Слайд 2Facts
Founded in 2003 by engineers in Silicon Valley
Tesla’s CEO –
Elon Musk
Electric car with instant torque, incredible power, and zero
emissions
Tesla's first assembly plant occupies the former NUMMI plant in Fremont, California. It is known as the Tesla Factory.
The company is expanding its manufacturing footprint into other areas, including in Tilburg, the Netherlands, where it has an assembly facility, and Lathrop, California, where it has a specialized production plant.
Слайд 3Mission & Vision
Mission
Is to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable
energy.
Vision
The TESLA group of companies aim to be the premier
global provider of energy industry forecasting solutions.
Слайд 4Core Values
Always do your best
No forecast is perfect, but try
anyway
Respect and encourage people
Always be learning
Respect the environment
Слайд 5Pricing Strategy
Demand:
Testa aims to satisfy current demand and attract all
residual consumers in each segment.
Segmentation:
Model S – E-Segment (Executive)
Model X
– J-Segment (Sport Utility)
Model 3 – D-Segment (Large Cars)
Innovation:
R&D of each previous model lowers innovation costs for later models, raising profit margins
Слайд 6Competitors
BMW
Volvo
Audi
Ford
Mercedes-Benz
Toyota
Слайд 7Life Cycle
https://adizes.com/lifecycle/
Слайд 8Quality Management
When Tesla launching the new product doesn’t care so
much about its quality as it needs to meet deadlines.
For the company the most important product quality is the safety of the car, being possible to change the following aspects over time.
Слайд 10PEST Analysis
Political Factors
Governmental entities are among the main societal forces
that affect businesses and industries.
For example, policies on trade
can limit industry performance and the company's revenue.
Economic Factors
The effects of economic conditions on the remote or macro-environment include market growth, trade levels, currencies, and other variables that influence the automotive business.
For example, the solar energy market’s growth rate determines the growth opportunities of the company’s solar panel business.
Слайд 11PEST Analysis
Social/Sociocultural Factors
Social conditions considers how the business aligns with
the social trends in its target markets.
For example, Tesla
has growth opportunities based on the rising popularity of low-carbon lifestyles and increasing preference for renewable energy.
Technological Factors
The advancement of Tesla’s automotive and energy solutions business depends on available technologies.
For example, materials engineering technology determines the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of the company’s batteries.
Слайд 126 Leadership Principles at TESLA
1. Move fast
The ability to rapidly
respond to trends and changes in the market drives competitive
advantage.
2. Do the Impossible
Go beyond conventional limits of productivity and creativity in automotive design.
3. Constantly Innovate
Tesla must innovate continuously to maintain its competitive advantage.
4. Reason from “First Principles”
Use first principles to fulfill your job.
5. Think Like Owners
Act like owners. Take responsibility.
6. We are ALL IN
Teamwork develops synergy and makes the corporate culture effective in maximizing benefits
Слайд 13Competitive Advantages
Customer loyalty
The cohesive vision Tesla works
Remarkable design
Слайд 14Innovation
Constant innovation and product differentiation to retain monopoly power in
the face of increased competition.
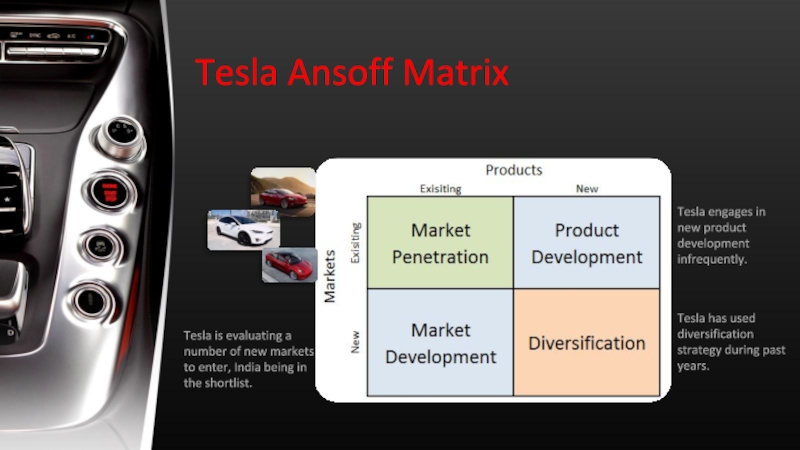
Слайд 16Tesla Ansoff Matrix
Tesla engages in new product development infrequently.
Tesla is
evaluating a number of new markets to enter, India being
in the shortlist.
Tesla has used diversification strategy during past years.
Слайд 17Stakeholders’ Analysis
Communities
Communities are stakeholders that determine brand image through their
significant lobbying activities and responses to the business. One of
the interests of this stakeholder group is to ensure that the natural environment is conserved or protected.
In this business analysis case, the company’s electric automobiles, batteries and solar panels (through the subsidiary SolarCity) address such interest.
Customers
Customers affect Tesla’s revenues and are interested in product quality and reasonable pricing. The company gives high priority to these stakeholders in its corporate social responsibility programs, seek new ways of minimizing costs.
For example, instead of continuing to buy battery cells from Panasonic, Tesla shifts to manufacture, in collaboration with Panasonic, its own batteries to make its electric automobiles more affordable.
Слайд 18Stakeholders’ Analysis
Employees
Tesla believes that employees are a critical success factor
in its automotive and energy solutions business. Their interests include
high compensation and significant career opportunities.
Tesla’s corporate responsibility approach satisfies these interests through a competitive compensation strategy, as well as HR programs for skills development and leadership development.
Investors/Shareholders
Tesla’s early years depended on a series of funding from investors. These stakeholders are important in influencing the company’s capitalization. Investors and shareholders have interests in the profitability and growth of the business.
For example, the company’s decision to allow other firms and individuals to use its technology patents is expected to increase market demand for electric vehicles and related products.
Слайд 19Stakeholders’ Analysis
Governments
Tesla experiences the effects of governmental action. Governments are
stakeholders that present requirements, limits and opportunities to businesses. This
stakeholder group’s interests include legal compliance, as well as business contribution to economic growth.
With plans for strategic global expansion and an excellent sustainability record, Tesla’s corporate social responsibility strategy satisfies these interests.
Слайд 20Tesla’s Change
Tesla has changed the design over the years giving
a more futuristic look to its vehicles.
Tesla has decided to
create insurance for its vehicles so that people who buy their cars do not spend more money on other companies. Being this insurance cheaper and especially covering these cars since insurance for these is very expensive.
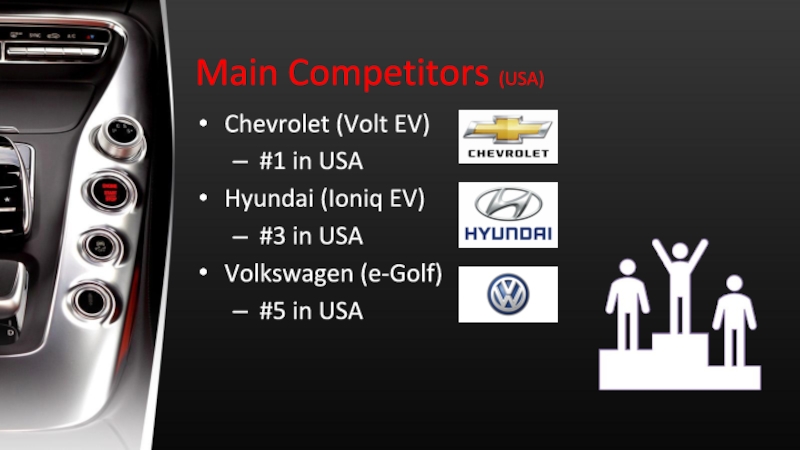
Слайд 22Main Competitors (USA)
Chevrolet (Volt EV)
#1 in USA
Hyundai (Ioniq EV)
#3 in
USA
Volkswagen (e-Golf)
#5 in USA
Слайд 24Profitability (based on latest data)
Tesla: $24.4B Revenue ($1.2B Total Funding)
Elon
Musk: “Given that Tesla has never made an annual profit
in the almost 15 years since it existed, profit is obviously not what motivates us.“
Volkswagen: $271.3B Revenue
Hyundai: $87.1B Revenue
GM (Chevrolet): $10.8B Revenue
But it still means big profit-sharing checks for about 46,500 union workers in the U.S. They'll get $10,750 each.
Слайд 25Global EV Sales
The Tesla Model 3 had its best off-peak month in
August with an estimated 21,000 sales. For the year, Model
3 is more than 100,000 above the 2nd best model.
SAIC Baojun E-Series was the second-best model in August with 8,698 (31,900), followed by BAIC EU-Series - 7,580 (65,593 YTD)
In general, other models are not able to reach five-digit results, and only four (besides the Model 3) were above 5,000.
Слайд 26Price
Tesla Model 3 (Standard)
$38,990
Chevrolet Bolt EV
$36,620
Hyundai Ioniq EV
$30,315
Volkswagen e-Golf
$31,895
Слайд 27Range
Tesla Model 3 (Standard)
354km
Chevrolet Bolt EV
383km
Hyundai Ioniq EV
200km
Volkswagen e-Golf
201km
Слайд 28Performance (km/h & 0-100)
Tesla Model 3 (Standard)
210 km/h & 5.6
sec
Chevrolet Bolt EV
145 km/h & 6.5 sec
Hyundai Ioniq EV
165 km/h
& 9.9 sec
Volkswagen e-Golf
150 km/h & 9.6 sec
Слайд 29Conclusion of Tesla competitors
Tesla is far better than most of
the competition when it comes to how far its cars
can go on a single charge.
Not only do Teslas go farther than the competition, they go faster and have more powerful engines than their counterparts, which explains that huge jump in cost.
Слайд 31ADKAR Model
Awareness:
Cars that are possible for everyone to buy.
Desire:
Manufacture cheaper cars for people who can't afford premium class
cars.
Knowledge:
Look for techniques that allow the manufacture of these cars reducing costs.
Ability:
Implement the knowledge gained by putting them into practice by making cheaper parts.
Reinforcement:
Review if everything that has changed works correctly, being possible the product purchased by any consumer.
Слайд 335I’s Model
Information: It’s transmitted by all possible means of communication,
internet, social networks, advertisements ...
Identity: With the changes that are
constantly made in the company
Incentivize: Through bonuses of good work done for workers, and for consumers with small gifts for being brand loyal
Infrastructure: Change what prevents the company from succeeding
Institutions: Who makes the rules in the company is the CEO, and for the company it is the consumers since they are the ones who decide whether they want the product or not.