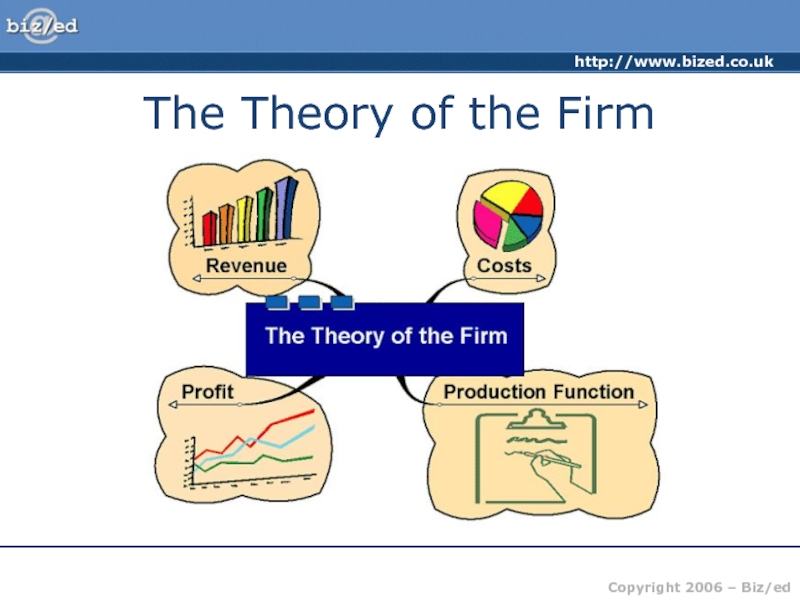
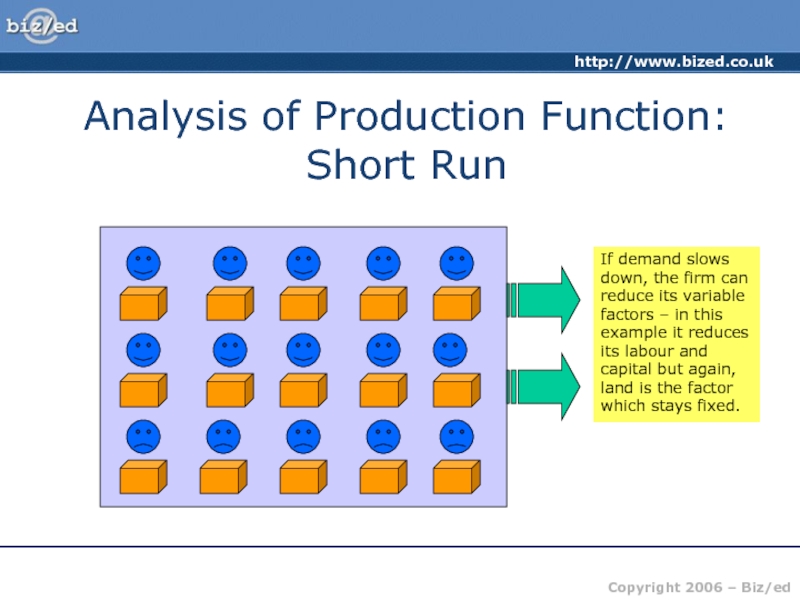
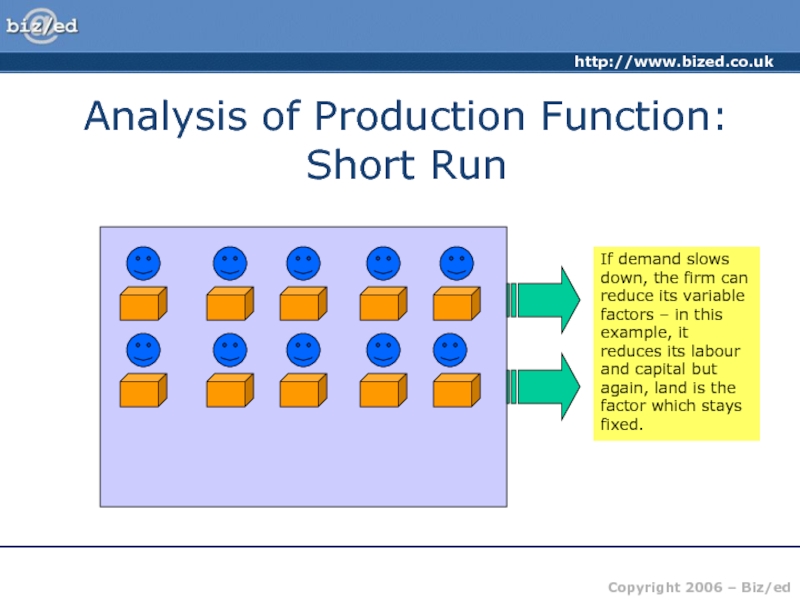
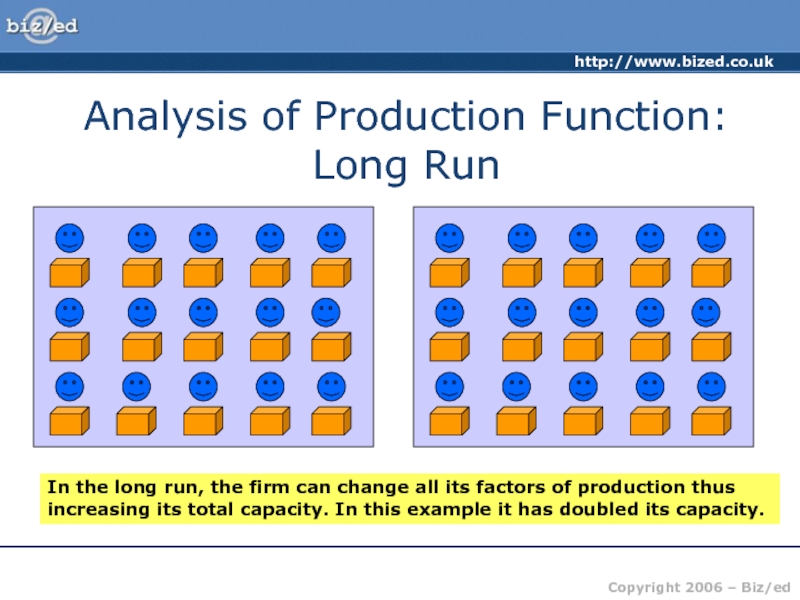
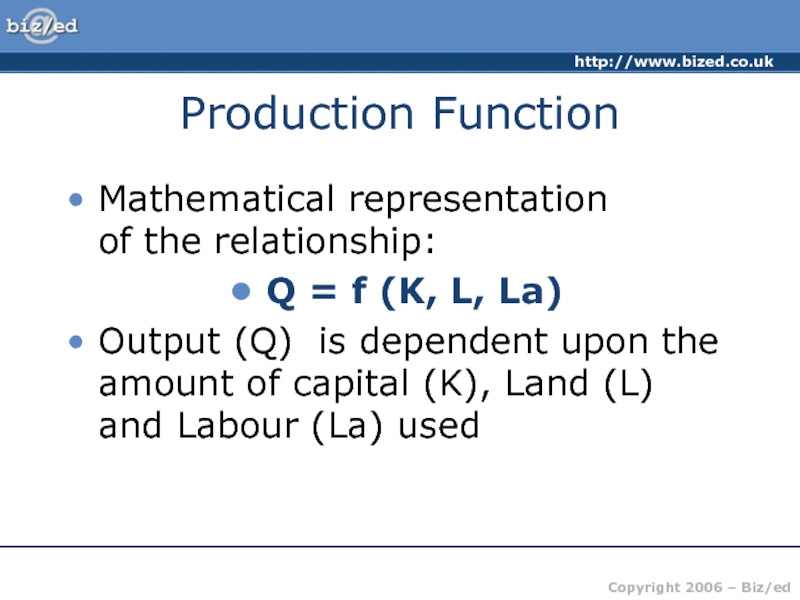
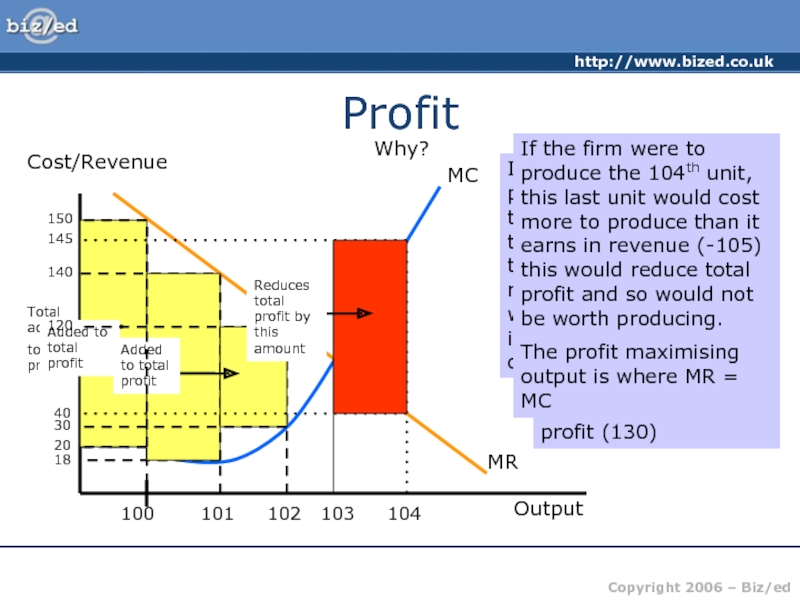
of producing one more unit of output – the price
received from selling that extra unit.
MC
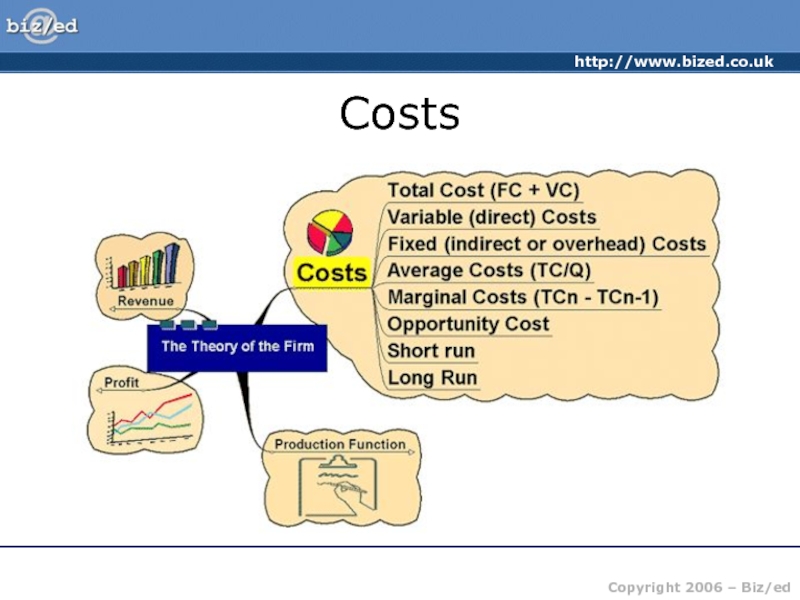
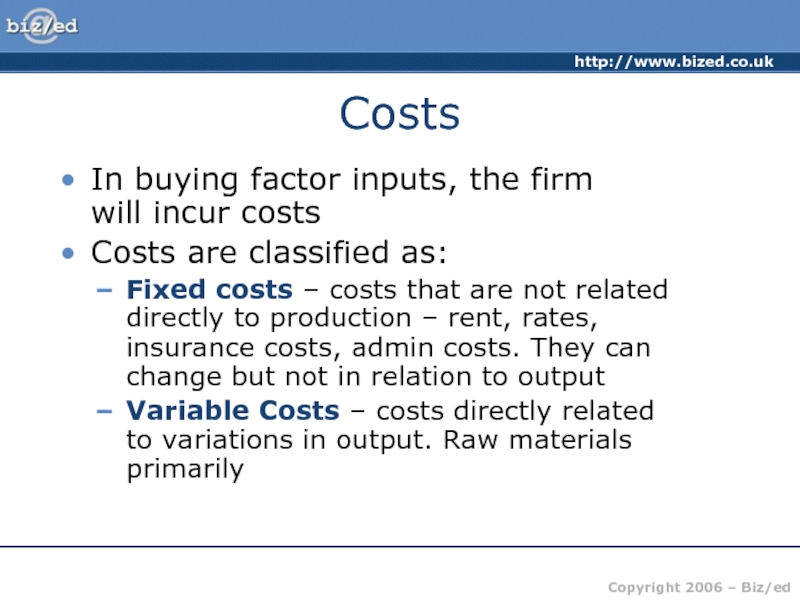
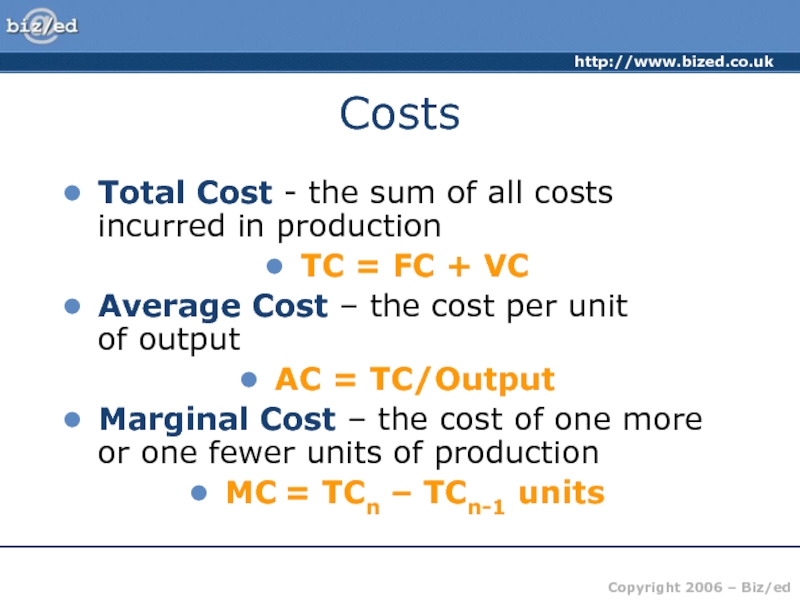
MC – The cost of producing ONE extra unit of production
100
Assume output is at 100 units. The MC of producing the 100th unit is 20.
The MR received from selling that 100th unit is 150. The firm can add the difference of the cost and the revenue received from that 100th unit to profit (130)
20
150
If the firm decides to produce one more unit – the 101st – the addition to total cost is now 18, the addition to total revenue is 140 – the firm will add 128 to profit. – it is worth expanding output.
101
18
140
30
120
The process continues for each successive unit produced. Provided the MC is less than the MR it will be worth expanding output as the difference between the two is ADDED to total profit
102
40
145
104
103
If the firm were to produce the 104th unit, this last unit would cost more to produce than it earns in revenue (-105) this would reduce total profit and so would not be worth producing.
The profit maximising output is where MR = MC