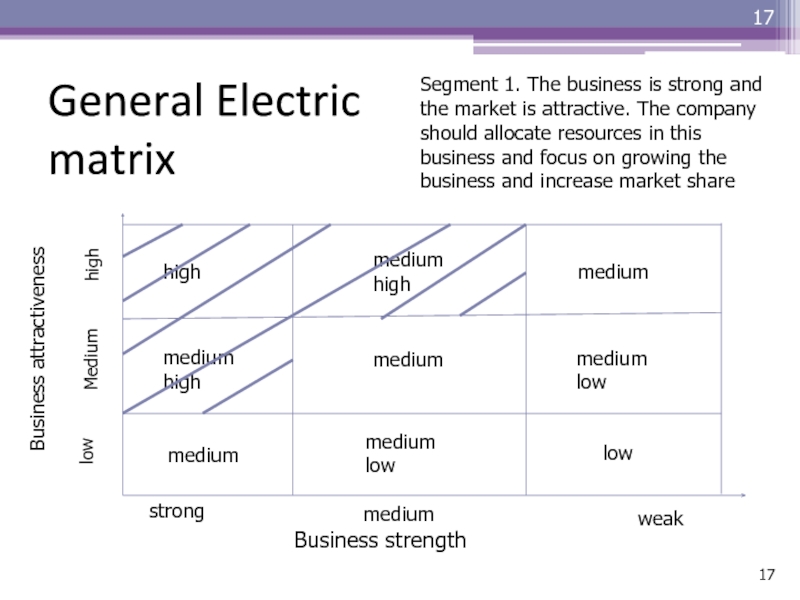
Слайд 17General Electric matrix
Business attractiveness
Business strength
strong
medium
weak
low
Medium
high
medium
low
medium
medium high
medium high
medium low
medium low
high
medium
Segment 1.
The business is strong and the market is attractive. The
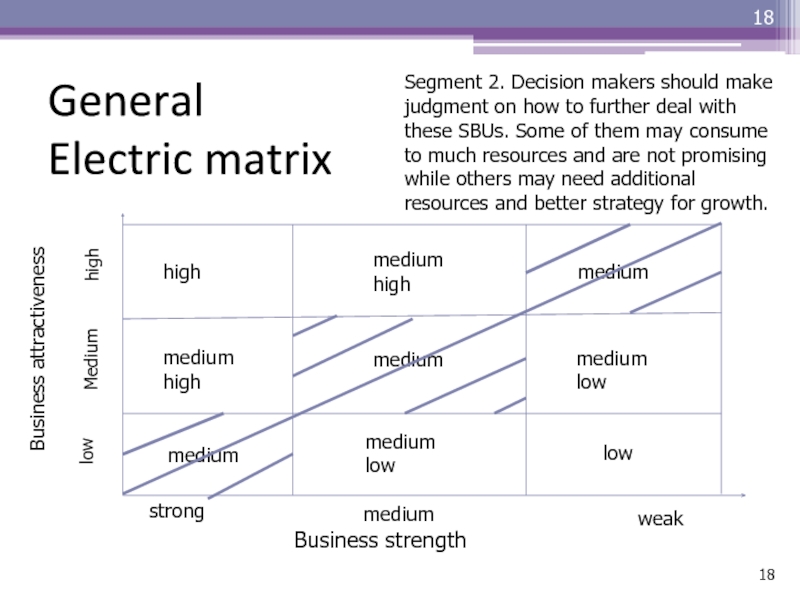
company should allocate resources in this business and focus on growing the business and increase market shareСлайд 18General Electric matrix
Business attractiveness
Business strength
strong
medium
weak
low
Medium
high
medium
low
medium
medium high
medium high
medium low
medium low
high
medium
Segment 2.
Decision makers should make judgment on how to further deal
with these SBUs. Some of them may consume to much resources and are not promising while others may need additional resources and better strategy for growth.Слайд 19General Electric matrix
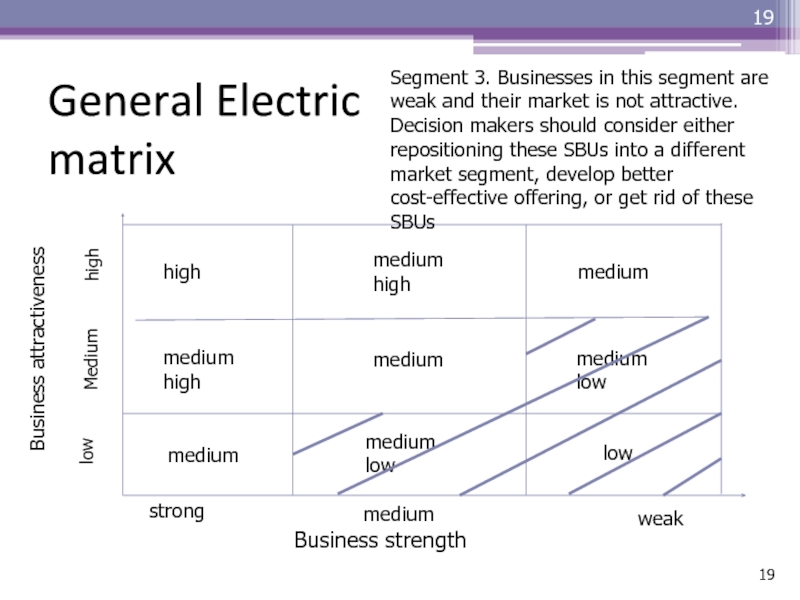
Business attractiveness
Business strength
strong
medium
weak
low
Medium
high
medium
low
medium
medium high
medium high
medium low
medium low
high
medium
Segment 3.
Businesses in this segment are weak and their market is
not attractive. Decision makers should consider either repositioning these SBUs into a different market segment, develop better cost-effective offering, or get rid of these SBUsСлайд 20Shortcomings of the GE matrix
No generic or simplified criteria for
business strength & uniqueness
Parent company can't use core competencies across
multiple SBUsBiased criteria can be used for strengths and uniqueness
Difficult to find a location for an SBU on the grid