Слайд 1Section 4
Regulation of the Respiration
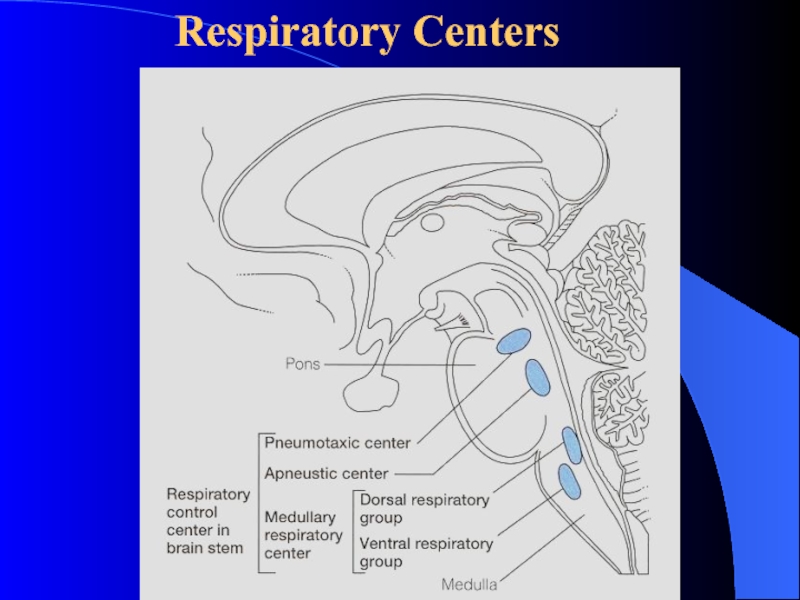
Слайд 2Respiratory Center and Formation of the Respiratory Rhythm
1 Respiratory Center
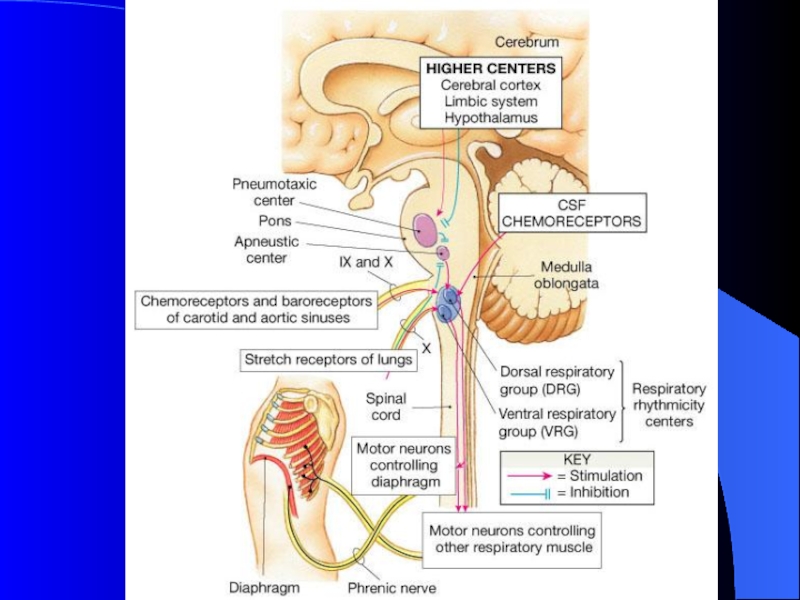
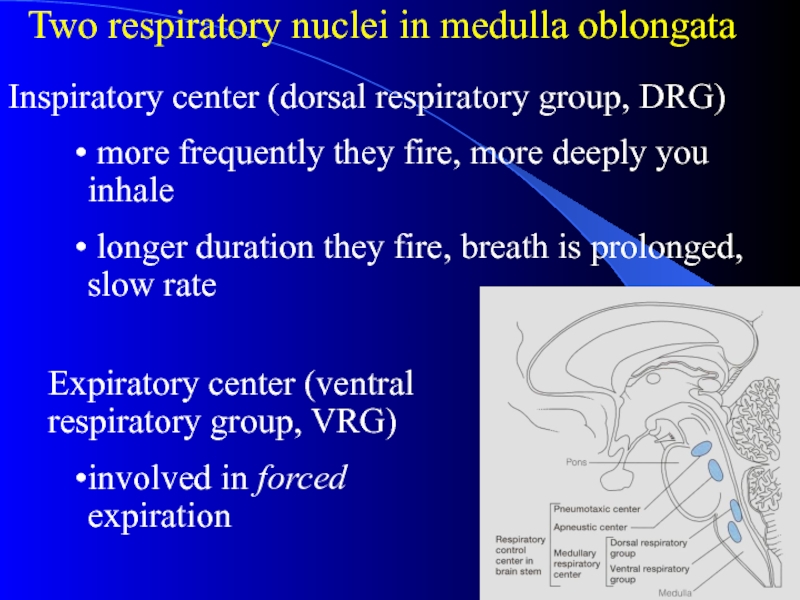
Слайд 6Two respiratory nuclei in medulla oblongata
Expiratory center (ventral respiratory group,
VRG)
involved in forced expiration
Inspiratory center (dorsal respiratory group, DRG)
more
frequently they fire, more deeply you inhale
longer duration they fire, breath is prolonged, slow rate
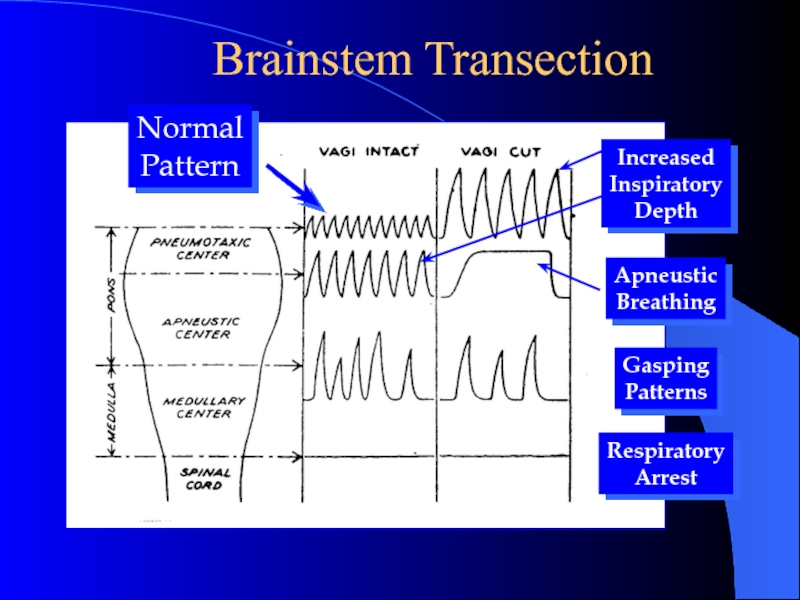
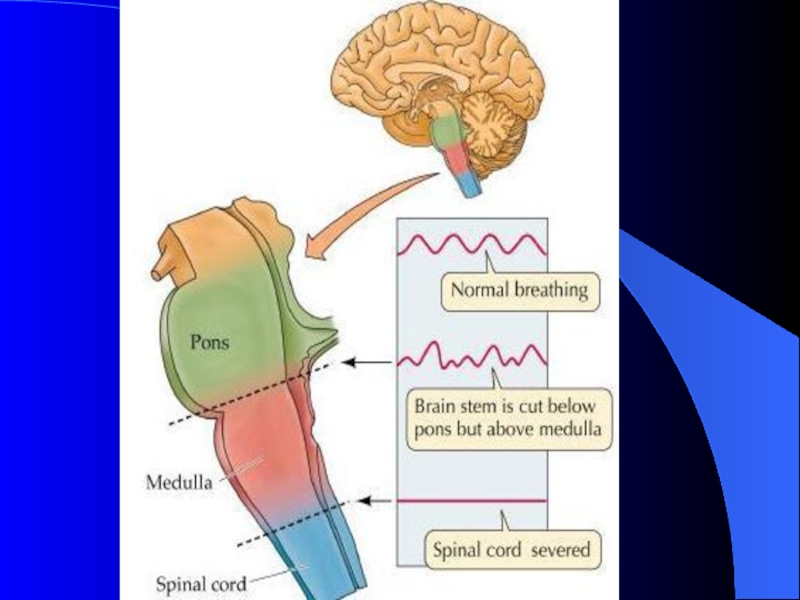
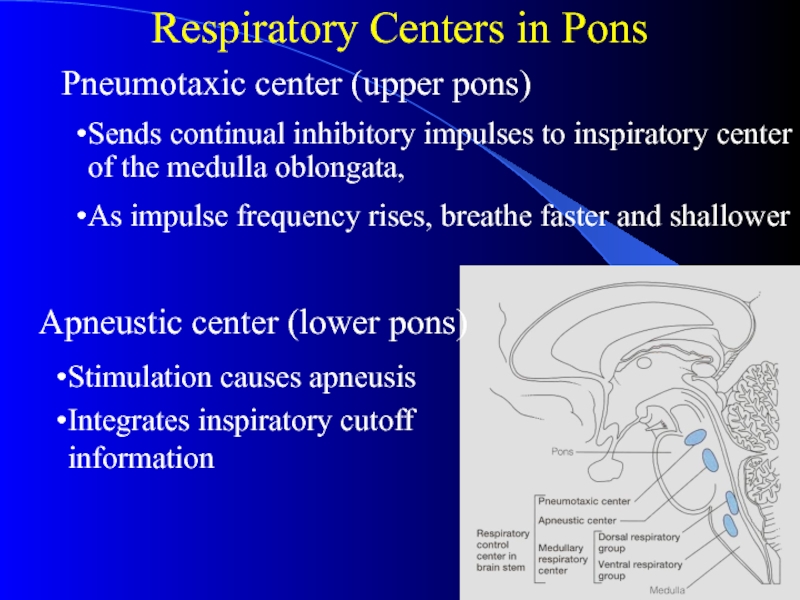
Слайд 7Respiratory Centers in Pons
Apneustic center (lower pons)
Sends continual
inhibitory impulses to inspiratory center of the medulla oblongata,
As
impulse frequency rises, breathe faster and shallower
Stimulation causes apneusis
Integrates inspiratory cutoff information
Pneumotaxic center (upper pons)
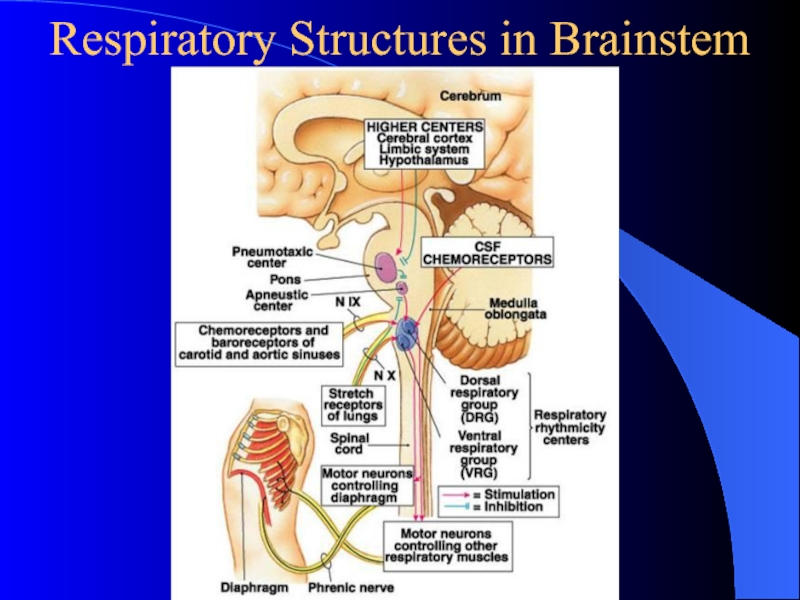
Слайд 8Respiratory Structures in Brainstem
Слайд 92. Rhythmic Ventilation (Inspiratory Off Switch)
Starting inspiration
Medullary respiratory center neurons
are continuously active (spontaneous)
Center receives stimulation from receptors and brain
concerned with voluntary respiratory movements and emotion
Combined input from all sources causes action potentials to stimulate respiratory muscles
Слайд 10Increasing inspiration
More and more neurons are activated
Stopping inspiration
Neurons receive input
from pontine group and stretch receptors in lungs.
Inhibitory neurons
activated and relaxation of respiratory muscles results in expiration.
Inspiratory off swithch.
Слайд 113. Higher Respiratory Centers
Modulate the activity of the more primitive
controlling centers in the medulla and pons.
Allow the rate
and depth of respiration to be controlled voluntarily.
During speaking, laughing, crying, eating, defecating, coughing, and sneezing. ….
Adaptations to changes in environmental temperature --Panting
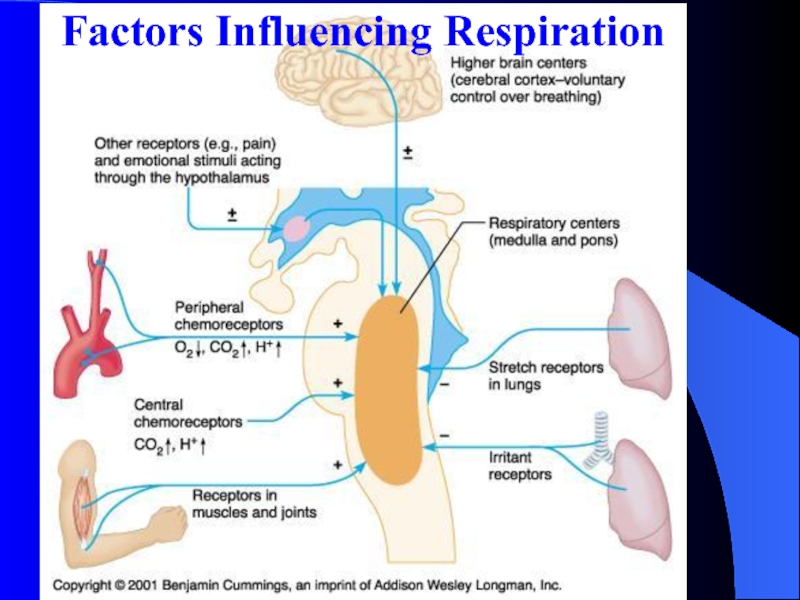
Слайд 12II Pulmonary Reflex
Chemoreceptor Reflex
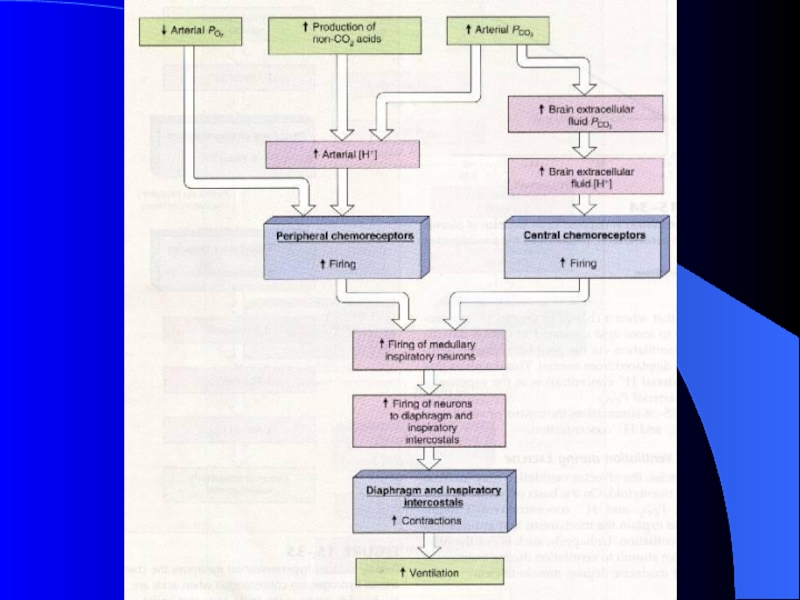
Слайд 13Two Sets of Chemoreceptors Exist
Central Chemoreceptors
Responsive to increased arterial PCO2
Act by way of CSF [H+] .
Peripheral Chemoreceptors
Responsive to decreased
arterial PO2
Responsive to increased arterial PCO2
Responsive to increased H+ ion concentration.
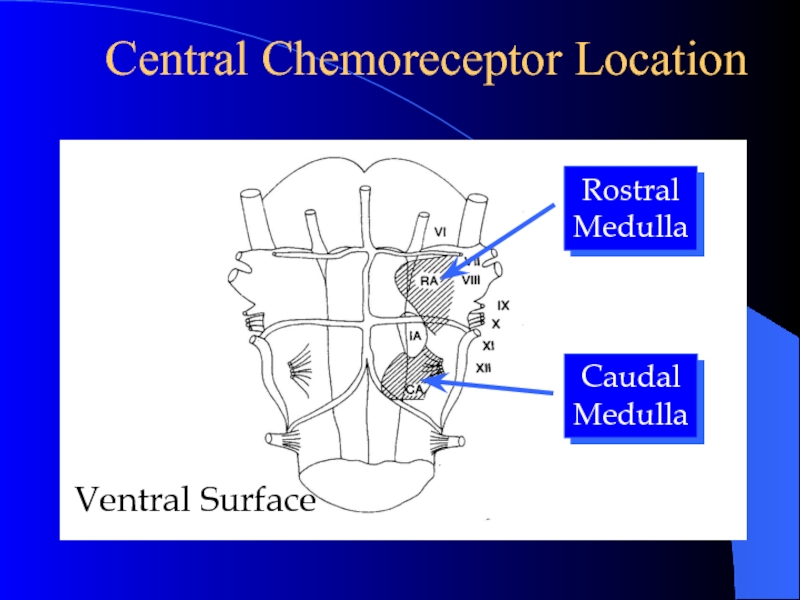
Слайд 14Central Chemoreceptor Location
Rostral
Medulla
Caudal
Medulla
Ventral Surface
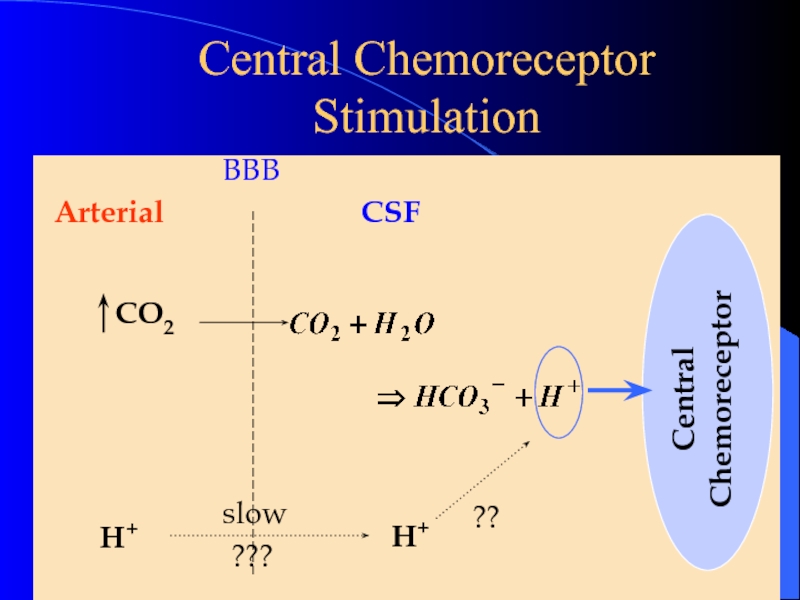
Слайд 15Central Chemoreceptor Stimulation
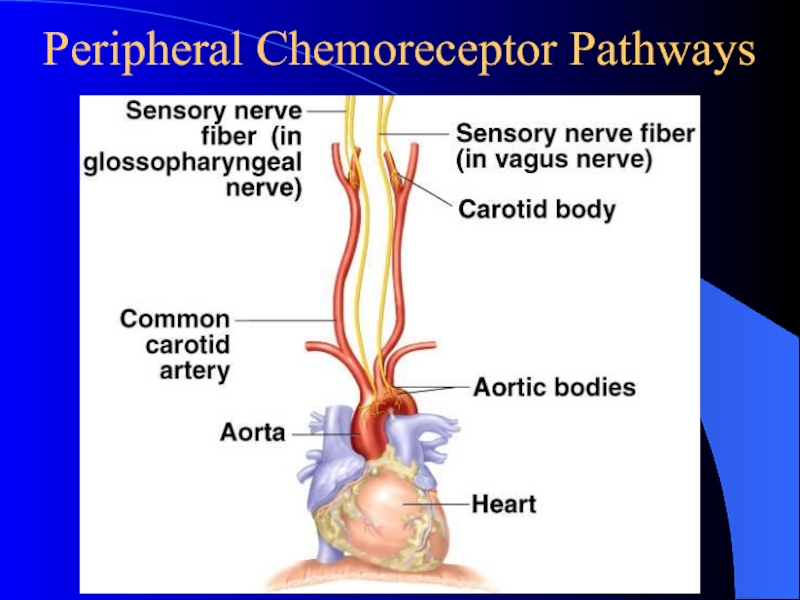
Слайд 16Peripheral Chemoreceptor Pathways
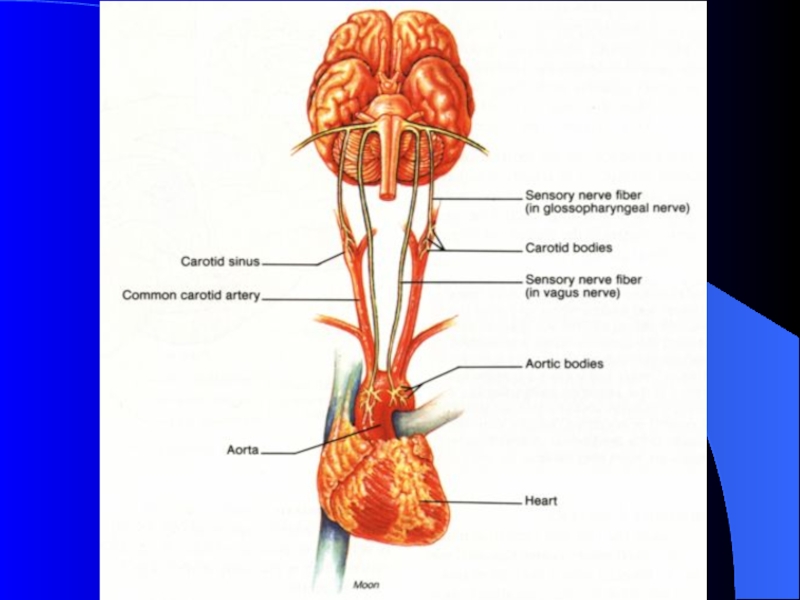
Слайд 17Peripheral Chemoreceptors
Carotid bodies
Sensitive to: PaO2, PaCO2, and pH
Afferents in glossopharyngeal
nerve.
Aortic bodies
Sensitive to: PaO2, PaCO2, but not pH
Afferents in vagus
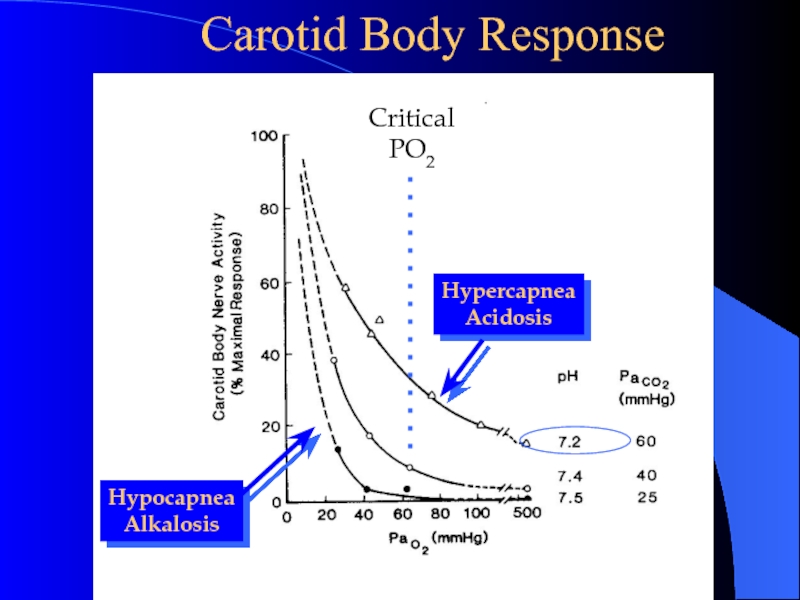
Слайд 19Carotid Body Function
High flow per unit weight:
(2 L/min/100 g)
High
carotid body VO2 consumption:
(8 ml O2/min/100g)
Tiny a-v O2 difference:
Receptor cells see arterial PO2.
Responsiveness begins at PaO2 (not the oxygen content) below about 60 mmHg.
Слайд 20 Carotid Body Response
Critical
PO2
Hypercapnea
Acidosis
Hypocapnea
Alkalosis
Слайд 21
Carbon Dioxide, Oxygen and pH Influence Ventilation (through peripheral receptor)
Peripheral
chemoreceptorssensitive to PO2, PCO2 and pH
Receptors are activated by increase
in PCO2 or decrease in PO2 and pH
Send APs through sensory neurons to the brain
Sensory info is integrated within the medulla
Respiratory centers respond by sending efferent signals through somatic motor neurons to the skeletal muscles
Ventilation is increased (decreased)
Слайд 22Effects of Hydrogen Ions (through central chemoreceptors)
pH of CSF (most
powerful respiratory stimulus)
Respiratory acidosis (pH < 7.35) caused by failure
of pulmonary ventilation
hypercapnia (PCO2) > 43 mmHg
CO2 easily crosses blood-brain barrier, in CSF the CO2 reacts with water and releases H+, central chemoreceptors strongly stimulate inspiratory center
corrected by hyperventilation, pushes reaction to the left by “blowing off ” CO2
CO2 (expired) + H2O H2CO3 HCO3- + H+
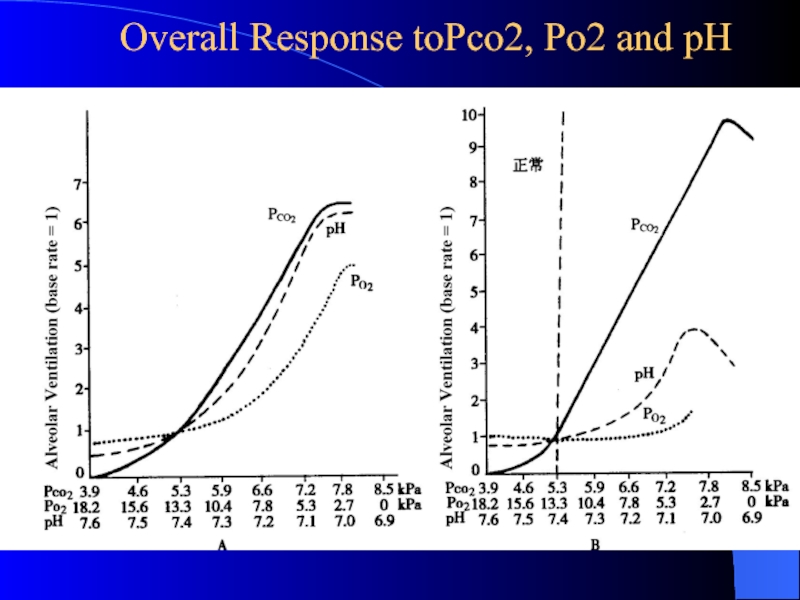
Слайд 23Carbon Dioxide
Indirect effects
through pH as seen previously
Direct effects
CO2
may directly stimulate peripheral chemoreceptors and trigger ventilation more
quickly than central chemoreceptors
If the PCO2 is too high, the respiratory center will be inhibited.
Слайд 24Oxygen
Direct inhibitory effect of hypoxemia on the respiratory center
Chronic hypoxemia,
PO2 < 60 mmHg, can significantly stimulate ventilation
emphysema, pneumonia
high altitudes
after several days
Слайд 25 Overall Response toPco2, Po2 and pH
Слайд 28Hering-Breuer Reflex or Pulmonary Stretch Reflex
Including pulmonary inflation reflex and
pulmonary deflation reflex
Receptor: Slowly adapting stretch receptors (SARs) in bronchial
airways.
Afferent: vagus nerve
Pulmonary inflation reflex:
Terminate inspiration.
By speeding inspiratory termination they increase respiratory frequency.
Sustained stimulation of SARs: causes activation of expiratory neurons
Слайд 30Significance of Hering-Breuer
Normal adults. Receptors are not activated at end
normal tidal volumes.
Become Important during exercise when tidal volume is
increased.
Become Important in Chronic obstructive lung diseases when lungs are more distended.
Infants. Probably help terminate normal inspiration.






![Section 4
Regulation of the Respiration Two Sets of Chemoreceptors ExistCentral ChemoreceptorsResponsive to increased arterial PCO2 Act Two Sets of Chemoreceptors ExistCentral ChemoreceptorsResponsive to increased arterial PCO2 Act by way of CSF [H+] .Peripheral](/img/thumbs/d9449fcea6d50d8447060a012793198a-800x.jpg)