Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
The role of intrauterine infections in the developing of pathology in
Содержание
- 1. The role of intrauterine infections in the developing of pathology in
- 2. About 2500 different infections are known in
- 3. "TORCH" A group of infections widespread
- 4. The rate of the Intrauterine Infections as
- 5. According to some literary facts, in the
- 6. Factors of risk of the development of
- 7. The risk of infections in the I
- 8. Analyzable materials Medical documentation: individual card of
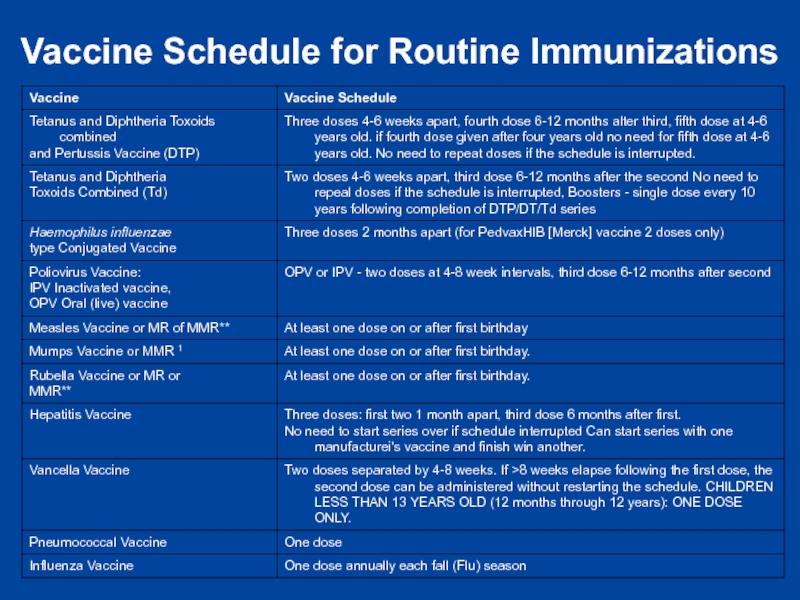
- 9. Vaccine Schedule for Routine Immunizations
- 10. Слайд 10
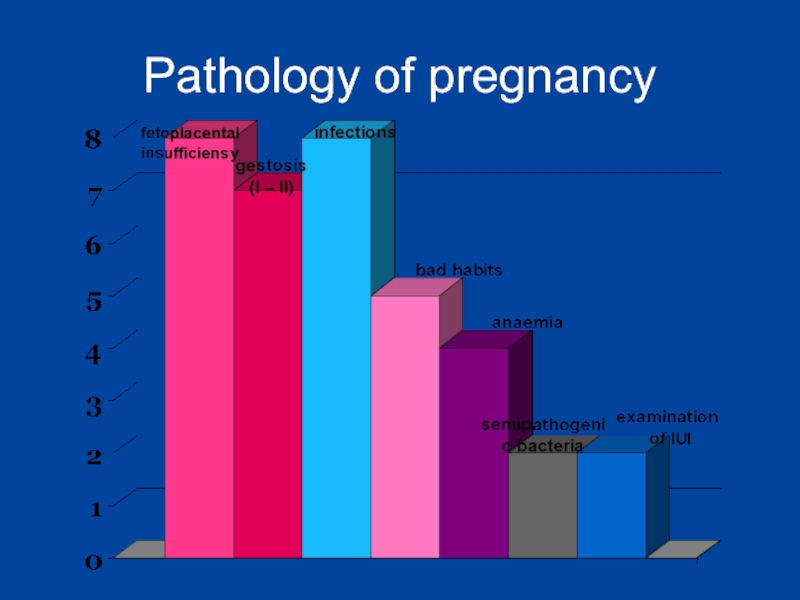
- 11. Pathology of pregnancy
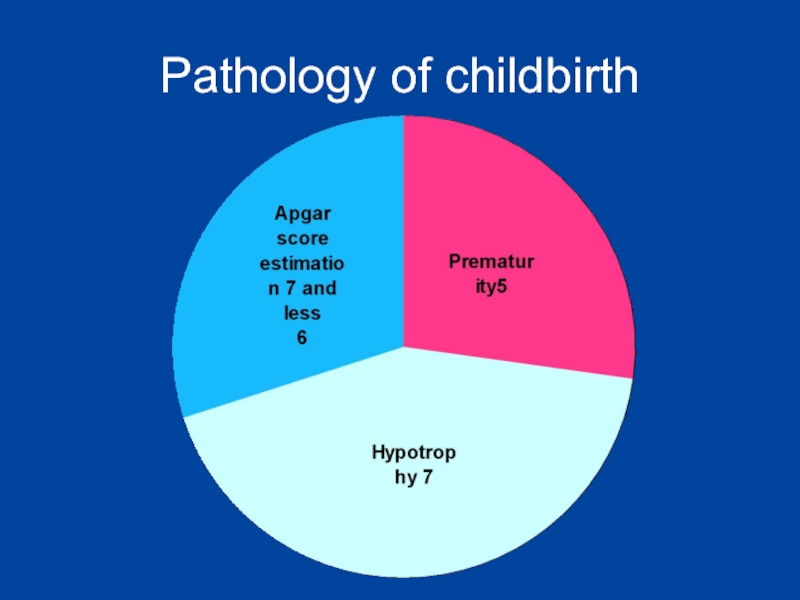
- 12. Pathology of childbirth
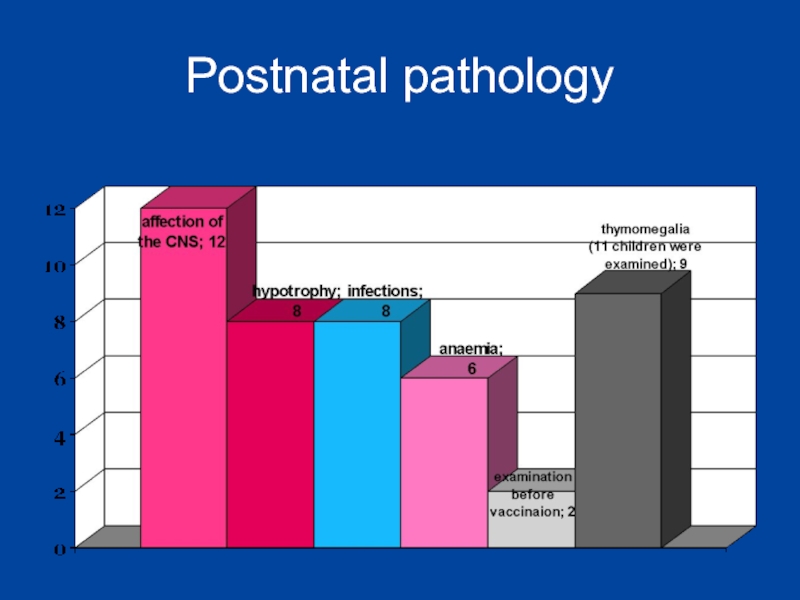
- 13. Postnatal pathology
- 14. Слайд 14
- 15. Morphological markers of intrauterine infections
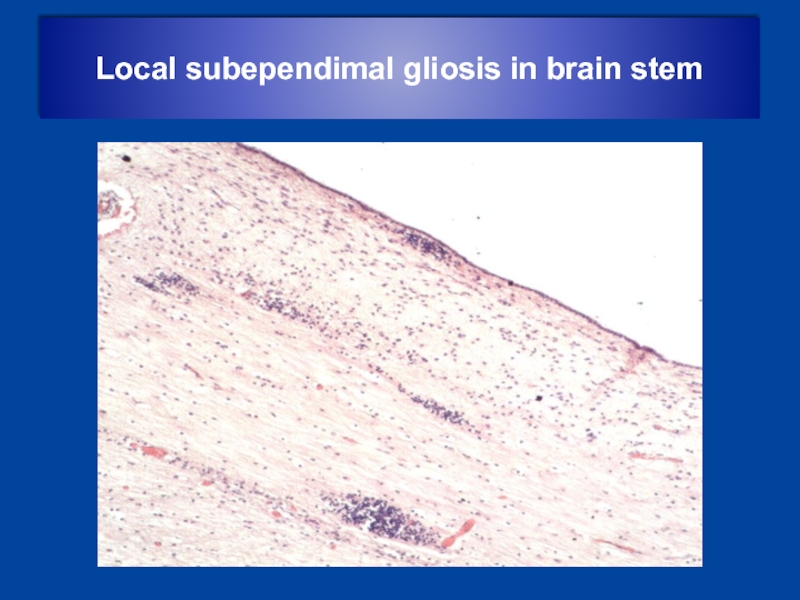
- 16. Local subependimal gliosis in brain stem
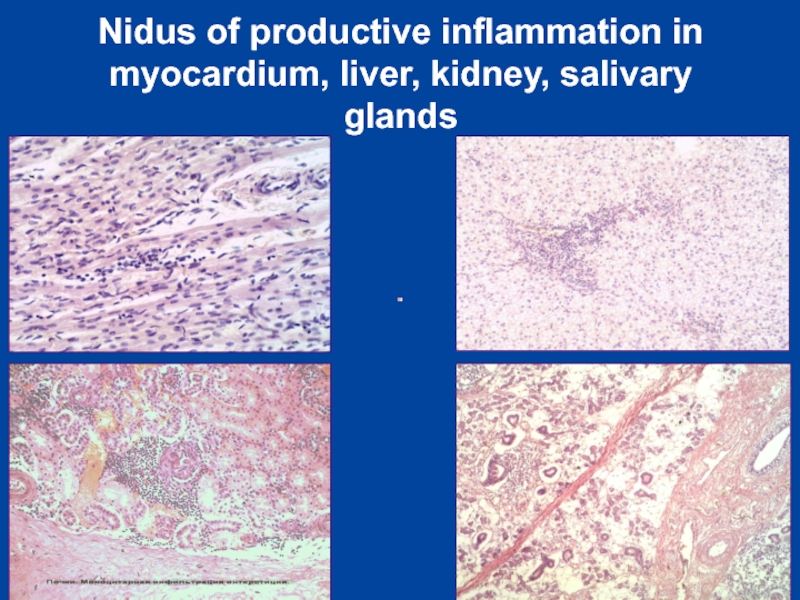
- 17. Nidus of productive inflammation in myocardium, liver, kidney, salivary glands
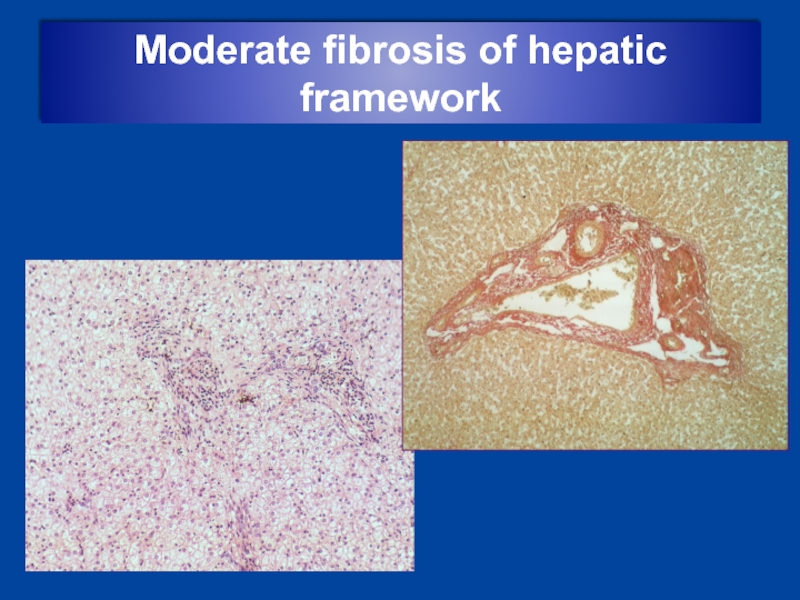
- 18. Moderate fibrosis of hepatic framework
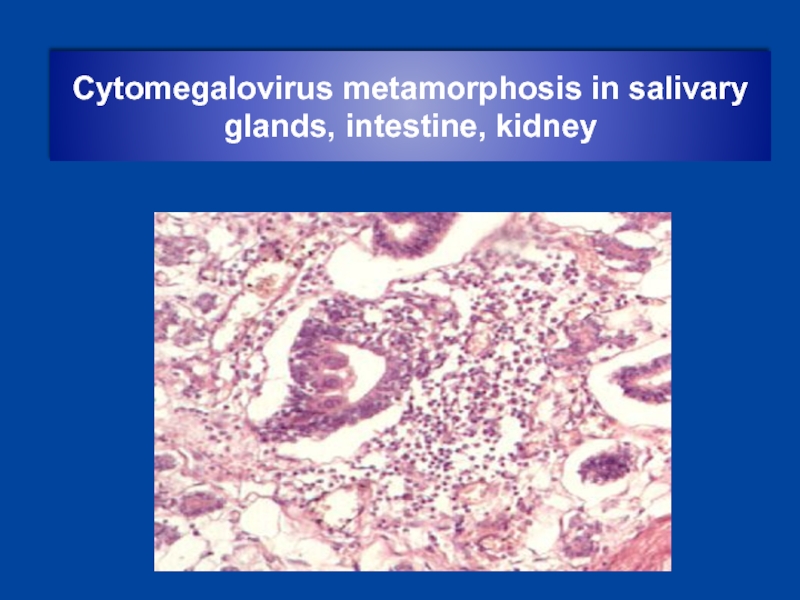
- 19. Cytomegalovirus metamorphosis in salivary glands, intestine, kidney
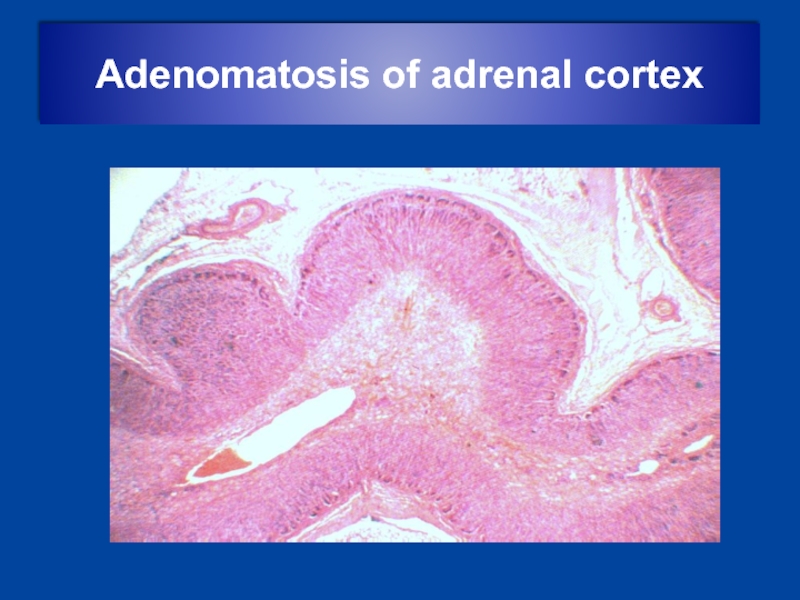
- 20. Adenomatosis of adrenal cortex
- 21. Tymomegalia, prematury fat metamorphosis of tymus
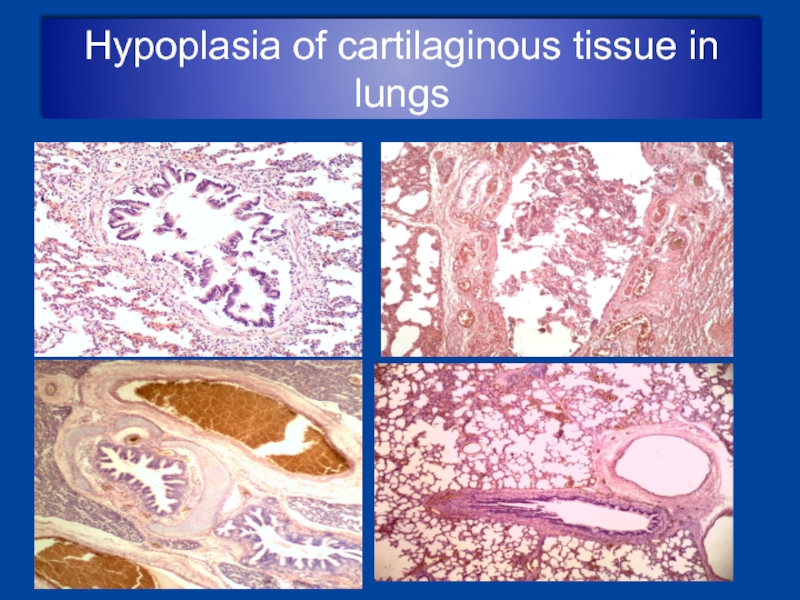
- 22. Hypoplasia of cartilaginous tissue in lungs
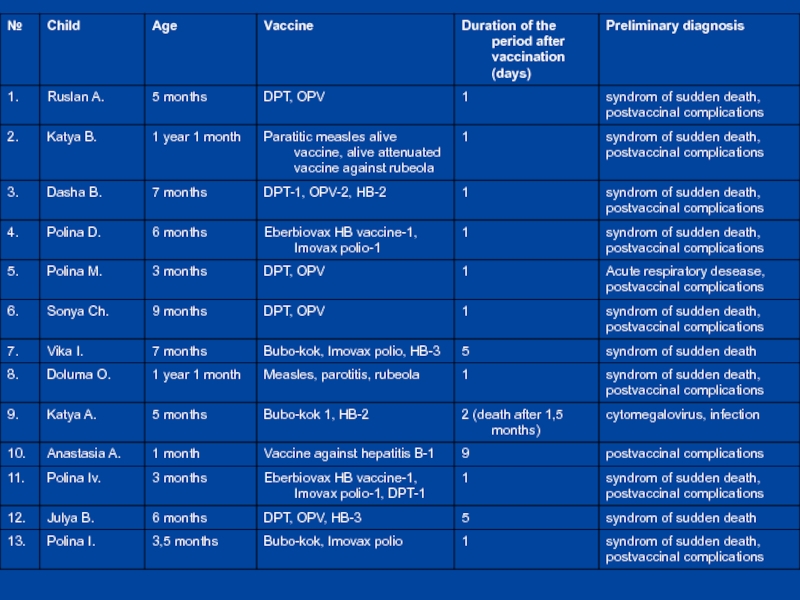
- 23. ConclusionIn this 13 cases vaccine was not
- 24. Algorithm of examination of mothers and children
- 25. Thank you for your attention!
- 26. Скачать презентанцию
About 2500 different infections are known in modern medical science.Theoretically every infection in the period of pregnancy can influence badly on the embryo and the foetus.If a pregnant woman have a
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2About 2500 different infections are known in modern medical science.
Theoretically
every infection in the period of pregnancy can influence badly
on the embryo and the foetus.If a pregnant woman have a light infection even without symptoms, it can lead to grave injures and even death of the foetus.
The range of the perinatal infections is very wide.
Слайд 3"TORCH"
A group of infections widespread in a population,
which have similar clinical presentations and cause firm structural defects
of different systems and organs of the foetus.Т — toxoplasmosis
О — other (syphilis, chlamydia, enterovirus, hepatitis A, В, gonorrhoea, listeriosis, measles, parotiditis and papilloma virus infection)
R — rubeola
С — cytomegalia
Н — herpes
Слайд 4The rate of the Intrauterine Infections as the main reason
of the perinatal mortality has grown up the last years
by 3,5-4,2 times. The reasons:Deterioration of the women’s health level of the reproductive age before the pregnancy
The increase of extragenital diseases, severe
anaemia, diseases of the urino-genital system by 2-16 times
The decrease of the immuno-endocrine status
Слайд 5According to some literary facts, in the autopsy material from
the dead foetuses and newborns the revelation of the causative
agents of the Interauterine Infections was detected in more than 60%. This fact points out considerably higher importance of the infectious pathology in the development of the perinatal mortality in comparison to the facts of the official statistic accountancy.Слайд 6Factors of risk of the development of the intrauterine infection
Aggravation of the chronic infection that a pregnant woman have
(chronic diseases of the breathing organs, digestion, caries, tonsillitis)Urogenital infections (pyelonephritis, bacteriuria, colpitis, endocervicitis)
Disbacteriosis of the intestine and bacterial vaginosis
Complication of the pregnancy: anemia, gestosis, fetoplacental insufficiency, acute respiratory viral infection - in the second half of pregnancy
Acute respiratory viral infection in the childbirth, prenatal moving of amniotic fluid away, pathology of childbirth activity, using of obstetric supplies
Слайд 7The risk of infections
in the I trimester of pregnancy
- 15%
in the II trimester - 45%
in the III trimester
- 70%Слайд 8Analyzable materials
Medical documentation:
individual card of the pregnant woman
and the puerpera
history of the childbirth
history
of the development of the newborn history of the development of the child
card of preventive vaccinations form 063/у
conclusion of an expert in forensic medicine or a pathoanatomist
conclusion of the commission of investigation of postvaccinal complications
Ready histological materials
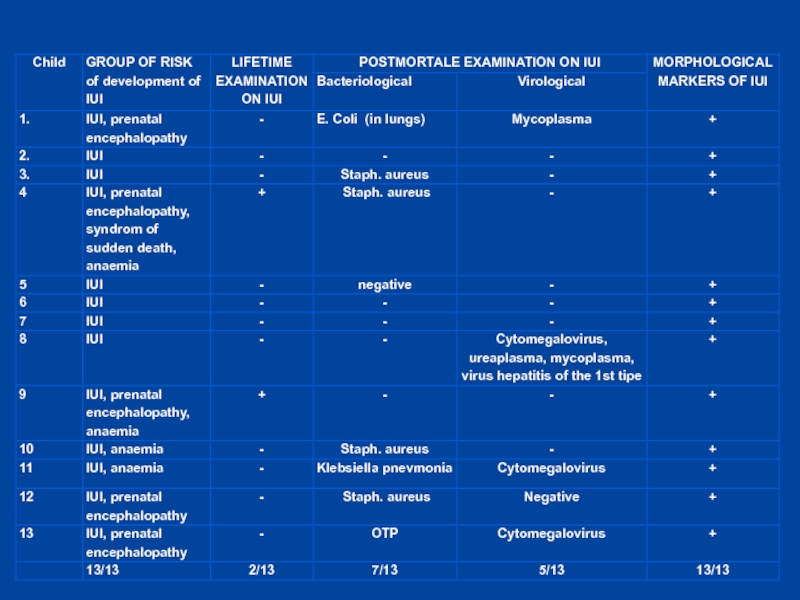
Слайд 23Conclusion
In this 13 cases vaccine was not the cause of
death. An intrauterine infection was the cause.
Women should be examined
during the pregnancy to find out if they have a risk of intrauterine infections.The immunity of girls is stronger than the immunity of boys.
Слайд 24Algorithm of examination of mothers and children having high risk
of intrauterine infections
careful collecting of anamnoses data (pregnancy, childbirth)
full
clinical and laboratory examination of children and mothers with high risk of infectionsverification of infection by not less than two methods (virological, cytological, seroimmunological, PCR)
in case of revelation of intrauterine infection, the child must complete a course of etiotropic therapy before the vaccination
the vaccination should be done only after negative results of the second examination, according to an individual plan