Слайд 1Topic 6:
Strategies for Competing in Global Markets
Слайд 2Why is the World Economy Globalizing?
Previously closed national economies are
opening up their markets to foreign companies
Importance of geographic distance
is shrinking due to the Internet
Growth-minded companies are racing to stake out positions in the markets of more and more countries
Слайд 3Why Do Companies Expand into Foreign Markets?
To gain access to
new customers
To obtain access to valuable natural resources
To capitalize on
resource strengths and capabilities
To achieve low-cost & competitiveness
Spread business risk across wider market base
Слайд 4International vs. Global Competition
International or Multinational Competitor
Company operates in a
select few foreign countries, with modest ambitions to expand further
Global
Competitor
Company markets products in many foreign countries and is expanding operations into additional country markets annually
Слайд 5Characteristics of
Foreign Markets
Market differences among countries
Cost variations across countries
Fluctuating
exchange rates
Differences in host government trade policies
Pattern of International competition
Multi-Country
competition or
Global competition
Слайд 6How Markets Differ from Country to Country
Consumer tastes and preferences
Consumer
buying habits
Market size and growth potential
Distribution channels
Driving forces
Competitive pressures
One of
the biggest concerns of companies
competing in foreign markets is whether to customize their product offerings in each different country market to match the tastes and preferences of local buyers or whether to offer a mostly standardized product worldwide.
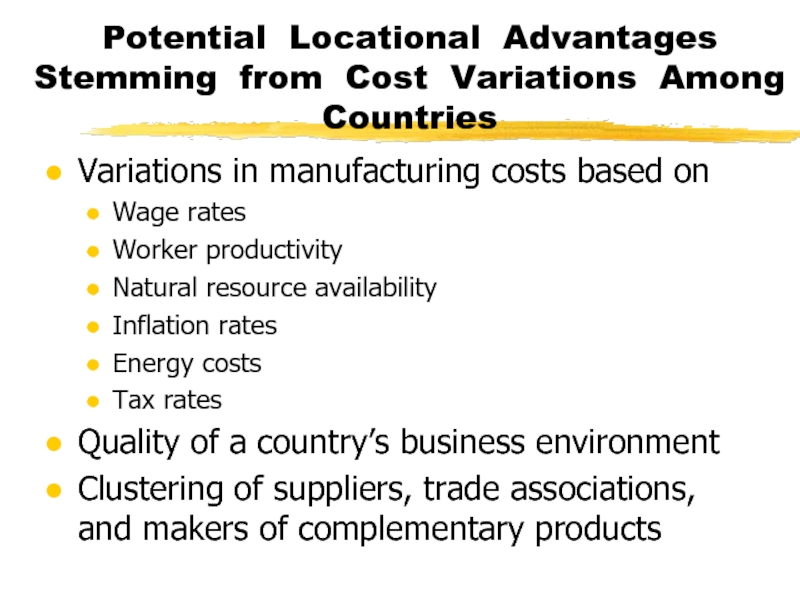
Слайд 7Potential Locational Advantages Stemming from Cost Variations Among Countries
Variations in
manufacturing costs based on
Wage rates
Worker productivity
Natural resource availability
Inflation rates
Energy costs
Tax
rates
Quality of a country’s business environment
Clustering of suppliers, trade associations, and makers of complementary products
Слайд 8Differences in Host
Government Trade Policies
Local content requirements
Import tariffs or quotas
Restrictions
on exports
Regulations regarding prices of imports
Other regulations
Technical standards
Product certification
Prior approval
of capital spending projects
Withdrawal of funds from country
Minority ownership by local citizens
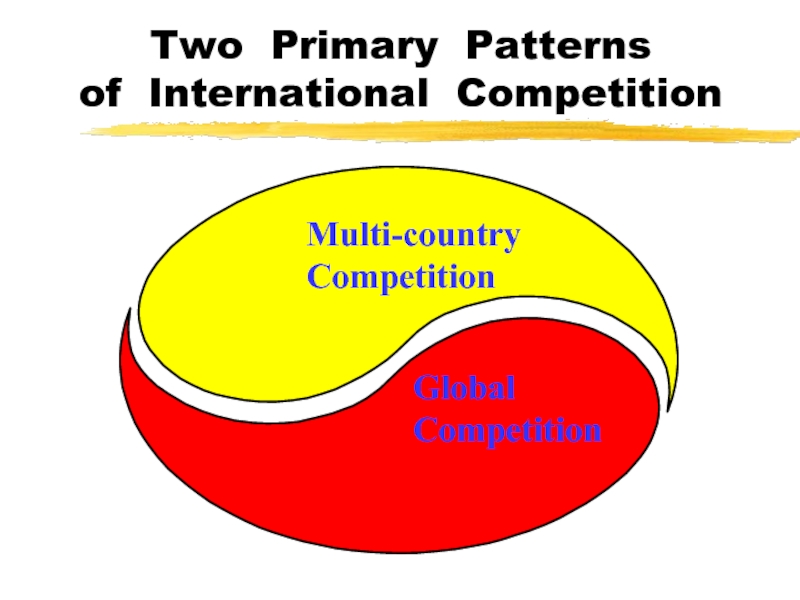
Слайд 9Two Primary Patterns
of International Competition
Multi-country
Competition
Global
Competition
Слайд 10Characteristics of Multi-Country Competition
Each country market is self-contained
Competition in one
country market is independent of competition in other country markets
Rivals
competing in one country market differ from set of rivals competing in another country market
Rivals compete for national market leadership
No “international” market, just a collection of country markets
Слайд 11Characteristics of Global Competition
Competitive conditions across country markets are strongly
linked together
Many of the same rivals compete in many of
the same country markets
Rivals compete for world-wide leadership
A true international market
A firm’s competitive position in one country is affected by its position in other countries
A firm’s overall competitive advantage is based on its entire world-wide operations
Слайд 12Strategy Options for Entering & Competing in Foreign Markets
Exporting
Licensing
Franchising strategy
Multi-country
strategy
Global strategy based on
Low cost
Differentiation
Focus
Integrated Low cost-Differentiation
Strategic alliances or
joint ventures
Слайд 13Characteristics of
Export Strategies
Involves using domestic plants as a production
base for exporting to foreign markets
Excellent initial strategy to pursue
international sales
Advantages
Minimizes both risk and capital requirements
Conservative way to test international waters
Minimizes direct investments in foreign countries
An export strategy is vulnerable when
Manufacturing costs in home country are higher than in foreign countries where rivals have plants
High shipping costs are involved
Слайд 14Characteristics of
Licensing Strategies
Licensing makes sense when a firm
Has valuable
technical know-how or a patented product but does not have
international capabilities or resources to enter foreign markets
Desires to avoid risks of committing resources to markets which
Are unfamiliar
Present economic uncertainty
Are politically volatile
Disadvantage
Risk of providing valuable technical know-how to foreign firms and losing some control over its use
Слайд 15Characteristics of Franchising Strategies
Often is better suited to global expansion
efforts of service and retailing enterprises (e.g., McDonalds, Hilton Hotels,
Tricon Global Restaurants, etc.)
Advantages
Franchisee bears most of costs and risks of establishing foreign locations
Franchiser has to expend only the resources to recruit, train, and support franchisees
Disadvantage
Maintaining cross-country quality control
Слайд 16Multi-Country Strategy
Strategy is matched to local market needs
Different country strategies
are called for when
Significant country-to-country differences in customers’ needs exist
Buyers
in one country want a product different from buyers in another country
Host government regulations preclude uniform global approach
Two drawbacks
1. Poses problems of transferring competencies across borders
2. Works against building a unified competitive advantage
Слайд 17Multi-Country
Strategies: Examples
Microsoft in PC Software
Localizes PC software to reflect
local languages
Products localized into more than 30 languages
Nestle in Instant
Coffee
Produces 200 types of coffees
From light blend for the US market to dark roast for the Latin American market
McDonald’s in Fast Food
Different hamburgers for different markets
Слайд 18Global Strategy
Strategy for competing is similar in all country markets
Involves
Coordinating
strategic moves globally
Selling in many, if not all, nations where
a significant market exists
Works best when products and buyer requirements are similar from country to country
Слайд 19Competitive Strategy Principle
A multi-country strategy is appropriate for industries where
multi-country competition dominates!
A global strategy works best in
markets that are
globally
competitive or beginning to globalize!
Слайд 20 Competing Multinationally
Three ways to gain competitive advantage
1. Locating activities
among nations to lower costs or achieve greater product differentiation
2.
Efficient/effective transfer of competitively valuable competencies and capabilities from domestic to foreign markets
3. Coordinating dispersed activities in ways a domestic-only competitor cannot
Слайд 21Locating Activities to Build a
Global Competitive Advantage
Two issues
Whether to
Concentrate
each activity in a few countries or
Disperse activities to many
different nations
Where to locate activities -Which country is best location for which activity?
Слайд 22Concentrating Activities
Activities should be concentrated when
Costs of manufacturing or other
value chain activities are meaningful lower in certain locations than
in others
There are sizable scale economies in performing the activity
There is a steep learning curve associated with performing an activity in a single location
Certain locations have superior resources, allow better coordination of related activities, or offer other valuable advantages
Слайд 23Dispersing Activities
Activities should be dispersed when
They need to be performed
close to buyers
Transportation costs, scale diseconomies, or trade barriers make
centralization expensive
Buffers for fluctuating exchange rates, supply interruptions, and adverse politics are needed
Слайд 24Transferring Valuable Competencies & Capabilities
Transferring competencies, capabilities, and resource strengths
across borders contributes to
Development of broader competencies and capabilities
Achievement of
dominating depth in some competitively valuable area
Dominating depth in a competitively valuable capability is a strong basis for sustainable competitive advantage over
Other multinational or global competitors and
Small domestic competitors in host countries
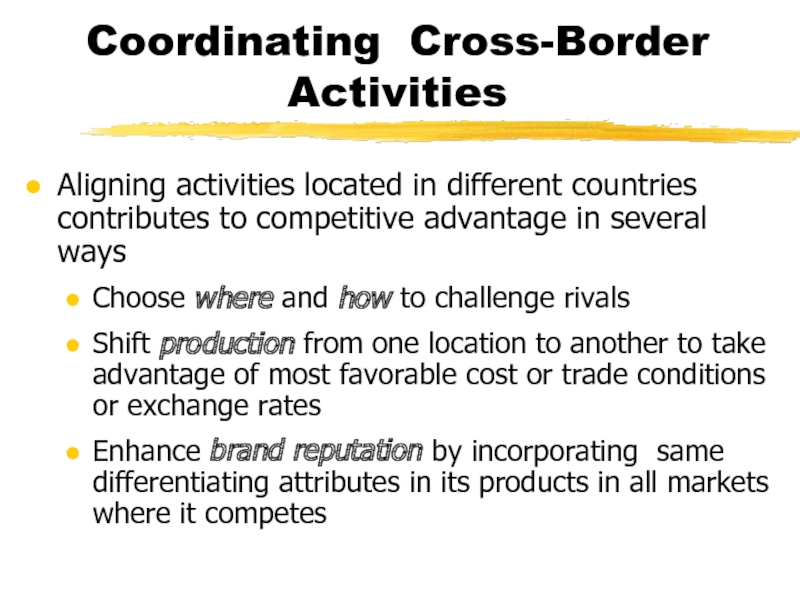
Слайд 25Coordinating Cross-Border Activities
Aligning activities located in different countries contributes to
competitive advantage in several ways
Choose where and how to challenge
rivals
Shift production from one location to another to take advantage of most favorable cost or trade conditions or exchange rates
Enhance brand reputation by incorporating same differentiating attributes in its products in all markets where it competes
Слайд 26What Are Profit Sanctuaries?
Profit sanctuaries are country markets where a
firm
Has a strong or protected market position and
Derives substantial
profits
Generally, a firm’s most strategically crucial profit sanctuary is its home market
Profit sanctuaries are a valuable competitive asset in global industries!
Слайд 27What is Cross-Market Subsidization
Involves supporting competitive offensives in one market
with resources/profits diverted from operations in other markets
Competitive power of
cross-market subsidization results from a multinational firm’s ability to
Draw upon its organizational resources and profits in other country markets to
Help mount an attack on single-market or one-country rivals and
Try to lure away their customers with lower prices, discount promotions, heavy advertising, or other offensive tactics
Слайд 28Achieving Global Competitiveness
via Cooperation
Cooperative agreements / strategic alliances with foreign
companies are a means to
Enter a foreign market or
Strengthen a
firm’s competitiveness in world markets
Purpose of alliances
Joint research efforts
Technology-sharing
Joint use of production or distribution facilities
Marketing / promoting one another’s products
Слайд 29Benefits of Strategic Alliances
Gain scale economies in production and/or marketing
Fill
gaps in technical expertise or knowledge of local markets
Share distribution
facilities and dealer networks
Direct combined competitive energies toward defeating mutual rivals
Useful way to gain agreement on important technical standards
Слайд 30Pitfalls of Strategic Alliances
Becoming too dependent on another firm for
essential expertise over the long-term
Different motives and conflicting objectives
Time
consuming; slows decision-making
Language and cultural barriers
Mistrust when collaborating in competitively sensitive areas
Clash of egos and company cultures
Слайд 31Guidelines in Forming Strategic Alliances
Pick a good partner, one that
shares
a common vision
Be sensitive to cultural differences
Recognize the alliance must benefit both sides
Both parties have to deliver on their commitments in the agreement
Structure decision-making process so actions can be taken swiftly when needed
Parties must do a good job of managing the learning process, adjusting the alliance agreement over time to fit new circumstances
Слайд 32Characteristics of Competing in
Emerging Foreign Markets
Tailoring products for the big,
emerging markets often involves
Making more than minor product changes and
Becoming
more familiar with the local cultures
Companies have to attract buyers with bargain prices as well as better products
Specially designed and/or specially packaged products may be needed to accommodate local market circumstances
Management team must usually consist of a mix of expatriate and local managers
Слайд 33Strategies for Local Companies
in Emerging Markets
Optimal strategic approach hinges on
Whether a firm’s competitive assets are suitable only for the
home market or can be transferred abroad
Whether industry pressures to move toward global competition are strong or weak
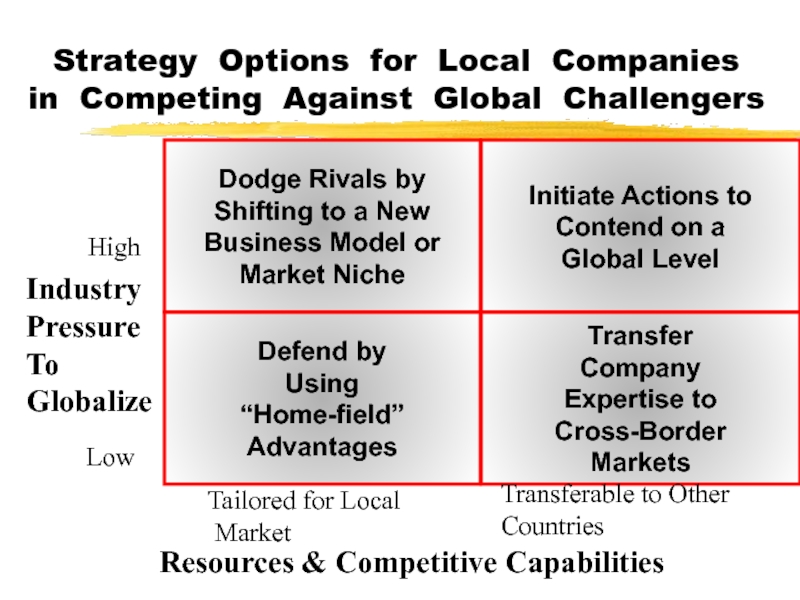
Слайд 34Strategy Options for Local Companies in Competing Against Global Challengers
Tailored
for Local
Market
Transferable to Other
Countries
Resources & Competitive Capabilities
High
Industry
Pressure
To
Globalize
Low