Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Working on Master Thesis: Spring Semester
Содержание
- 1. Working on Master Thesis: Spring Semester
- 2. Summarizing the Fall Semester AchievementsOutcomes:Potential topics
- 3. Research Guide: General Remarks on Choosing a
- 4. Research Guide: Choosing a TopicStep 1: Choose
- 5. Research Guide: Choosing a TopicHow to Find
- 6. Research Guide: Choosing a TopicStep 3: Narrow
- 7. Research Guide: Choosing a TopicStep 3: Narrow
- 8. Research Guide: Choosing a TopicStep 3: Narrow
- 9. Assignments in the Spring Semester (assignments 5-7)
- 10. Assignment 5: Summary of Research Survey
- 11. Assignment 6: Summary of Research Article Select
- 12. Assignment 7 The literature review: the content and structure requirements
- 13. Assignment 7Develop a literature review on the
- 14. Overall StructureTitle of research topic or research
- 15. General overview of theoretical background and
- 16. Volume RequirementsA reasonable number of references in
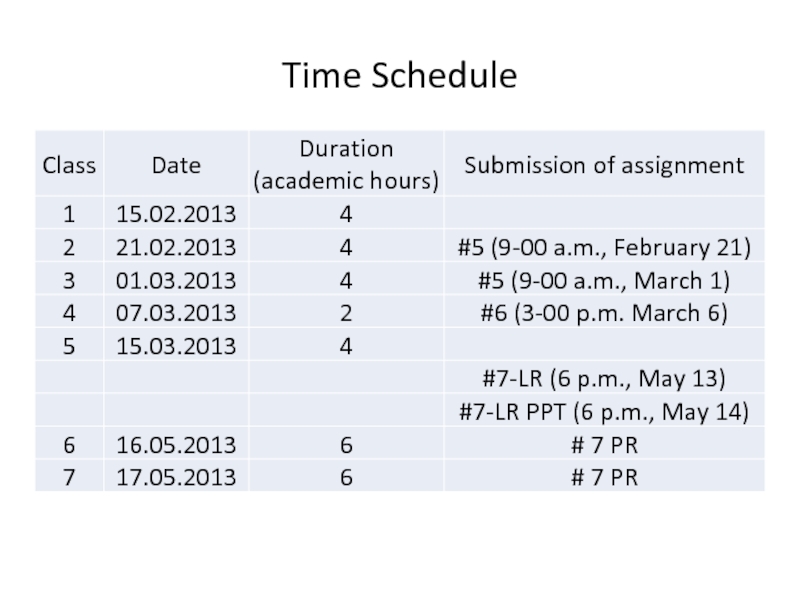
- 17. Time Schedule
- 18. Скачать презентанцию
Summarizing the Fall Semester AchievementsOutcomes:Potential topics for your research and names of desirable research advisors List of references on the potential topic of your researchResearch questions and research objectives (≈draft
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Summarizing
the Fall Semester Achievements
Outcomes:
Potential topics for your research and
names of desirable research advisors
List of references on the
potential topic of your researchResearch questions and research objectives (≈draft research proposal) for one of the topics from (1)
Слайд 3Research Guide: General Remarks on Choosing a Topic
What Is a
Topic?
A research paper gives information about something, called a topic.
Writing
a research paper (Master thesis) starts with choosing the topic to be dealt withIt continued with finding information about the topic.
The information about the topic must be factual (true) and accurate (correct). These pieces of information are called facts. Finding facts about your topic is called doing research.
How to Choose a Topic?
Choose a topic that you want to know more about.
Pick a topic that you already know something about.
When to Start Doing Research?
Start doing research before you choose your topic finding information on the object of study and possible subject(s) of study ( stage of preliminary research).
Слайд 4Research Guide: Choosing a Topic
Step 1: Choose a subject or
area of interest Decide on a tentative subject or area of
interest (at this point in, it is perfectly acceptable if you only have a very general idea of what you'd like to pursue).Step 2: Conduct a preliminary exploration of your subject When a general subject area for your research is selected, it is important to gain a sense of what your subject area entails (what is your subject all about and how much information exists on this subject). Look for the answers to the following questions:
What discipline(s) or profession(s) fall under this subject?
How has this subject developed or changed over time?
What key concepts and terms are used in this subject area?
What are some of the currently disputed or controversial questions concerning this subject?
Who are the key thinkers and researchers in this area?
What are some of the key publications in this subject?
Слайд 5Research Guide: Choosing a Topic
How to Find the Information Needed?
While doing preliminary research you figure out how many resources
(also called sources, the places you look to get information about your topic) you can find about your topic. Some examples of resources:Research and professional journals, books
Encyclopedias and handbooks
Internet (websites of journals, databases, professional and academic associations, consulting companies, governmental agencies, ministries, research centres, companies, universities, etc.).
It is important to make sure that the information you are getting from the Internet is factual and accurate, however. Make sure that the information you are getting from the Internet is factual and accurate, however.
What If Topic Is Too Broad or Too Narrow?
A topic is very big, or broad Ask yourself what part of the topic you are most interested in or ask your mentor which part of the topic is most purposeful for organization (practitioners)
A topic is too narrow, or too small enhance the object, the subject of study or both (research advisor).
Слайд 6Research Guide: Choosing a Topic
Step 3: Narrow and shape your
subject into a specific topic
Starting point – articulated topic for
your research project, at least a tentative. Beware of choosing a topic that is too narrow or too broad, a good rule to remember:
If there are entire books written about your topic, it is too broad for a Master thesis research. Conversely, if research question can be fully answered in a few paragraphs, your topic is too limited.
Beware of choosing a topic that is too recent, obscure, or specialized for you to find published material in a variety of formats.
If, however, you initially choose a topic that is too narrow, too broad, or too esoteric, keep in mind that zeroing in on an appropriate topic can sometimes continue well into later stages of the research process (as you gather more information on your topic in Stages 5 through 7, you are free to modify your research topic if you discover through your reading that you have defined your topic too narrowly or too broadly).
Слайд 7Research Guide: Choosing a Topic
Step 3: Narrow and shape your
subject into a specific topic
Research topics are often stated in
the form of a question. Ex.: "How does illegal immigration affect the Russian Federation economy?" (keep in mind it will usually include at least two aspects or main ideas, often referred to as concepts)Assume, you may have chosen economics as your general subject, in particular economic performance. After some preliminary research and background reading, you might discover that one major area of debate is illegal immigration and whether or not it provides a harm for economic growth of Russia. Your first concept, or main idea, is illegal immigration . The second concept is economic growth. The two (or often three) concepts of a research topic can often be phrased in relation to each other as follows:
"The effect of ___(concept #1)___ on ___(concept #2)___ ."
"The role of ___(concept #1)___ in ___(concept #2)___ ."
"The use of ___(concept #1)___ in ___(concept #2)___ ."
Слайд 8Research Guide: Choosing a Topic
Step 3: Narrow and shape your
subject into a specific topic
When wording your research question, it
is best to begin with the words How or Why (research questions beginning with these words automatically suggest a somewhat broad investigation and substantive discussion, thus helping to avoid phrasing the topic too narrowly). Avoid starting your research question with the words Who, Where, or When. These words tend to force your research into a limited aspect of selected subject (it may lead to a shortage with enough material for your project).
Research questions beginning with What can be acceptable or unacceptable, depending on how much scope and breadth the rest of the question implies.
Note the difference between these two research questions, each beginning with "What ….":
Too narrow for most research assignments: "What percentage of unemployment in RF is caused by illegal immigration?"
A broader research question appropriate for most research projects: "What is the effect of illegal immigration on Russian labour market?"
Слайд 10Assignment 5:
Summary of Research Survey Article
Find a published,
peer-reviewed literature review or literature survey for your research topic
or topic relevant to the subject area of your research by searching the databases available at the GSOM library (EBSCO, eLibrary, JSTOR, ProQues, ScienceDirect - Elsevier, etc.).Submit the electronic copy of the survey to fedotov@gsom.pu.ru
Due date: 9-00 a.m., February 21, 2013
Provide a summary for this survey (max.4 pages) in which you have to:
Formulate the topic or field is being examined
Explain how the topic or field under review is related to the topic of your research proposal
Divide the works reviewed into categories
Due date: 9-00 a.m., March 1, 2013
Слайд 11Assignment 6: Summary of Research Article
Select the article you
want to review from an academic journal and respond to
the following questions:What is the research question? Why is this research question important?
How this research question is related to your research topic?
What is the author’s conceptual model of the phenomenon? Describe the conceptual model in writing, and also provide a sketch of the key conceptual relationships.
Consider the author’s empirical model of the phenomenon. What are the key empirical indicators of the concepts? Sketch the observed relationship between the key empirical indicators.
How good is the match between the conceptual model and the empirical model? Does the empirical evidence give you more or less confidence in the conceptual model, or is it indeterminate?
How did the author arrive at his or her evidence? What are the key advantages of the chosen research design? What are the key disadvantages?
Suggest a (feasible) way to address the shortcomings you see in this research, either using the available data or by collecting additional evidence.
Any other comments on the methodology in the article you have chosen?
Due date: 3-00 p.m. March 6, 2013
Слайд 13Assignment 7
Develop a literature review on the selected research topic
Due Date: 6 p.m., May 13, 2013;
Develop a PowerPoint
presentation for your literature reviewDue Date: 6 p.m., May 14, 2013;
Provide a critical review of the literature review produced by you classmate.
Due Date: May 16 or May 17, 2013;
Слайд 14Overall Structure
Title of research topic or research area (listing topics
and variables – subjects and objects of study)
Summary of the
literature review (number of sources surveyed, units of analysis, gaps detected, implications for your research)Introduction (listing topics and variables – subjects and objects of study, methodologies and concepts that might be used to explore the topic)
General overview of theoretical background and research, with emphasis on seminal works in your area (textbooks, books, handbooks, journals, dissertations)
Слайд 15General overview
of theoretical background and research
Basic concepts and definitions
(survey and comparative analysis)
Research results (describe relationships and results established
in publications)Review of relevant research methodologies and models
Problem formulation—which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues?
Empirical data employed in the studies
Bibliography
Слайд 16Volume Requirements
A reasonable number of references in a literature review
to be submitted in May, 2012 would be 20+ titles
(Masters thesis: 40+ titles)The paper should be, at least, 20 pages (long single spaced, Times New Roman 12 script) or 40,000 characters