the creation of the EU half a century ago, Europe
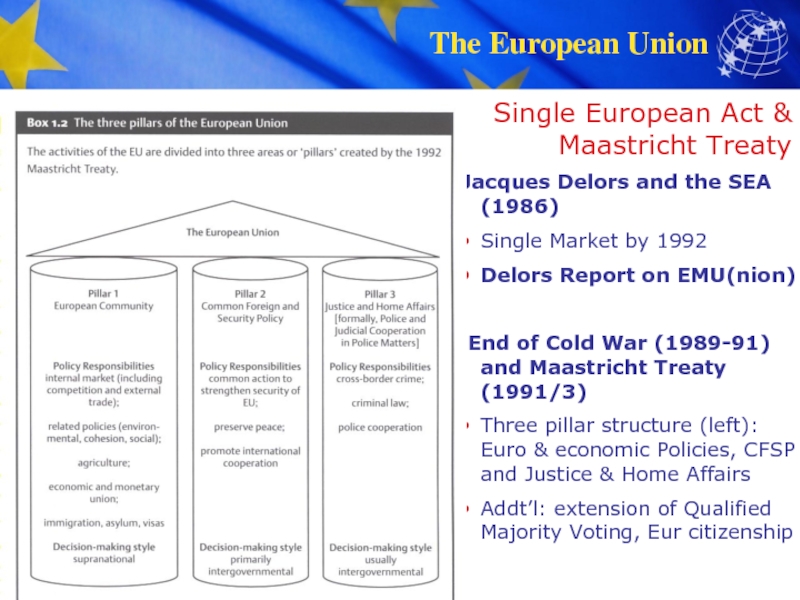
has enjoyed the longest period of peace in its history.European political integration is unprecedented in history.
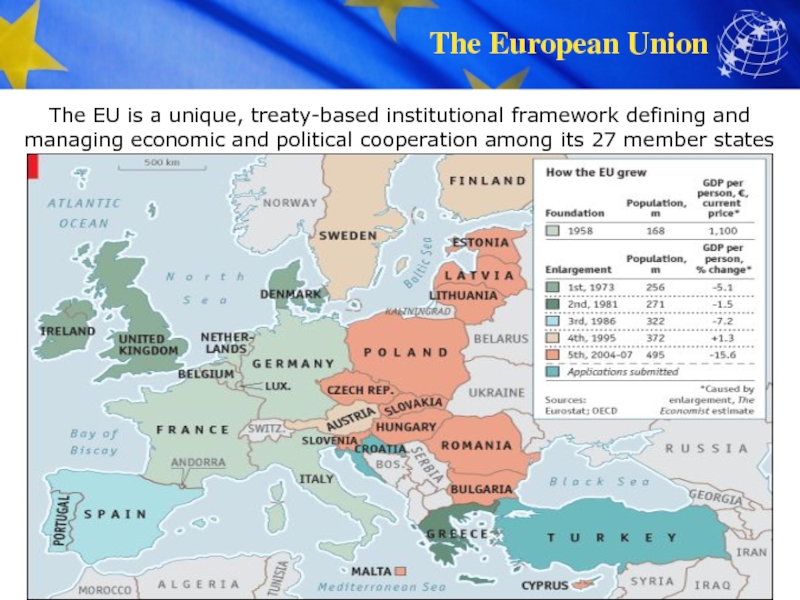
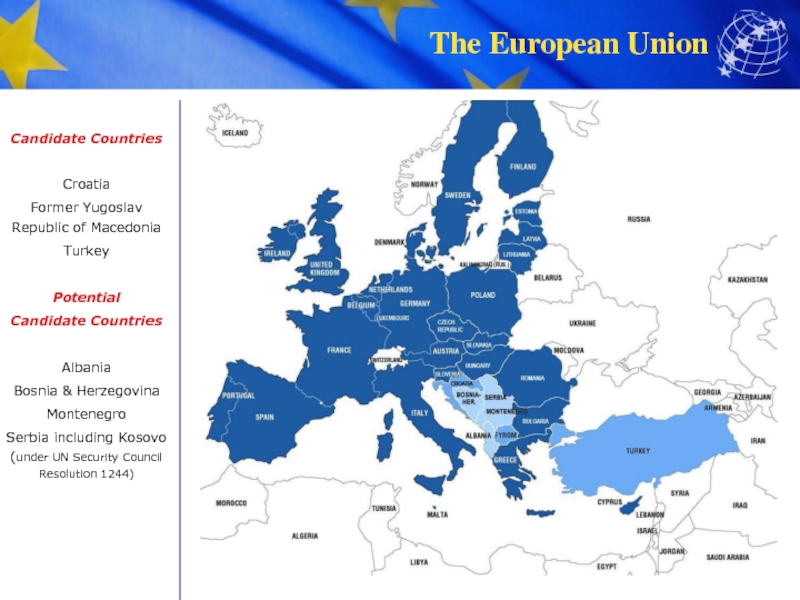
EU enlargement has helped overcome the division of Europe – contributing to peace, prosperity, and stability across the continent.
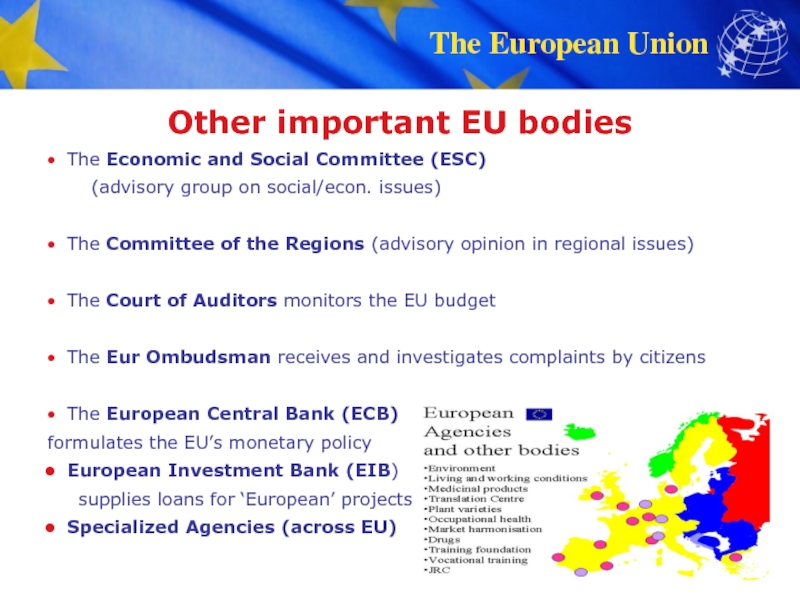
A single market and a common currency conditions for companies and consumers.
European Union
United in diversity