Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Sensory testing of food products
Содержание
- 1. Sensory testing of food products
- 2. PLANSensory analysisSensory analysis of food productsSensory Testing
- 3. I. Sensory analysisOVERVIEWA consumer's direct sensory experience
- 4. I. Sensory analysisDefinitionUtilizing both expert analysis and
- 5. I. Sensory analysisBenefitsIndustry knowledge, analytical expertise and
- 6. I. Sensory analysisShelf-life and Stability Studies UL
- 7. I. Sensory analysisProduct Cuttings UL’s product cutting
- 8. II. Sensory analysis of food productsConsumer tastes,
- 9. II. Sensory analysis of food productsSensory analysis
- 10. II. Sensory analysis of food productsConsumer research
- 11. II. Sensory analysis of food productsAbout the
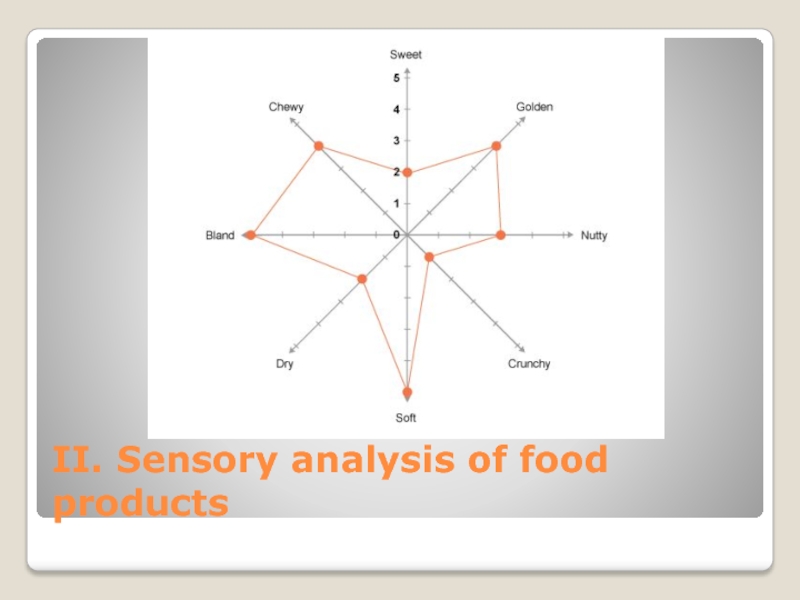
- 12. II. Sensory analysis of food products
- 13. III. Sensory TestingSensory analysis (or sensory evaluation) is a scientific discipline
- 14. III. Sensory TestingEffective testingThis type of testing
- 15. III. Sensory TestingEffective testingThere are several types
- 16. III. Sensory TestingAffective testingAlso known as consumer testing,
- 17. III. Sensory TestingPerceptionPerception involves the biochemical and psychological theories relating to human
- 18. III. Sensory TestingPerception In dealing with the fact
- 19. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 4I. Sensory analysis
Definition
Utilizing both expert analysis and consumer feedback, UL's
sensory testing services help companies evaluate whether their products meet
consumers' preferred sensory characteristics. Our customers gain a detailed view of consumers' responses to a tested product and a deeper understanding of that product's prospective competitive value.Слайд 5I. Sensory analysis
Benefits
Industry knowledge, analytical expertise and technical skill come
together in UL’s state-of-the-art facilities to evaluate how tested products
will influence consumer purchase decisions and build brand loyalty.Trained Descriptive Panels
Our customers’ products are evaluated by panels of people who are experienced in sensory science. UL uses an established framework during testing in order to help ensure standardized responses across product lines and quantitative result data.
Слайд 6I. Sensory analysis
Shelf-life and Stability Studies
UL evaluates a product’s sensory
appeal over a period of time in order to determine
the appropriate messaging on product packaging.Degree of Difference Testing
Our tests help customers know whether appreciable differences occur between test and control products, and help establish a product’s intrinsic variability rate due to variances in production time, component sourcing and other circumstances.
Слайд 7I. Sensory analysis
Product Cuttings
UL’s product cutting tests help assess general
product quality, competitive value and consumer acceptance.
Claim Substantiation and Product
Optimization
UL’s testing and analysis help customers verify their advertising, packaging and marketing claims and assist in their efforts to maximize consumer satisfaction potential.
On-site Sensory Testing and Product Evaluations
UL can help customers create in-house programs using accepted sensory testing methods in order to evaluate specific product attributes.
Слайд 8II. Sensory analysis of food products
Consumer tastes, preferences and buying
behaviours are changing constantly. Researchers at the Health and Food
Sciences Precinct can help your business:understand your target market characteristics
define products and their acceptability
test product concepts
understand product quality issues.
Слайд 9II. Sensory analysis of food products
Sensory analysis for food and
beverage products
Sensory analysis can reveal how consumers perceive the appearance,
aroma, taste and texture of your product. Testing includes:difference testing to understand if new product formulations differ in taste and texture from old ones
shelf-life trials (in combination with microbial count testing)
acceptability testing to understand if a product suits consumer palates
flavour profiling to identify consumer preferences for product
fault detection to identify undesirable flavours.
Слайд 10II. Sensory analysis of food products
Consumer research for food and
beverage products
Consumer research gives you information about potential customers. We
use focus groups, surveys, experimental auctions, at-home trials and novel interview methods to understand how consumers think and feel about food and beverage products.Some of the ways our methods have helped business and industry include:
product concept and prototype testing
domestic and export market consumer profiles
customer motivation and how this can shape marketing strategies
demand, purchase intent and consumer willingness to pay
consumer threshold for defects.
Слайд 11II. Sensory analysis of food products
About the facilities
The food science
laboratory has been purpose-built and includes:
computerised sensory booths
access to a
trained taste panelfocus group room with audio and visual recording, and viewing window
commercial kitchen and cold storage.
Слайд 13III. Sensory Testing
Sensory analysis (or sensory evaluation) is a scientific discipline that applies principles
of experimental design and statistical analysis to the use of human senses (sight, smell, taste, touch and hearing) for the purposes
of evaluating consumer products. The discipline requires panels of human assessors, on whom the products are tested, and recording the responses made by them. By applying statistical techniques to the results it is possible to make inferences and insights about the products under test. Most large consumer goods companies have departments dedicated to sensory analysis. Sensory analysis can mainly be broken down into three sub-sections:Effective testing (dealing with objective facts about products)
Affective testing (dealing with subjective facts such as preferences)
Perception (the biochemical and psychological aspects of sensation)
Слайд 14III. Sensory Testing
Effective testing
This type of testing is concerned with
obtaining objective facts about products. This could range from basic discrimination testing (e.g. Do
two or more products differ from each other?) to descriptive profiling (e.g. What are the characteristics of two or more products?). The type of panel required for this type of testing would normally be a trained panel.Слайд 15III. Sensory Testing
Effective testing
There are several types of sensory tests.
The most classic is the sensory profile. In this test,
each taster describes each product by means of a questionnaire. The questionnaire includes a list of descriptors (e.g., bitterness, acidity, etc.). The taster rates each descriptor for each product depending on the intensity of the descriptor he perceives in the product (e.g., 0 = very weak to 10 = very strong). In the method of Free choice profiling, each taster builds his own questionnaire.Another family of methods is known as holistic as they are focused on the overall appearance of the product. This is the case of the categorization and the napping.