Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
PRESENTATION An ICT role in key sectors of society development. Standards in
Содержание
- 1. PRESENTATION An ICT role in key sectors of society development. Standards in
- 2. PLANІ. IntroductionІІ. Main partThe strategic and effective use of ICTICT in EducationICT in HealthІІІ. СonclusionІV. Bibliography
- 3. introductionThe potential of ICT as a development
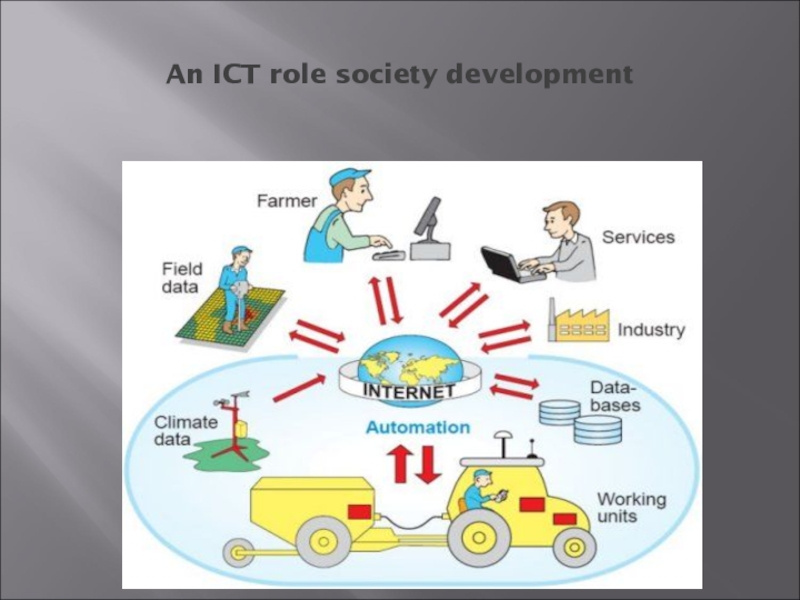
- 4. An ICT role society development
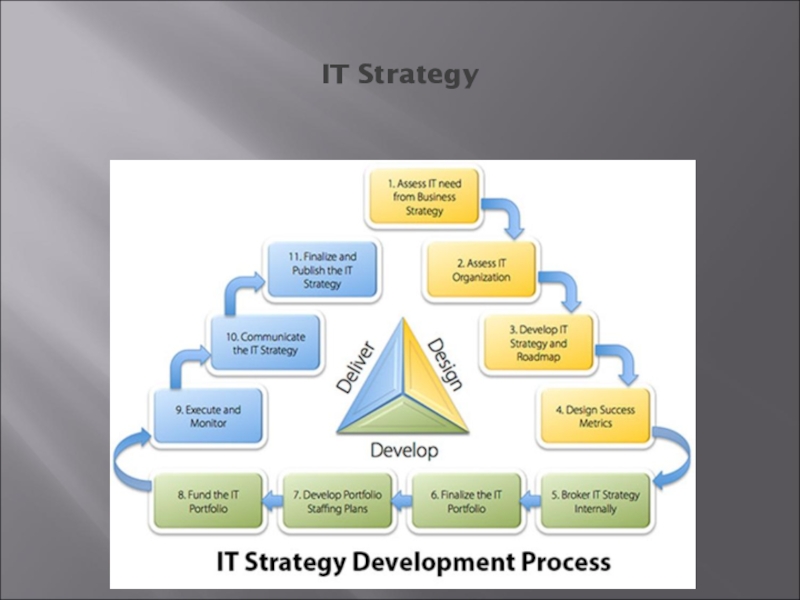
- 5. IT Strategy
- 6. The strategic and effective use of ICTThe
- 7. ICT in EducationICT can improve the efficiency
- 8. ICT in Education
- 9. ICT in Public Sector ManagementADB encourages governments
- 10. ICT in Public Sector Management
- 11. ICT in HealthICT can be a powerful
- 12. ICT in Health
- 13. СONCLUSION The paper discusses the foundations for establishing
- 14. BibliographyZimbabwe National ICT Policy – December 2005Partnership
- 15. Thank you for attention!!!
- 16. Скачать презентанцию
PLANІ. IntroductionІІ. Main partThe strategic and effective use of ICTICT in EducationICT in HealthІІІ. СonclusionІV. Bibliography
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1PRESENTATION
An ICT role in key sectors of society development. Standards
in the field of ICT.
its purposes. An ICT role in key sectors of society development. Standards in the field of ICT.Слайд 2PLAN
І. Introduction
ІІ. Main part
The strategic and effective use of ICT
ICT
in Education
ICT in Health
ІІІ. Сonclusion
ІV. Bibliography
Слайд 3introduction
The potential of ICT as a development tool rests on
its ability to improve the way people do things. The
rapid changes and advancements in modern technology present a unique opportunity for developing countries to leapfrog intermediate steps in development while improving the quality and broadening the reach of public services.Слайд 6The strategic and effective use of ICT
The strategic and effective
use of ICT—combined with a reform-oriented mindset, necessary set of
skills, institutional structure and capacity, appropriate business models, as well as policy and regulatory environments—can facilitate fast and efficient delivery of public services in key sectors.Слайд 7ICT in Education
ICT can improve the efficiency and quality of
education at all levels. Part of ADB's strategy to support
itseducation policy principles is promoting "experimentation with, and dissemination of, innovative strategies and technologies in education." This involves developing appropriate e-applications to help DMCs leapfrog conventional means of learning and teaching.Слайд 9ICT in Public Sector Management
ADB encourages governments to adopt both
innovative approaches and modern technologies to promote good governance. This
is done not just by shifting from manual, paper-based processes to automated systems, but also by creating new skills, building human and institutional capacity, and creating an enabling policy and regulatory environment to facilitate public sector reforms.Слайд 11ICT in Health
ICT can be a powerful tool for improving
health and related services. ADB projects are helping to improve
dissemination of public health information, bridge the gap in consultation, diagnosis, and treatment between resource-rich and resource-poor hospitals, facilitate learning, enhance the ability to monitor diseases and other health issues, and make health administration more efficient.Слайд 13СONCLUSION
The paper discusses the foundations for establishing a viable and
sustainable Information and Communication Technology (ICT) industry and the opportunities
it offers against the challenges many African countries face in their concerted efforts to participate fully in the information society and knowledge economy. Key ICT Policy thrusts are discussed focusing on the ICT as a sector, egovernment, e-governance and the education and training sectors.Слайд 14Bibliography
Zimbabwe National ICT Policy – December 2005
Partnership Framework for ICT
Infrastructure development in Africa ‘S M Kundishora at World Congress
on ICT for Knowledge Society, Seoul, July 2006Information Kerala Mission – e-Governance with people at the centre
Afrosoft Corporation Limited