Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Solution Methods for Bilevel Optimization
Содержание
- 1. Solution Methods for Bilevel Optimization
- 2. OverviewDefinition and general form of a bilevel
- 3. Stackelberg Game (Bilevel problem)Players: the Leader and
- 4. ExampleTaxation of a factoryLeader – governmentObjectives: maximize profit and minimize pollutionFollower – factory ownerObjectives: maximize profit
- 5. General structure of a Bilevel problem
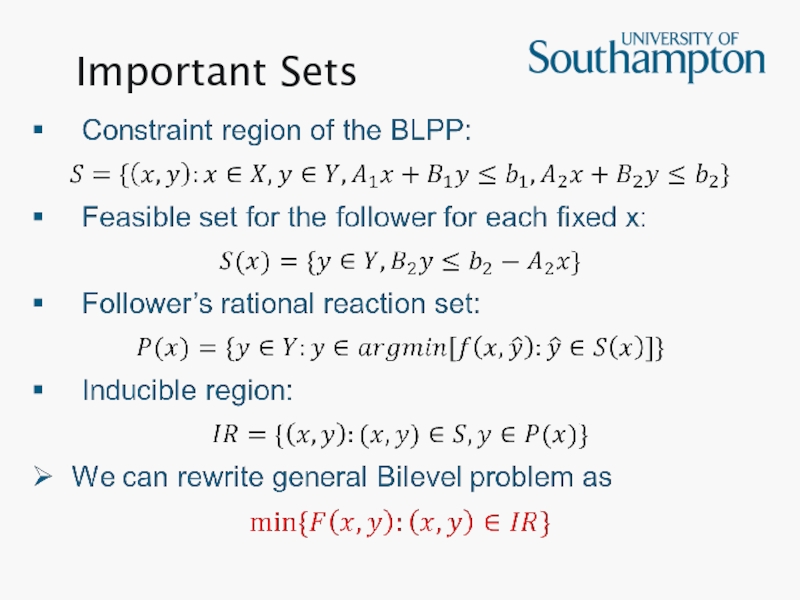
- 6. Important Sets
- 7. Solution methodsVertex enumeration in the context of
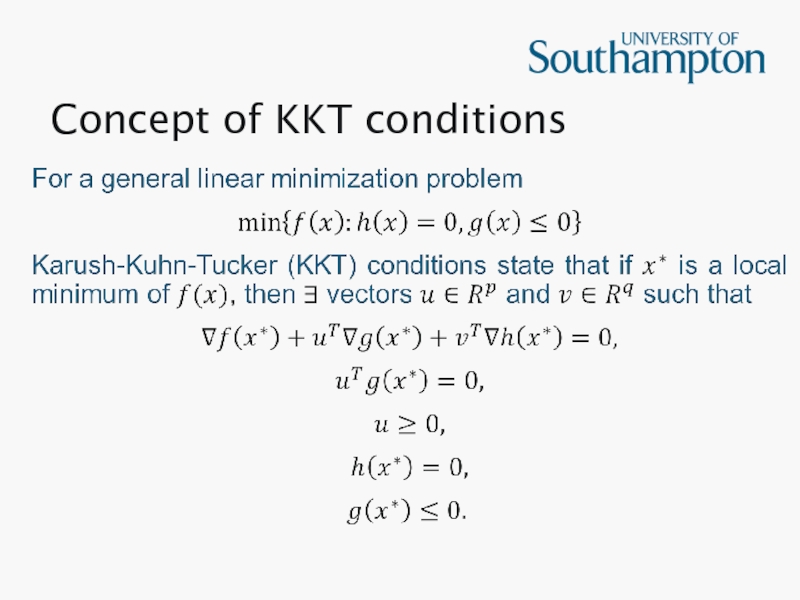
- 8. Concept of KKT conditions
- 9. Value function reformulation
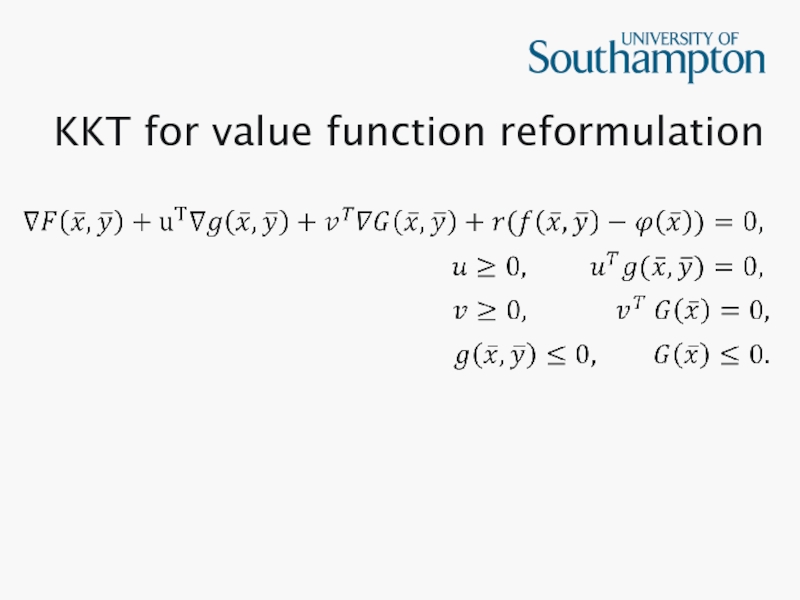
- 10. KKT for value function reformulation
- 11. Assumptions
- 12. KKT-type optimality conditions for Bilevel
- 13. Further Assumptions (for simpler version)
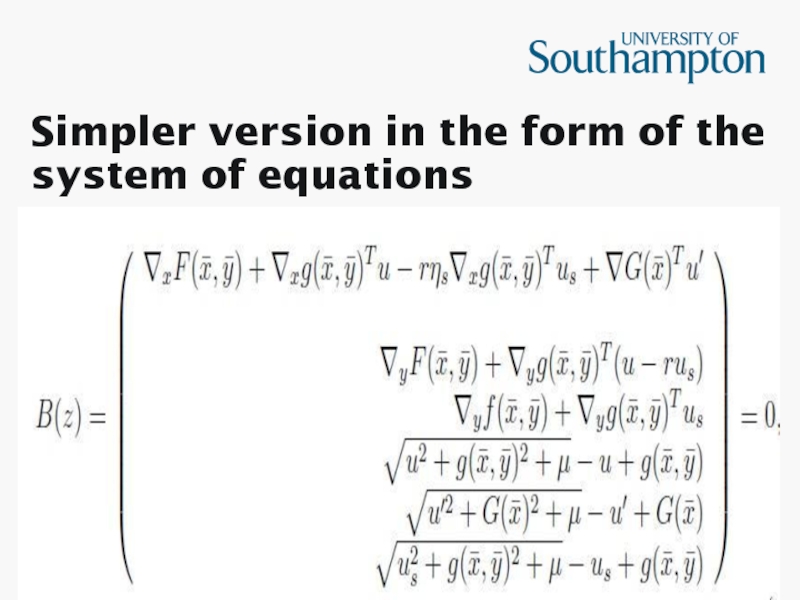
- 14. Simpler version
- 15. NCP-FunctionsDefineGive a reason (non-differentiability of constraints)Fischer-Burmeister
- 16. Simpler version in the form of the system of equations
- 17. Iterative methods
- 18. For Bilevel case
- 19. Newton methodDefineExplain that we are dealing with non-square systemSuggest pseudo inverse Newton
- 20. Pseudo inverse
- 21. Newton method with pseudo inverse
- 22. Gauss-Newton methodDefineMention the wrong formulationRefer to pseudo-inverse Newton
- 23. Gauss-Newton method
- 24. Convergence of Newton and Gauss-NewtonTalk about starting point conditionInterest for future analysis
- 25. Levenberg-Marquardt method
- 26. Numerical results
- 27. Plans for further work
- 28. Plans for further work6. Construct the own
- 29. Слайд 29
- 30. Слайд 30
- 31. References
- 32. References
- 33. Скачать презентанцию
OverviewDefinition and general form of a bilevel problemDiscuss optimality (KKT-type) conditionsReformulate general bilevel problem as a system of equationsConsider iterative (descent direction) methods applicable to solve this reformulationLook at the numerical
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Solution Methods for Bilevel Optimization
Andrey Tin
A.Tin@soton.ac.uk
School of Mathematics
Supervisors: Dr Alain
B. Zemkoho, Professor Jörg Fliege
Слайд 2Overview
Definition and general form of a bilevel problem
Discuss optimality (KKT-type)
conditions
Reformulate general bilevel problem as a system of equations
Consider iterative
(descent direction) methods applicable to solve this reformulationLook at the numerical results of using Levenberg-Marquardt method
Слайд 3Stackelberg Game (Bilevel problem)
Players: the Leader and the Follower
The Leader
is first to make a decision
Follower reacts optimally to Leader’s
decisionThe payoff for the Leader depends on the follower’s reaction
Слайд 4Example
Taxation of a factory
Leader – government
Objectives: maximize profit and minimize
pollution
Follower – factory owner
Objectives: maximize profit
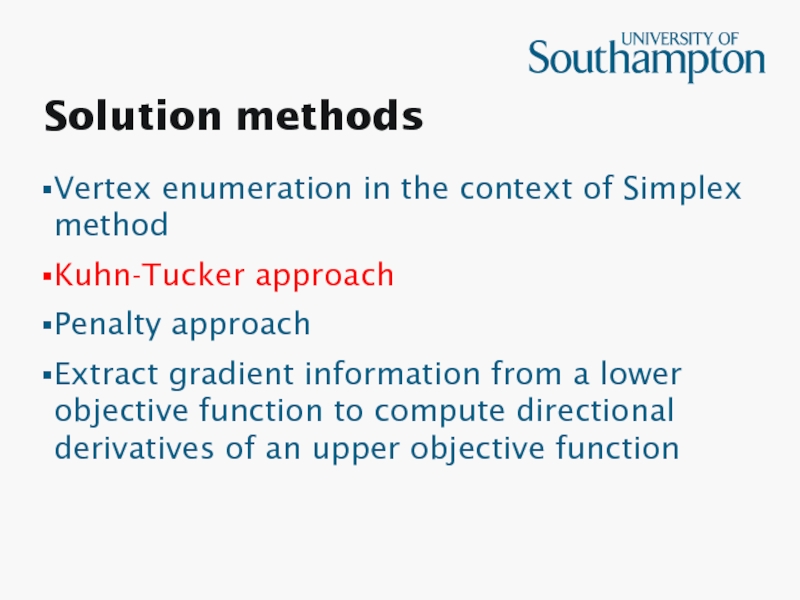
Слайд 7Solution methods
Vertex enumeration in the context of Simplex method
Kuhn-Tucker approach
Penalty
approach
Extract gradient information from a lower objective function to compute
directional derivatives of an upper objective functionСлайд 19Newton method
Define
Explain that we are dealing with non-square system
Suggest pseudo
inverse Newton
Слайд 24Convergence of Newton and Gauss-Newton
Talk about starting point condition
Interest for
future analysis
Слайд 28Plans for further work
6. Construct the own code for Levenberg-Marquardt
method in the context of solving bilevel problems within defined
reformulation.7. Search for good starting point techniques for our problem. 8. Do the numerical calculations for the harder reformulation defined .
9. Code Newton method with pseudo-inverse.
10. Solve the problem assuming strict complementarity
11. Look at other solution methods.