Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Musculoskeletal Disorders
Содержание
- 1. Musculoskeletal Disorders
- 2. Osteomyelitis
- 3. OsteomyelitisSevere infection of theBoneBone marrowSurrounding soft tissueCaused
- 4. Etiology and PathophysiologyAntibiotics in conjunction with surgical
- 5. Direct EntryCan occur at any age Open
- 6. Direct EntrySequestrum continues to be an infected
- 7. Direct EntryOnce outside boneSequestrum may Revascularize and
- 8. Indirect EntryFrequently affects growing bone in boys
- 9. Indirect EntryAdults with increased riskVascular disordersGenitourinary and
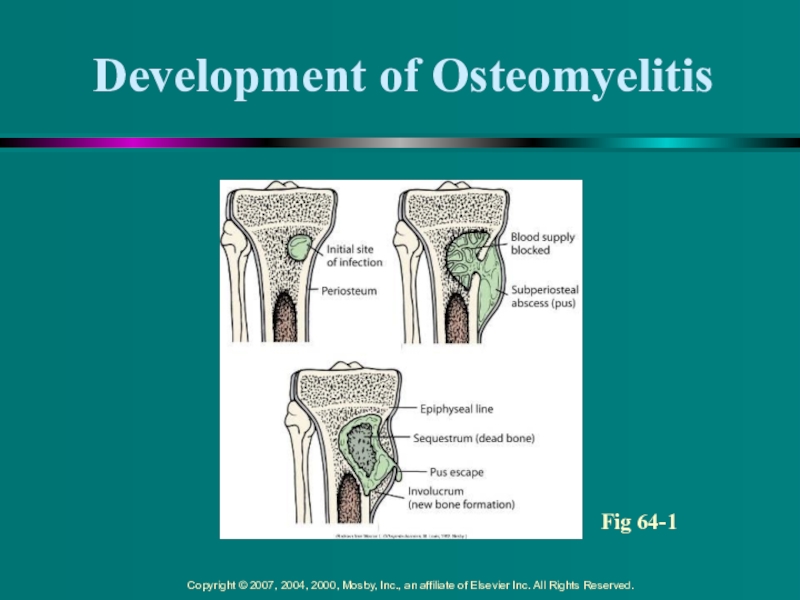
- 10. Development of OsteomyelitisFig 64-1
- 11. Clinical Manifestations Acute OsteomyelitisInitial infection Infection of
- 12. Clinical Manifestations Acute OsteomyelitisSystemic LocalConstant bone
- 13. Clinical Manifestations of Chronic OsteomyelitisChronic –
- 14. Diagnostic Studies Bone or soft tissue biopsy
- 15. Radiologic Studies Radiologic signs Usually do not
- 16. Collaborative Care Acute OsteomyelitisVigorous and prolonged intravenous
- 17. Collaborative Care Acute OsteomyelitisPatients are often discharged
- 18. Collaborative Care Acute OsteomyelitisAntibiotic therapy may be
- 19. Collaborative Care Chronic OsteomyelitisAdults with chronic
- 20. Nursing CareToxic effects: Aminoglycosides - Nephrotoxic, ototoxic,
- 21. Nursing Care/Patient TeachingMeasure Preventive measures:Monitor _ _
- 22. Collaborative Care Chronic OsteomyelitisSurgical treatment for
- 23. Collaborative Care Chronic OsteomyelitisAfter debridement, wound
- 24. Collaborative Care Chronic OsteomyelitisHyperbaric oxygen therapy
- 25. Collaborative Care Chronic OsteomyelitisBone grafts may
- 26. Collaborative CareLong-term and mostly rare complicationsSepticemiaSeptic arthritisPathologic fractures Amyloidosis
- 27. Nursing AssessmentImportant health informationPast health historyBone trauma,
- 28. Nursing AssessmentSubjective dataIV drug use, malaiseAnorexia, weight
- 29. Nursing AssessmentObjective dataGeneral: Restlessness, high, spiking temperature,
- 30. Nursing DiagnosesAcute painRT Inflammatory process secondary to
- 31. Nursing DiagnosesImpaired physical mobilityRT Pain, immobilization devices, weight-bearing limitationsAEB Inability or unwillingness to change positions
- 32. Nursing DiagnosesIneffective therapeutic regimen managementRT Lack of
- 33. Other Nursing Diagnosis LabelsFear, AnxietyPowerlessness, Hopelessness
- 34. PlanningOverall goals Have satisfactory pain and fever
- 35. Nursing ImplementationHealth promotionControl infections already in bodySusceptible
- 36. Nursing ImplementationAcute interventionImmobilization and non-weight bearing on
- 37. Nursing ImplementationAcute intervention (cont’d)Patient is frequently on
- 38. Nursing ImplementationAcute intervention (cont’d)Patient frequently positions affected
- 39. Nursing ImplementationAcute intervention (cont’d)Instruct patient to avoid
- 40. Nursing ImplementationAcute intervention (cont’d)Teach patient potential adverse
- 41. Nursing ImplementationAcute intervention (cont’d)Patient and family often
- 42. Nursing ImplementationAmbulatory and home care IV antibiotics
- 43. Nursing ImplementationAmbulatory and home care Importance of
- 44. Скачать презентанцию
Osteomyelitis
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 3Osteomyelitis
Severe infection of the
Bone
Bone marrow
Surrounding soft tissue
Caused by a variety
of microorganisms
Слайд 4Etiology and Pathophysiology
Antibiotics in conjunction with surgical treatments have decreased
mortality rate and complications
Infecting microorganisms can invade by
Indirect entry
Direct
entryСлайд 5Direct Entry
Can occur at any age
Open wound where microorganisms
can gain entry to body
May also occur in presence of
foreign bodyСлайд 6Direct Entry
Sequestrum continues to be an infected island of bone,
surrounded by pus
Difficult for blood-borne antibiotics or white blood cells
(WBCs) to reach sequestrumSequestrum can move out of bone and into soft tissue
Слайд 7Direct Entry
Once outside bone
Sequestrum may
Revascularize and then undergo removal
by normal immune process
Be surgically removed through debridement of necrotic
boneIf necrotic sequestrum is not resolved, it may develop a sinus tract resulting in chronic, purulent cutaneous drainage
Слайд 8Indirect Entry
Frequently affects growing bone in boys
---Why???
Most common sites of indirect entry
Distal femur
Proximal tibia
Humerus
Radius
Слайд 9Indirect Entry
Adults with increased risk
Vascular disorders
Genitourinary and respiratory infections
Spread infection
from blood to bone
Vascular-rich bone sites
Pelvis
Tibia
Vertebrae
Слайд 11Clinical Manifestations
Acute Osteomyelitis
Initial infection
Infection of
duration
Both systemic and local
Слайд 12Clinical Manifestations
Acute Osteomyelitis
Systemic
Local
Constant bone pain that worsens with
activity
Swelling, tenderness, warmth at infection site
Restricted movement of affected part
Later
signs: drainage from sinus tractsСлайд 13Clinical Manifestations
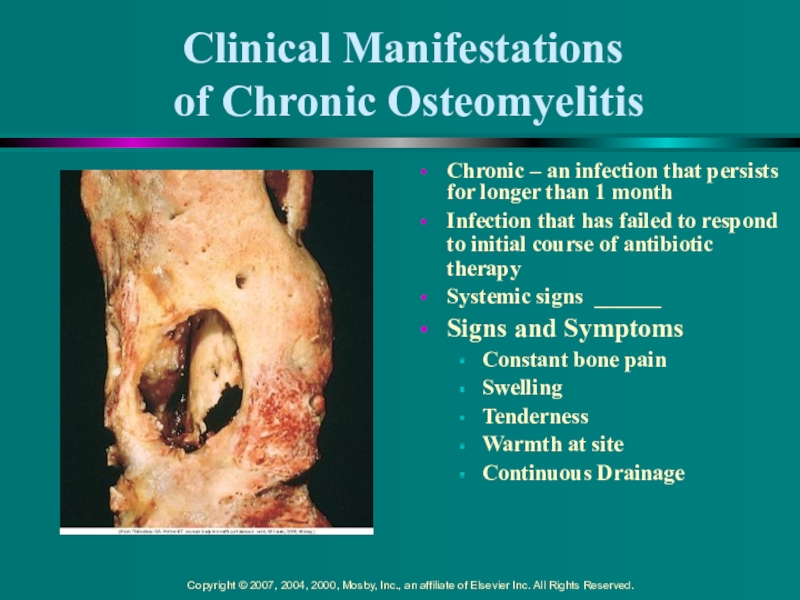
of Chronic Osteomyelitis
Chronic – an infection that persists
for longer than 1 month
Infection that has failed to respond
to initial course of antibiotic therapySystemic signs ______
Signs and Symptoms
Constant bone pain
Swelling
Tenderness
Warmth at site
Continuous Drainage
Слайд 14Diagnostic Studies
Bone or soft tissue biopsy
Definitive way to
determine causative microorganism
Patient’s blood and/or wound culture
Frequently positive for presence
of microorganism Lab Studies
WBC
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
Слайд 15Radiologic Studies
Radiologic signs
Usually do not appear until 10
days to weeks after start of clinical symptoms
Radionuclide bone
scans Helpful in diagnosis and usually positive in areas of infection
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Computed tomography (CT)
Help identify extent of infection, including soft tissue involvement
Слайд 16Collaborative Care
Acute Osteomyelitis
Vigorous and prolonged intravenous (IV) antibiotic therapy
Treatment of
choice for acute osteomyelitis
As long bone ischemia has not
occurredCultures or bone biopsy should be done if possible
Delaying antibiotic treatment may require surgical debridement and decompression
Слайд 17Collaborative Care
Acute Osteomyelitis
Patients are often discharged to home care or
skilled nursing facility (SNF) with IV antibiotics delivered via
Слайд 18Collaborative Care
Acute Osteomyelitis
Antibiotic therapy may be continued for at home
for _ to _ _____ or as long as _
__ _ ______Variety of antibiotics may be prescribed
Penicillin, nafcillin (Nafcil)
Neomycin, vancomycin
Cephalexin (Keflex)
Cefazolin (Ancef)
Слайд 19Collaborative Care
Chronic Osteomyelitis
Adults with chronic osteomyelitis may be prescribed
oral therapy + fluoroquinolone for 6 to 8 weeks instead
of IV antibioticsOral antibiotics may be given after acute IV therapy to ensure resolution of infection
Monitoring patient’s response
Слайд 20Nursing Care
Toxic effects:
Aminoglycosides - Nephrotoxic, ototoxic, optic neuritis, fluid
retention
Cephalosporins and Quinolones – jaundice, colitis,
photosensitivity, crystalluriaСлайд 21Nursing Care/Patient Teaching
Measure
Preventive measures:
Monitor _ _ _; Keep
patient well hydrated to prevent ____________ or __________
Avoid direct sunlight,
wear sunscreenMonitor urinary function, hearing, vision
Assess for signs of yeast infections in genitourinary and mouth
Слайд 22Collaborative Care
Chronic Osteomyelitis
Surgical treatment for chronic osteomyelitis
Removal of poorly
vascularized tissue and dead bone
Extended use of antibiotics
Antibiotic-impregnated polymethyl
methacrylate bead chains may also be implanted Слайд 23Collaborative Care
Chronic Osteomyelitis
After debridement, wound may be closed and
a suction irrigation system inserted
Intermittent or constant irrigation of affected
bone with antibiotics Protection on limb or surgical site with casts or braces
Negative pressure to draw wound together
Слайд 24Collaborative Care
Chronic Osteomyelitis
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy with 100% oxygen as
adjunct therapy
Stimulate circulation and healing
Orthopedic prosthetic devices, if source of
infection must be removedMuscle flaps, skin grafting provide wound coverage over dead space (cavity) in bone
Слайд 25Collaborative Care
Chronic Osteomyelitis
Bone grafts may help restore blood flow
Amputation
may be indicated if
Слайд 26Collaborative Care
Long-term and mostly rare complications
Septicemia
Septic arthritis
Pathologic fractures
Amyloidosis
Слайд 27Nursing Assessment
Important health information
Past health history
Bone trauma, open fracture, open
or puncture wounds, other infections
Medications
Surgery or other treatments
Слайд 28Nursing Assessment
Subjective data
IV drug use, malaise
Anorexia, weight loss, chills
Weakness, paralysis,
muscle spasms
Local tenderness over affected area, increase in pain in
affected areaСлайд 29Nursing Assessment
Objective data
General: Restlessness, high, spiking temperature, night sweats
Integumentary: Diaphoresis,
erythema, warmth, edema at infected bone
Musculoskeletal: Restricted movement, wound drainage,
spontaneous fractures Слайд 30Nursing Diagnoses
Acute pain
RT Inflammatory process secondary to infection
AEB Guarding,
moaning, crying, restlessness, altered muscle tone, decreased activity; Statement of
painСлайд 31Nursing Diagnoses
Impaired physical mobility
RT Pain, immobilization devices, weight-bearing limitations
AEB Inability
or unwillingness to change positions
Слайд 32Nursing Diagnoses
Ineffective therapeutic regimen management
RT Lack of knowledge regarding long-term
management of osteomyelitis
AEB Verbalization of concern and uncertainty about
procedures and skills needed for home care Слайд 34Planning
Overall goals
Have satisfactory pain and fever control
Not experience any
complications associated with osteomyelitis
Cooperate with treatment plan
Maintain a positive outlook
on outcome of diseaseСлайд 35Nursing Implementation
Health promotion
Control infections already in body
Susceptible adults
Instruct susceptible adults and their families on local and systemic
manifestationsСлайд 36Nursing Implementation
Acute intervention
Immobilization and non-weight bearing on affected limb will
decrease pain
Limb should be handled carefully to avoid excessive manipulation
and decrease painManage patient’s pain level using pharmacologic and non-pharmacologic strategies
Слайд 37Nursing Implementation
Acute intervention (cont’d)
Patient is frequently on bed rest in
early stages of acute infection
Good body alignment and frequent position
changes prevent complications associated with immobility and promote comfortFlexion contracture is a common sequela of osteomyelitis
Слайд 38Nursing Implementation
Acute intervention (cont’d)
Patient frequently positions affected extremity in a
flexed position to promote comfort
Contracture may then progress to deformity
___
____ can develop quickly in lower extremity if foot is not supported in a neutral position by a splint or if there is excessive pressure from a splint Слайд 39Nursing Implementation
Acute intervention (cont’d)
Instruct patient to avoid activities that
increase
circulation and swelling and serve as stimuli to spread infection
Exercise,
____ application Dressings to absorb exudate from draining wounds
Слайд 40Nursing Implementation
Acute intervention (cont’d)
Teach patient potential adverse and toxic reactions
with prolonged and high-dose antibiotic therapy
Lengthy antibiotic therapy can result
in an overgrowth of …Слайд 41Nursing Implementation
Acute intervention (cont’d)
Patient and family often frightened and discouraged
Continued psychologic and emotional support is an integral part of
nursing managementСлайд 42Nursing Implementation
Ambulatory and home care
IV antibiotics can be administered
to patient in a skilled nursing facility or home setting
If
at homePatient and family must be instructed on correct care and management of venous access device
Must also be taught how to administer antibiotic
Слайд 43Nursing Implementation
Ambulatory and home care
Importance of continuing antibiotics after
symptoms have subsided should be stressed
Periodic nursing visits provide support
and decrease anxiety Frequent dressing changes for open wounds
May require supplies and instruction in technique