Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Word Stress
Содержание
- 1. Word Stress
- 2. PlanGeneral Notes on Word Stress.Types of Word
- 3. The Nature of Word Stress
- 4. The Nature of Word StressWord Stressis a
- 5. The Nature of Word StressScientists about Word
- 6. The Nature of Word StressScientists about Word
- 7. The Nature of Word StressThe effect of
- 8. The Nature of Word StressIn the stressed
- 9. The Nature of Word StressWord Stress
- 10. Types of Word Stress
- 11. Types of Word StressWe distinguish the following
- 12. Types of Word StressEnglish Word Stress
- 13. Degrees of Word Stress
- 14. Degrees of Word Stress The syllables in a
- 15. Degrees of Word Stress In American English there
- 16. Degrees of Word Stress In transcription stress is
- 17. Placement of Word Stress
- 18. Placement of Word StressAccording to its placement in a word, stress can be:fixed free shifting
- 19. Placement of Word StressFixed(the position of the
- 20. Placement of Word StressFree(the location of the
- 21. Placement of Word StressShifting(the word stress can
- 22. Placement of Word StressTo define the position
- 23. Placement of Word Stress The phonological structure of
- 24. Placement of Word Stress The number of syllables
- 25. Placement of Word Stress Morphological factor shows that
- 26. Placement of Word Stress stress-neutral (-al, -able, -en,
- 27. Placement of Word StressThe grammatical category the
- 28. Placement of Word Stress The semantic factor (for
- 29. Common Rules of Word Stress
- 30. Common Rules of Word Stress Two-syllable
- 31. Common Rules of Word Stress Three-syllable
- 32. Common Rules of Word Stress Three-syllable
- 33. Common Rules of Word Stress Words
- 34. Common Rules of Word Stress Words
- 35. Common Rules of Word Stress Words
- 36. Common Rules of Word Stress Compound
- 37. Common Rules of Word Stress Compound
- 38. Common Rules of Word Stress The
- 39. Functions of Word Stress
- 40. Word Stress
- 41. Functions of Word Stress The constitutive
- 42. Questions:What is WORD STRESS? What types of
- 43. Literature Леонтьева С.Ф. Теоретическая
- 44. Thank you for your attention!
- 45. Скачать презентанцию
PlanGeneral Notes on Word Stress.Types of Word Stress.Degrees of Word Stress.Placement of Word Stress.Common Rules of Word Stress in English.Functions of Word Stress.
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Plan
General Notes on Word Stress.
Types of Word Stress.
Degrees of Word
Stress.
of Word Stress.Слайд 4The Nature of Word Stress
Word Stress
is a greater degree of
prominence of a syllable or syllables as compared to the
other syllables of the wordСлайд 5The Nature of Word Stress
Scientists about Word Stress:
D. Jones: Word
Stress is the degree of force, which is accompanied by
a strong force of exhalation and gives an impression of loudness.A. C. Gimson: English word stress or accent is a complex phenomenon, marked by the variations in force, pitch, quality and quantity.
Слайд 6The Nature of Word Stress
Scientists about Word Stress:
B. A. Bogoroditsky:
Stress as an increase of energy, accompanied by an increase
of expiratory and articulatory activity.S. F. Leontyeva: Word stress can be defined as the singling out of one or more syllables in a word, which is accompanied by the change of the force of utterance, pitch of the voice, qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the sound which is usually a vowel.
Слайд 7The Nature of Word Stress
The effect of prominence of the
stressed syllable is achieved by a number of phonetic parameters:
Pitch
Loudness
Length
Vowel
QualityThese 4 factors usually work together in combination, but they are not equally important. The strongest effect is produced by pitch and length.
Слайд 8The Nature of Word Stress
In the stressed syllable:
the force of
utterance is greater, which is connected with more energetic articulation;
the
pitch of the voice is higher, which is connected with stronger tenseness of the vocal cords and the walls of resonance cavity;the quantity of the vowel is greater, the vowel becomes longer;
the quality of the vowel is different (in unstressed syllables it is usually narrow).
Слайд 9The Nature of Word Stress
Word Stress
is singling out
of one or more syllables in a word, which is
accompanied by the change of the force of utterance, pitch of the voice, qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the sound, which is usually a vowel.Слайд 11Types of Word Stress
We distinguish the following types of Word
Stress:
dynamic (force) stress is achieved by greater force with which
the syllable is pronounced (Russian, English, French, German); musical (tonic) stress is achieved through the change of pitch/musical tone (Japanese, Korean);
quantitative stress is achieved through the changes in the quantity of the vowels, which are longer in the stressed syllables (Russian);
qualitative stress is achieved through the changes in the quality of the vowel (Russian).
Слайд 12Types of Word Stress
English Word Stress
is traditionally
defined as dynamic, but in fact, the special prominence of
the stressed syllables is manifested not only through the increase of intensity, but also through the changes in the vowel quantity, consonant and vowel quality and pitch of the voice.Слайд 14Degrees of Word Stress
The syllables in a word are characterized
by different degrees of prominence. There are as many degrees
of stress in a word as there are syllables.In English there are 3 degrees of stress:
primary (strong, main, principal);
secondary (half-stressed, half-strong);
weak (unstressed).
Слайд 15Degrees of Word Stress
In American English there are 4 degrees
of stress:
primary (strong, main, principal);
secondary (half-stressed, half-strong);
tertiary (on the last
but one syllable in the words with suffixes -ary, -ory, -ony: ´dictioˏnary.weak (unstressed).
Слайд 16Degrees of Word Stress
In transcription stress is indicated by placing
the stress mark before the symbol of the first sound
of the stressed syllable.Primary stress is marked by a raised short vertical stroke and secondary stress is marked by a lowered one:
examination [ɪgˏzᴂmɪ´neɪʃ(ǝ)n]
Слайд 18Placement of Word Stress
According to its placement in a word,
stress can be:
fixed
free
shifting
Слайд 19Placement of Word Stress
Fixed
(the position of the word stress is
always the same,
it is restricted to a particular syllable):
in French (the last syllable),
in Finnish and Czech (the first syllable),
in Polish (the last but one syllable).
Слайд 20Placement of Word Stress
Free
(the location of the word stress is
not
confined to a specific position,
it can fall on
any syllable of the word): English, Russian, Italian, Greek, Spanish, etc.
Слайд 21Placement of Word Stress
Shifting
(the word stress can change
its position
in different forms
of the word and its derivatives):
´music
- mu´sicianСлайд 22Placement of Word Stress
To define the position of word stress
it is necessary to take into account
a number of
factors: phonological structure of the syllable;
the number of syllables in a word;
morphological factor;
the part of speech the word belongs to;
the semantic factor.
Слайд 23Placement of Word Stress
The phonological structure of the syllable is
related to the status of a particular syllables in terms
of the degree of sonority.The sounds that possess a greater degree of sonority contribute to the greater prominence of the syllable. A syllable is strong when it contains a long vowel or a diphthong or a short vowel followed by two consonants:
a´rrive - de´velop
Слайд 24Placement of Word Stress
The number of syllables in a word
influences the number of stresses and the position of stress.
There
are stress patterns typical of two-syllable words, three-syllable words and so on. In multi-syllable words there appears secondary stress.
Слайд 25Placement of Word Stress
Morphological factor shows that in complex words
the placement of stress depends on the type of suffix.
Suffixes
are divided into:stress-neutral (which do not affect the stress placement in the stem);
stress-fixing (which influence stress in the stem);
stress-attracting (which carry stress themselves).
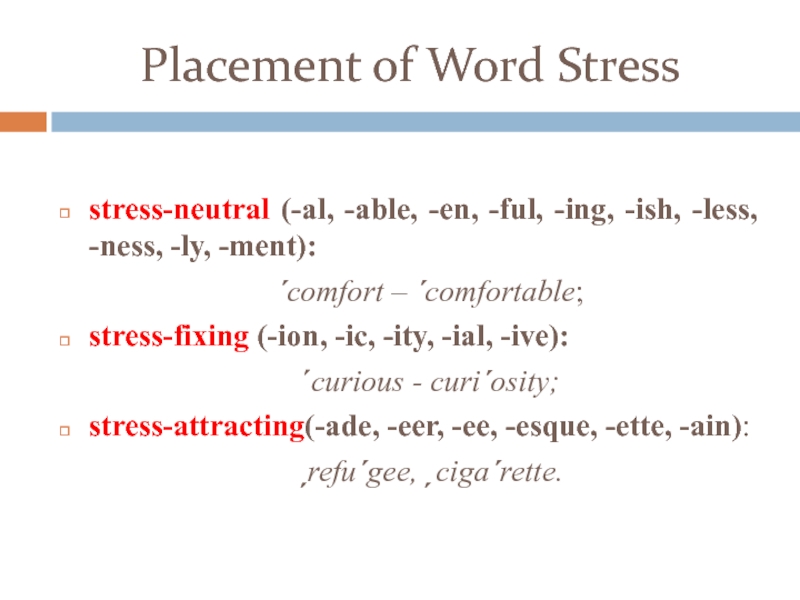
Слайд 26Placement of Word Stress
stress-neutral (-al, -able, -en, -ful, -ing, -ish,
-less, -ness, -ly, -ment):
´comfort – ´comfortable;
stress-fixing (-ion, -ic, -ity,
-ial, -ive): ´curious - curi´osity;
stress-attracting(-ade, -eer, -ee, -esque, -ette, -ain):
ˏrefu´gee, ˏciga´rette.
Слайд 27Placement of Word Stress
The grammatical category the word belongs to:
´contrast
– to con´trast
´habit – ha´bitual
´music – mu´sician
´insult – to in´sult
´record
– to re´cord´present – to pre´sent
Слайд 28Placement of Word Stress
The semantic factor (for compound words and
words with the so-called separable prefixes).
The majority of such
words have two equally strong stresses, both stressed parts are considered to be of equal semantic importance:compound adjectives: ´hard-´working, ´blue-´eyed,
verbs with post positions : ´sit´down, ´take´off,
numerals from 13 to 19: ´ four´teen, ´six´teen.
Слайд 30
Common Rules of Word Stress
Two-syllable words (verbs, adjectives, adverbs):
the second
syllable is stressed if it contains a long vowel or
a diphthong, or if it ends with more than one consonant: a´pply, a´ssist. But! ´honest.the first syllable is stressed if the final syllable contains a short vowel and one (or no) final consonant: ´enter, ´open.
Two-syllable words (nouns):
the first syllable is stressed if the second syllable contains a short vowel: ´money;
the second syllable is stressed if the second syllable contains a long vowel or a diphthong: es´tate.
Слайд 31
Common Rules of Word Stress
Three-syllable words (verbs):
the last but one
syllable is stressed if the last syllable contains a short
vowel and ends with one consonant: de´termine.the final syllable is stressed if it contains a long vowel or a diphthong, or ends with more than one consonant: enter´tain.
Слайд 32
Common Rules of Word Stress
Three-syllable words (nouns, adjectives):
the middle syllable
is stressed if the syllable preceding the final syllable contains
a long vowel or a diphthong, or if it ends with more than one consonant:di´saster;
the first syllable is stressed if the final syllable contains a short vowel and the middle syllable contains a short vowel and ends with not more than one consonant:
´cinema
´insolent
Слайд 33
Common Rules of Word Stress
Words with prefixes:
in words with prefixes
the primary stress typically falls on the syllable following the
prefix:im´possible, re´call ;
in words with prefixes with their own meaning, the place of secondary stress is on the prefix:
ˏex-´minister.
in prefixal verbs which are distinguished from similarly spelt nouns and adjectives, the second syllable is stressed:
to in´crease – ´increase.
Слайд 34
Common Rules of Word Stress
Words with suffixes:
suffixes -esce, -esque, -ate,
-ize, -fy, -ette, -ique, -ee, -eer, - ade have stress
on themselves or the preceding syllable:ˏmari´nade, ˏspecia´lize;
suffixes -ical, -ic, -ion, -ity, -ial, -cient, -iency, -eous,-ual, -uous, -ety, -itous, -ive, -ative, -itude, -ident, -inal, -wards have stress on the preceding syllable:
eco´nomic, ma´jority.
Слайд 35
Common Rules of Word Stress
Words of 4 or more syllables:
The
stress is on the antepenultimate syllable (third from the end):
e´mergency
his´torical
Слайд 36
Common Rules of Word Stress
Compound words:
The first element is stressed
when:
Compounds are written as one word: ´bedroom.
Nouns are compounded of
a verb and an adv.:´make-up.The second element is stressed when:
Food items have the first element which is of a material used in manufacturing the whole: ˏapple ´tart.
Parts of the house are implied: ˏfront ´door.
Слайд 37
Common Rules of Word Stress
Compound words:
The first element is stressed
when:
Adjectives with past participle characterize people:
ˏthick-´skinned.
Nouns ending in -er, -ing
are followed by adverbs:ˏpasser´by.
The first element of compounds is a number:
second-´class, three -´wheeler.
Compound function as an adverb:
head-´first.
Слайд 38
Common Rules of Word Stress
The most common types of English
stress pattern
´_ _ (´after)
_´_ (be´fore)´_ _ _ (´family)
_´_ _ (im´portance)
Some words have 2 variants of stress:
ki´lometer – ´kilometer
Слайд 41
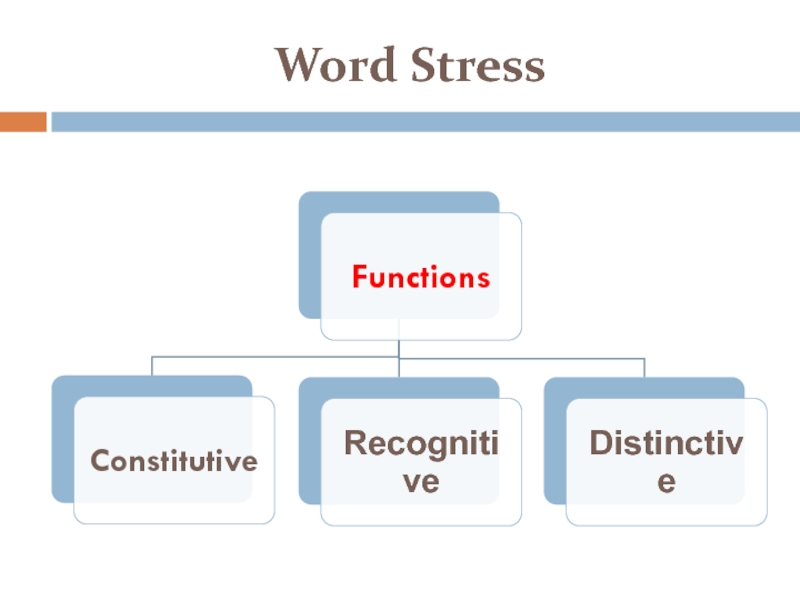
Functions of Word Stress
The constitutive function:
word stress organizes the
syllables into a word
The recognitive (identicatory) function:
word stress makes it
possible to identify and recognize a word in the chain of speech.The distinctive function:
word stress is capable of differentiating the meaning of words or their forms: ´import - im´port.
Слайд 42Questions:
What is WORD STRESS?
What types of word stress do
you know?
How does stress perform constitutive, distinctive and recognitive function?
What
is the terminology suggested by different authors to distinguish between different degrees of word stress?What factors determine the place of word stress?
Слайд 43
Literature
Леонтьева С.Ф. Теоретическая фонетика современного английского языка (на
англ. яз.) /С.Ф. Леонтьева.- М., 2002. – 336 с.
Соколова
М.А. Практическая фонетика английского языка /М.А. Соколова. – М.: Гуманит. изд. центр ВЛАДОС, 1997. – 384 с.O’Connor L.D. Phonetics /L.D. O’Connor. Penguin, 1977.
Sokolova M.A. English Phonetics. A theoretical course /M.A. Sokolova. M., 1996. – 286 p.
Vassilyev V.A. English Phonetics: A theoretical Course /V.A. Vassilyev. M., 1980. – 323 p.