Слайд 1PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT
Sayed Gheyasuddin “SAADAT”
sayedbba@gmail.com
01
Слайд 2A formal and coordinated group of people who function to
achieve particular goals
An organization consists of a group
of people striving
to reach goals
that individuals acting alone
could not achieve.
What is an Organization?
Слайд 3What is Management
Management is the process of achieving organizational goals
by engaging in the four major functions of planning, organizing,
leading, and controlling.
Management is the process of managing the organizational resources efficiently and effectively to achieve the organizational goals.
Слайд 4Important Terms
Process: On going activity, Continuation.
Goal: Purpose that an organization
strives to achieve; organizations often have more than one goal,
goals are fundamental elements of organization.
Efficiency: The ability to make the best use of the available resources in the process of achieving goals.
Effectiveness: The ability to choose appropriate goals and achieve them
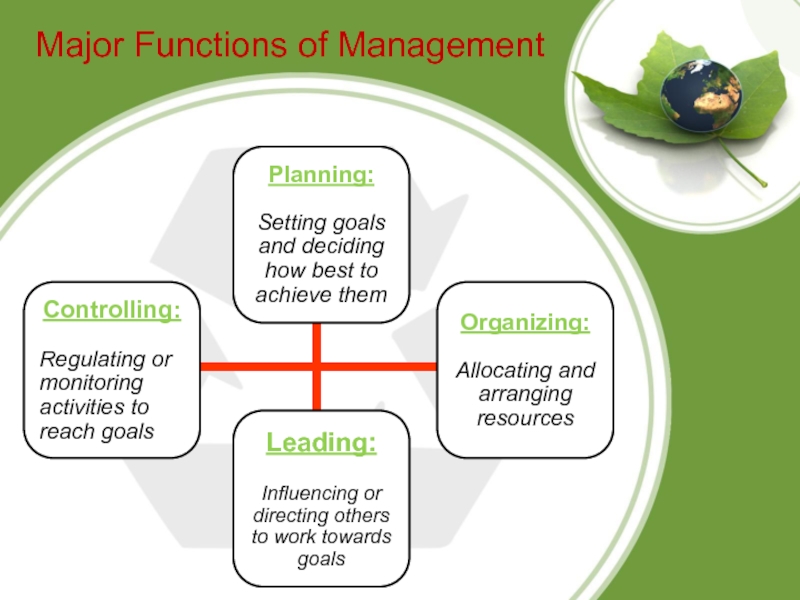
Слайд 5Major Functions of Management
Planning: The process of setting goals and
deciding how best to achieve them.
Organizing: The process of allocating
and arranging human and non-human resources so that plans can be carried out successfully.
Leading: The process of influencing others to engage in the work behaviors necessary to reach organizational goals.
Controlling: The process of regulating organizational activities so that actual performances conforms to expected organizational standards and goals.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Resources: The total means available to a company for increasing production or profit, including plant, labour, and raw material; assets.
Слайд 6Major Functions of Management
Слайд 7Who’s a Manager?
A Manager is a person who is managing
the resources of an organization in order to achieve organizational
goals.
An employee who is charged with making decisions, leading people, and delegating authority in order to accomplish the goals of the organization.
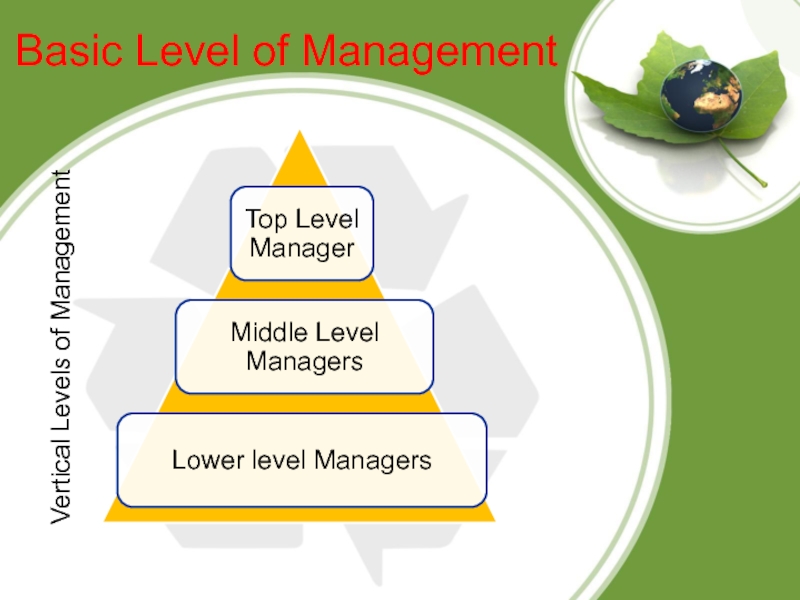
Слайд 8Basic Level of Management
Vertical Levels of Management
Слайд 9Top Level Managers
Top Level Managers are those who are at
the very top levels of the organizational hierarchy and who
are ultimately responsible for the entire organization.
They are few of them and typical titles include ‘Chief Executive Officer (CEO), General Manager’ etc.
They typically supervise overall organization planning, work with the middle managers in implementing the planning and maintain control over the organization’s progress
Слайд 10Middle Level Managers
Middle Level Managers include those Managers who are
at the Mid level of the organizational hierarchy. They are
below the top level managers and are directly responsible for the work of lower-level managers.
Middle Level Managers’ titles include “Director, Chief, Department Head, Division Head etc.”
They are mainly responsible for implementing overall organizational plans to achieve organizational goals.
Слайд 11Lower Level Managers
First Line Managers work at the lowest hierarchy
level and are directly responsible for the work of non-managerial
employees. Their titles often include the word “Supervisor”.
First-line managers are very important for the success of organization as they are responsible for smooth day-to-day operations in order to achieve those goals.
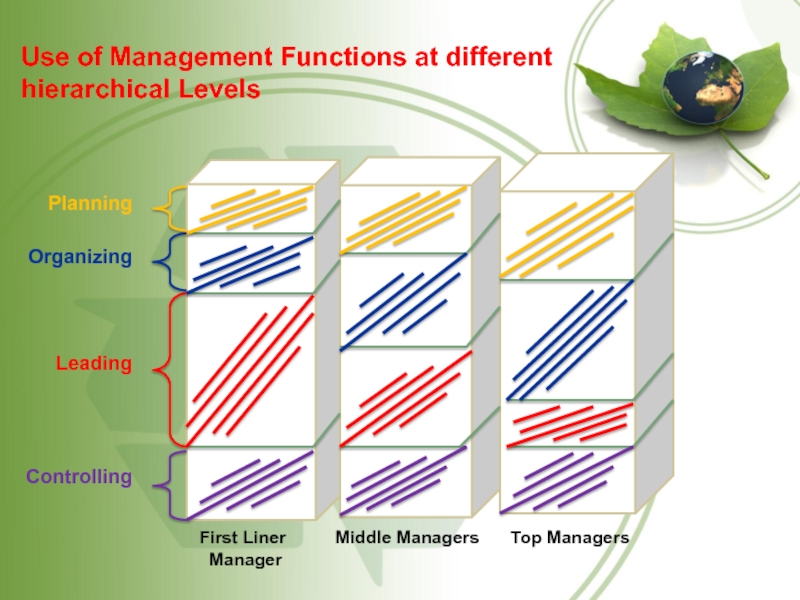
First Liner Middle Managers Top
Managers
Manager
Planning
Organizing
Leading
Controlling
Use of Management Functions at different hierarchical Levels
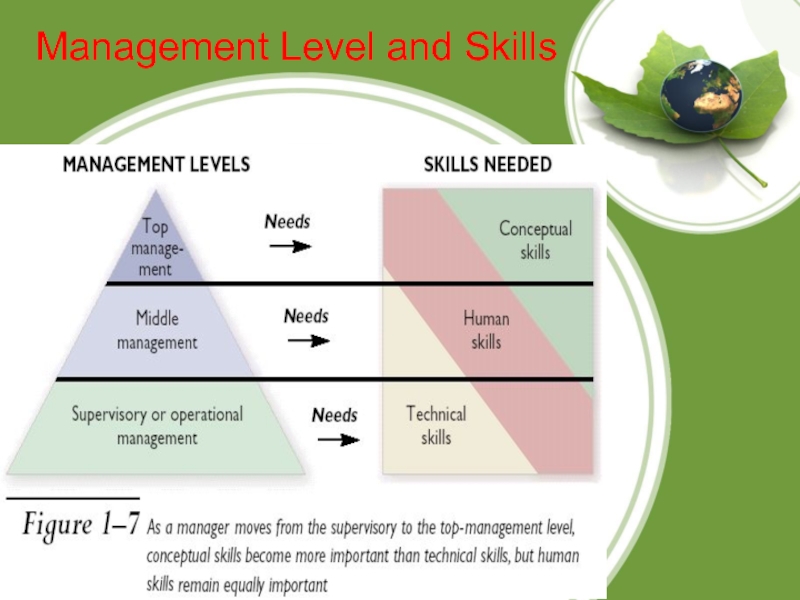
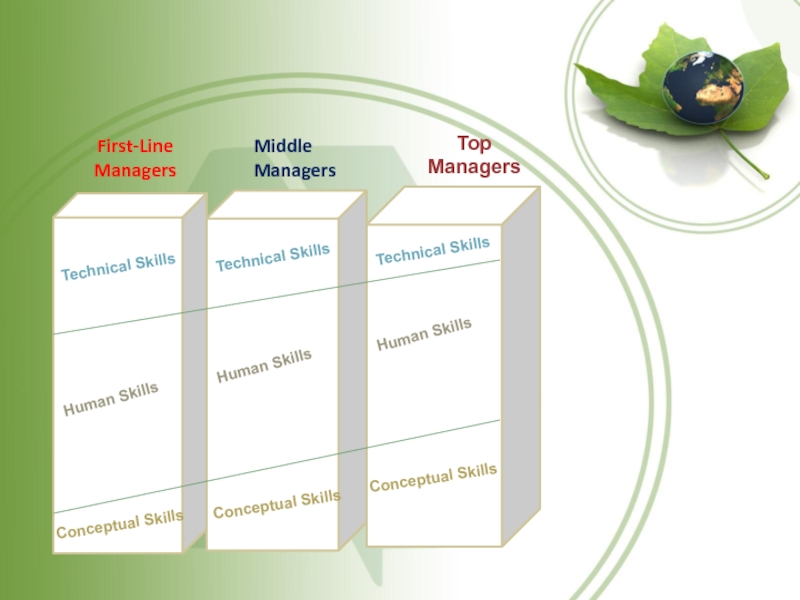
Слайд 14Conceptual Skills
Human Skills
First-Line
Managers
Middle
Managers
Top
Managers
Conceptual Skills
Conceptual Skills
Human Skills
Human Skills
Technical Skills
Technical Skills
Technical Skills
Слайд 15Key management skills
Not everyone can be a manager. Certain skills,
or abilities to translate knowledge into action that results in
desired performance are required to help other employees become more productive. These skills fall under the following categories:
Conceptual skills: Skills related to the ability to visualize the organization as a whole, discern, interrelationships among organizational parts, and understand how they organization fit into the wider context of the industry community and world.
Слайд 16Conceptual skills. Continued…
This skill calls for the ability to think
analytically.
Analytical skills enable managers to break down problems into
smaller parts, to see the relations among the parts, and to recognize the implications of any one problem for others.
As managers assume ever-higher responsibilities in organizations, they must deal with more ambiguous problems that have long-term consequences.
Again, managers may acquire these skills initially through formal education and then further develop them by training and job experience. The higher the management level, the more important conceptual skills becomes.
Слайд 17Human Skills: Skills associated with a manager’s ability to work
well with others, both as a member of group and
as a leader who gets things done through others.
This skill demonstrates the ability to work well in cooperation with others. Human skills emerge in the workplace as a spirit of trust, enthusiasm, and genuine involvement in interpersonal relationships.
Key management skills
Слайд 18Human Skills. Continued…
A manager with good human skills has a
high degree of self-awareness and a capacity to understand or
empathize with the feelings of others. Some managers are naturally born with great human skills, while others improve their skills through classes or experience. No matter how human skills are acquired, they're critical for all managers because of the highly interpersonal nature of managerial work.
Слайд 19
Technical Skills: Skills reflecting both an understanding of and proficiency
in a specialized field.
This skill requires the ability to use
a special proficiency or expertise to perform particular tasks. Accountants, engineers, market researchers, and computer scientists, as examples, possess technical skills.
Managers acquire these skills initially through formal education and then further develop them through training and job experience. Technical skills are most important at lower levels of management.
Key management skills
Слайд 20Functions of a Manager:
1. Planning: It is the basic function of
management. Planning is deciding in advance - what to do,
when to do & how to do. A plan is a future course of actions.
Planning is determination of courses of action to achieve desired goals. Thus, planning is a systematic thinking about ways & means for achievement of goals.
Planning is necessary to ensure proper utilization of human & non-human resources. It is all pervasive, it is an intellectual activity and it also helps in avoiding confusion, uncertainties, risks, wastages etc.
Planning deals with chalking out a future course of action & deciding in advance the most appropriate course of actions for achievement of goals.
Слайд 21 Example for a running organization, the organization's goal is to
improve company sales.
The manager first needs to decide which
steps are necessary to achieve that goal. These steps may include
increasing advertising,
inventory and Distribution,
Increase sales staff.
Training the current sales staff
These necessary steps are developed into a plan. When the plan is in place, the manager can follow it to accomplish the goal of improving company sales.
Planning… Continued…
Слайд 222. Organizing:
After a plan is made, a manager needs to
organize the organization according to his plan.
Organizing function of
a manager involves the following tasks:
Making department in the organization Hiring the staff for the organization acquiring the Resources for each department of the organization.
Слайд 23
Leading:
A manager needs to do more than just plan,
organize, and staff his team to achieve a goal. He
or She must also Lead.
Leading involves motivating the employees of the organization by communicating with them, guiding them and encouraging them. It requires the manager to coach, assist, and solve problems with employees.
Controlling:
After the other elements are in place, a manager's job is not finished. He needs to continuously check results against the goals and take any corrective actions necessary to make sure that his plans remain on track.
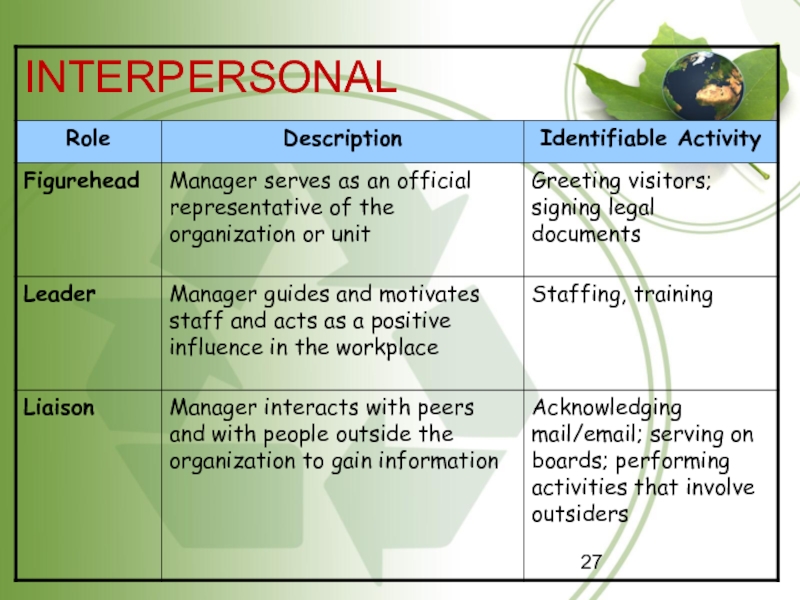
Слайд 25Mintzberg’s Managerial Roles
A role is a set of behaviours associated
with a particular job or position.
Henry Mintzberg studied CEOs at
work and created a scheme to define what managers do on the job. These are commonly referred to as Mintzberg’s Managerial Roles.
These can be grouped into three primary headings: Interpersonal, Informational and Decisional
Слайд 26Interpersonal roles grow directly from a manager’s position authority and
involve development and maintaining positive relationships with significant others.
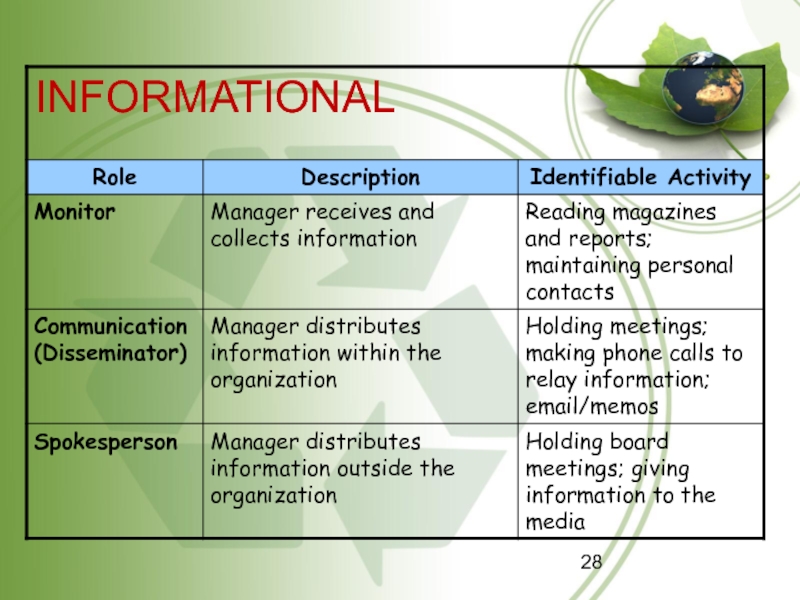
Informational
roles relate to the receiving and transmitting information so managers can serve as their organizational units’ nerve centers.
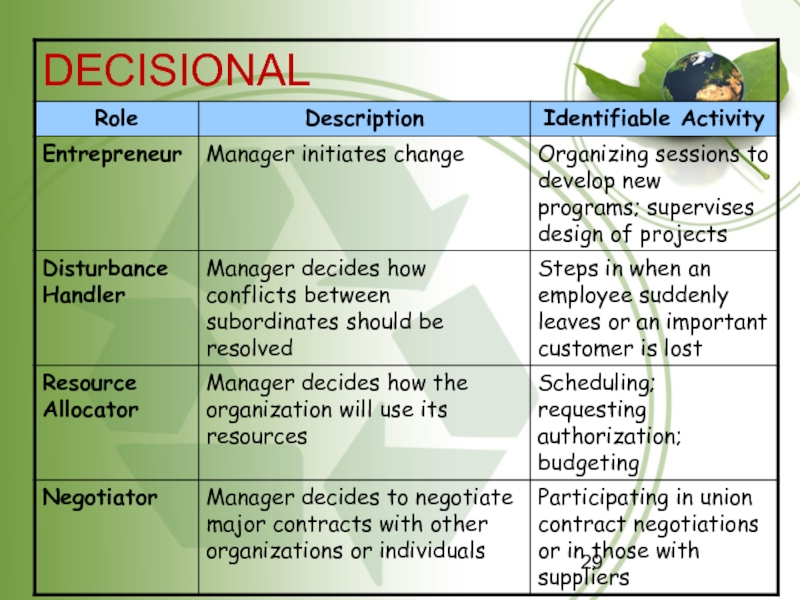
Decisional roles involve making significant decisions affecting the organization.
Mintzberg’s Managerial Roles
Слайд 30Horizontal Dimension: Responsibility Areas
Functional Managers
Specific, technical focus
General Managers
Broad, whole of
organisation/unit responsibilities
Project Managers
Integrative, team focus
Слайд 31Functional Managers
Managers with responsibility for a specific, specialized area of
the organization who supervise mainly individuals with expertise and training
in that area.
Слайд 32General Managers
Managers with responsibility for a whole organization or a
substantial subunit including most of the common specialized areas.
Слайд 33Project Managers
Managers with responsibility for coordinating efforts involving individuals in
several different organizational units all working on a particular project