Prepared by: Abdildina Akbota
Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Turner Syndrome Prepared by: Abdildina Akbota
Содержание
- 1. Turner Syndrome Prepared by: Abdildina Akbota
- 2. Plan1. History2. Frequency3. Genetic mechanisms 4. Symptoms of Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome4. Phenotip5. Diagnosis6. Videoclip
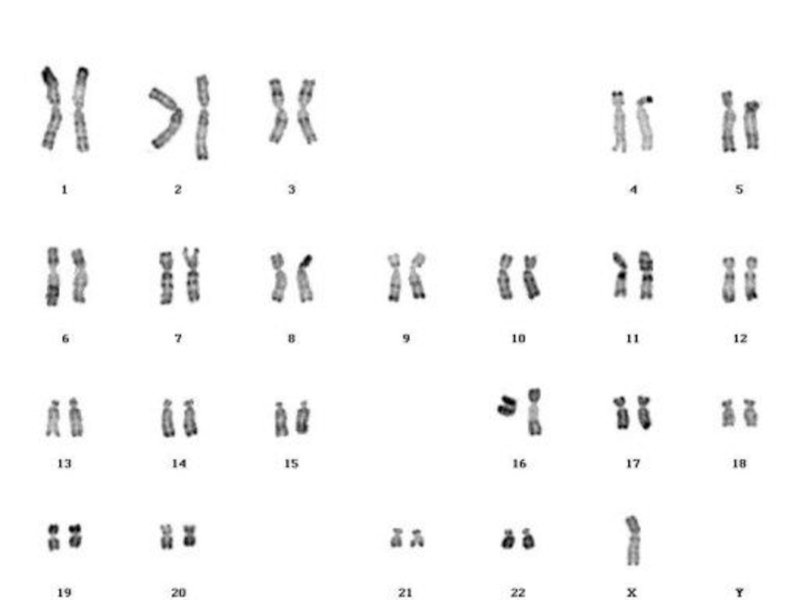
- 3. 45 X Karyotype syndrome. Bonnevie-Ullrich syndrome. Gonadal dysgenesis. Monosomy X. Synonyms and related keywords
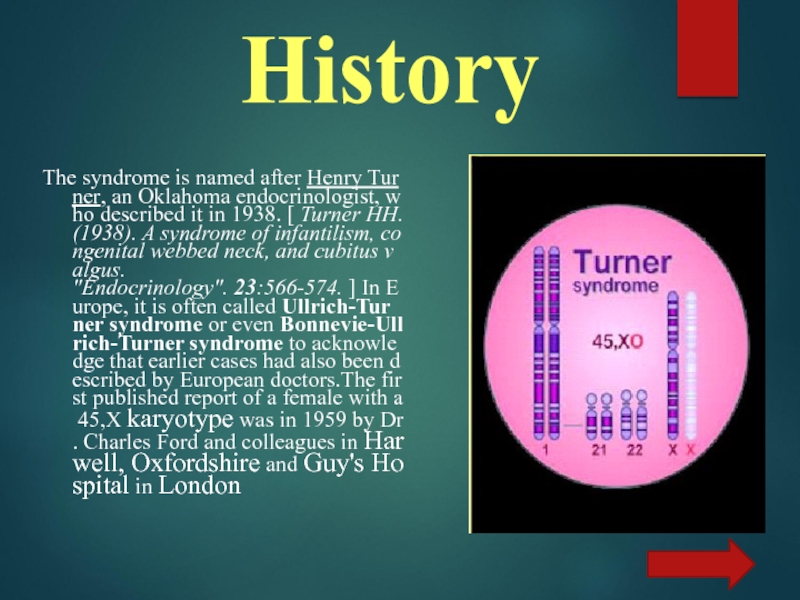
- 4. HistoryThe syndrome is named after Henry Turner, an Oklahoma endocrinologist, who described it in 1938. [ Turner HH. (1938). A syndrome of infantilism, congenital webbed neck, and cubitus valgus. "Endocrinology". 23:566-574. ] In Europe, it is often called Ullrich-Turner syndrome or even Bonnevie-Ullrich-Turner syndrome to acknowledge that earlier cases had also been described by European doctors.The first published report of a female with a 45,X karyotype was in 1959 by Dr. Charles Ford and colleagues in Harwell, Oxfordshire and Guy's Hospital in London
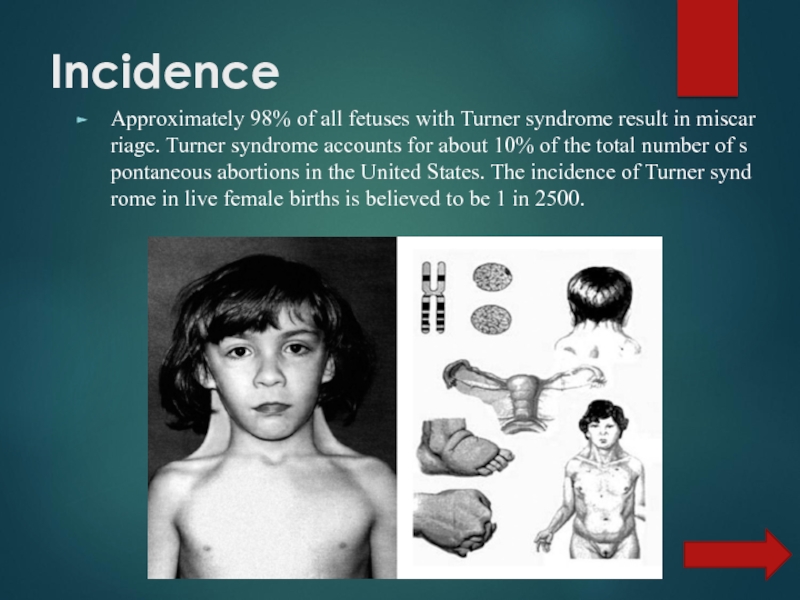
- 5. Incidence Approximately 98% of all fetuses with Turner syndrome result in miscarriage. Turner syndrome accounts for about 10% of the total number of spontaneous abortions in the United States. The incidence of Turner syndrome in live female births is believed to be 1 in 2500.
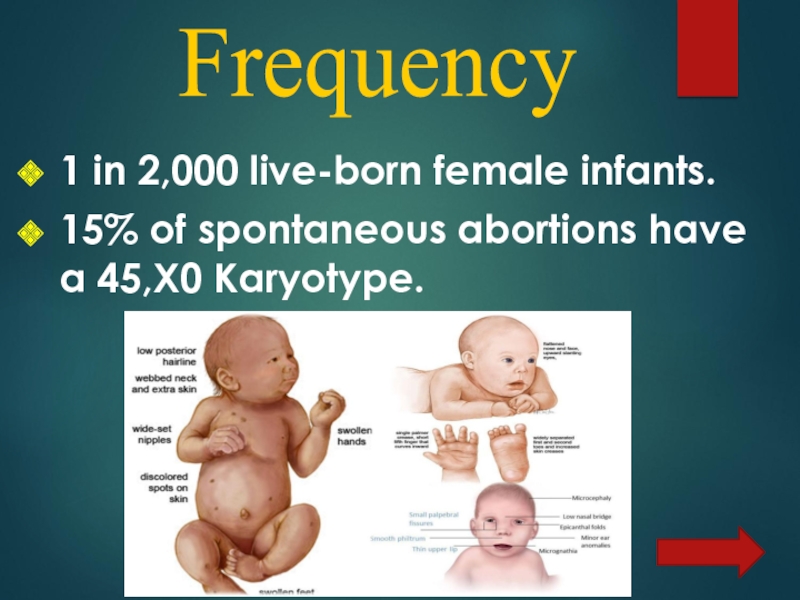
- 6. 1 in 2,000 live-born female infants. 15% of spontaneous abortions have a 45,X0 Karyotype.Frequency
- 7. Genetic mechanisms 1. Absence of one copy
- 8. Mental retardation is rare, but many patients
- 9. Symptoms of Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome Many newborns have
- 10. 45, X0 – Turner syndromesTotal fetal hydropsnormal
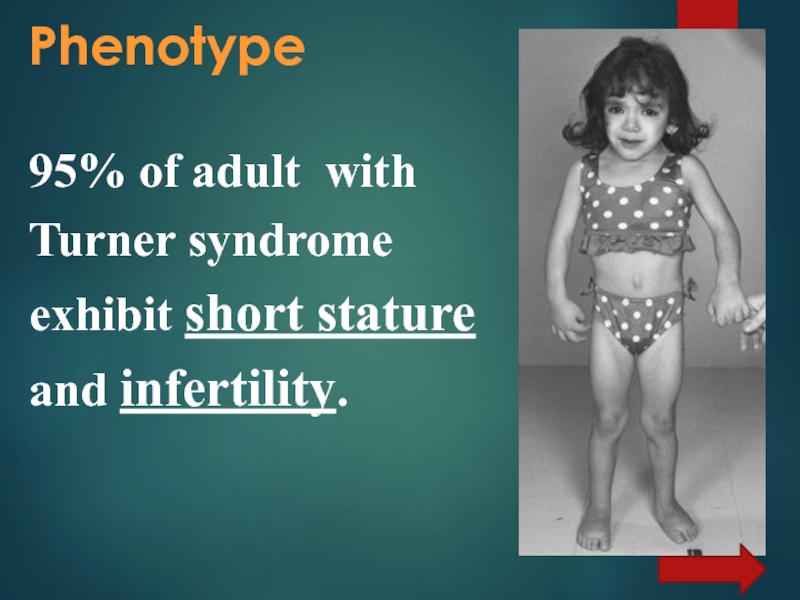
- 11. Phenotype 95% of adult with Turner syndrome exhibit short stature and infertility.
- 12. 94% of patients are infertile
- 13. LymphedemaMay be present at any age. It
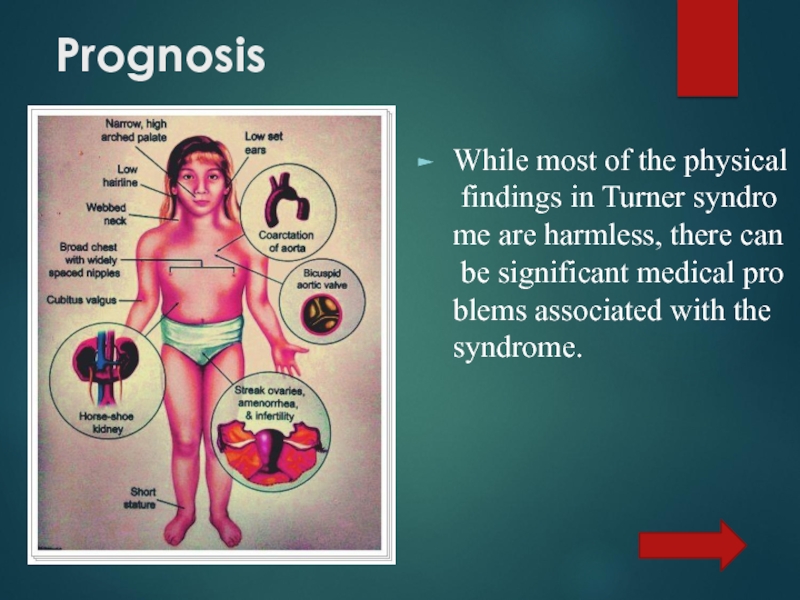
- 14. Prognosis While most of the physical findings in Turner syndrome are harmless, there can be significant medical problems associated with the syndrome.
- 15. Should be considered in Individuals with :Primary
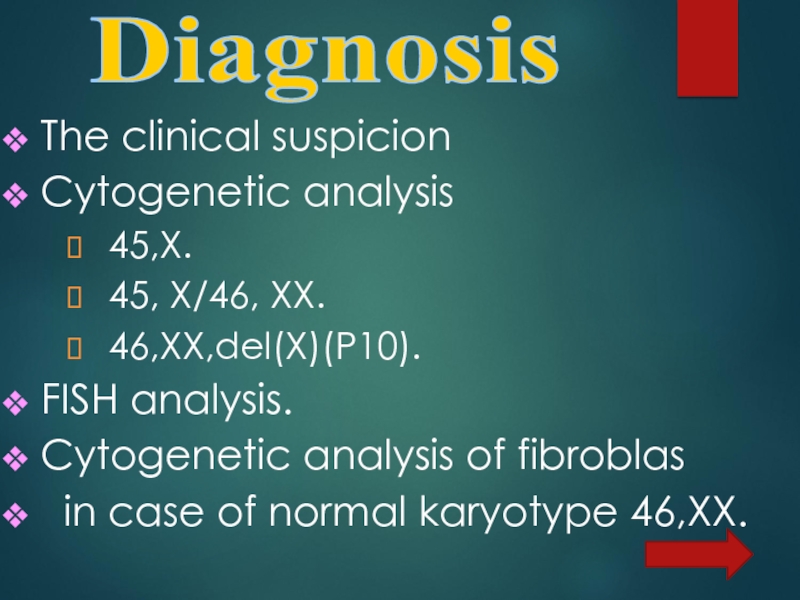
- 16. The clinical suspicion Cytogenetic analysis 45,X.
- 17. Слайд 17
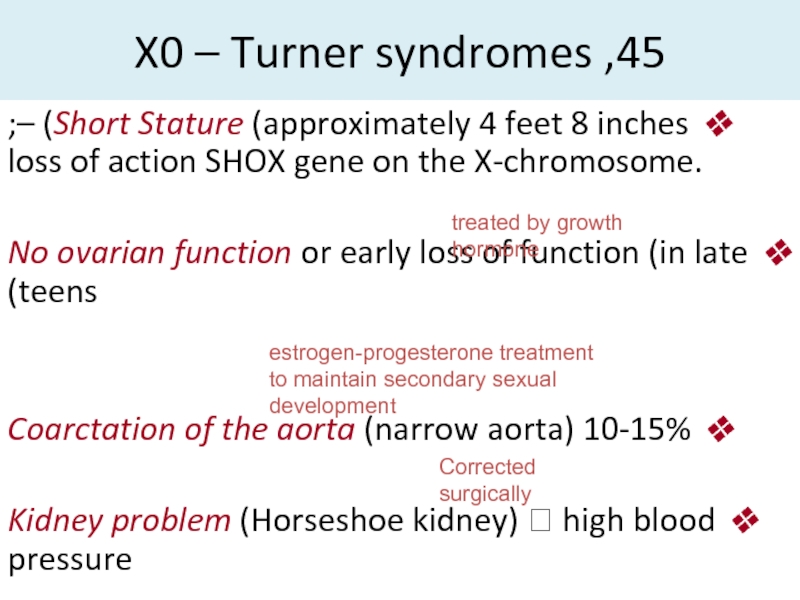
- 18. 45, X0 – Turner syndromesShort Stature (approximately
- 19. Слайд 19
- 20. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Plan
1. History
2. Frequency
3. Genetic mechanisms
4. Symptoms of Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome
4.
Phenotip
5. Diagnosis
6. Videoclip
Слайд 3 45 X Karyotype syndrome.
Bonnevie-Ullrich syndrome.
Gonadal
dysgenesis.
Monosomy X.
Synonyms and related keywords
Слайд 4History
The syndrome is named after Henry Turner, an Oklahoma endocrinologist, who described it in 1938. [ Turner HH. (1938). A syndrome of infantilism, congenital webbed neck, and cubitus valgus. "Endocrinology". 23:566-574. ] In Europe, it is often called Ullrich-Turner syndrome or even Bonnevie-Ullrich-Turner syndrome to acknowledge that earlier cases had also been described by European doctors.The first published report of a female with a 45,X karyotype was in 1959 by Dr. Charles Ford and colleagues in Harwell, Oxfordshire and Guy's Hospital in London
Слайд 5Incidence
Approximately 98% of all fetuses with Turner syndrome result in miscarriage. Turner syndrome accounts for about 10% of the total number of spontaneous abortions in the United States. The incidence of Turner syndrome in live female births is believed to be 1 in 2500.
Слайд 61 in 2,000 live-born female infants.
15% of spontaneous abortions
have a 45,X0 Karyotype.
Frequency
Слайд 7Genetic mechanisms
1. Absence of one copy of X chromosome.
Paternal loss in 62%
Maternal in 48%
2. Patient
with Mosaic karyotype. Ex. 46,XX/45,X
3. Structural rearrangement result in loss of
Xp material.
Ex. 46,iX(Xq)
4. Loss of the SHOX gene.
Variety of Turner syndrome.
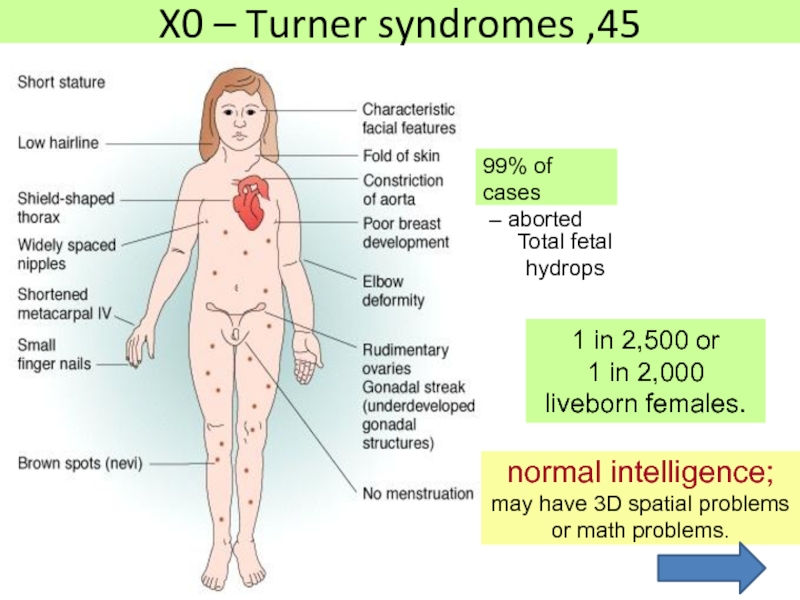
Слайд 8Mental retardation is rare, but many patients experience a reduction
in some perceptual possibilities and, as a result, low scores
in nonverbal tests and in mathematics, even though the scores obtained for the verbal component of the intelligence tests are average or even high.Growth retardation, often from birth (100%).
Gonadal dysgenesis with amenorrhea and sterility.
Lymphatic edema of the rear of the hands and feet (40%).
Broad chest with combined sternum deformity.
Widely placed, hypoplastic and inverted nipples (80%).
Anomalous in shape and protruding ears (80%).
Low level of hair growth.
Short neck with excess skin and pterygoid folds (80%).
Cubitus valgus (70%).
Narrow, hyper-concave and depressed nails (70%).
Congenital malformations of the kidneys (60%).
Hearing loss (50%).
Congenital heart and aortic defects (coarctation of the aorta and valve pathology, enlargement and dissection of the aorta) (20-40%).
Idiopathic arterial hypertension (AH) (27%).
Слайд 9Symptoms of Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome
Many newborns have only very mild manifestations;
but some have marked dorsal lymphedema of the hands and
feet, as well as lymphedema or skin folds on the posterior surface of the neck. Other common anomalies include the pterygoid folds of the neck, the broad thorax and the retracted nipples. The affected girls have a low growth rate compared to family members. Less common signs are a low line of hair growth on the back of the neck, ptosis, multiple pigmented nevuses, short fourth metacarpal and metatarsal bones, protruding pads of fingers with curls at the ends of the fingers, and hypoplasia of the nails. Also marked cubitus valgus (valgus deviation in the elbow joint).Слайд 1045, X0 – Turner syndromes
Total fetal
hydrops
normal intelligence;
may have
3D spatial problems
or math problems.
99% of cases
–
aborted1 in 2,500 or
1 in 2,000
liveborn females.
Слайд 12 94% of patients are infertile
Pregnancy
has been achieved by:
1. Fresh embryo.
2.
Frozen embryo transfer. Delivery by caesarean section is
related to small pelvic outlet size.
Infertility
Слайд 13Lymphedema
May be present at any age.
It is the cause
of the webbed neck and low
posterior hairline.
In infants, the
combination of dysplastic orhypoplastic nails and lymphedema gives a
characteristic sausage-like appearance to the fingers and toes.
Слайд 14Prognosis
While most of the physical findings in Turner syndrome are harmless, there can be significant medical problems associated with the syndrome.
Слайд 15Should be considered in Individuals with :
Primary or secondary amenorrhea.
Adult women with unexplained infertility
Unexplained short stature.
Turner syndrome may
be diagnosed prenatally by:1. Amniocentesis.
2. Chorionic villous sampling.
Diagnosis
Слайд 16 The clinical suspicion
Cytogenetic analysis
45,X.
45, X/46,
XX.
46,XX,del(X)(P10).
FISH analysis.
Cytogenetic analysis of fibroblas
in case of normal karyotype 46,XX.Diagnosis
Слайд 1845, X0 – Turner syndromes
Short Stature (approximately 4 feet 8
inches) –;
loss of action SHOX gene on the X-chromosome.
No
ovarian function or early loss of function (in late teens)Coarctation of the aorta (narrow aorta) 10-15%
Kidney problem (Horseshoe kidney) high blood pressure
treated by growth hormone
estrogen-progesterone treatment
to maintain secondary sexual development
Corrected surgically