Слайд 1The first Russian revolution (1905-1907
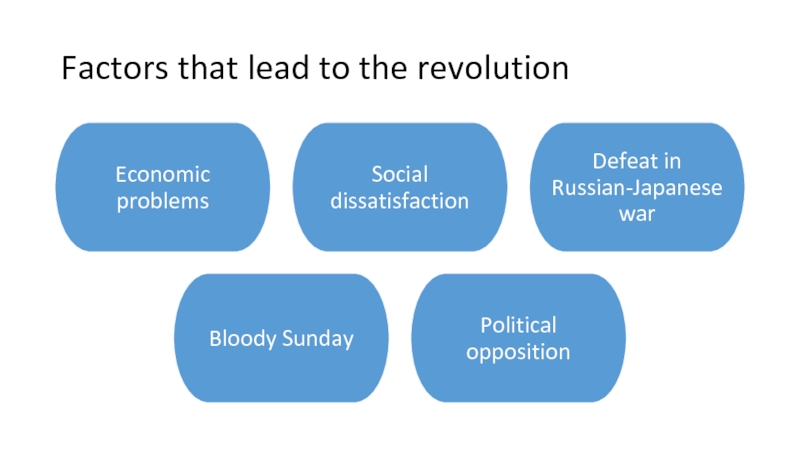
Слайд 2Factors that lead to the revolution
Слайд 3Bloody Sunday
One of the main figures of this event is
George Apollonovich Gapon-priest of The Russian Orthodox Church, politician and
trade Union leader, outstanding speaker and preacher. Creator and Permanent head of the working organization " Meeting of Russian factory workers of St. Petersburg»
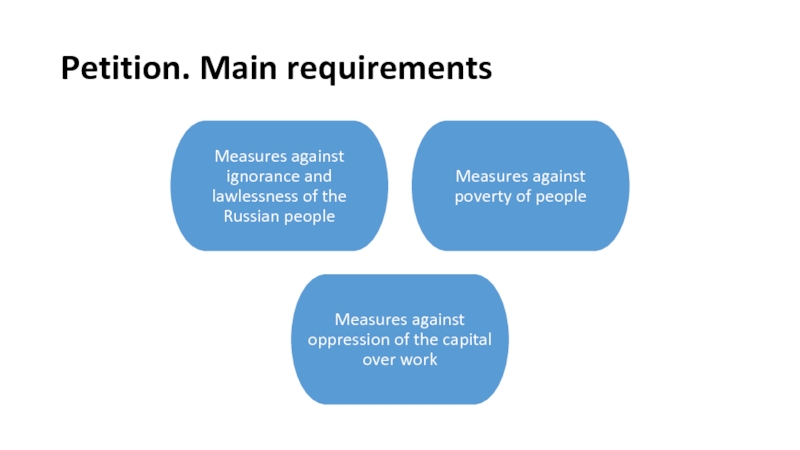
On January 6 Gapon drew up a petition addressed to the Emperor On the working needs.
Слайд 5Bloody Sunday
On 9 January 1905, Father Gapon led a march
to deliver a petition to the empreror. Thousands of workers
took part in this peaceful protest.
This demonstration of factory workers was brutally put down by Russian soldiers. During the 'bloody Sunday‘ more than 1000 people were killed by rifle fire and Cossack charges, and injured 2000 people.
Слайд 6Bloody Sunday
In strikes were involved 440000 people. A major event
was the beginning in may 25, 1905 General strike of
textile workers in the city of Ivanovo-Voznesensk, which lasted 72 days. A Council of workers commissioners was created.
After the events of January 9, p. D. Svyatopolk-Mirsky was dismissed from the post of Minister of internal Affairs and replaced by Bulygin
Слайд 7Sevastopol Uprising of 1905
Distempers and opened oppositions were taking place
in the fleet. The biggest event of the first Russian
revolution was armed revolt at "Potemkin Tavrichesky" ship
Слайд 8Sevastopol Uprising of 1905
On June 14 revolt on the battleship
" Potemkin Tavrichesky" began.
Слайд 9Sevastopol Uprising of 1905
From Sevastopol the ship goes to Odessa,
where there were massive demonstrations. On June 25 was forced
to surrender to the Romanian authorities. Punishment: from a lifetime of hard labor to the execution
Слайд 10The October strikes
In October 13, 1905 began the St. Petersburg
Council of workers ' deputies, which became the organizer of
the all-Russian October 1905 political strike and tried to disorganize the financial system of the country, calling not to pay taxes and take money from banks. Members of the Council were arrested on 3 December 1905.
Слайд 11Manifesto
On October 17, the Emperor signed a Manifesto. In fact,
the Manifesto is an extremely special document, in this case
a prototype of the Constitution.
Слайд 12Contents Of The Manifest:
To grant the population an inviolable basis
of civil freedom
To begin the immediate development of the
electoral system in Russia, on the basis of which to hold elections to the state Duma.
To give the state Duma legislative powers. Not to enact any law without the approval of the state Duma.
Слайд 13Activities Of the first and Second state Duma 1 января
1906 - 1 января 1907
Слайд 14The convening of the First State Duma
First state Duma operated
from 27 April to 9 July 1906.
On August 6, 1905,
the Manifesto of Nicholas II established the state Duma as"a special law-making institution, which is provided with the preliminary development and discussion of legislative assumptions and consideration of the list of state revenues and expenditures" .
At the same time, the Regulation on elections of August 6, 1905 was published, which established the rules of elections to the state Duma. Most of the Russian population was deprived of voting rights: women, soldiers, workers, students, vagrants, etc.
Слайд 15The convening of the First State Duma
The dissolution of the
state Duma, announced in the morning of 9 July 1906.
Слайд 16The Second State Duma
February 20, 1907 was the opening of
the 2nd state Duma.In 2nd State Duma there were more
semi-literate peasants, more semi-intelligentsia than in the 1st one
Слайд 17Dissolution of the Second State Duma
Replaced Goremykin P.A. Stolypin still
hoped to establish cooperation and constructive work with the people's
representation. Nicholas II was less optimistic, saying that"does not see practical results from the Duma work."
On Sunday, June 3, the II state Duma was dissolved by the decree of the emperor. At the same time, contrary to article 86 of the Basic laws, a new regulation on elections to the state Duma was published,. Thus, the government and the Emperor made a coup, named the "June third", which marked the end of the revolution of 1905-1907 and the onset of the reaction.
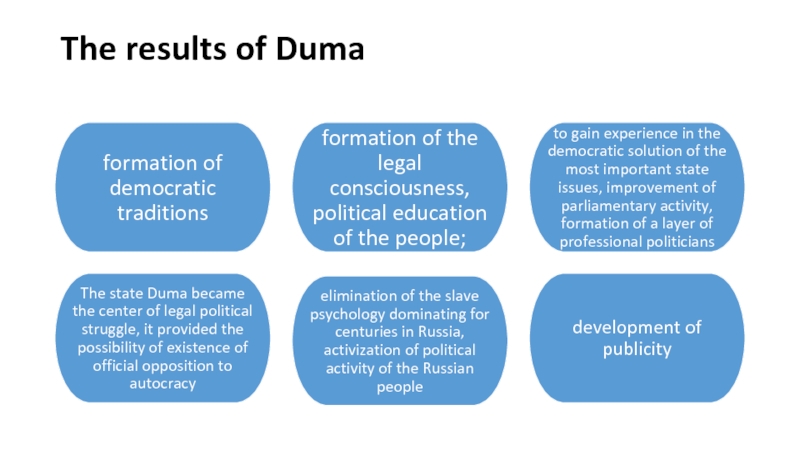
Слайд 19Results of the revolution
In the Russian Empire autocracy was for
the first time limited by the legislative authorities.
Civil rights and
freedoms were proclaimed and partially respected.
The workers were given the right to create their own organizations – trade unions – which defended the rights of the proletarians in the fight against entrepreneurs.
The state made concessions to the peasants – in 1906 the redemption payments were canceled, which the peasants had to pay since the reform of 1861. At the same time, in 1906, the government of Stolypin began agrarian reforms.
Слайд 20Results of the revolution
The revolution failed but it served as
a serious warning of what might happen in the future.
Слайд 21List of sources
https://bigenc.ru/military_science/text/3543245
https://histrf.ru/biblioteka/b/rievoliutsiia-1905-1907-ghodov-zanoza-istorii
https://www.bbc.com/bitesize/guides/zwxv34j/revision/6
https://medium.com/@LemarAlexander/the-russian-revolutions-of-1905-and-1917-1a81ab0dc37a
https://works.doklad.ru/view/rMEqn29mCIU/all.html