Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
паталогии ЦНС
Содержание
- 1. паталогии ЦНС
- 2. Increased Intracranial Pressure (pg. 666)The cranium consists
- 3. Слайд 3
- 4. Increased Intracranial pressureThe skull cannot expand so
- 5. Increased Intracranial PressureIf not recognized, the brainstem
- 6. ICPSigns and symptoms develop rapidly or slowlyIf
- 7. Level Of ConsciousnessConfusion, restlessness, disorientation and drowsiness
- 8. HeadachePain is usually intermittent--if constant condition usually
- 9. Vomiting and ICP Commonly occurs without warning
- 10. PapilledemaPapilledema (edema of optic nerve caused by
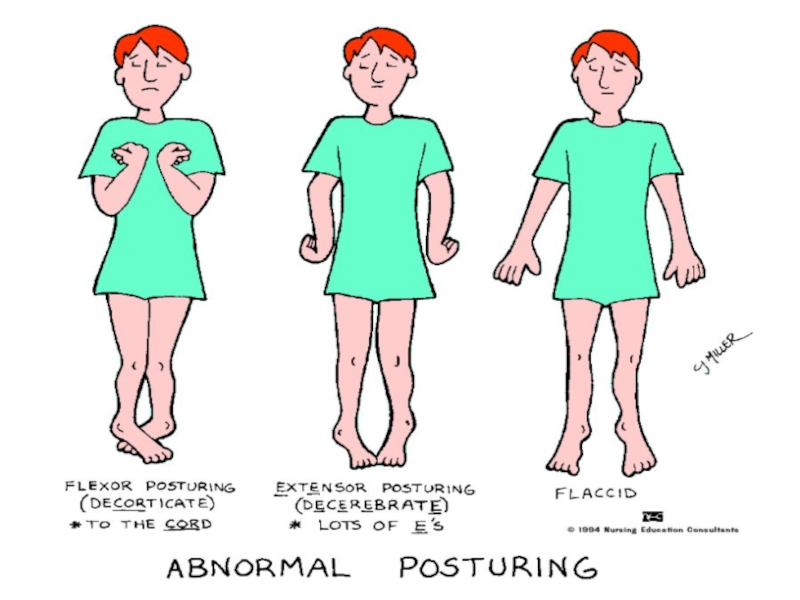
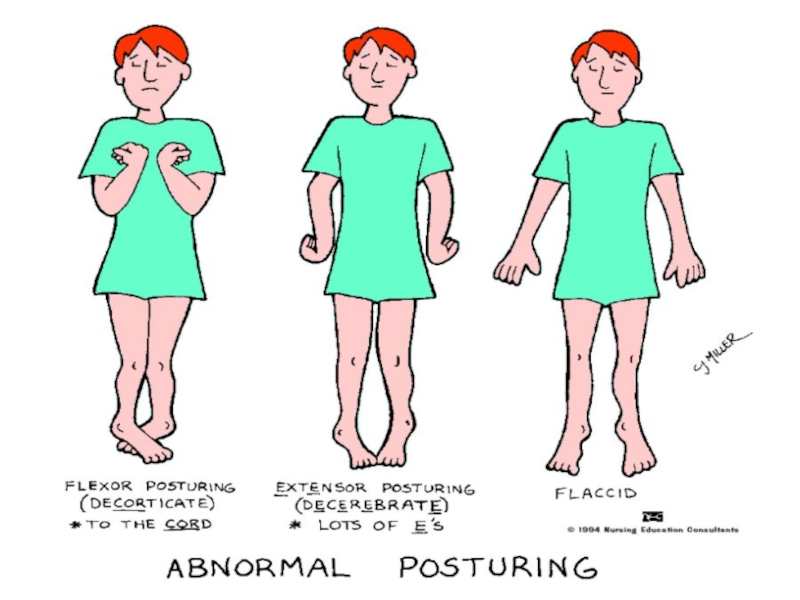
- 11. PosturingDecorticate--arms flexed--problem with cervical spinal tract or
- 12. Слайд 12
- 13. Symptoms of ICPChange in LOCheadachevomitingpapilledemavital signs--temp rises,
- 14. Vital signsTemp rises, B/P rises and pulse
- 15. Medical and surgical managementOsmotic diuretics (mannitol, glycerol);
- 16. Medical & surgical managementRestrict fluids, lumbar punctures
- 17. Medical ManagementMay order:insertion of foleyNG tube for
- 18. Normal ICP In the Ventricles Norm: 1
- 19. Nursing care ICPTeach to remain quiet in
- 20. Nursing Care ICPICP can affect temp regulation
- 21. Nursing Care ICPA neurologic flow sheet that
- 22. Nursing Care ICPLaboratory findings such as serum
- 23. Nursing Care ICPKeep head straight and head
- 24. Activities That increase ICPCoughingrange of motion exercisessneezinghip flexion of 90 degrees or greatervomiting suctioning
- 25. Activities that increase ICPStraining to have a
- 26. Nursing Care ICPHourly I&O may be doneIf
- 27. Nursing Care ICPMonitor I&O…fluids may be restricted
- 28. Infectious & Inflammatory DisordersMeningitisEncephalitisGullian-Barre SyndromePoliolmyelitisBrain Abscess
- 29. Meningitis (Covering of the Brain) pg
- 30. Слайд 30
- 31. MeningitisMost adults with bacterial meningitis recover without
- 32. Meningitis S/SFever, nuchal rigidity (pain and stiffness
- 33. Kernig’s Sign Positive Kernig’s sign ( inability
- 34. Brudzinsi’s Sign Brudzinski’s sign--flexion of neck produces flexion of knees and hips
- 35. Diagnostic findings: MeningitisLumbar puncture doneif bacterial meningitis
- 36. Слайд 36
- 37. Medical Management IV fluids, antibiotics, anticonvulsants are
- 38. Encephalitis (Brain Inflammation) pg 676 Infectious disease
- 39. Encephalitis (brain inflammation)Symptoms similar to meningitisCaused by
- 40. Encephalitisoccurs after a viral infection elsewhere (measles
- 41. EncephalitisOnset of viral is sudden with fever,
- 42. EncephalitisMuscle weakness, incoordination, incontinence and visual disturbances
- 43. Encephalitis--brain inflammationLumbar puncture done…CSF pressure elevated but
- 44. EncephalitisMild cases are common and may go
- 45. Guillain-Barre’ syndrome Pg.677Rare, inflammatory condition involving the
- 46. Guillain-Barre’ SyndromeMay be autoimmune response to viral
- 47. Guillain Barre’ SyndromeWeakness, tingling, and numbness in
- 48. Medical Management Guillian Barre’Plasmaphoresis removal of plasma
- 49. Слайд 49
- 50. Nursing ManagementMonitory respiratory status/distressUse ISR/T incapacitated by
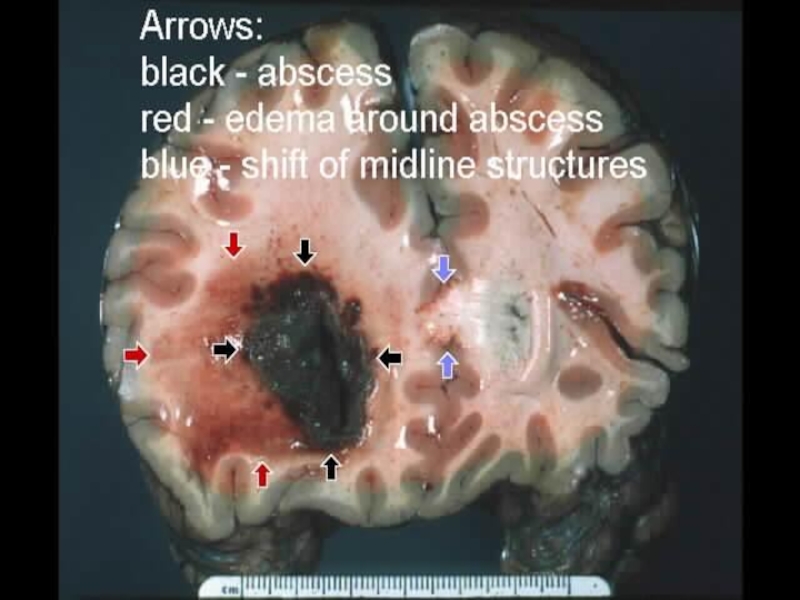
- 51. Brain abscess Pg. 678A collection of pus
- 52. Слайд 52
- 53. Brain abscessMay occur from infection of teeth,
- 54. Brain abscessRisk increases with head injury, illness
- 55. Brain abscessI&O fluids may be restricted as
- 56. General Nursing Care for Inflammatory DisordersSwallowing may
- 57. Nursing Care for Inflammatory DisordersMonitor vitals…complete careneuro
- 58. Neuromuscular disorders PG 678Involves the nervous system
- 59. Multiple sclerosis PG 678Chronic, progressive disease of
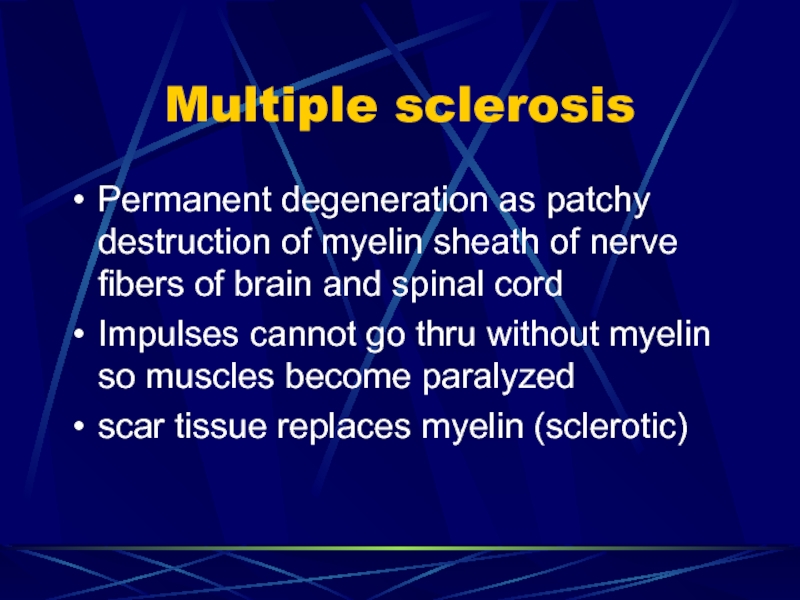
- 60. Multiple sclerosisPermanent degeneration as patchy destruction of
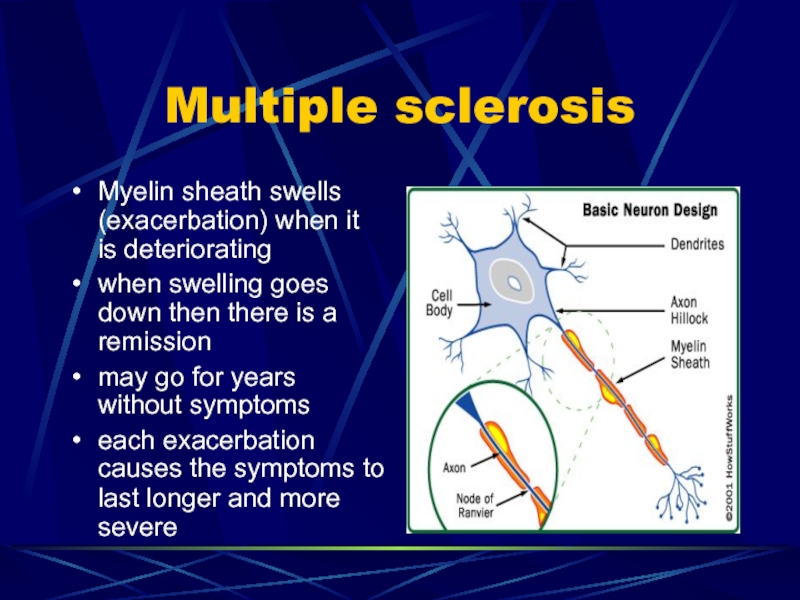
- 61. Multiple sclerosisMyelin sheath swells (exacerbation) when it
- 62. Multiple sclerosisWeakness of arms and legs may
- 63. Multiple sclerosisIntellectual functioning may be impaired late
- 64. Drugs for MSLioresal and Dantrium--muscle spasticity and
- 65. NursingSensory impairment: be careful with hot, cold,
- 66. Myasthenia Gravis pg 681Disorder of muscles, with
- 67. Myasthenia GravisMost common symptoms are ptosis of
- 68. Myasthenia GravisDiagnosed by giving IV Tensilon which
- 69. Myasthenia gravisTreatment is Mesitonon or MyelelaseAtropine is
- 70. Mestinon or MytelaseObserve for drug overdose….abdominal cramps,
- 71. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis--Lou Gehrig’s Disease 682Progressive, fatal
- 72. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis--Lou Gehrig’s Disease 682Periods of
- 73. Cranial Nerve disorders Pg. 683Trigeminal Neuralgia (Tic douloureux)Bell’s palsyTemporomandibular Disorder (TMD)
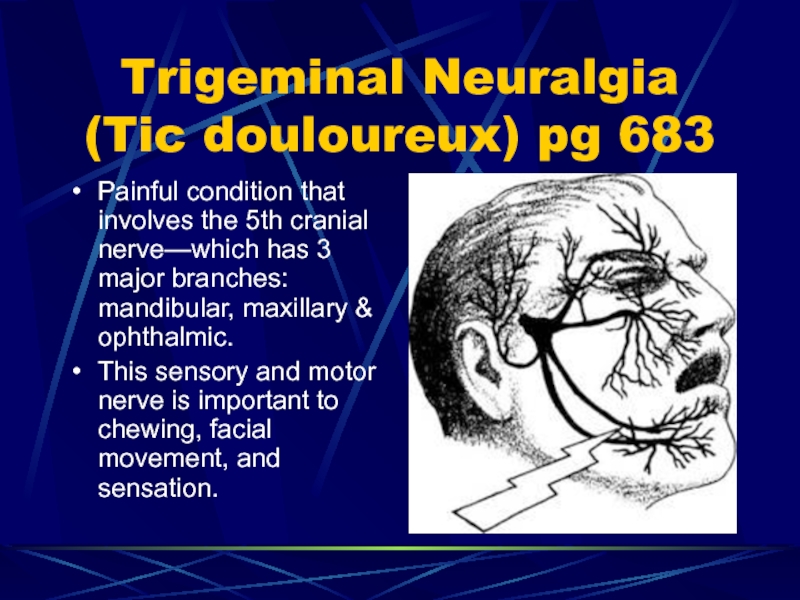
- 74. Trigeminal Neuralgia (Tic douloureux) pg 683Painful condition
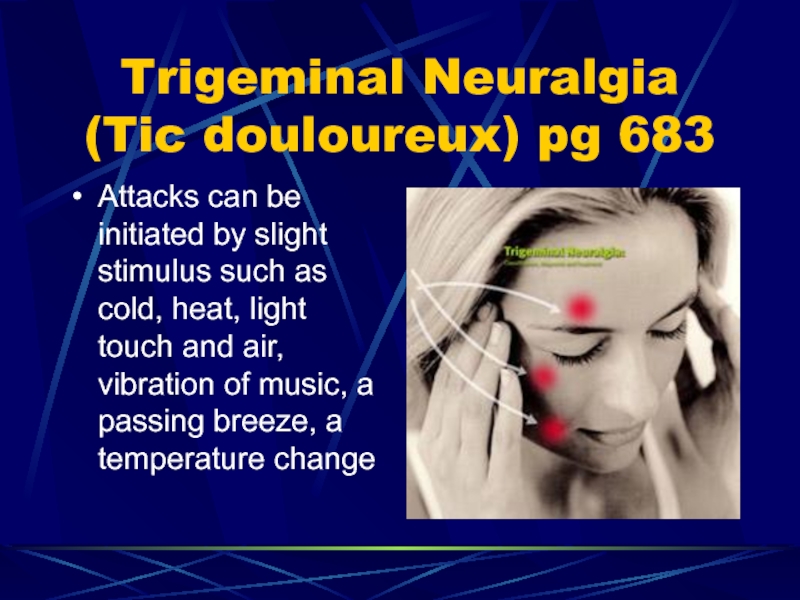
- 75. Trigeminal Neuralgia (Tic douloureux) pg 683Attacks can
- 76. Trigeminal Neuralgia The pain is described as
- 77. Trigeminal NeuralgiaAnalgesics, surgery on nerve root or
- 78. Trigeminal NeuralgiaSlightest stimulus may start attack (vibration
- 79. Trigeminal NeuralgiaPost-op eating may be a problem
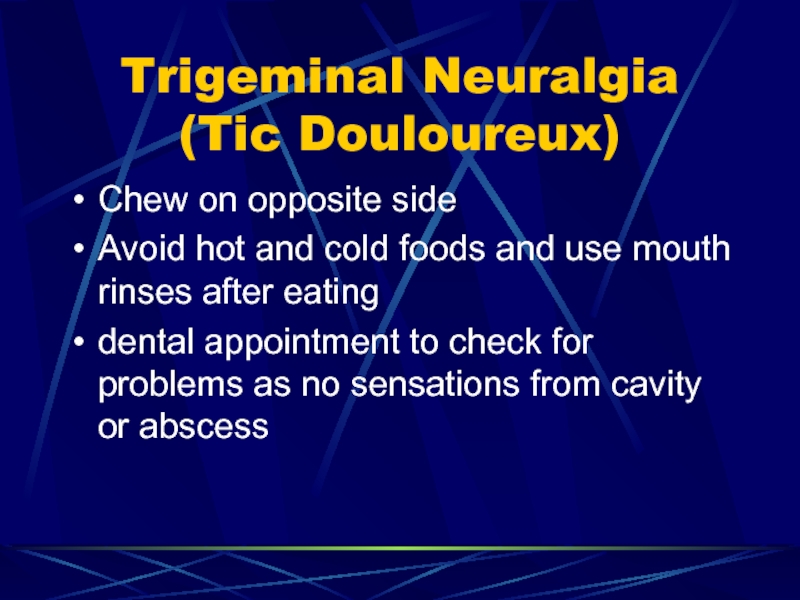
- 80. Trigeminal Neuralgia (Tic Douloureux)Chew on opposite sideAvoid
- 81. Trigeminal NeuralgiaDilantin and tegretol used to reduce
- 82. Bell’s Palsy7th cranial nerve—responsible for movement of the facial musclesfacial nerve usually affects one side
- 83. Bell’s Palsycauses weakness and paralysis of facial
- 84. Bell’s PalsySpeech and chewing difficulty may occurMust
- 85. Bell’s palsyIf ptosis and blinking reflex affected
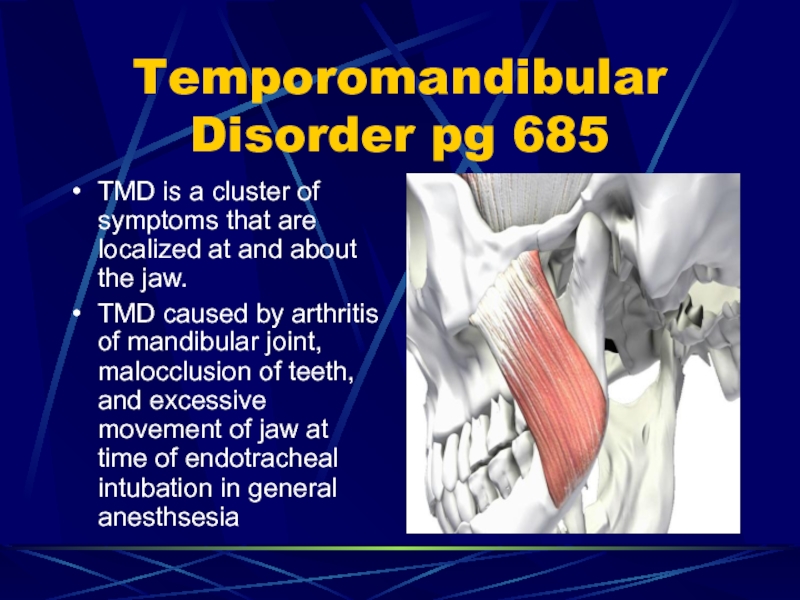
- 86. Temporomandibular Disorder pg 685TMD is a cluster
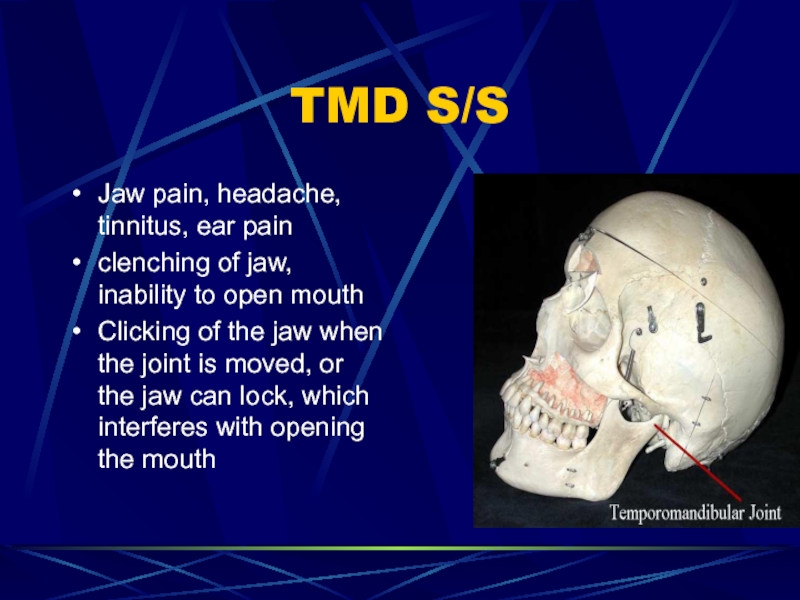
- 87. TMD S/S Jaw pain, headache, tinnitus, ear
- 88. TMD S/S Pronounced spasm and tenderness of the masseter and temporalis musclesDental x-rays help with diagnosis
- 89. TMD Medical ManagementTreatment is referred to a dentistAnalgesics are prescribedCustom-fitted mouth guard is worn during sleep
- 90. TMD Medical Management TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve
- 91. Extrapyramidial disorders pg 686Parkinson’s diseaseHuntington’s diseaseOne primary characteristic is abnormal movement.
- 92. Parkinson’sUsually begins after age 50early signs include
- 93. Parkinson’sIntention tremor: when tremors increase during voluntary
- 94. Parkinson’sHave difficulty turning or redirecting forward motionarms
- 95. Parkinson’sLevodopa and cogentin are drugs of choicephysical
- 96. Parkinson’sSymptoms usually begin on one side and
- 97. Huntington’s Disease pg. 689Hereditary, degeneration of basal
- 98. Huntington’sTreatment is supportive, no curetranquilizers and antiparkinsonian
- 99. Huntington’s1/2 children of affected parent will develop
- 100. Huntington’sPersonality changes (obstinanacy, moodiness and lack of
- 101. Huntington’s choreaDifficulty chewing and swallowing, speech difficulty,
- 102. Nursing care extrapyramidial 43-2 pg 690Offer fluids
- 103. Nursing Care extrapyramidialAvoid stress, fatiguebowel and bladder
- 104. Seizure disorders pg 692Abnormal electrical discharge of
- 105. Слайд 105
- 106. Seizure disordersEpilepsy is a permanent, recurrent seizure
- 107. Seizure disordersToo much electrical discharges from nerve
- 108. Seizure disorderJacksonian: begins at one place and
- 109. SeizuresGeneralized seizure: Entire brain involved; can last
- 110. Generalized seizureMyoclonic: brief involuntary muscular jerks of
- 111. Seizure--Grand malClonic phase; alternating spasms and relaxations---thrashing
- 112. Слайд 112
- 113. Grand mal seizurePostictal stage: consciousness is regained,
- 114. During a seizureTurn to side to keep
- 115. Слайд 115
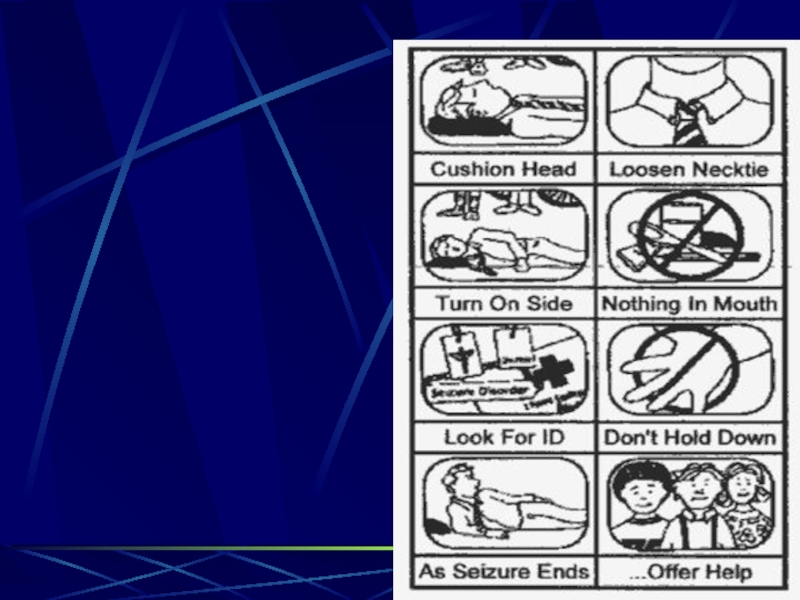
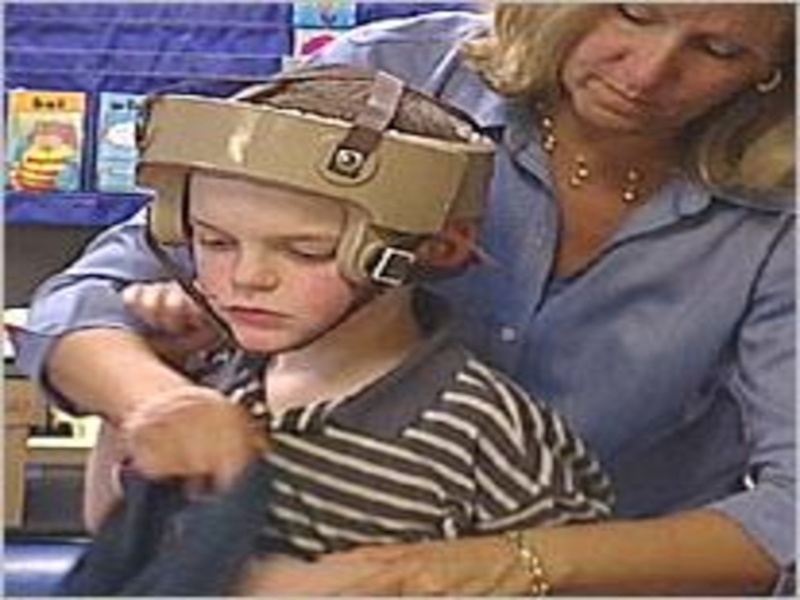
- 116. During a SeizureProtect from injury…do not forcibly restrain arms, legs or headstay with patientGive privacy…clear onlookers
- 117. Слайд 117
- 118. After a seizureKeep bed flat; turn to
- 119. Слайд 119
- 120. NursingObserve closely and chart activity before and
- 121. NursingAssess for injury, allow to rest, report
- 122. Слайд 122
- 123. Status EpilepticusSeveral tonic-clonic seizures without consciousness returningthis is an emergencymay be from stopping seizure medslife threatening
- 124. Слайд 124
- 125. Medications for seizuresDilantinphenobarbitalTegretolZarontindepakeneValium drug of choice to stop status epilepticus
- 126. Brain Tumor pg. 697Can result in death
- 127. Brain tumorProjectile type vomiting without nausea, speech
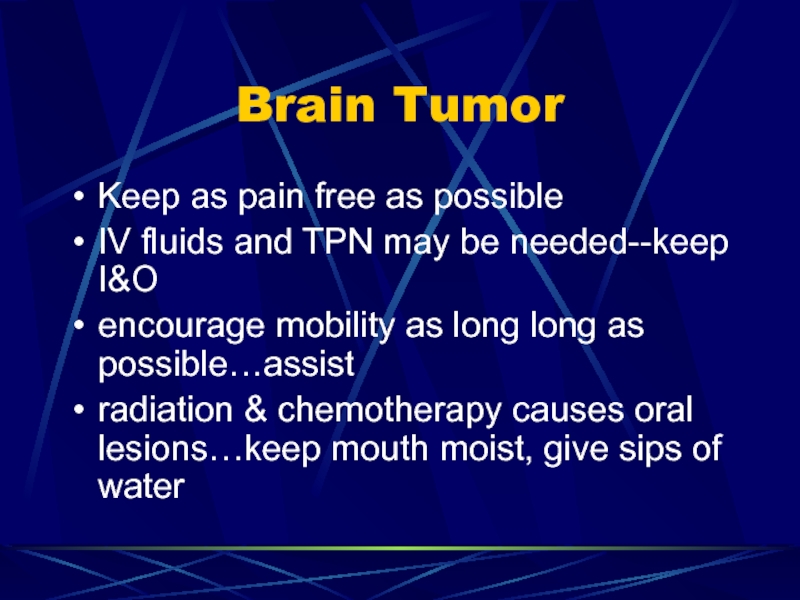
- 128. Brain TumorKeep as pain free as possibleIV
- 129. Brain TumorChemotherapy, radiation and surgery used to
- 130. Слайд 130
- 131. Слайд 131
- 132. Скачать презентанцию
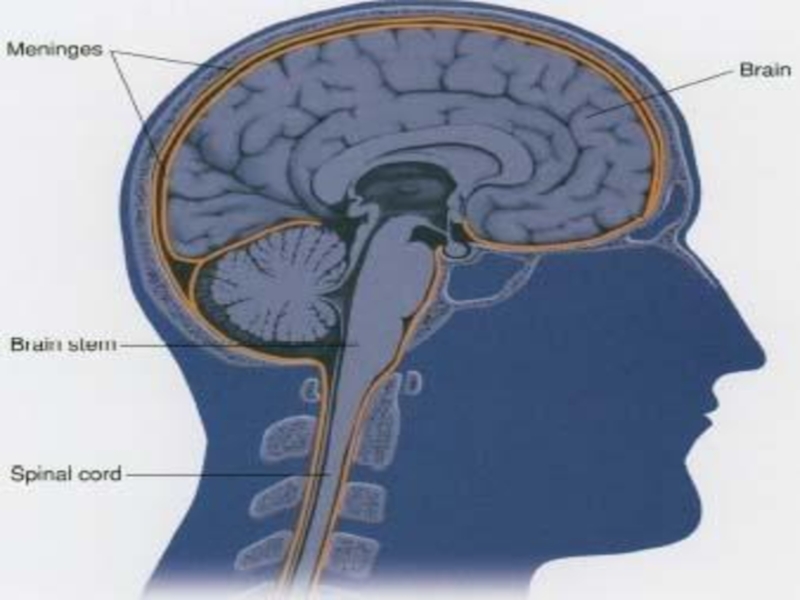
Increased Intracranial Pressure (pg. 666)The cranium consists of 1. Brain tissue 2. Blood3. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)If one or more of these increases significantly without a decrease in one or the
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Increased Intracranial Pressure (pg. 666)
The cranium consists of
1. Brain
tissue
of these increases significantly without a decrease in one or the other two, ICP becomes elevated.Слайд 4Increased Intracranial pressure
The skull cannot expand so a tumor, cerebral
edema, brain abscess, or bleeding compresses the brain and causes
increased intracranial pressure (ICP)As pressure increases, the cerebral blood flow decreases and PCO2 increases causing cerebral edema which increases the ICP even more
Слайд 5Increased Intracranial Pressure
If not recognized, the brainstem will herniate thru
the foramen magnum
brainstem controls vital signs so death will occur
Слайд 6ICP
Signs and symptoms develop rapidly or slowly
If slow it may
be over looked
Keep check on baseline and observe closely
change in
LOC is usually earliest signalterations may be difficult to determine
Слайд 7Level Of Consciousness
Confusion, restlessness, disorientation and drowsiness may or may
not be a symptom of impending change in LOC
Report sudden
change to Dr statChange in LOC is one of the earliest signs of ICP
Слайд 8Headache
Pain is usually intermittent--if constant condition usually grave
coughing, sneezing, straining
at stool increases headache
lying in bed with head elevated reduces
ICP and headacheСлайд 9Vomiting and ICP
Commonly occurs without warning of nausea and without
a relationship to eating
projectile in nature
Слайд 10Papilledema
Papilledema (edema of optic nerve caused by obstruction of venous
drainage due to ICP
Can be seen only with an ophthalmoscope
Affects
pupillary response to light.Normal pupil response to strong light is rapid constriction. In IICP the response is sluggish or nonexistent (fixed)
Слайд 11Posturing
Decorticate--arms flexed--problem with cervical spinal tract or cerebral hemisphere
Decerebrate--arms extended
(more serious as brainstem damage, problems within midbrain or pons
see
page 660 for pictureСлайд 13Symptoms of ICP
Change in LOC
headache
vomiting
papilledema
vital signs--temp rises, b/p rises and
pulse pressure widens
pupils sluggish or fixed
decorticate or decerebrate position
Слайд 14Vital signs
Temp rises, B/P rises and pulse pressure widens. These
3 s/s are called Cushing’s triad. A late sign in
IICP.Pulse may increase at first but later becomes slow (40-60) and bounding
resp rate is irregular or cheyne-stokes (shallow, rapid, then decreases and then apnea)
Слайд 15Medical and surgical management
Osmotic diuretics (mannitol, glycerol); steroids to reduce
cerebral edema
If clot then it is removed;
surgery for depressed skull
fx, tumor or bleeding…fix the cause statСлайд 16Medical & surgical management
Restrict fluids, lumbar punctures to remove CSF
and hyperventilation via ventilator to cause resp alkalosis which constricts
cerebral arteries and reduces ICPСлайд 17Medical Management
May order:
insertion of foley
NG tube for gastric decompression or
feedings
Stool softener to prevent straining
Histamine antagonist (Pepcid) to prevent stress
ulcersCooling blankets if hyperthermia
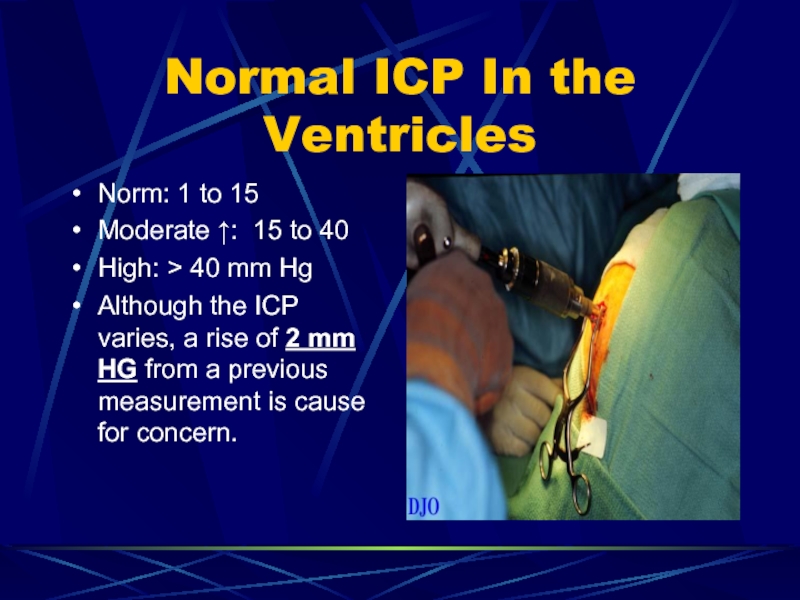
Слайд 18Normal ICP In the Ventricles
Norm: 1 to 15
Moderate ↑:
15 to 40
High: > 40 mm Hg
Although the ICP
varies, a rise of 2 mm HG from a previous measurement is cause for concern. Слайд 19Nursing care ICP
Teach to remain quiet in bed and not
to turn in bed without help
avoid ROM until ICP normal
and Dr orderssuction only when absolutely necessary…gently remove secretions with gauze
give oxygen before suctioning
Слайд 20Nursing Care ICP
ICP can affect temp regulation so cooling blanket
may be needed
Neuro assessment should be done q 30 min
Avoid
extreme flexion of hip because this increases intraabdominal, ICP and intrathoracic pressureСлайд 21Nursing Care ICP
A neurologic flow sheet that includes the Glasgow
Coma Scale or Ranchos Los Amigos Scale and ICP pressure
measurement (see chapter 42) is used to establish a data base and recordIntake and output and daily weights are recorded to monitor the fluid and nutritional status of the client.
Слайд 22Nursing Care ICP
Laboratory findings such as serum electrolyte levels and
arterial blood gas measurements are analyzed to detect fluid, electrolyte,
and acid-base complications, or to evaluate the effectiveness of medical management.Bowel sounds are present in all quad’s and palpated to determine if there is distention.
Bowel elimination patterns are monitored.
Слайд 23Nursing Care ICP
Keep head straight and head of bed slightly
elevated
If a basal skull fx and ICP may be kept
flat but in no case must the head be allowed to be lower than bodyReduce noise and bright lights, limit movement, space activity
Слайд 24Activities That increase ICP
Coughing
range of motion exercises
sneezing
hip flexion of 90
degrees or greater
vomiting
suctioning
Слайд 25Activities that increase ICP
Straining to have a BM (valsalva maneuver
holding
breath
digging heels into bed to help in repositioning
turning in bed
without helpСлайд 26Nursing Care ICP
Hourly I&O may be done
If steroids given, monitor
glucose as ordered
test stools for blood
assess bowel and bladder elimination
and prevent strainingcomplete care given until ICP normal
monitor temp q 4 hours & prn
Слайд 27Nursing Care ICP
Monitor I&O…fluids may be restricted to reduce cerebral
edema and prevent vomiting and coughing which raise pressures
calculate IV
fluids so given over 24 hoursnutrition may be total parenteral nutrition (TPN)
assess skin turgor and electrolytes
Слайд 28Infectious & Inflammatory Disorders
Meningitis
Encephalitis
Gullian-Barre Syndrome
Poliolmyelitis
Brain Abscess
Слайд 29Meningitis
(Covering of the Brain) pg 669
Inflammation of meninges (three
membranes that cover the brain-dura, arachnoid, & pia mater)
May affect
cerebral cortex and decrease blood flow to the brainMeningococcus, strept, staph and pneumococcus most common cause (contagious—meningococcal)
Reaches brain by the bloodstream or ear or sinus infection
Слайд 31Meningitis
Most adults with bacterial meningitis recover without permanent neurologic damage
or dysfunction.
When complications do occur, they usually are serious.
Слайд 32Meningitis S/S
Fever, nuchal rigidity (pain and stiffness of neck); inability
to place chin on chest
nausea and vomiting, photophobia, headache, restlessness,
irritability and seizuressevere may cause opisthotonus (arching of back and neck hyperextended
Слайд 33Kernig’s Sign
Positive Kernig’s sign ( inability to extend the
leg when the thigh is flexed on abdomen
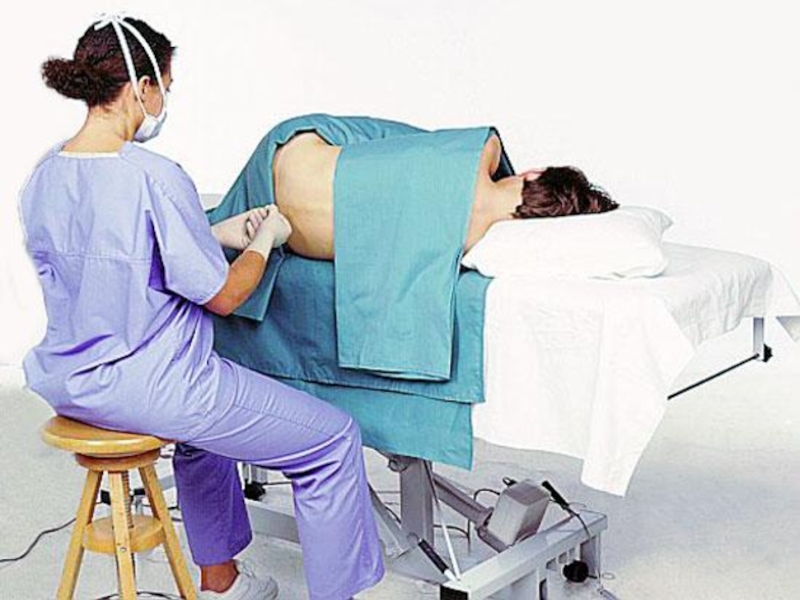
Слайд 35Diagnostic findings: Meningitis
Lumbar puncture done
if bacterial meningitis the CSF is
cloudy and pressure is elevated, glucose is decreased, protein is
elevated and WBC & RBCs are elevatedCultures are done
If culture negative then it is viral in nature
Слайд 37Medical Management
IV fluids, antibiotics, anticonvulsants are used to treat
sulfonamide
given to people who are exposed
observe for altered LOC, signs
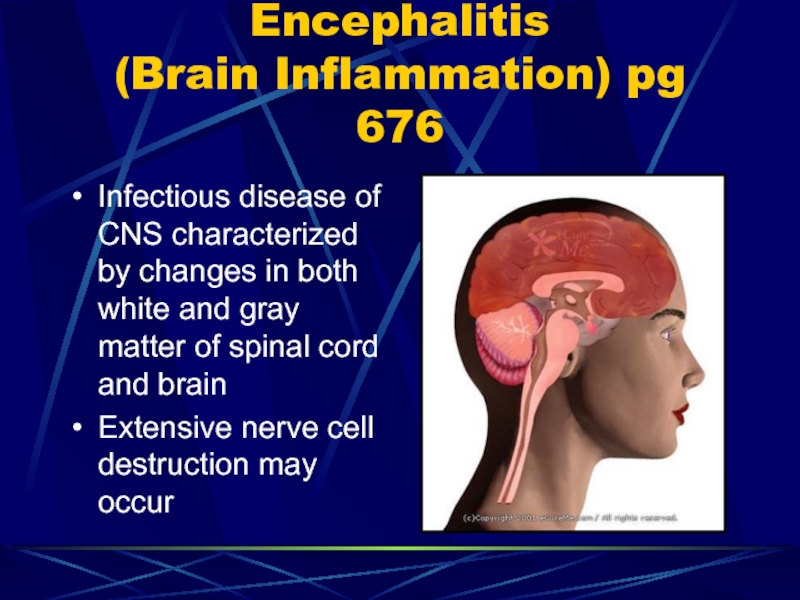
of airway obstruction and cardiac arrhythmiasСлайд 38Encephalitis
(Brain Inflammation) pg 676
Infectious disease of CNS characterized by changes
in both white and gray matter of spinal cord and
brainExtensive nerve cell destruction may occur
Слайд 39Encephalitis (brain inflammation)
Symptoms similar to meningitis
Caused by bacteria, fungi, or
virus
cause virus: Polio, herpes, measles, mumps, chickenpox, mono, hepatitis,,St. Louis
virus and Eastern and Western equine virusСлайд 40Encephalitis
occurs after a viral infection elsewhere (measles or vaccinations)
Poisoning by
drugs and chemicals, such as lead, arsenic, or Carbon monoxide,
may closely resemble encephalitis clinically!!!Слайд 41Encephalitis
Onset of viral is sudden with fever, severe headache, stiff
neck, vomiting and drowsiness
lethargy is a prominent symptom and coma
and delirium may occurTremors, seizures, spastic or flaccid paralysis, irritability
Слайд 42Encephalitis
Muscle weakness, incoordination, incontinence and visual disturbances (photophobia, involuntary eye
movement, double or blurred vision may occur
speech changed, increased ICP
and shockСлайд 43Encephalitis--brain inflammation
Lumbar puncture done…CSF pressure elevated but fluid clear
EEG has
slow wave forms
treatment supportive only as viral
Total care, LOC, vital
signs monitored Слайд 44Encephalitis
Mild cases are common and may go unrecognized
complications and deaths
are more common in infants and elderly
usually recover in 2-3
weeks unless severeСлайд 45Guillain-Barre’ syndrome Pg.677
Rare, inflammatory condition involving the CNS that causes
rapid weakness and loss of sensation.
History of recent infection (esp.
resp tract); recent surgery or vaccinationsalso seen in malignancy and Lupus.
The affected nerves become inflamed and edematous.
Mild to severe ascending muscle weakness or paralysis develops.
Слайд 46Guillain-Barre’ Syndrome
May be autoimmune response to viral infection
Takes approx 1
month to start improving and may take 1 year or
longer to recoverMuscle weakness or paralysis can occur and be permanent.
Immobility complications kills (pneumonia & infection)
Слайд 47Guillain Barre’ Syndrome
Weakness, tingling, and numbness in arms and legs
may be 1st symptoms
Weakness usually starts in legs and moves
to arms and facemay affect the muscle of respiration
Muscle weakness may be followed by paralysis.
chewing, talking, and swallowing become difficult if cranial nerves involved
Слайд 48Medical Management Guillian Barre’
Plasmaphoresis removal of plasma from the blood
and reinfusion of the cellular components with saline, has been
shown to shorten the course of the DX. If performed within the first 2 weeks.If the respiratory muscles are involve, endotracheal intubation & mechanical ventilation become necessary.
Difficulty chewing—may need IV fluids, gastric feedings, or TPN
Слайд 50Nursing Management
Monitory respiratory status/distress
Use IS
R/T incapacitated by immobility, provide meticulous
skin care and change position every 2 hours.
Give passive ROM
q 2 hoursСлайд 51Brain abscess Pg. 678
A collection of pus caused by a
bacterial infection in the brain—if untreated it can be fatal!!
Causes:
infection that spreads from an infected skull (osteomyelitis, mastoiditis, sinusitis)infection spreads thru bloodstream or trauma
Слайд 53Brain abscess
May occur from infection of teeth, sinus, middle ear,
or from an infection in other organs.
common after endocarditis, pulmonary
or abdominal infection, or intracranial surgeryfever, headache, ↑ IICP s/s, seizures, muscle weakness, paralysis and lethargy
Слайд 54Brain abscess
Risk increases with head injury, illness that lowers resistance
(esp. diabetes) recent infection (esp around eye, nose, or face)
Iv drug users and immuno-suppressedСлайд 55Brain abscess
I&O fluids may be restricted as over-hydration may cause
cerebral edema
antibiotics usually given 4 to 6 weeks; craniotomy may
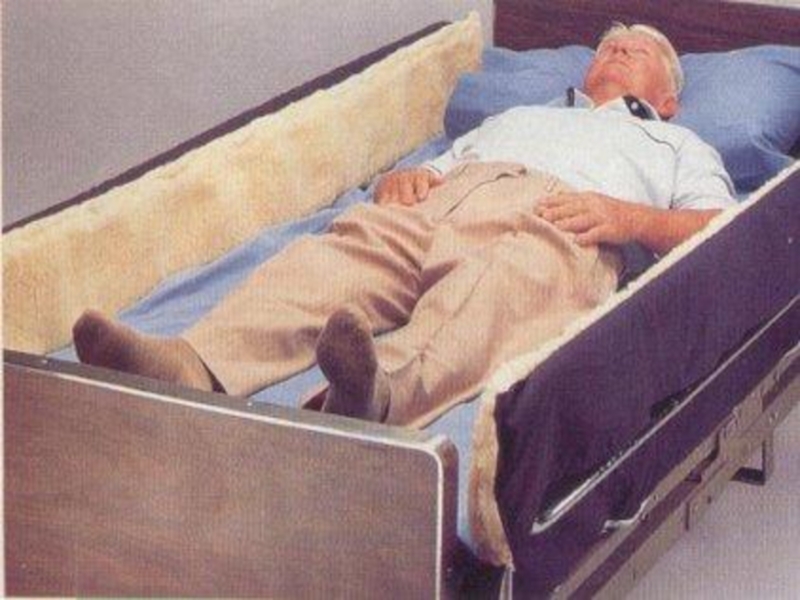
be neededseizure precautions; pad side rails, decrease stimuli
Слайд 56General Nursing Care for Inflammatory Disorders
Swallowing may be affected---give PO
drugs slowly…no narcotics
REPORT sudden increase in headache
Dr. must order ROM
but turn and give skin care….cooling blanket may be needed for tempСлайд 57Nursing Care for Inflammatory Disorders
Monitor vitals…complete care
neuro checks…use Glasgow Coma
scale
Seizure precautions—insert a padded tongue blade in the mouth ONLY
IF THE TEETH ARE NOT TIGHTLY SHUT!!lung sounds and suction PRN******caution it raises ICP
elevate head of bed 30 degrees
keep oral airway at bedside
Слайд 58Neuromuscular disorders PG 678
Involves the nervous system and indirectly affects
the muscles
Multiple Sclerosis
Myasthenia Gravis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (Lou Gehrig)
Слайд 59Multiple sclerosis PG 678
Chronic, progressive disease of the peripheral nerves.
Onset
in young adult and early middle life (20 to 40)
May
be autoimmunepeople in colder climates at higher risk
Слайд 60Multiple sclerosis
Permanent degeneration as patchy destruction of myelin sheath of
nerve fibers of brain and spinal cord
Impulses cannot go thru
without myelin so muscles become paralyzedscar tissue replaces myelin (sclerotic)
Слайд 61Multiple sclerosis
Myelin sheath swells (exacerbation) when it is deteriorating
when swelling
goes down then there is a remission
may go for years
without symptomseach exacerbation causes the symptoms to last longer and more severe
Слайд 62Multiple sclerosis
Weakness of arms and legs may progress to paraplegia
may
be incontinent
visual disturbances may eventually progress to blindness
infection and emotional
upsets may cause exacerbationsNO CURE
Слайд 63Multiple sclerosis
Intellectual functioning may be impaired late in disease
loss of
memory, impaired judgment
shallow breathing can cause pneumonia (most common cause
of death)may live 20 years with the disease
Слайд 64Drugs for MS
Lioresal and Dantrium--muscle spasticity and rigidity
Antibiotics, urinary infectives,
tranquilizers for mood swings
Ditropan---urinary incontinence
Urecholine for retention
Steroids
Слайд 65Nursing
Sensory impairment: be careful with hot, cold, avoid injury
REST, conserve
energy
Polyunsaturated fate, linoleic acid--found in sunflower oil may help
Слайд 66Myasthenia Gravis pg 681
Disorder of muscles, with increasing fatigue and
weakness as muscles are used
Fatigue appears to be caused by
a defect in nerve impulses from nerve endings to musclesReceptor sites destroyed
Thought to be autoimmunne
Слайд 67Myasthenia Gravis
Most common symptoms are ptosis of eyelids, difficulty chewing
and swallowing, diplopia, voice weakness, masklike facial expressions and weakness
of arms and legsMay affect respirations
Слайд 68Myasthenia Gravis
Diagnosed by giving IV Tensilon which relieves symptoms in
a few seconds if it is Myasthenia
Chest x-ray may show
tumor of thymusСлайд 69Myasthenia gravis
Treatment is Mesitonon or Myelelase
Atropine is antidote for mestinon
and other anticholinesterase drugs
Thymus gland may be surgically removed as
it may cause destruction of nerve endingsСлайд 70Mestinon or Mytelase
Observe for drug overdose….abdominal cramps, clenched jaws, muscle
rigidity
Give drug at exact intervals to maintain therapeutic blood levels
Watch
for resp distress if drugs not affectiveMay aspirate as cannot swallow
Слайд 71Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis--Lou Gehrig’s Disease 682
Progressive, fatal neuro disorder of
unknown cause
Degeneration of motor neurons of CNS which causes wasting
and weakness of musclesFasciculations (twitching) and difficulty speaking or swallowing
Слайд 72Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis--Lou Gehrig’s Disease 682
Periods of inappropriate laughter or
crying
Causes resp failure and total paralysis
No specific tests or treatment
Care
is supportive…may need help with ADLsWill become total care
Слайд 73Cranial Nerve disorders Pg. 683
Trigeminal Neuralgia (Tic douloureux)
Bell’s palsy
Temporomandibular Disorder
(TMD)
Слайд 74Trigeminal Neuralgia (Tic douloureux) pg 683
Painful condition that involves the
5th cranial nerve—which has 3 major branches: mandibular, maxillary &
ophthalmic.This sensory and motor nerve is important to chewing, facial movement, and sensation.
Слайд 75Trigeminal Neuralgia (Tic douloureux) pg 683
Attacks can be initiated by
slight stimulus such as cold, heat, light touch and air,
vibration of music, a passing breeze, a temperature changeСлайд 76Trigeminal Neuralgia
The pain is described as sudden, severe, and
burning
It ends as quickly as it began, usually lasting a
few seconds to several minutes.The cycle is repeated many times a day
During a spasm, the face twitches and the eyes tear.
Слайд 77Trigeminal Neuralgia
Analgesics, surgery on nerve root or branches
post op there
is no feeling in the area
corneal reflex (blinking) may be
gone so need eye drops and shieldСлайд 78Trigeminal Neuralgia
Slightest stimulus may start attack (vibration from music, breeze,
temp change
they avoid washing face, shaving
forehead over eyebrow is a
common trigger spot so avoid touching faceDo not jar the bed
Слайд 79Trigeminal Neuralgia
Post-op eating may be a problem as may bite
tongue without knowing it
food gets caught in mouth and swallowing
is difficult as they lose sensation after nerve cutsmall sips, inspect mouth for breaks in mucus membranes
Слайд 80Trigeminal Neuralgia (Tic Douloureux)
Chew on opposite side
Avoid hot and cold
foods and use mouth rinses after eating
dental appointment to check
for problems as no sensations from cavity or abscessСлайд 81Trigeminal Neuralgia
Dilantin and tegretol used to reduce pain as analgesics
not too successful
narcotics may be given
Dentist should be seen as
may be caused by dental deformitiesСлайд 82Bell’s Palsy
7th cranial nerve—responsible for movement of the facial muscles
facial
nerve usually affects one side
Слайд 83Bell’s Palsy
causes weakness and paralysis of facial muscles and eyelid
facial
pain, pain behind ear, numbness
diminished blink reflex
ptosis of eyelid, tearing
of affected sideСлайд 84Bell’s Palsy
Speech and chewing difficulty may occur
Must rule out CVA,
tumor
no specific test
Prednisone, analgesics, electrotherapy to prevent atrophy of facial
musclesmost show improvement in a few weeks
Слайд 85Bell’s palsy
If ptosis and blinking reflex affected must wear eye
patch
corneal ulcerations and infection of eye may develop
eye shield at
nightantibiotic ointment in eye
eye assessment needed
Слайд 86Temporomandibular Disorder pg 685
TMD is a cluster of symptoms that
are localized at and about the jaw.
TMD caused by
arthritis of mandibular joint, malocclusion of teeth, and excessive movement of jaw at time of endotracheal intubation in general anesthsesiaСлайд 87TMD S/S
Jaw pain, headache, tinnitus, ear pain
clenching of jaw,
inability to open mouth
Clicking of the jaw when the joint
is moved, or the jaw can lock, which interferes with opening the mouthСлайд 88TMD S/S
Pronounced spasm and tenderness of the masseter and
temporalis muscles
Dental x-rays help with diagnosis
Слайд 89TMD Medical Management
Treatment is referred to a dentist
Analgesics are prescribed
Custom-fitted
mouth guard is worn during sleep
Слайд 90TMD Medical Management
TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation), injection of a
local anesthetic to relieve muscle spasm, and ice water oral
irrigations are also used to reduce and relieve discomfort.Surgery is available if conservative methods are ineffective
Слайд 91Extrapyramidial disorders pg 686
Parkinson’s disease
Huntington’s disease
One primary characteristic is abnormal
movement.
Слайд 92Parkinson’s
Usually begins after age 50
early signs include stiffness, tremors of
hands, pill rolling and difficulty performing movement
Tremors decrease with voluntary
movementСлайд 93Parkinson’s
Intention tremor: when tremors increase during voluntary movement…may be seen
in some patients
Later, tremors of head, mask-like expression, stooped posture
Monotonous
speech and shuffling gaitСлайд 94Parkinson’s
Have difficulty turning or redirecting forward motion
arms seldom swing while
walking
rigidity develops more than tremors
reflexes and power of contraction are
not affected but speed and movement areСлайд 95Parkinson’s
Levodopa and cogentin are drugs of choice
physical therapy…in extreme cases
surgery done to destroy part of the thalamus so excessive
muscle contraction decreasedfetal tissue transplanted in brain has helped some patients
Слайд 96Parkinson’s
Symptoms usually begin on one side and may take 15
years to spread bilaterally
late symptom is drooling and problems with
swallowingeyes may roll up or down and stay in that position for days
Слайд 97Huntington’s Disease pg. 689
Hereditary, degeneration of basal ganglia and cerebral
cortex
Causes mental apathy, emotional disturbances, choreiform movement (uncontrollable withering and
twisting of body) grimacingСлайд 98Huntington’s
Treatment is supportive, no cure
tranquilizers and antiparkinsonian drugs to relieve
choreiform movements
late in the disease, may have hallucinations, delusions, impaired
judgment, and becomes totally dependentСлайд 99Huntington’s
1/2 children of affected parent will develop the disease but
will not find out about it until well past child
bearing agemust have disease to transmit trait
most do not develop disease until between age 30 to 50
Слайд 100Huntington’s
Personality changes (obstinanacy, moodiness and lack of interest
Inappropriate behavior may
start before the involuntary jerky, irregular choreic movements
gait is wide
paced and prancing (ST. vitus dance)Слайд 101Huntington’s chorea
Difficulty chewing and swallowing, speech difficulty, intellectual decline
loss of
bowel and bladder control
severe depression may lead to suicide
paranoia is
commonСлайд 102Nursing care extrapyramidial 43-2 pg 690
Offer fluids hourly
I&O, keep suction
available to prevent aspiration
soft diet, allow time to chew, cut
food into small bitesmay need to feed in later stages
skin care,
maintain self care as long as possible
Слайд 103Nursing Care extrapyramidial
Avoid stress, fatigue
bowel and bladder incontinent retraining program
may be helpful early, not too effective late
Prone to injury,
assist when ambulating or getting up…may climb over rails or wanderobserve frequently
Слайд 104Seizure disorders pg 692
Abnormal electrical discharge of neurons
can be focal
or generalized
idiopathic (no known cause
causes---high fever, electrolyte imbalance, uremia, hypoglycemia,
hypoxia, brain tumorСлайд 106Seizure disorders
Epilepsy is a permanent, recurrent seizure disorder
causes include brain
injury at birth, head injury, metabolic disorders or idiopathic
convulsive disorder
and seizure disorder the sameСлайд 107Seizure disorders
Too much electrical discharges from nerve cells in the
brain
Different types: partial or focal--from a localized area, cause specific
symptoms and may spread to entire brainlasts from seconds to about one minute
Слайд 108Seizure disorder
Jacksonian: begins at one place and spreads to another
in an orderly fashion
psychomotor and psychosensory: seizure with hallucinatory sights,
sounds and odorsmumbles and non-sense words, smacking lips
Слайд 109Seizures
Generalized seizure: Entire brain involved; can last several minutes, loss
of consciousness
absence; brief change of consciousness lasting 1 to 10
seconds, mostly childrenblank stare, mouth arm or eyelid movement, vacant stare, Petit mal
Слайд 110Generalized seizure
Myoclonic: brief involuntary muscular jerks of extremities or body
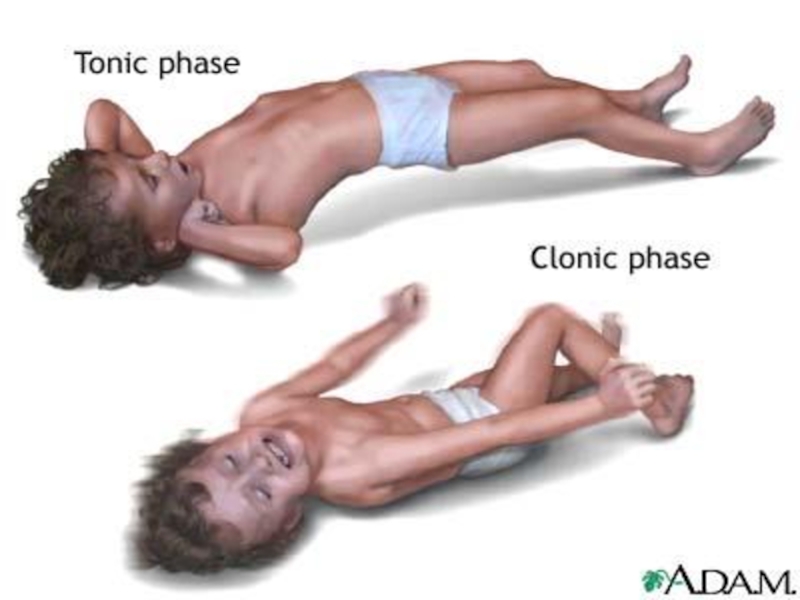
Tonic-clonic:
Grand mal--emotional changes, aura (seconds or minutes before), epileptic cry,
loss of consciousnesstonic-stiffness and rigidity
Слайд 111Seizure--Grand mal
Clonic phase; alternating spasms and relaxations---thrashing and jerking
breathing is
spasmodic
frothing saliva, jaws clenched, incontinence
labored breathing and cyanosis
lasts 2 to
5 minutesСлайд 113Grand mal seizure
Postictal stage: consciousness is regained, does not remember
seizure
confused, difficulty speaking, headache
fatigue, soreness and may sleep for hours
Слайд 114During a seizure
Turn to side to keep airway patent and
to prevent aspiration of saliva and vomitus
suction PRN
remove pillow, bedding
and clothing that can obstruct breathingloosen restrictive clothing
Слайд 116During a Seizure
Protect from injury…do not forcibly restrain arms, legs
or head
stay with patient
Give privacy…clear onlookers
Слайд 118After a seizure
Keep bed flat; turn to side until awake
and responding
keep room lighting dim and noise to a minimum
Take
vitals stat and q 30 minutes until awakeinspect lips, tongue, oral cavity for injury
change linen if incontinent
Слайд 120Nursing
Observe closely and chart activity before and after
turn on side--prevent
aspiration, protect from injury
do not restrain, do not force objects
in mouthStay with patient
take vitals after a seizure
Слайд 121Nursing
Assess for injury, allow to rest, report activity, time elapsed
and client reaction
pad side rails
good mouth care--gingival hyperplasia
dilantin levels
give meds
on scheduleСлайд 123Status Epilepticus
Several tonic-clonic seizures without consciousness returning
this is an emergency
may
be from stopping seizure meds
life threatening
Слайд 125Medications for seizures
Dilantin
phenobarbital
Tegretol
Zarontin
depakene
Valium drug of choice to stop status epilepticus
Слайд 126Brain Tumor pg. 697
Can result in death even if benign
They
take up space and block flow and absorption of CSF
so cause ICP to occurheadache, vomiting and papilledema is common
headache usually early in AM and becomes more severe as tumor grows