Слайд 1
OSTEOMYELITIS and SEPTIC ARTHRITIS
Слайд 2Objectives
1. Pyogenic osteomyelitis
1. List routes by which bacteria reach bone
2.
List organisms commonly responsible for pyogenic infection in bone
3. Understand
how location of osteomyelitis is influenced by vascular supply to the bone.
4. Know morphology of acute and chronic lesions
5. Define the terms involucrum and sequestrum
2. Tuberculous osteomyelitis (Pott disease
Describe the following aspects of tuberculous osteomyelitis:
1. Incidence
2. Bones affected
3. Clinical consequences
3. Pyogenic suppurative arthritis
Describe the following aspects of pyogenic suppurative arthritis:
1. Pathogenesis
2. Bacteria commonly involved
3. Characteristics of joint fluid
Слайд 3 OSTEOMYELITIS:
Denotes inflammation of bones and marrow
the common
use of the term almost always implies infection.
May be a
complication of any systemic infection but frequently manifests as a primary solitary focus of disease.
All types of organisms, including viruses, parasites, fungi and bacteria can produce osteomyelitis.
The most common are infections caused by certain pyogenic bacteria and mycobacteria
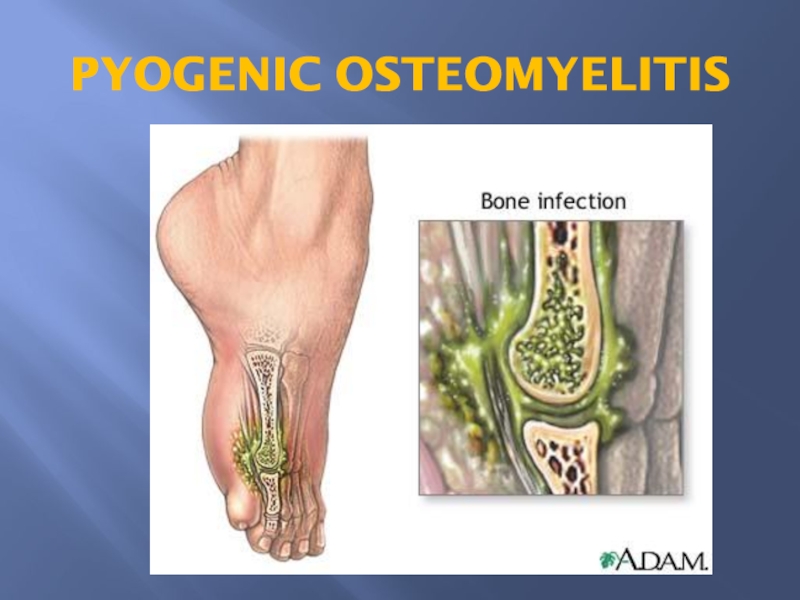
Слайд 4PYOGENIC OSTEOMYELITIS:
is almost always caused by
bacteria.
Hematogenous spread.
Extension from a contiguous site.
Direct implantation.
Слайд 5PYOGENIC OSTEOMYELITIS
CAUSES:
Staphylococcus aureus is responsible for 80% to 90%
the cases of pyogenic osteomyelitis in which an organism is
recovered.
Staph. aureus expresses receptors to bone matrix components, may be related to the fact that facilitating its adherence to bone tissue.
Слайд 6PYOGENIC OSTEOMYELITIS
E.coli, Klebsiella and Pseudomonas are more frequently isolated from
patients with genitourinary tract infections or with intravenous drug abusers.
Mixed
bacterial infections can be seen in the setting of direct spread during surgery or open fractures.
Salmonella infections for unknown reasons common in sickle cell patients.
Слайд 7PYOGENIC OSTEOMYELITIS
In 50% of the cases no organisms can be
isolated.
Слайд 8PYOGENIC OSTEOMYELITIS
Sites of involvement:
Influenced by the vascular circulation,
which varies with age.
Neonates: the metaphyseal vessels penetrate the growth
plate, resulting in frequent infection of the metaphysis, epiphysis or both.
Children: metaphyseal.
Adults: epiphyses and subchondral regions.
Слайд 9PYOGENIC OSTEOMYELITIS
Stages :
Acute
Sub acute
Chronic.
Слайд 10PYOGENIC OSTEOMYELITIS
Necrosis of the bone within first 48hrs.
Spread of bacteria
and inflammation within the shaft of the bone and may
percolate through the haversian systems to reach the periosteum.
In children, the periosteum is loosely attached to the cortex; therefore sizable subperiosteal abscess formation occurs.
Further ischemia and bone necrosis occurs.
Слайд 12SEQUENCE OF INFECTION:
Once localized in bone, the bacteria proliferate
and induce an acute inflammatory reaction and cause cell death.
Dead
pieces of bone is known as the sequestrum.
Rupture of the periosteum→soft tissue abscess formation→draining sinuses.
In infants epiphyseal infection may spread to the adjacent joint and causes septic or suppurative arthritis; may lead to permanent disability.
Слайд 13After the first week chronic inflammatory cells become more numerous
with the release of cytokines and deposition of new bone
formation at the periphery.
New bone may be deposited as a sleeve of living tissue known as the Involucrum.
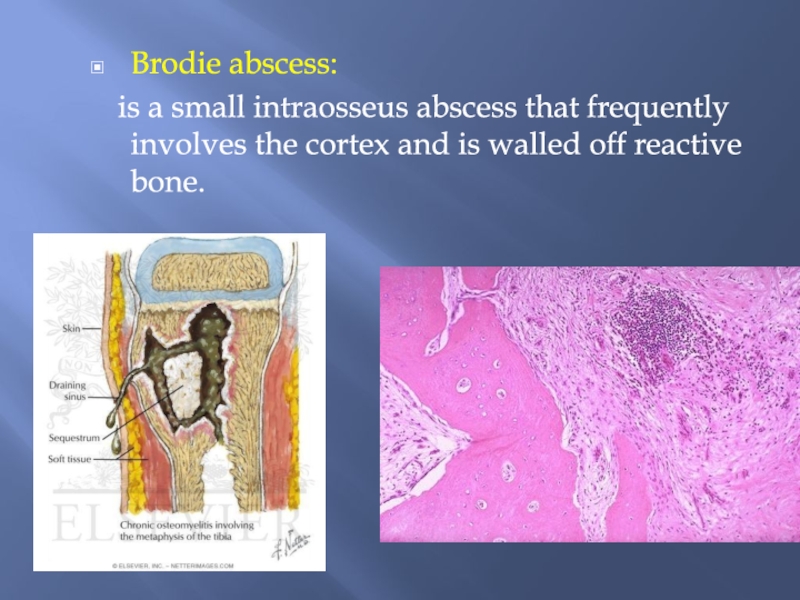
Слайд 14Brodie abscess:
is a small intraosseus abscess that frequently
involves the cortex and is walled off reactive bone.
Слайд 15PYOGENIC OSTEOMYELITIS
Clinical Course:
Fever ,chills, malaise, marked to intense throbbing pain
over the affected region.
Diagnosis;
Sign/symptoms.
X-ray
Blood cultures
biopsy
Слайд 16PYOGENIC OSTEOMYELITIS
Rx :
combination of antibiotics and surgical drainage.
Слайд 17PYOGENIC OSTEOMYELITIS
Complications:
Pathologic fracture.
Secondary amyloidosis
Endocarditis
Sepsis
Squamous cell carcinoma.
Rarely sarcoma in the affected
bone
Слайд 19Tuberculous osteomyelitis
Routes of entry;
Usually blood borne and originate
from a focus of active visceral disease.
Direct extension (e.g. from
a pulmonary focus into a rib or from tracheobronchial nodes into adjacent vertebrae) or spread via draining lymphatics.
Слайд 20Tuberculous osteomyelitis
The most common sites of skeletal involvement are:
thoracic
and lumber vertebrae followed by the knees and hips
In patients
with AIDS frequently multifocal.
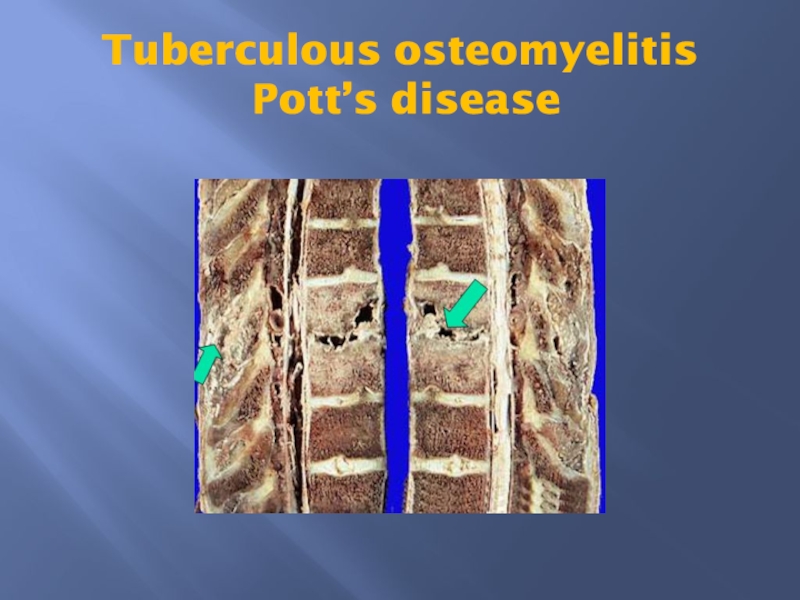
Pott disease is the involvement of spine.
The infection breaks through the intervertebral discs and extends into the soft tissues forming abscesses.
Слайд 21Tuberculous osteomyelitis
Pott’s disease
Слайд 22Tuberculous osteomyelitis
Clinical features and complications:
Pain
Fever
weight loss
May form an
inguinal mass “ psoas abscess”.
Bone destruction.
Tuberculous arthritis.
sinus tract formation
amyloidosis
Слайд 24
Infectious Arthritis
(suppurative arthritis)
Infectious arthritis is serious because it can cause
rapid joint destruction and permanent deformities.
Routes of infection:
hematogenous
direct inoculation
contiguous spread
from osteomyelitis or a soft tissue abscess
Слайд 25Infectious Arthritis
Any bacteria can be causal:
Haemophilus influenzae predominates in children under
age 2 years
S. aureus is the main causative agent in older
children and adults
gonococcus is prevalent during late adolescence and young adulthood.
Individuals with sickle cell disease are prone to infection with Salmonella at any age.
Both genders are affected equally
Слайд 26Infectious Arthritis
The infection involves only a single joint
usually the knee-followed
in order by hip, shoulder, elbow, wrist, and sternoclavicular joints.
Joint aspiration is typically purulent
Culture allows identification of the causal agent.
Слайд 27Infectious Arthritis
Clinical features:
sudden onset of pain
redness, and swelling of
the joint with restricted range of motion.
Fever, leukocytosis, and
elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate