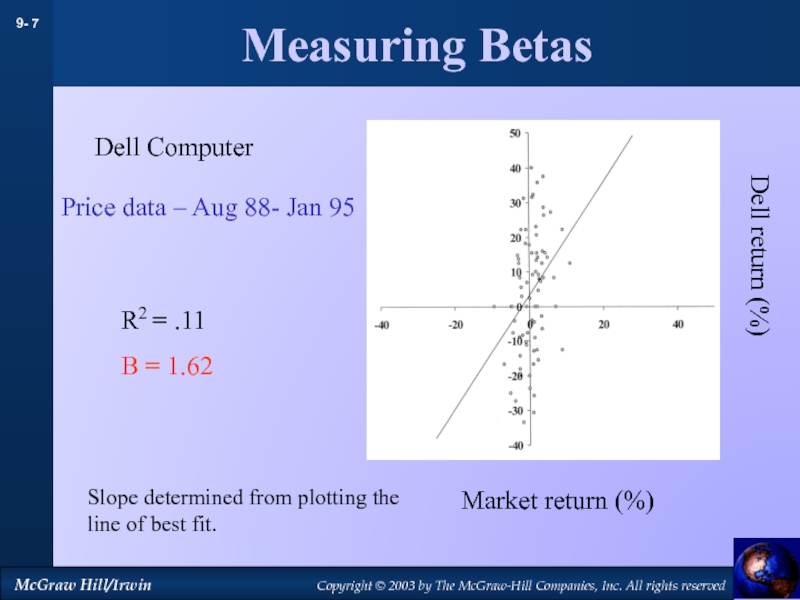
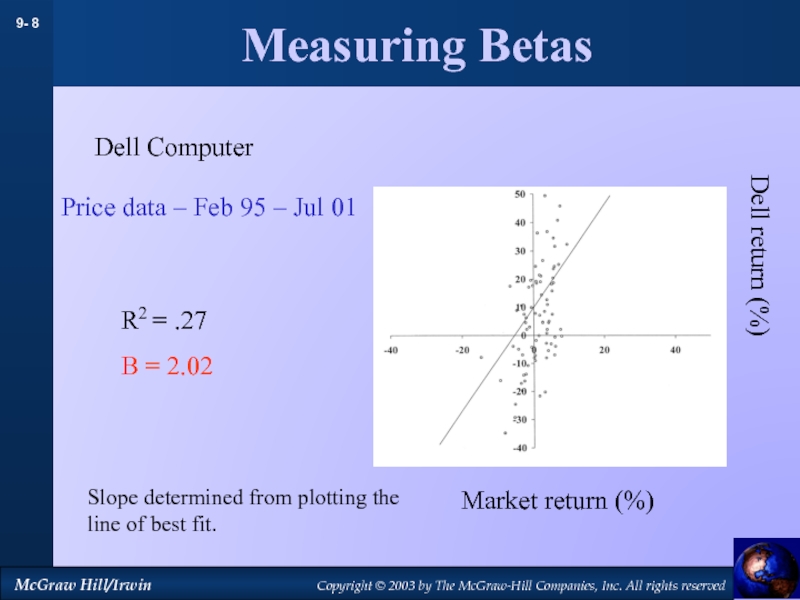
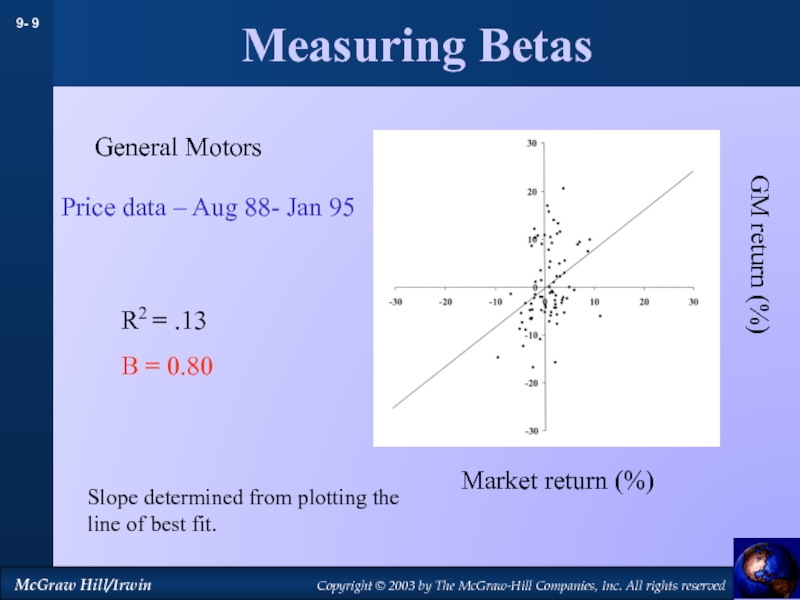
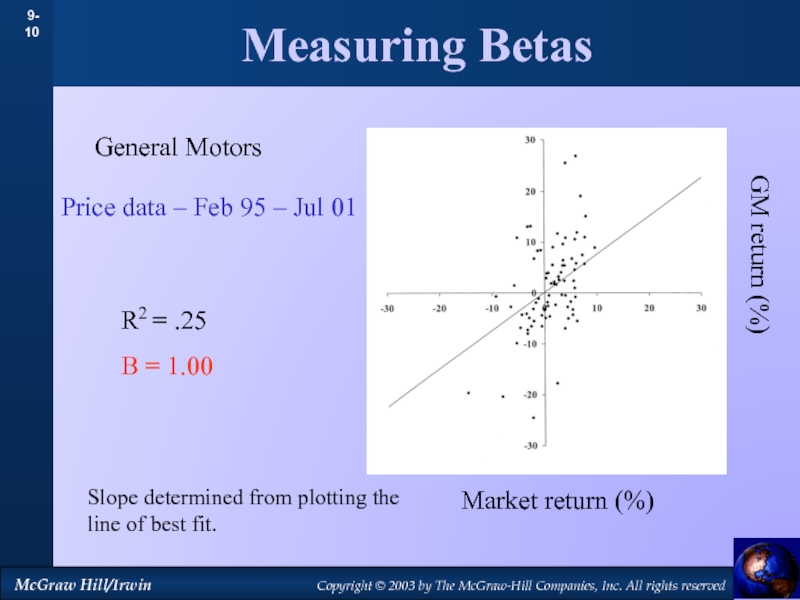
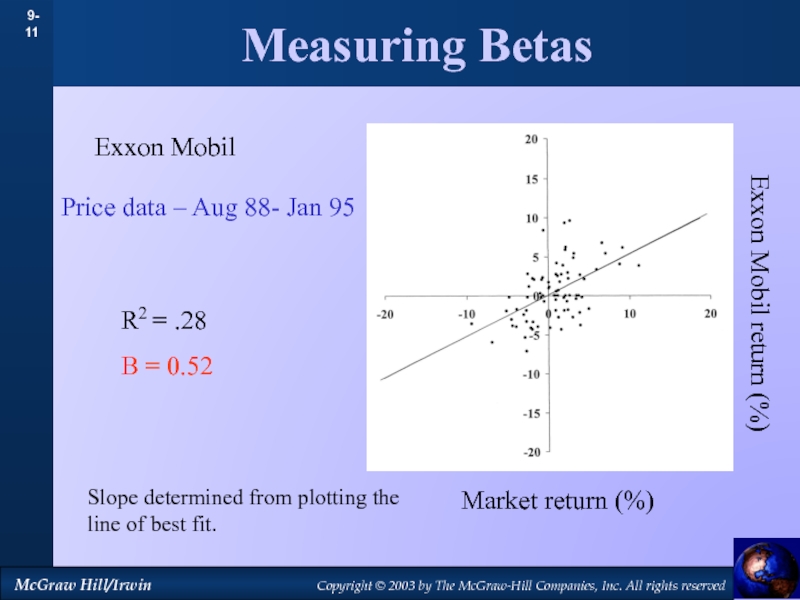
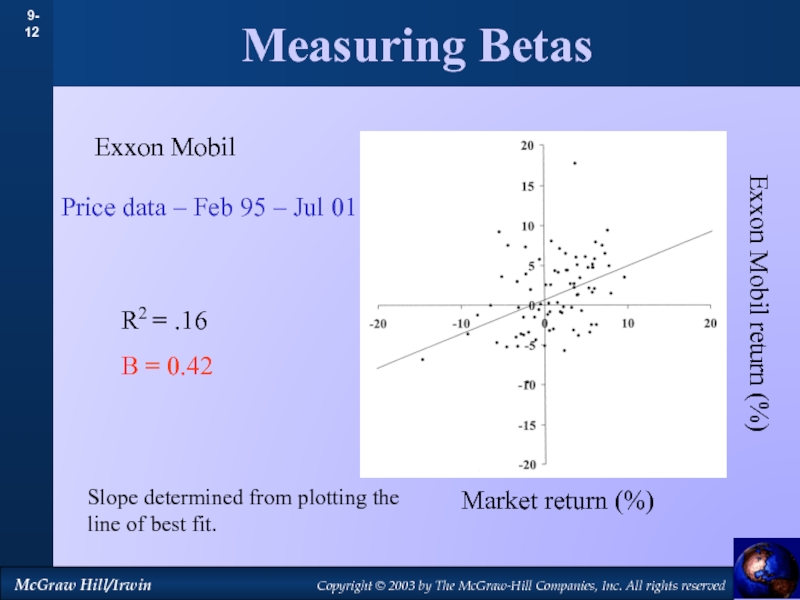
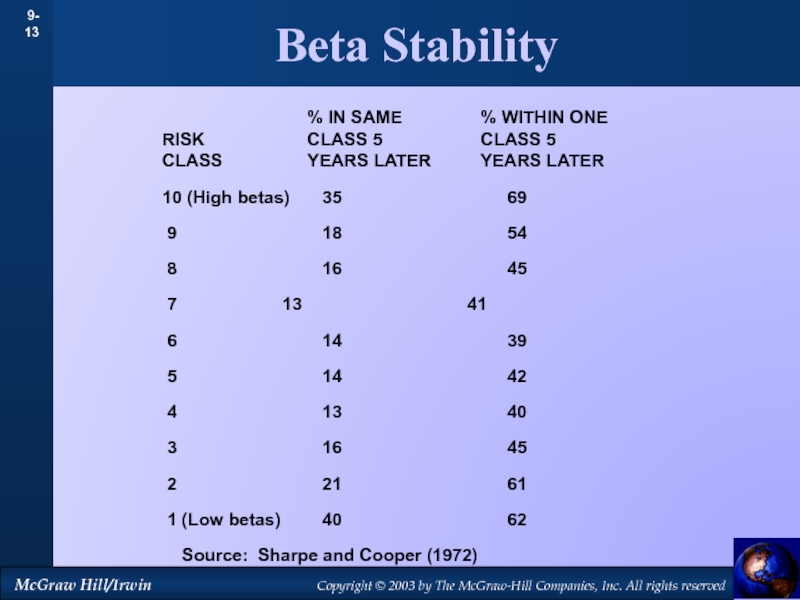
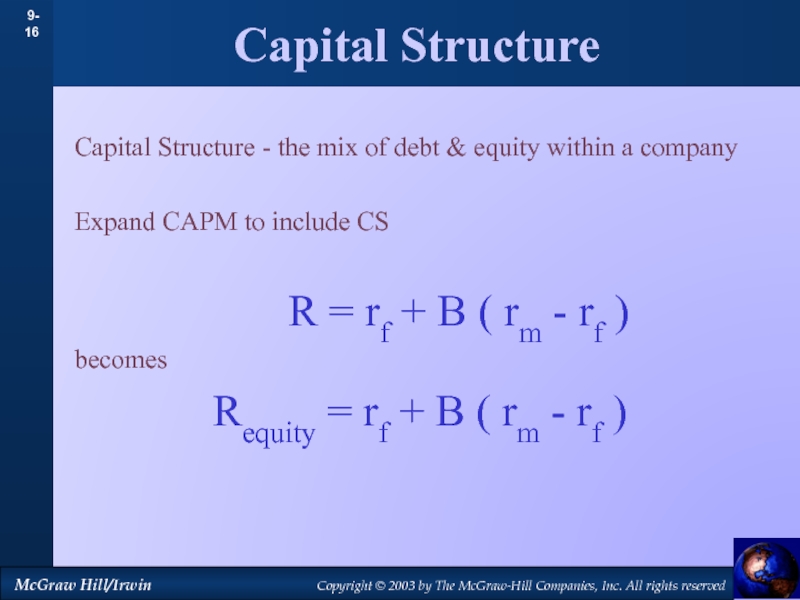
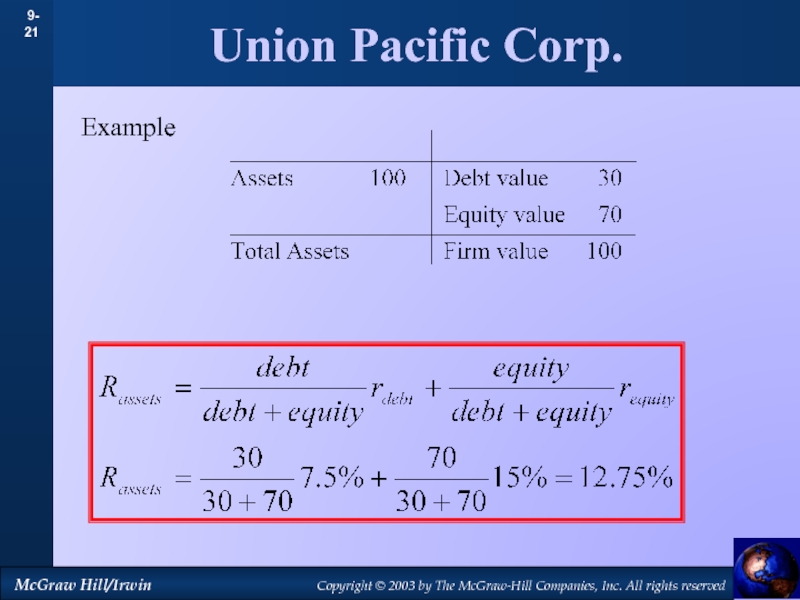
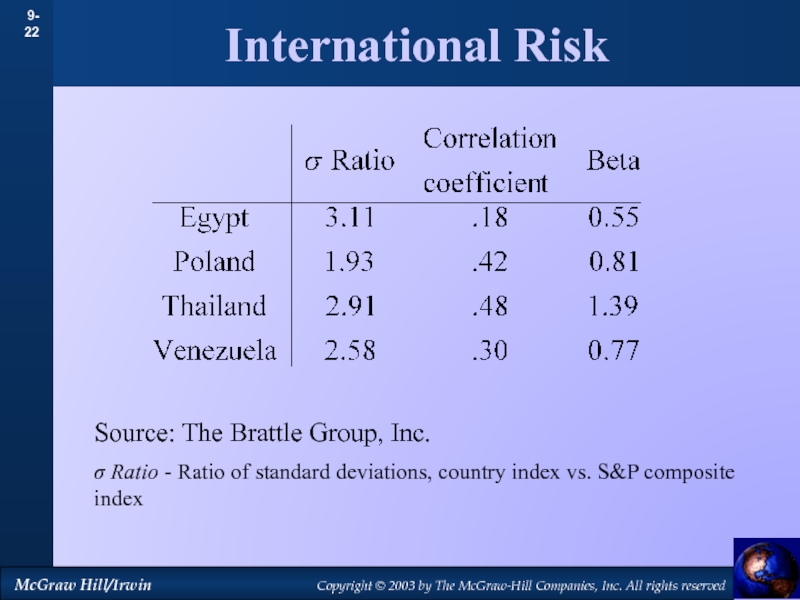
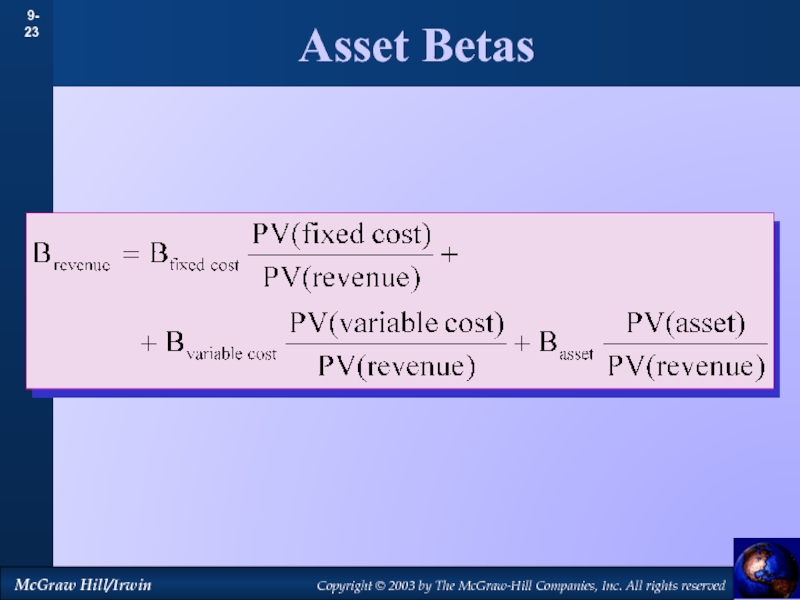
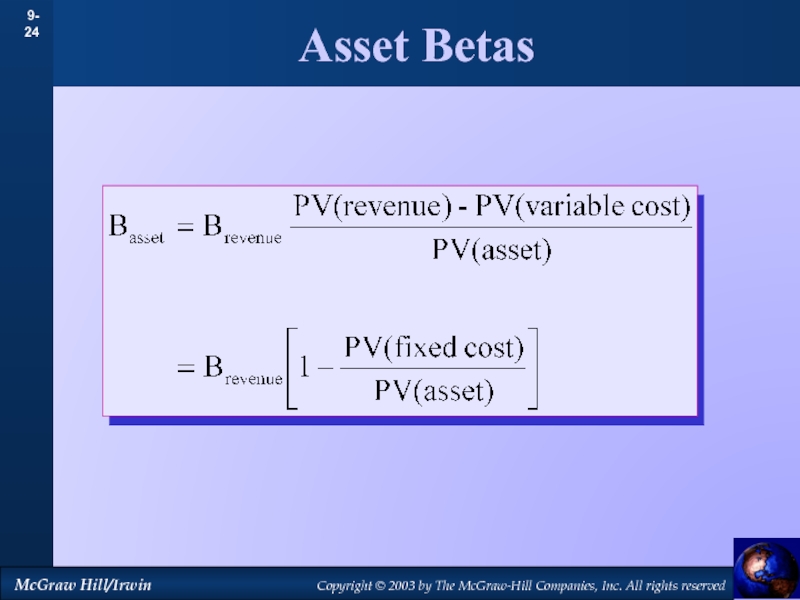
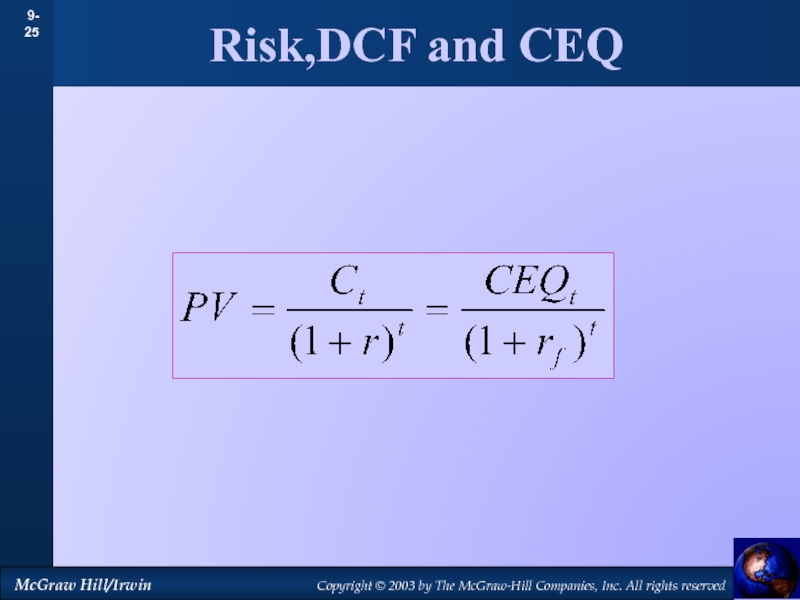
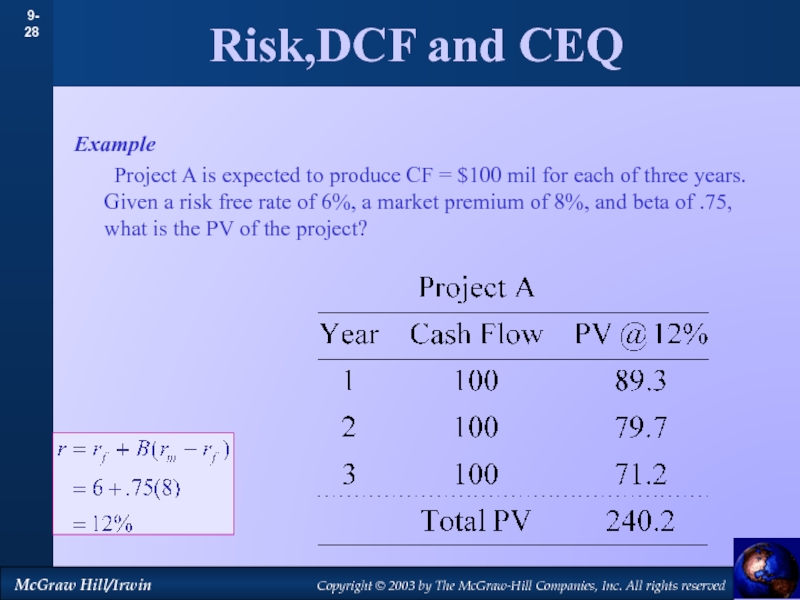
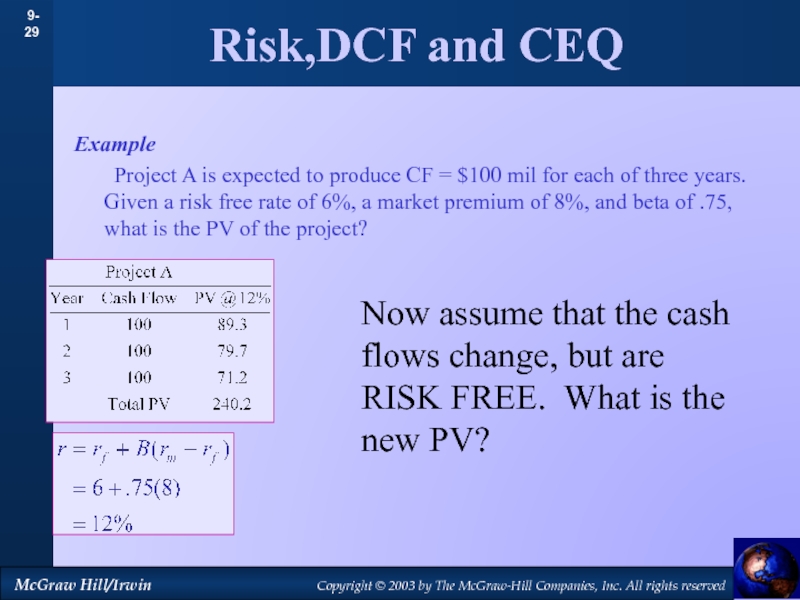
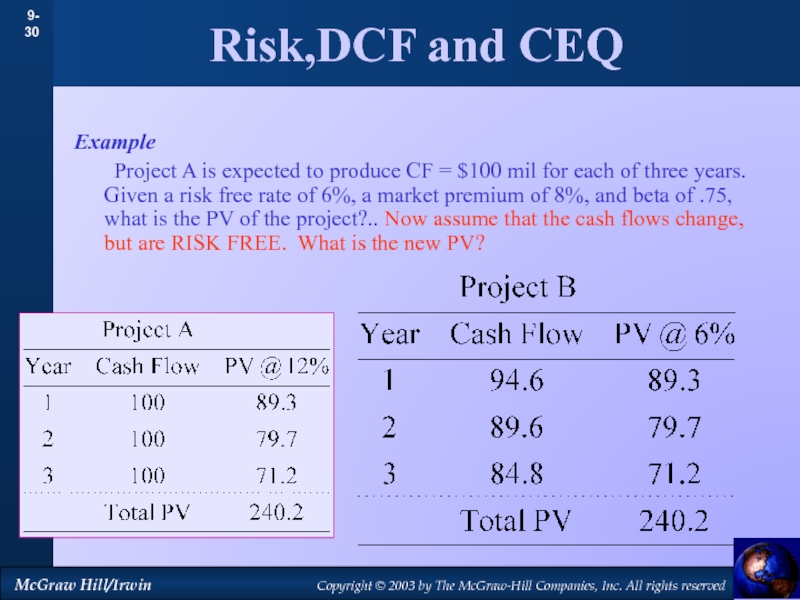
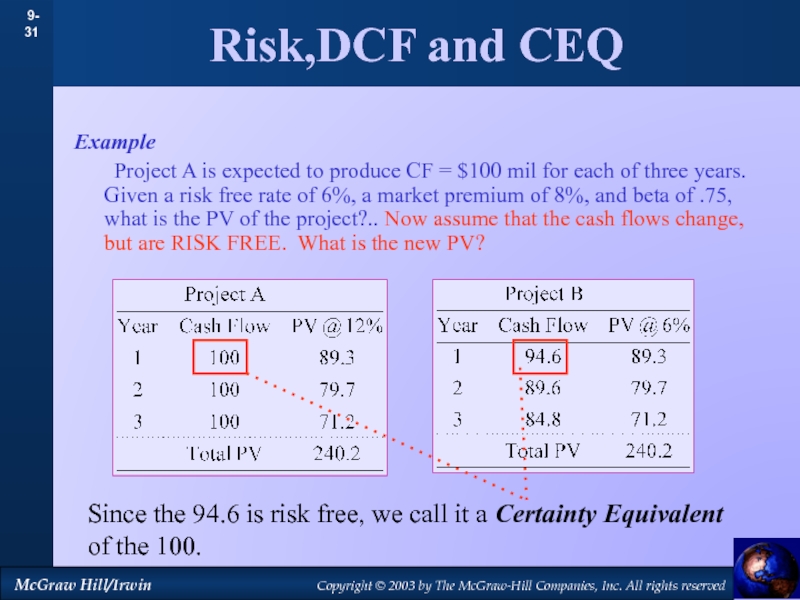
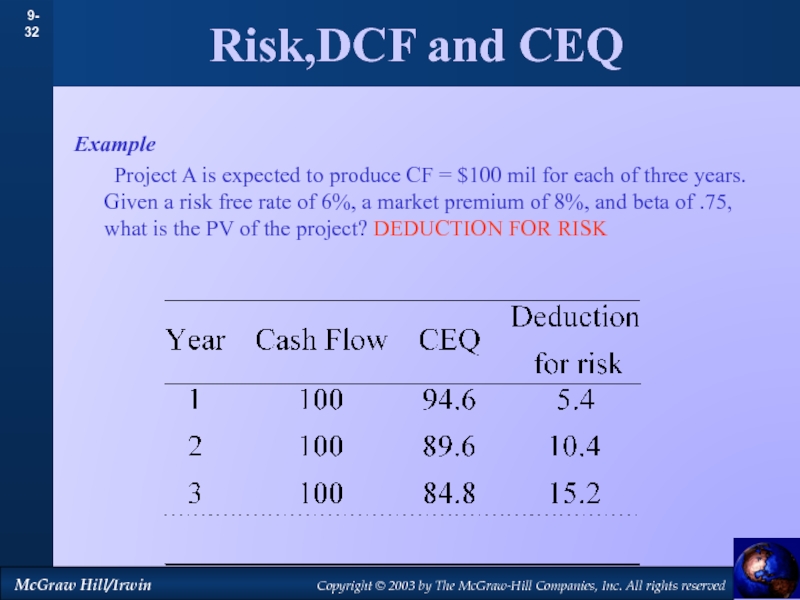
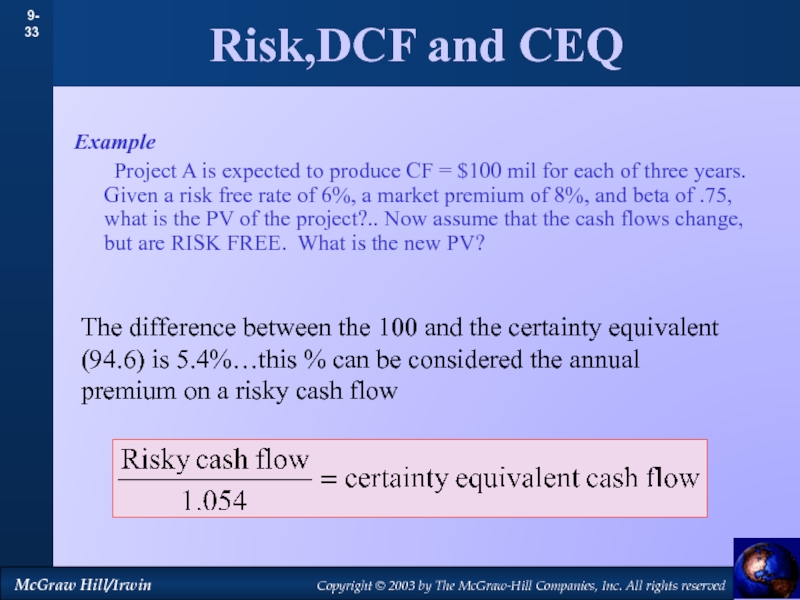
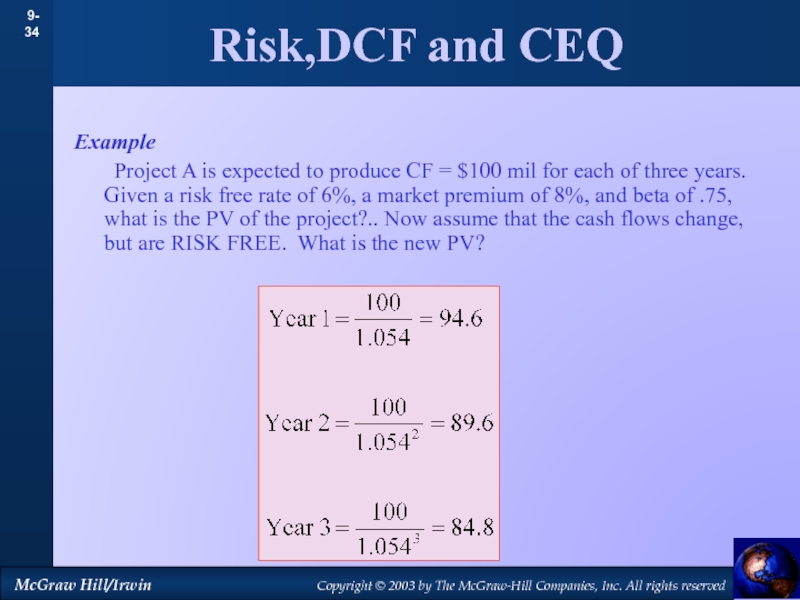
by
Matthew Will
Chapter 9
McGraw Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2003 by The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Inc. All rights reserved Capital Budgeting and Risk