Слайд 2Food & Drug Administration (FDA)
1862, started with a single chemist
in the USDA
1927, Bureau of Chemistry changed to the Food,
Drug, & Insecticide Administration
1930, name was shortened to the present version
2001, staff ~9,100 employees & a budget of $1.3 billion
Слайд 3Adulteration and misbranding of foods & drugs have always been
a problem in the U.S.
The problem increased by the
late 19th C.
Drugs such as Quinine were cut with fillers to increase profit
Sufferers of serious illnesses were sold worthless drugs or therapies
Preservatives added to foods & drugs were useless or worse toxic
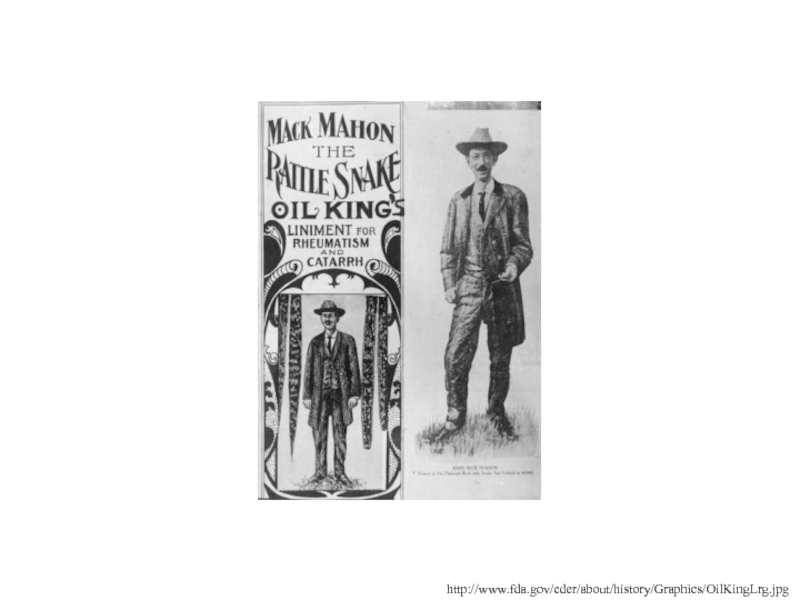
Слайд 4http://www.fda.gov/cder/about/history/Graphics/OilKingLrg.jpg
Слайд 5http://www.fda.gov/cder/about/history/Gallery/gallery21.htm
Слайд 6Harvey Washington Wiley, chief chemist concerned about chemical preservatives, initiated
"poison squad" experiments
Healthy volunteers consumed varying amounts of questionable food
additives to determine their impact on health
Officially designated the “Hygienic Table.”
Chemicals fed to the young men included borax, salicylic, sulfurous, and benzoic acids, & formaldehyde
Слайд 7Wiley became convinced that chemical preservatives should be used in
food only when necessary
That the burden of proving safety should
fall on the producer
That none should be used without informing the consumer on the label
Wiley unified a variety of groups behind a federal law to prohibit the adulteration and misbranding of food and drugs
Слайд 8Food and Drugs Act of 1906
First nationwide consumer protection law
made it illegal to distribute misbranded or adulterated foods, drinks
and drugs across state lines
Offending products could be seized & condemned; persons could be fined & jailed
Drugs had either to abide by standards of purity and quality set forth in the UNITED STATES PHARMACOPEIA & the NATIONAL FORMULARY
Presence & quantity of alcohol or certain narcotic drugs had to be stated on proprietary labels
Слайд 9There were however, shortcomings in the 1906 law
Law prevented blatant
fraud, but it did not prevent deception
Numerous examples of foods
deceptively packaged or labeled began to show up
The law also did not insist that products be tested for safety
Слайд 10http://www.fda.gov/oc/history/slideshow/Slide_182_139.html
Flavoring Extract Bottle
thick glass obscures how much expensive flavoring extract
is really in the bottle
Слайд 11Lash-Lure, an eyelash dye that blinded many women
http://www.fda.gov/oc/history/
Слайд 12A disaster in 1937 prompted Congress to act
A Tennessee drug
company marketed a form of the new sulfa wonder drug
that would appeal to pediatric patients, Elixir Sulfanilamide
The solvent in this untested product was diethylene glycol
Over 100 people died, many of whom were children
Слайд 13http://www.fda.gov/cder/about/history/Page18.htm
Elixir Sulfanilamide
Слайд 141938 Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act
For the first time,
required companies to prove the safety of new drugs before
putting them on the market
Over the years new responsibilities were added including the requirement that drugs and medical devices be proven effective as well as safe before they can be sold
Слайд 15Currently the FDA is charged with:
Safeguarding the nations food supply,
by ensuring that all ingredients used in foods are safe,
& that food is free of contaminants
Approves all new food additives before they can be used
Monitors the safety of dietary supplements & the content of infant formulas & medical foods
Protects the public from unnecessary exposure to radiation from electronic products. (microwave ovens, cell phones, x-ray equipment, lasers, medical ultrasound & MRI machines)
Monitors cosmetic products to be sure that they are safe & properly labeled
Слайд 16Medical products need to be proven safe and effective before
they can be used by patients
The product categories covered by
this requirement include:
Medicines used for the treatment and prevention of disease
Biologics, vaccines, blood products, biotechnology products and gene therapy
Medical Devices, FDA regulates all medical devices, from very simple items like tongue depressors or thermometers to very complex technologies such as heart pacemakers and dialysis machines.
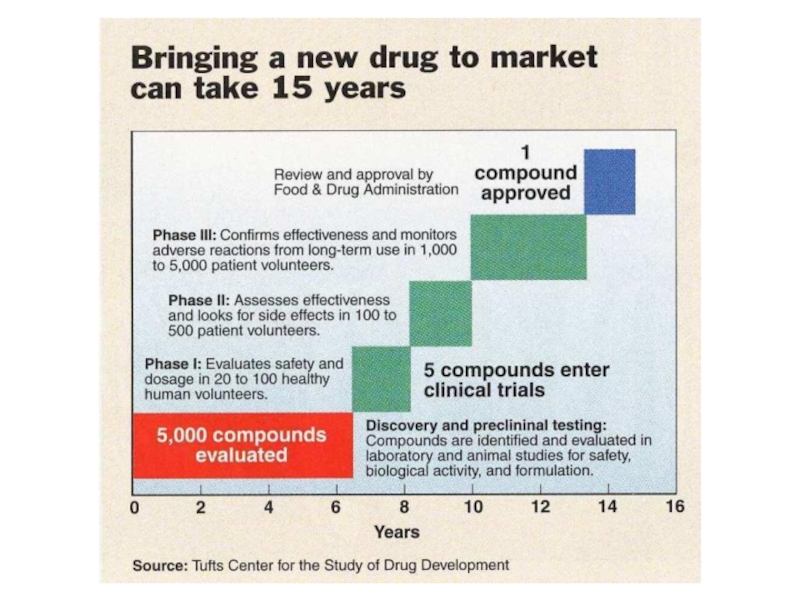
Слайд 19The majority of prospective new drugs fail testing, many never
make it passed the pre-clinical stage
The pre-clinical stage involves testing
in either animals or cells and looks at the potential drugs efficacy in a model of the the disease
This stage also involves looking for possible toxicity or side-effects that may be significant if the compound moves ahead to human studies
Слайд 20If a compound shows promise during the pre-clinical phase the
drug maker may decide to move forward with human testing
Human
testing of a drug is known as a clinical trial
For a drug to be tested in humans the Sponsor must submit an application to The Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), part of the FDA
This application is known as an
Investigational New Drug Application (IND)
Слайд 21Investigational New Drug Application (IND)
The IND is reviewed by both
the FDA and a local IRB
An Institutional Review Board (IRB)
is a panel of physicians, scientists, & lay persons who oversee research done using humans
Each hospital or research institution must have an IRB if it allows human research
The IRB approves the clinical trial protocols, these describe who may participate in the trial, the schedule of tests and procedures, the medications and doses, the study’s length, and finally its objectives
Слайд 22After approval by the IRB and the FDA, clinical trials
can begin
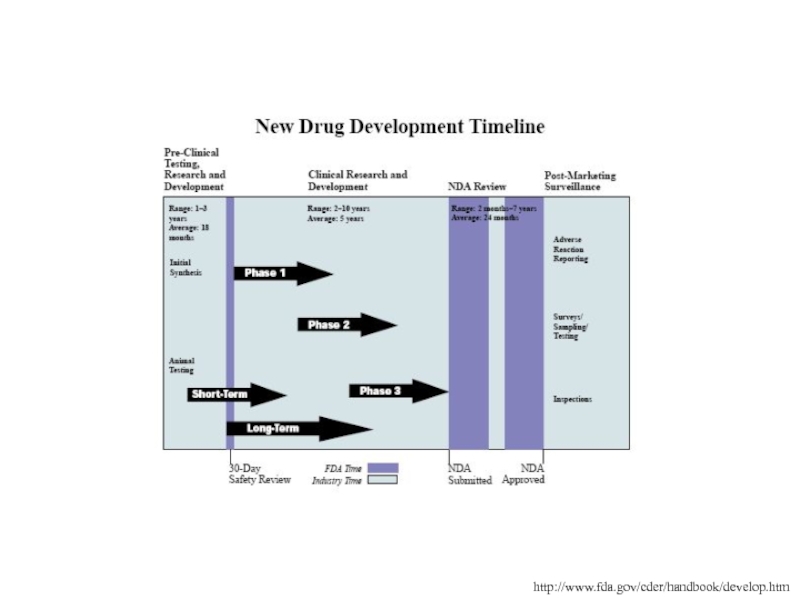
There are up to four different phases of trials,
each with a specific objective.
If any problems arise during any of these phases the FDA is notified and the IND application is canceled
Слайд 23Phase I Studies
Conducted in healthy volunteers, between 20 to 80
Goal
is to determine safety and look for possible side effects
The
studies are usually open-label meaning the volunteers & the physicians know who is getting the drug
The Pharmacokinetics of the drug is often investigated
If no unacceptable toxicity is revealed, phase II studies can be initiated
Слайд 24Phase II Studies
Shift in emphasis from safety to effectiveness
Collection of
preliminary data on whether the drug works in people who
have a certain disease or condition
Usually two groups of patients are compared, one group receiving the drug is compared to a second group who receives either a placebo or a different drug
Studies are often done in the double blind method, this means the neither the patient, physician, nor the drug company know which patients are getting the drug & which are getting the placebo
The number of subjects rages from a few dozen to 300
Слайд 25Phase III Studies
If effectiveness is shown during phase II the
study is expanded to a phase III
The goal during this
phase is the continued collection of safety and effectiveness data
These data are collected on a larger population that is more varied than that studied during phase II
Phase III also often studies the drug at different doses and in combination with other drugs
The number of subjects ranges from a few hundred to a few thousand
Слайд 26Phase IV Studies
Occur after a drug is approved
Explore other aspects
of the drug such as usage in new populations, such
as children
Long term effects are also explored
Often after approval, some drugs are found to have unintended usages
These are referred to as off-label uses
It is legal for a physician to prescribe a drug for off-label use, but the drug company cannot advertise these uses until further studies are performed
Слайд 27New Drug Application (NDA)
Once clinical trials are finished the sponsor
places a formal request with the FDA to consider approving
the drug
This request is known as a New Drug Application (NDA)
Once a NDA is filed the FDA has 60 days to review the application for filing
If the FDA decides to file the application a review team of physicians, chemists, statisticians, microbiologist, and pharmacologists is assembled
Only 1 in 5 drugs that enter clinical trials is ultimately approved by the FDA
Слайд 28Review Process
The review team analyzes all aspects of the study
results looking for possible problems, such a weaknesses in the
study design or analyses
Reviewers determine if they agree with the sponsor’s results and conclusions or if additional information is needed
Each reviewer then prepares a written evaluation with their recommendation about the application
Слайд 29If the FDA decides that the benefits of the drug
outweigh any risks the drug can then be marketed in
the US
If there are problems with the NDA, the FDA may decide that the drug is approvable or not approvable
Approvable means that the drug may eventually be approved, but that some issues need to be resolved first
Not approvable means there are significant problems that cannot be overcome without substantial additional data
These could be safety problems or failure to demonstrate the drug’s effectiveness
Слайд 30Accelerated Approval
Given to drugs for serious and life-threatening illnesses that
lack satisfactory treatments
Uses surrogate endpoints instead of traditional measures
These can
be laboratory findings that are not directly related to patient survival or function
Most HIV drugs have been approved through this process with the provision that the companies continue to perform studies to confirm the drug’s ultimate benefit
If future studies do not confirm initial results the FDA may withdraw approval
Слайд 31http://www.fda.gov/cder/handbook/develop.htm
Слайд 32Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA)
Provides for the review and ultimate
approval of a generic drug
A generic drug is one
that is comparable to an innovator drug in dosage form, strength, route of administration, quality, performance characteristics and intended use
Termed abbreviated because they are generally not required to include preclinical and clinical data to establish safety and effectiveness
Applicants must scientifically demonstrate that their product is bioequivalent
Слайд 33Bioequivalence
In order to demonstrate bioequivalence scientists measure the time it
takes the generic drug to reach the bloodstream in 24
to 36 healthy, volunteers
This gives them the rate of absorption, or bioavailability, of the generic drug, which they can then compare to that of the innovator drug
The generic version must deliver the same amount of active ingredients into a patient's bloodstream in the same amount of time as the innovator drug
Слайд 34Orphan Drugs
In 1982 Congress passed the Orphan Drug Act
The goal
was to promote the development of products that demonstrate promise
for the diagnosis and/or treatment of rare diseases or conditions
More than 200 drugs & biological products for rare diseases have been brought to market since 1983
Prior to 1983 fewer than ten such products came to market
Слайд 35Adverse Events Reporting System (AERS)
The FDA requires manufacturers to report
adverse drug reactions
Health care professionals & consumers can also send
reports voluntarily through the MedWatch program
If there are significant adverse effects the FDA may take regulatory actions to improve product safety and protect the public health
Such as updating a product’s labeling information, sending out a "Dear Health Care Professional" letter, or re-evaluating an approval decision
Слайд 36If a drug has severe side effects, but is kept
on the market a black box warning is placed on
the label
Recent black box warnings have been issued for:
Advair/Serevent: small, but significant increase in asthma deaths particularily in African-Americans
Depo-Provera: significant decrease in bone density
Serzone: life-threatening liver failure
All antidepressants for increased adolescent suicide
Acetaminophen: life-threatening liver failure increased when taken with alcohol
Слайд 37Recent Drug Controversies
Vioxx, voluntarily withdrawn due to increases in heart
attacks & strokes
Prempro, Premarin; hormone replacement therapy, a long term
study showed increases in breast cancer & coronary heart disease
Baycol (cerivastatin), removed from the market because of ~31 reports of fatal rhabdomyolysis, destruction of muscle tissue that can lead to kidney failure
Crestor (Rosuvastatin) approved in August, 2003 has the same problem
Слайд 38If you have questions about medications your or your family
are taking:
http://www.fda.gov/medwatch/index.html