Слайд 1The essence and specific features of Russian centralized state
Слайд 2Ivan Kalita
All the actions of Ivan Kalita were aimed at
raising Moscow above the rest of the principalities.
Successful were
the actions in the fight against the Tver Principality. In 1327, there was an uprising in Tver against the Horde rule. The punitive action of Uzbek Khan so weakened the Tver forces that the Principality no longer competed with Moscow.
The policy of Prince Ivan Kalita led to the favor of Uzbek Khan.
Слайд 3Stages of formation of Russian centralized state
The end of 13th-the
beginning of 14th centuries - the rise of Moscow principality
The second half of 14th - the beginning of 15th centuries – the beginning of state centralization around Moscow
The end of 15th – beginning of 16th centuries – the completion of the formation of the centralized Russian state
Слайд 4Three centres prendended to integrate Rus
Moscow principality
Tver principality
Lithuanian principality
Слайд 5Reasons for the rise of Moscow
Objective
Moscow was far away from
dangerous outskirts
Important trade routs
Lands appropriate for agriculture
Developed feudal tenure (prince
relied on nobles)
Subjective
Wisdom and far-sightedness of Moscow princes
There were no strifes in Moscow princely family
The principality was passed to one single heritor.
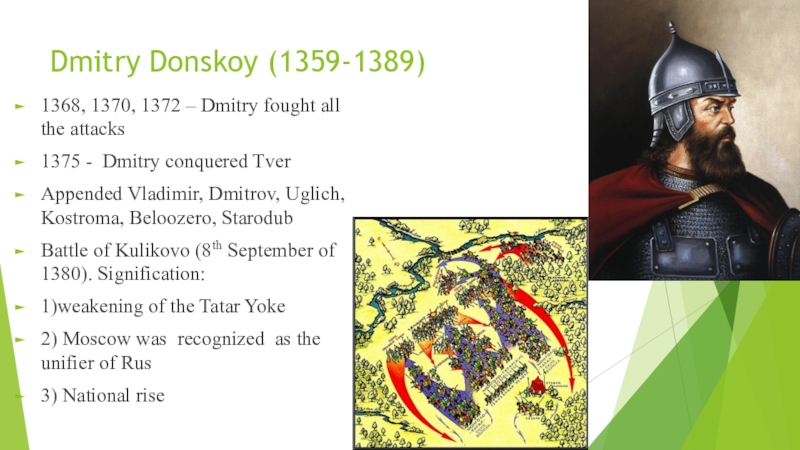
Слайд 6Dmitry Donskoy (1359-1389)
1368, 1370, 1372 – Dmitry fought all the
attacks
1375 - Dmitry conquered Tver
Appended Vladimir, Dmitrov, Uglich, Kostroma, Beloozero,
Starodub
Battle of Kulikovo (8th September of 1380). Signification:
1)weakening of the Tatar Yoke
2) Moscow was recognized as the unifier of Rus
3) National rise
Слайд 7Vasiliy I Dmitrievich (1389-1425) ; Vasily II the Dark (1425
– 1462)
Vasiliy I Dmitrievich
Began to reign without asking the Golden
Horde for permission
Appended Nizhniy Novgorod, Vologda, Murom, Torzhok, Volokalamsk
The Feodal war 1433-1453; Vasily II asserted power
Vasily II the Dark
Liquidated apanage principalities
1456 – march on Novgorod; appended Novgorod territories
Слайд 8Ivan III Vasilievich (1462-1505)
Accession: Yaroslavl, Rostov, Novgorod, Tver, Vyatka
1476
– stopped paying tribute
1480 – standoff on the Ugra river
1487
– Kazan khanate was conquered
1485 – Gosudar of all Russia
Слайд 9Vasily III Ivanovich (1505-1533)
Formation of Russian unified state was completed
Accession:
Pskov, Smolensk, Ryazan
Слайд 10The system of management of the centralized state
Since 1485, the
Moscow Grand Duke Ivan III became known as the Grand
Duke of all Russia.
During the reign of Ivan III, the system of state power of a single state is formed. The highest institution was the boyar Duma-the Council under the Grand Duke.
The order of service was based on the system of localism. Localism - the order of appointment to positions of nobility and merit of the family.
The Executive branch is beginning to take shape. Orders - Central management bodies.
The Country was divided into counties, counties into volosts. The County was ruled by a Governor, a parish - Veloster. The basis of local government was the feeding system.
The sudebnik of 1497 - the first code of laws of United Russia-fixed the unified structure and management in the state.
Слайд 11Specific features of Russian centralized state
In Europe
Socio-economic factor
growth of
cities, domestic and foreign trade
formation of the bourgeoisie
emancipation of
the peasants
In Russia
Foreign policy factor
Tatar Yoke, external danger from Lithuania and the Livonian order
Unification of lands through strong princely power
Enslavement of the peasants
Слайд 12Russian state by 1533
By the end of the reign of
Vasily III, the unification of Russian lands was completed
The state
became unified, but it was not centralized yet
Centralization – the main task of power in the 2nd half of the XVI century
Слайд 13The Reign Of Elena Glinsky (1533-1538)
After the death of Vasily
III (1533), his son Ivan became Grand Duke. But in
fact, the power was in the hands of Elena Glinskaya-Ivan's mother.During her reign, a number of reforms were initiated to strengthen the Grand Ducal power.
Local government reform began (which was completed by Ivan IV)
Increased control over the growth of Church land ownership
Ban on buying land from serving people was introduced
On her orders, the Kitaygorodskaya wall was built
Armistice with Lithuania (1536)
Financial reform: the Moscow and Novgorod monetary systems were merged and a single Moscow ruble was introduced. There appeareda new Moscow coin-kopek
Слайд 14Ivan IV the Terrible - The first «Tsar of all
Russia»
In January 1547, when Ivan was 16 years old, Metropolitan
Makarii crowned him in the Uspensky Cathedral of the Moscow Kremlin.
Historical significance of the proclamation of Ivan IV as Tsar: Lifted of Ivan IV over the other princes. He was revered as a great gosudar
Слайд 15Judicial reform of the Elected Rada
1550-Ivan IV's law book was
adopted.
Elimination of tax privileges of monasteries
Limit the power of governors
and volostile - strengthening the control of the Royal administration
A single amount of court fees
Слайд 16The reform of Central and local government
Creating an ordered management
system
Cancellation of feedings (1555)
Сontinuing the lip reform(1555-1556) all power
in the uyezd passed to the provincial and Zemstvo prefects, and in the cities – to the izlublennyi golova
Слайд 17Church reform
1551-adoption of Stoglav. It designed the Pantheon (list) of
all Russian saints; regulated Church life-services, rites
Introduction of the unified
tax system, inventory of Church lands
Strengthening state control
Rigid iconographic Canon
Prohibition of usury by priests
Слайд 18Results of reforms of The elected Rada
A new set of
laws has been adopted
A number of privileges of former independent
princes were eliminated
Unified Church Canon approved
The role of the Central government in judicial proceedings has been strengthened
A professional Central management unit has been created
A permanent army has been created
Cancelled feeding
Limited locality
Слайд 19Oprichnina
A special order – oprichnina, i.e. provided for the division
of the entire territory of the state into two parts:
oprichnina
– lands taken under special tsarist administration
zemschina – land that should be in charge of the boyars, power of voivodes and governors was preserved
Some historians think that oprichnina was Ivan IV trial to put part of the territory under absolute power