Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
The Renal Transplant Patient
Содержание
- 1. The Renal Transplant Patient
- 2. IntroductionRenal transplantation is the preferred treatment for
- 3. EMPs encounter transplant pts at 2 critical
- 4. Diabetic nephropathy accounts for 40% of the
- 5. The Transplantation ProcessTransplant coordinators should be called
- 6. Following brain death, a number of physiological
- 7. About 75% of organ donors develop diabetes
- 8. DefinitionsAllograft : graft between genetically dissimilar individuals
- 9. The Surgical ProcedureWet ischaemia time (time from
- 10. The transplant renal a is anastomosed to
- 11. Living donor transplants fxn immediately after transplant,
- 12. Слайд 12
- 13. Слайд 13
- 14. Graft PrognosisDirectly related to source of donor
- 15. MorbidityInfection (most common cause of M&M in
- 16. Osteoporosis 60%Malignant neoplasm 14% - related to the degree of immunosupression.
- 17. MortalitySurvival of pts after transplantation from a
- 18. Hx of a pt with organ transplant
- 19. Immunosuppressive RxCompliance with RxPrevious infectionsRecent exposure to ill pts
- 20. Examination of the PatientInspect, palpate and auscultate
- 21. Immunosuppressive TherapyRenal transplant pts require lifelong immunosuppression
- 22. Cyclosporine: inhibits both cellular and humoral immunity
- 23. Azathioprine: antimetabolite derivative of 6-mercatopurine. Inhibits DNA
- 24. Tacrolimus: newer macrolide compound that binds to
- 25. Immunosuppressant minimisation protocols are becoming more popular.Triple
- 26. The initial Rx of rejection involves the
- 27. Слайд 27
- 28. Слайд 28
- 29. Слайд 29
- 30. Surgical Complications affecting AllograftsUsual postop generic complications:
- 31. 2. Peritransplant haematoma Early postop complication
- 32. 3. Urinary Leak First transplant month.
- 33. 4. Lymphocoele Occurs within the first
- 34. 5. Obstructive Uropathy Occurs in early
- 35. 6. Renal artery stenosis Late presentation.
- 36. Fever in the Transplant PtCommom problem.Opportunistic infections occur frequently.Remember that fever may be non-infectious.
- 37. Infections in the 1st post transplant monthUsual
- 38. Infections in the remainder of the 1st
- 39. Most reliable diagnosis is PCR for viral
- 40. Infections after the 1st post transplant yearCommunity-acquired infections unrelated to immune suppression are more common.
- 41. Non-infectious causes of feverPulmonary atelectasis (early post op)Severe acute rejectionAdministration of antilymphocyte AbsPost transplant lymphoma
- 42. Initial Work-up for febrile post transplant ptFBC
- 43. Cardiovascular disordersThe risk of CVS disease is
- 44. HT ComplicationsPrevalence is 70-90% in renal transplant
- 45. Pulmonary ComplicationsMost common pulmonary problem is pneumonia.Nonopportunistic
- 46. GIT ProblemsAbnormalities in LFTs occur frequently.The clinical
- 47. Neurologic + Psychiatric DisordersCyclosporine and tacrolimus cause
- 48. Meningitis: Listeria monocytogenes, cryptococcus + TB.Encephalitis or
- 49. Haematological DisordersAnaemia, leukopaenia, thrombocytopaenia alone or in
- 50. Post transplant erythrocytosis occurs in 10-20% of
- 51. Musculoskeletal DisordersCorticosteroids, and to a lesser extent
- 52. With pts on azothioprine, the use of
- 53. Dermatological DisordersA variety of disorders can occur:
- 54. Electrolyte AbnormalitiesCyclosporin + tacrolimus cause hyperkalaemia (decreased
- 55. New Onset DMDe nova DM occurs in
- 56. MalignancyTransplant recipients are at significantly higher risk
- 57. Stress-dose Corticosteroid CoverageSeverely ill renal transplant pts
- 58. Acute RejectionIndirect pathway: soluble donor Ag that
- 59. Acute rejection appears within the first 3
- 60. Chronic RejectionUsually apparent from 3 months onwards
- 61. Take Home Massage1. If a transplant pt
- 62. References1. Care of the Renal Transplant Recipient
- 63. Скачать презентанцию
IntroductionRenal transplantation is the preferred treatment for patients with end-stage renal disease. It offers better quality of life and confers greater longevity than long-term dialysis.
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 3EMPs encounter transplant pts at 2 critical stages:
Initial doctors to
identify potential donors from a pool of critically ill patients
who are admitted to hospital.They care for pts once they have been transplanted and present with complications related to their immunosuppressive therapy, infections or ARF.
Слайд 4Diabetic nephropathy accounts for 40% of the diseases resulting in
renal transplantation. This subgroup of pts are also more prone
to complications after renal transplantation.The spectrum of diseases in transplant pts is different from the general population.
The classical presentation of common medical disorders may be modified by immunosuppressive medication.
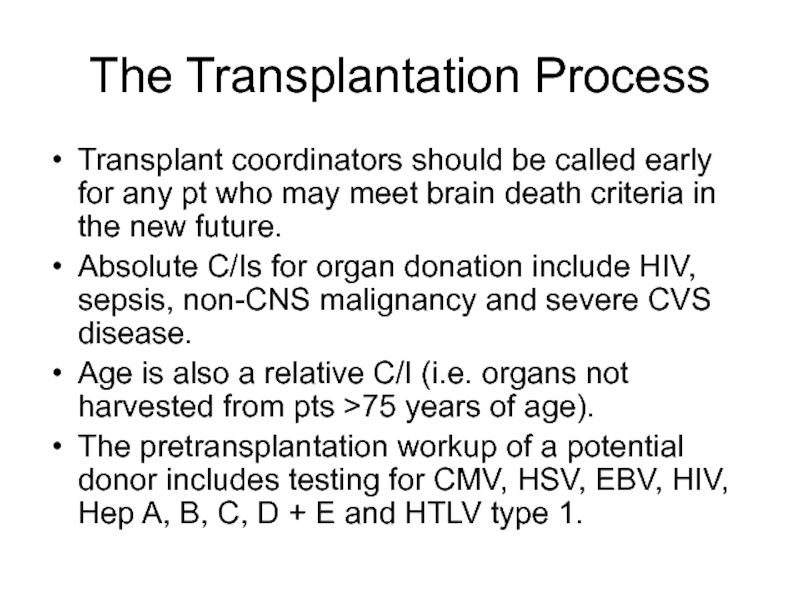
Слайд 5The Transplantation Process
Transplant coordinators should be called early for any
pt who may meet brain death criteria in the new
future.Absolute C/Is for organ donation include HIV, sepsis, non-CNS malignancy and severe CVS disease.
Age is also a relative C/I (i.e. organs not harvested from pts >75 years of age).
The pretransplantation workup of a potential donor includes testing for CMV, HSV, EBV, HIV, Hep A, B, C, D + E and HTLV type 1.
Слайд 6Following brain death, a number of physiological changes occur that
need to be rectified if donor organ perfusion is to
be preserved.Increased cerebral oedema after trauma or stroke results in catecholamine release and HT.
With brainstem necrosis, catecholamine levels drop rapidly resulting in hypotension. This should be corrected with fluid and vasopressors.
Слайд 7About 75% of organ donors develop diabetes insipidus due to
pituitary necrosis and this leads to hypovolaemia.
Systemic thermal control is
often lost due to hypothalamic ischaemia which results in coagulopathy, hepatic dysfunction and cardiac dysfuction.Слайд 8Definitions
Allograft : graft between genetically dissimilar individuals of the same
species.
Autograft : graft in which donor and recipient are the
same individual.Xenograft : Donor and recipient belong to different species.
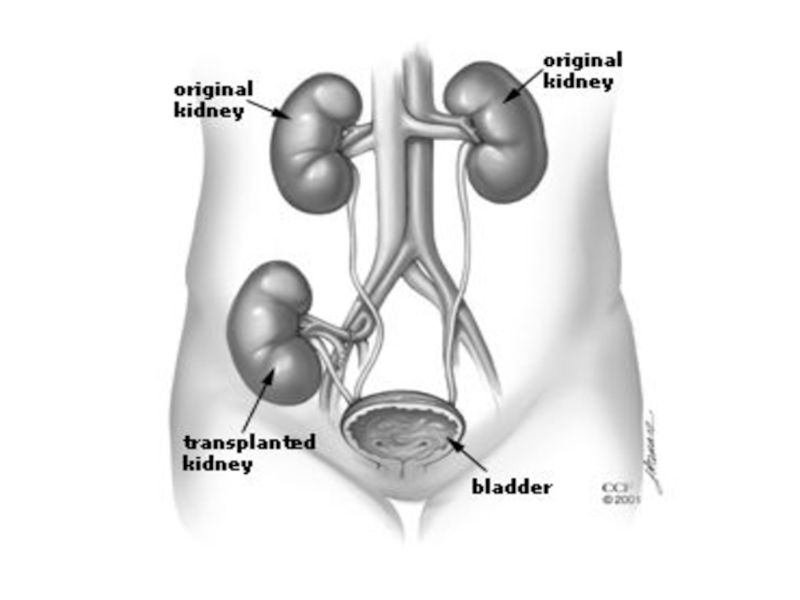
Слайд 9The Surgical Procedure
Wet ischaemia time (time from cessation of circulation
to removal of organ and its placement in cold storage)
should not exceed 30 mins.Transplanted kidney is placed in the R or L lower quadrant of the abdomen in an extraperitoneal position. On examination, the transplant is easily palpable.
Слайд 10The transplant renal a is anastomosed to the ipsilateral internal
or external iliac a, the renal v to internal or
external iliac v and the transplant ureter to the bladder.Generally a single kidney is transplanted.
When small, paediatric or older cadaveric donor kidneys with age-related loss of renal fxn are transplanted, both kidneys from the donor might be placed in a single recipient to provide adequate fxnal renal mass.
Слайд 11Living donor transplants fxn immediately after transplant, +/- 30% of
cadaveric transplants have delayed graft fxn because of more prolonged
ischaemic cold preservation. These pts need continued dialysis support until the kidney starts to fxn.Слайд 14Graft Prognosis
Directly related to source of donor kidney.
Recipients of cadaveric
kidneys have more episodes of rejection and lower graft survival
rates.Graft survival rates for kidneys from living donor is 95% @ 1 yr and 76% @ 5 yrs vs graft survival from a cadaveric kidney donor is 89% @ 1 yr and 61% @ 5 yrs.
Слайд 15Morbidity
Infection (most common cause of M&M in first year post
transplantation) and graft failure occur.
HT occurs in 75-85% of all
renal transplant recipients.Hyperlipidaemia 60%
CVS disease 15.8 – 23%
DM 16.9 – 19.9% (more likely to be present before transplantation and new onset DM after transplantation is related to corticosteriod use.)
Слайд 17Mortality
Survival of pts after transplantation from a liver donor is
98% at 1 yr and 91% @ 5 yrs.
Survival of
pts who receive cadaveric organs is 95% @ 1 yr and 81% @ 5 yrs.Слайд 18Hx of a pt with organ transplant presenting to ED
Current
symptoms (esp. fever)
Transplant age (interval since transplant)
Living or cadaveric source
Previous
episodes of rejectionCurrent medications (including over the counter preparations)
Recent medicine changes
Слайд 20Examination of the Patient
Inspect, palpate and auscultate the graft site.
Graft
tenderness and swelling is often observed in acute rejection, outflow
obstruction, pyelonephritis and renal vein occlusion.Bruits are heard in RA stenosis and AV malformations.
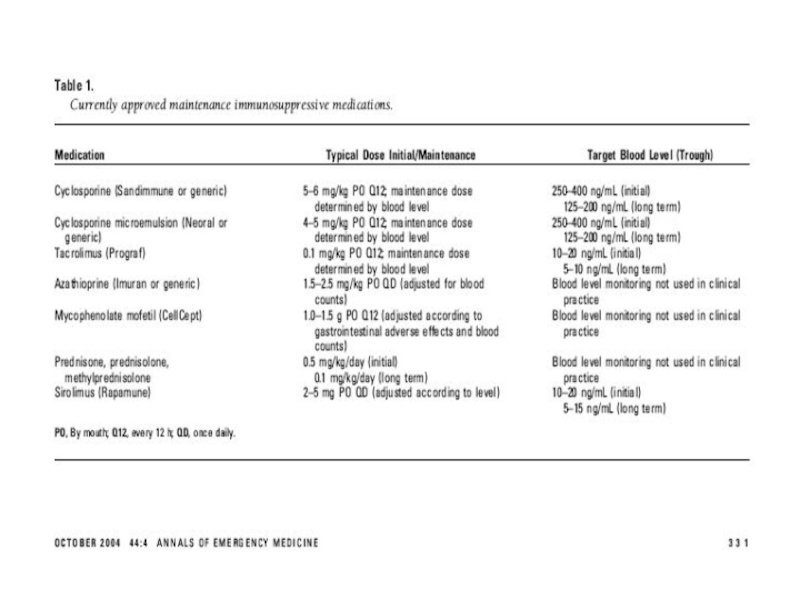
Слайд 21Immunosuppressive Therapy
Renal transplant pts require lifelong immunosuppression to prevent rejection.
Current
“triple” regimes include cyclosporine-microemulsion or tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil or azathiopine
and corticosteroids.Sicrolimus became available in 1994 and has become incorporated into protocols.
Слайд 22Cyclosporine: inhibits both cellular and humoral immunity by binding to
cyclophilins which block cytokine transcription and production resulting in the
inhibition of lymphocyte signal transduction.Results in potent immunosuppression of helper T cells, without affecting suppressor T cells.
Слайд 23Azathioprine: antimetabolite derivative of 6-mercatopurine. Inhibits DNA + RNA synthesis,
resulting in suppression of lymphocyte proliferation.
Corticosteroids: wide range of effects
on immune system specifically the T lymphocytes. Because of long-term toxic effects, every effort is made to minimise the dosage of glucocorticoids.Слайд 24Tacrolimus: newer macrolide compound that binds to lymphocyte proteins and
inhibits cytokine synthesis. Used as either primary or rescue therapy
for allograft rejection.Слайд 25Immunosuppressant minimisation protocols are becoming more popular.
Triple Rx for 3-12
months after transplantation followed by withdrawal of 1 of the
3 drugs to minimise long term side effects (most commonly withdrawn drug is corticosteroid).Antilymphocyte Abs are also widely used in the pts (polyclonal & monoclonal Abs are available).
Слайд 26The initial Rx of rejection involves the administration of IVI
corticosteroids (methylpred 250-1000mg daily for 3/7 or dexamethasone 100mg daily
for 3/7).Слайд 30Surgical Complications affecting Allografts
Usual postop generic complications: atelectasis, pneumonia, wound
infection, ileus, bleeding and venous thromboembolism.
1. Acute occlusion of transplant
renal a or v.Occurs in first transplant week (0.5-8%). Causes oligoanuria and ARF. With renal vein thrombosis, there is graft tenderness, dark haematuria and decreased urine volume.
Diagnosis is via doppler U/S or radioisotope scanning to demonstrate lack of blood flow.
Rx is surgery.
Слайд 312. Peritransplant haematoma
Early postop complication or in setting
of perioperative anticoagulation (2-3%)
Severe pain over allograft, decreased
Hb or Hct, increased serum creatinine. Recurrent increased K due to lysis of RBC in haematoma.
Diagnosis via CT.
Rx is surgical and usually leads to allograft nephrectomy.
Слайд 323. Urinary Leak
First transplant month. (2-5%)
Presents
with urine extravasation and ARF, fever, pain and distended abdomen.
Diagnosis is via U/S which demonstrates a peritransplant fluid collection or via radioisotope scanning.Treatment is foley catheter insertion and surgery.
Слайд 334. Lymphocoele
Occurs within the first 3 post transplant
months and is due to lymph leaking from severed lymphatics
(5-15%).Large collections cause pain, ARF, urinary frequency, ipsilateral lower extremity oedema, occasionally iliac vein thrombosis or PE. Most of the s&s are due to pressure effects.
Diagnosis is via U/S.
Treatment is percutaneous drainage.
Слайд 345. Obstructive Uropathy
Occurs in early post transplant period
(3-6%). The commonest causes are extrinsic compression of the ureter
by a lymphocoele or due to a technical problem with the ureteric anastomosis to the bladder.Diagnosis is best achieved via U/S demonstrating hydronephrosis.
Treatment is surgical.
Слайд 356. Renal artery stenosis
Late presentation.
Pts
present with uncontrolled HT, allograft dysfunction and peripheral oedema.
Diagnosis is via U/S or MRA.Слайд 36Fever in the Transplant Pt
Commom problem.
Opportunistic infections occur frequently.
Remember that
fever may be non-infectious.
Слайд 37Infections in the 1st post transplant month
Usual post op infections:
pneumonia, wound infection, line sepsis, UTI secondary to foley catheter.
Opportunistic
infections are uncommon.Most common organisms: E.coli (UTI), S.aureus + S.viridans (line sepsis and wound infections) and S.pneumoniae (pneumonia).
Слайд 38Infections in the remainder of the 1st post transplant year
Opportunistic
infections are most common after the first month and then
uncommon 6-12 months after transplant.CMV (10-25% of recipients).
CMV disease: fever, elevated LFTs, leukopaenia, anaemia, thrombocytopaenia, arthralgias, myalgias and lymphadenopathy.
In more severe cases, tissue-invasive CMV infection occurs (pulmonary, upper or lower GIT, CNS).
Слайд 39Most reliable diagnosis is PCR for viral DNA in blood.
Untreated CMV has a mortality as high as 15%.
Bacterial, viral,
fungal and protozoan infections are all possible.Слайд 40Infections after the 1st post transplant year
Community-acquired infections unrelated to
immune suppression are more common.
Слайд 41Non-infectious causes of fever
Pulmonary atelectasis (early post op)
Severe acute rejection
Administration
of antilymphocyte Abs
Post transplant lymphoma
Слайд 42Initial Work-up for febrile post transplant pt
FBC + diff
Serum creatinine
Urine
dipstix and analysis
Urine and blood cultures
CXR
Consider transplant U/S
Additional tests done
according to clinical settingСлайд 43Cardiovascular disorders
The risk of CVS disease is increased 3 to
5 fold in kidney transplant recipients compared to the general
population.Atherosclerotic vascular disease accounts for 30-50% of deaths after the first post transplant year.
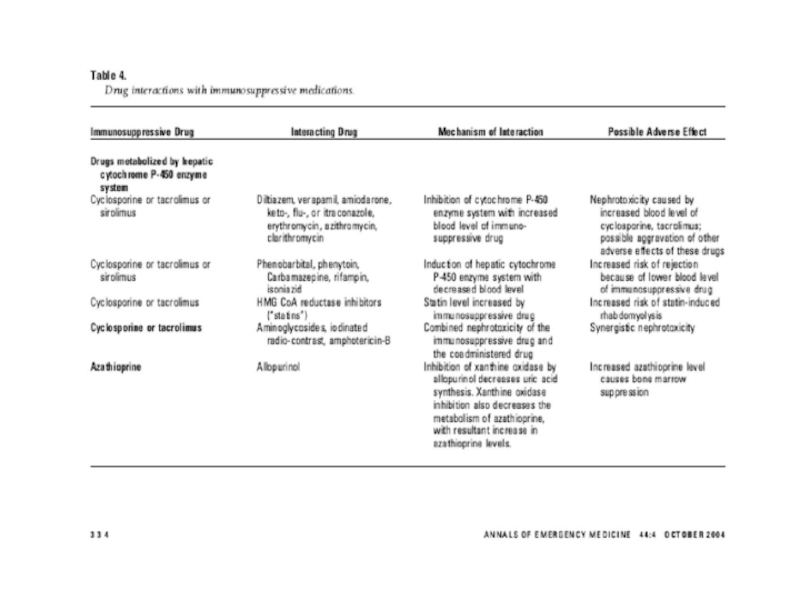
Diltiazem, Verapamil + Amiodarone inhibit hepatic cytochrome p450 enzyme system resulting in elevated levels + possible toxicity of cyclosporine, tracrolimus and sirolimus.
Слайд 44HT Complications
Prevalence is 70-90% in renal transplant recipients.
None of the
parentarel or oral antiHT agents commonly used to Rx severely
elevated BP is C/I in these pts.Possible aetiologies of HT include: graft rejection, cyclosporine toxicity, glomerulonephritis, graft renal artery stenosis, essential HT from native kidney, hypercalcaemia and steroid use.
Слайд 45Pulmonary Complications
Most common pulmonary problem is pneumonia.
Nonopportunistic post op pneumonia
in the 1st month, after which opportunistic pulmonary infection takes
over.After the 1st year, community-acquired infection is common.
If erythromycin, azithromycin or clarithromycin are used to treat pneumonia, then the dose of cyclosporine, tacrolimus + sirolimus should be reduced for duration of Rx.
Слайд 46GIT Problems
Abnormalities in LFTs occur frequently.
The clinical presentation of acute
cholecystitis may be blunted by immunosuppressive Rx (esp. by corticosteroid
use).The incidence and severity of acute pancreatitis is increased.
Слайд 47Neurologic + Psychiatric Disorders
Cyclosporine and tacrolimus cause similar neurological S/Es
(headache, insomnia, tremors, parasthesias, cramp of extremities). The S/Es are
dose + blood level related.Opportunistic CNS infections occur in 5-10% of renal transplant recipients.
Слайд 48Meningitis: Listeria monocytogenes, cryptococcus + TB.
Encephalitis or meningoencephalitis: CMV, toxoplasma
or HSV.
Post transplant lymphoma commonly involves CNS.
Depression and suicide are
more prevalent.Remember steroid psychosis.
Слайд 49Haematological Disorders
Anaemia, leukopaenia, thrombocytopaenia alone or in combination is common.
Often due to drugs.
HUS: anaemia, thrombocytopaenia, ARF, increased LDH, Decreased
haptoglobin, schistocytes on peripheral blood smear. HUS in renal transplant pts has been associated with cyclosporine or tacrolimus Rx, acute vascular rejection + CMV infection.Слайд 50Post transplant erythrocytosis occurs in 10-20% of pts during the
first post transplant year + persists long term in 50%
of affected individuals. Venesection may be required + ACE inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blocker Rx can decrease erythropoiesis.Слайд 51Musculoskeletal Disorders
Corticosteroids, and to a lesser extent cyclosporine + tacrolimus
predispose to osteoporosis.
Cyclosporine + tacrolimus cause hyperuricaemia which predisposes to
gout.NSAIDs can worsen renal fxn + colchicine can interact with cyclosporin causing raised LFTs, leukopaenia, proximal muscle weakness and rhabdomyolysis
Слайд 52With pts on azothioprine, the use of allopurinol can cause
severe bone marrow suppression unless the azothioprine dose is reduced.
Слайд 53Dermatological Disorders
A variety of disorders can occur: acne,herpes zoster, human
papilloma virus, squamous cell Ca (more comman than basal cell
Ca), human herpes virus 8 – related KS.Слайд 54Electrolyte Abnormalities
Cyclosporin + tacrolimus cause hyperkalaemia (decreased K excretion in
urine) and hypomagnesemia (increased Mg excretion in urine).
Non anion gap
metabolic acidosis can be due to tubular dysfunction due to acute or chronic rejection of kidney transplant.Слайд 55New Onset DM
De nova DM occurs in 5-20% of renal
transplant recipients.
Contributing to this complication are corticosteroids, cyclosporine + tacrolimus.
Слайд 56Malignancy
Transplant recipients are at significantly higher risk for cancers than
the general population because of (1) chronic immunosuppression, (2) chronic
antigenic stimulation, (3) increased susceptibility to oncogenic viral infections, and (4) direct neoplastic action of immunosuppressants. Transplant recipients have a significant overall 2-5 fold higher risk in both sexes for cancers of the colon, larynx, lung, and bladder and in men for cancers of the prostate and testis.Слайд 57Stress-dose Corticosteroid Coverage
Severely ill renal transplant pts presenting to ED
will require stress-dose corticosteroid coverage (hydrocortisone 50-100 mg IV 6-8
hrly) to avoid acute adrenal insufficiency, unless the pt has not been receiving corticosteroids for > 6-12 months.Слайд 58Acute Rejection
Indirect pathway: soluble donor Ag that is processed by
recipient APC + then presented to recipient T-cells in the
groves of MHC I + II molecules.Direct pathway: donor APC presenting both class I + class II epitopes to recipient T cells.
Hyperacute rejection occurs immediately in the operating room, when the graft becomes mottled and cyanotic. This type of rejection is due to unrecognised compatibility of blood groups A, AB, B, and O (ABO) or a positive T-cell crossmatch.
Слайд 59Acute rejection appears within the first 3 posttransplant months and
affects 30% of cadaveric transplants and 27% of transplants from
living donors. Approximately 20% of patients with transplants experience recurrent rejection episodes. Patients present with decreasing urine output, hypertension, rising creatinine, and mild leukocytosis. Fever, graft swelling, pain, and tenderness may be observed with severe rejection episodes.The final diagnosis depends upon a graft biopsy.
Слайд 60Chronic Rejection
Usually apparent from 3 months onwards and detected clinically
by gradual deteriation in graft fxn.
Factors associated with chronic rejection
are both immunological + non-immunological.Слайд 61Take Home Massage
1. If a transplant pt presents the ED,
always consider the possibility of organ rejection, infection or drug
toxicity.2. The signs + symptoms of medical problems are often subtle.
3. Inability of the pt to not take their oral immunosuppressants even for one day should be considered an emergency.
4. When prescribing in the ED, always be careful to avoid drug interactions + toxicity.
Слайд 62References
1. Care of the Renal Transplant Recipient in the Emergency
Department, KK Venkat + Arvind Venkat, Annals of Emergency Medicine,
44:4 October 2004.2. Principles of Surgical Patient Care, 2nd edition, CJ Mieny + V Mennen, 2003.
3. Rosen’s Emergency Medicine, Concepts and Clinical Practice, 5th edition.
4. Emedicine, Transplant, Renal, Richard Sinert + Mert Erogul.