Слайд 1“PLEKHANOV Russian University of Economics”
Discipline – “The economic
strategy of development of the hotel enterprise”
S. S. Skobkin,
Doctor of economics, Professor, Department of hospitality, tourist and sport industry
Theme 1: “Strategies for development of hotel business”
Слайд 2Lesson’s plan
the structural theory of three stages of the development
of demand in the hotel industry;
strategies of development of the
global hotel industry;
characteristics of Moscow hotel market and strategy of leading hotels.
Слайд 3Strategies in the hospitality industry
Modern hospitality industry is characterized by
a high degree of intensity of competition.
Enterprises of this
industry implement different strategies to achieve competitive advantages . However, there is considerable differentiation and fragmentation associated with the variety of various concepts of strategic development based on cost, resource and competent approaches.
Слайд 4Strategies in the hospitality industry
However there is an integrating factor
uniting these strategies - the formation of sustainable competitive advantages,
allowing it to achieve growth not only in sales of services and attract more customers, but the company's assets to its size and market cost.
Examining the growth strategies used by the hospitality industry, we are offering these classification model presented in the following diagram.
Слайд 5The structural theory of three stages of the development of
demand in the hotel industry and the place of the
Russian hotel industry in this process
Слайд 7Development of demand - Stage 1
The economy is dominated
by homogeneous companies, mainly in the mining and processing industries,
which are developing in local and regional markets.
Demand for accommodation in hotels is quite low, because a little number of employees of these enterprises (product sellers, researchers of new markets, etc.) are not regularly on business travel.
The distribution of the flow of business tourists in the country shows a high degree of consumption of hotel services in the capital (or in few large cities), while the demand for hotel services in regions is relatively low.
The number of domestic tourists using accommodation facilities, is generally less than the total number of tourists in the country.
Foreign businessmen are usually served in a special higher category hotels . Their activities require regional representation in the form of business centers that are typical for such hotels.
Слайд 8Development of demand - Stage 2
The business activity of
multinational companies is developing. Companies open branches in different regions
of their countries.
The process of corporate business from the primary to the secondary sectors in the industry is accelerating. That leads to an increase in production volumes of The gross national product (GNP).
Companies enter international markets and attract different specialists to research, promote and service these markets.
The construction of roads, airports, hotels is growing as well as means of communication.
Development of interregional companies coincides with the development of demand for hotels in all parts of the country. National and international hotel chains are emerging in the market to meet this demand.
Hotels continue to perform the function of the central office and are used for meetings, conferences and training.
Слайд 9Development of demand - Stage 3
The process of internationalization of
the economy intensifies and is evident in the increasing number
of emerging companies in the international market, as well as the penetration of foreign business in the national economy.
Demand is growing for business accommodation abroad.
Hotel business begins to go beyond national boundaries, and follows the movement of their businessmen, joint ventures and global corporations.
Слайд 10Position of the Russian hotel industry in the development of
demand in the hotel business
The distribution of the flow of
business tourism in the country shows a high degree of consumption of hotel services in the capital (or some large cities), while the demand for accommodation services in the regions is relatively low.
Russia's transition to the second stage has already taken place. In the near future we can expect the prevalence of inter-regional and trans-national companies in the Russian economy.
Further evidence of this transition are improvements in the transport and tourism sectors: air transportation becomes more intense, number of airports is increased , the road network is improved, new hotels are commissioned, and etc. All of these will lead to increased opportunities for business and leisure travelers.
Слайд 11Strategies of development of the global hotel industry
Слайд 12Strategies in the hospitality industry
The modern hospitality industry is characterized
by a high degree of intensive competition.
In order to achieve
competitive advantages different strategies are applied. In general they are based on the cost, resources and competency models.
The formation of a sustainable competitive advantage, allows for growth not only in sales of services, but the assets of the enterprise of its size and cost.
Слайд 13Geographic expansion strategy
The strategy assumes an increase in the coverage
of the market within a single country. First the hotel
companies developed on a small geographical area, outlined around their place of origin.
However, the hotel boom of the 80s, favorable growth opportunities, franchising deals and the established mentality of the top management, focused on quantitative indicators, allowed hotel companies in many countries to expand their presence first to the national and then to the international level.
Слайд 14International marketing strategy
International marketing has become a characteristic feature of
the activities of modern hotel corporations. Such hotel companies as
Marriott, Holiday Inn, Radisson, Accor, Choice Hotels International, Hilton and many others are represented all over the world. Brands of fast food companies can be seen in cities and airports of almost any country.
Domestic markets of many countries have become transparent for the penetration of foreign hotel operators, such as Meridian, Trusthouse Forte, Sofitel, Nikko and others.
The investment environment, the level of risk, the growth strategies and the reasons that push companies to expand into the foreign market, vary from one company to another, from one market to another.
Слайд 15Specialization strategy
Strategies for specialization and narrow specialization have merged into
one general strategy of specialization. Just as the development of
the Holiday Inn began with the concept of family living at an affordable price example, Inter Continental presents a specialized product - the services of high-class servicing of businessmen.
A similar process of specialization took place in the food sector: there were fast food enterprises, salad bars, pizzerias, specialized restaurants for delicacies, seafood, etc.
Слайд 16The strategy of differentiation by Marriott
Слайд 17Brand development strategy
The brand development strategy was influenced by the
strategy of diversification of the hotel product, as well as
in connection with the formation of corporate hotel chains.
The strategy for the development of the brand of the hotel product is aimed at accurately defining and "recognizing" the product or service in terms of their level and quality, position, price and other key parameters targeted at the consumer, such as, for example, prestige or thrift.
Слайд 18The strategy of combining brands
In the late 80's - early
90's a new strategy emerged, called “combining trademarks". Hotel operators
began to attract investors relatively low prices, which could buy brands or hotel chains that had a high growth potential due to their entry into global franchising programs.
Companies such as Hospitality Franchise Systems (also owning Howard Johnson, Ramada and the Days Inn) and Choice Hotels International (which also owns Quality Inns, Comfort Inns and Comfort Suites) currently represent the largest hotel association.
Слайд 19The strategy of an independent hotel
Usually independent companies (not affiliated
with franchising agreements) have greater freedom in control over the
quality, disposal of property and management of their own hotel.
Basically these companies are sufficiently financially stable, which allows them to be independent.
Examples of independent enterprises in the hospitality industry can be set a lot - it's Savoy in London, Sacher hotel in Vienna, Ginza Hotel in Tokyo and many others.
Слайд 20Franchising strategy
The franchising strategy is more common in the hotel
industry than the strategy of independence. The largest franchise hotel
chains are Holiday Inn, Radisson and Choice Hotels International.
In the food sector (especially fast food), examples of the largest franchise companies are McDonald's, Burger King, Wendy's, Dunkin Donuts and Arby's. Today, franchising is widespread in the entire hospitality industry - from the travel agency to the resorts.
Слайд 21The strategy of hotel management by the operator under the
contract
Management of the hotel by contract was a development of
the concept of franchising, where the operator not only transfers his trademark to another hotel along with the technology of service and positioning, but also takes over the management of the enterprise on behalf of the owner.
As a rule, in the face of hotel operators, the same hotel firms engaged in franchising are contracted.
Слайд 22Growth strategies in the hospitality industry
Слайд 23Growth strategies
The growth strategy of enterprises in the hospitality industry
is based on two main concepts: organic and inorganic growth.
Organic growth is considered as internal growth or growth from within. For enterprises this planned growth happens slowly, gradually increasing the amount of resources consumed.
The company can grow internally, putting profit every year in the development of their business. This approach leads to increased production and revenue.
Слайд 24Internal growth strategies
The internal growth can be achieved through
increased sales of existing products and services or by adding
new ones.
The internal growth does not require major changes in the existing production structure of the enterprise.
This process is easy to manage because it develops slowly.
Слайд 25Internal growth strategies
The strategy of product differentiation. These strategies
provide for timely and proper adaptation of enterprise and it’s
product policy to the needs of the market in the hospitality industry.
These strategies include:
the strategy of unification and uniqueness (customization) of the product. A striking example - the modern trend of adaptation of the hotel product to the needs and requirements of individual target segments of consumers. So, a very common hotel product focused on women entrepreneurs or managers of firms and corporations;
Слайд 26Internal growth strategies
The strategy of unique selling points. This
strategy involves the provision of additional hotels services to assist
in giving a basic hotel product additional elements of values and to form the concept of the extended hotel product.
The unique selling points that differentiate hotel product, giving it elements of uniqueness may include: restaurants, halls for conferences and business meetings, spas, fitness centers, massage parlours, night clubs and etc.
All these additional sources of income and value filling basic services together form and contribute to an extended hotel product, which contribute to an internal growth;
Слайд 27Internal growth strategies
The strategy of the concept. Today there
is a shift of emphasis from a product-oriented prerequisites for
the acquisition of expensive goods and services (quantity, material characteristics, money etc) in the background, reflecting the style and way of life (e.g., quality, intangible components, time, etc.).
Consumers strive to ensure that through products or services to find expression, to obtain certain experiences and emotions, and positive perception of the product or service is not based on satisfaction with the characteristics of the product and getting positive emotions.
Слайд 28Internal growth strategies
The development of networks of boutique hotels.
Judging by the number of publications on this topic is
the development of this strategy. For the first time this concept has been introduced to the U.S. in 1984 as opposed to a large number of similar hotels classic hotel chains.
The concept developed American entrepreneur Ian Schrager, who sought my first design hotel Morgans to combine three important components of a new concept: unique design, high quality service and intimate atmosphere.
Слайд 29Internal growth strategies
Entering the market of timeshares can be
attributed to differentiation strategies and tools to enhance concepts own
hotel brands.
In particular, in the framework of the Marriott a set up of separate unit Marriott Vacation Club International and relevant brands Horizons by Marriott Grand Residences by Marriott and Ritz-Carlton Club took place.
Hotel chains Hilton and Cendant submitted their brands of times hare in the same way .
Слайд 30Internal growth strategies
the strategy of intensive growth or expansion
allows you to increase the market share, income and profits
from the sale of enterprise services. This strategy is actively used by enterprises with a smaller market share.
We attribute the following advantages to the strategy of intensive growth:
Growth is slow and natural, so the process of implementing such a strategy does not involve insurmountable difficulties.
The required capital for business expansion can be taken from the firm's own funds.
Existing resources of the enterprise can be better used.
Слайд 31Internal growth strategies
A growing company is in a better
position relative to competitors in the market.
The organization of business
management requires minor changes.
Expansion provides the economy with large-scale enterprise activities.
We distinguish the following limitations of the intensive growth strategy:
Growth is slow, and it takes a long time to implement the strategy.
The company loses the opportunity to use competitive advantages, limiting its actions to providing existing services on existing segments to markets.
Слайд 32Internal growth strategies
the modernization strategy means renewal, bringing the
enterprise in line with modern market, technological, social conditions of
functioning and development.
Modernization mainly involves the improvement of technology that allows increasing production, improving the quality of services provided and reducing the cost of their production. The modernization plans may have the following features:
1) The firm is upgrading at a slow pace, maintaining only its position in the market.
2) The firm carries out modernization with full force, capturing new market segments.
Слайд 33Internal growth strategies
Modernization has the following advantages:
1) Modernization improves
the productivity and efficiency of the firm.
2) The company's profitability
is increased due to increased efficiency and a reduction in unprofitable operations.
3) Modernization improves the quality of services provided to customers.
4) The firm becomes more competitive as a result of modernization.
5) Modernization ensures systematic growth, and does not interrupt the normal functioning of the firm.
6) Employees of the company acquire modern skills, as a result of which their wages increase.
Слайд 34Internal growth strategies
The modernization strategy can only be used
if the firm has accumulated capital or is able to
obtain investment from various sources. An important role in modernization is played by timely training of workers in new methods of production.
The modernization has the following limitations:
1) The funds available to the firm may not be sufficient to finance modernization.
2) The duties of the company's top managers increase significantly due to the need to develop new types of services, the introduction of new technologies and the development of new markets.
3) The company's production personnel may face problems in mastering new technologies.
Слайд 35Internal growth strategies
The strategy of diversification. Diversification means not
easy adding a variety of services provided by the enterprise,
but providing completely different types of services not previously provided. An enterprise usually chooses a diversification strategy in the following situations:
1) When diversification promises greater profitability than expansion.
2) When an enterprise can not achieve the growth goal, using only the expansion strategy.
3) When the financial resources of the enterprise are not enough to expand.
Слайд 36Internal growth strategies
The difference between an intensive growth strategy
and a diversification strategy is that in the case of
intensive growth, the enterprise increases the production and sales of already existing services.
In the case of diversification, the company creates new types of services and covers new markets.
Слайд 37Internal growth strategies
Horizontal integration involves entering the parallel market
of services in addition to the existing one. The development
of a network of enterprises is an example of such a strategy.
Horizontal integration has the following advantages:
1) Wasteful competition among merging firms disappears.
2) The economy of large-scale production and distribution is provided.
3) Market control is being strengthened and the firm's competitiveness is increasing.
4) The firm receives greater control over the services provided and prices for them.
Слайд 38Internal growth strategies
Vertical integration means the addition of new
services to those already provided. New services are designed for
both the company's customers and for servicing its production tasks. Vertical integration distinguishes between "backward" integration and "forward" integration.
Integration "back" means moving to the production of raw materials, materials, etc. for the provision of services.
Слайд 39Internal growth strategies
Integration "forward" implies the entry of the
firm into the business of distribution or sale of the
services provided.
Integration "forward" has the following advantages:
1) The firm may exercise greater control over sales and prices for the services provided. This approach is actively used in the oligopoly market.
2) Own retail sales network serve as the best source of feedback to customers, which increases the control over quality.
3) The firm can increase profits by reducing distribution costs.
4) By reducing the cost of transporting customers to the place of service, the firm can ensure the growth of competitive advantages of the services provided in general.
Слайд 40Internal growth strategies
Under concentric diversification in the hospitality industry
is understood the multifaceted development in which new lines of
business of the firm are connected with the existing business only in terms of marketing and technologies. With concentric diversification, the creation of a new service is provided with the help of existing or similar technology, and its implementation through the existing distribution system.
Concentric diversification is used in the following cases:
1) When cyclical fluctuations in existing services should be neutralized.
2) When the cash flows generated by the existing service are in surplus.
Слайд 41Internal growth strategies
3) When the demand for an existing
service has reached saturation.
4) To strengthen managerial experience in the
new field of activity.
5) When the reputation of the existing service is high and can be used to develop new forms of service.
Слайд 42Internal growth strategies
Conglomerate diversification is the transformation of a
firm into a new type of activity that is not
related to its existing business, both in terms of marketing and technology.
Conglomerate diversification is used to achieve the following objectives:
1) Grow faster than growth through expansion can.
2) To use the potential of profitable investments.
3) To achieve competitive advantages and increase stability.
4) To better use the surplus cash generated by the provided service.
5) For an even distribution of risks.
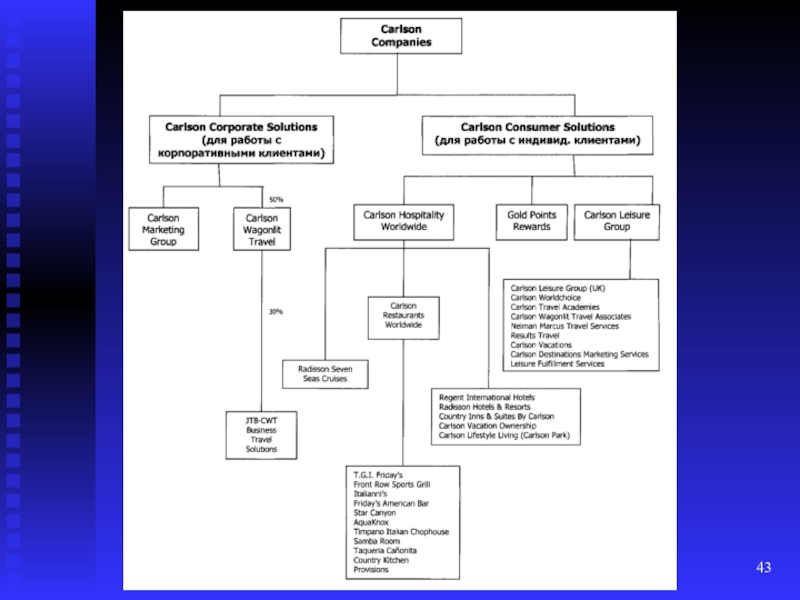
Слайд 44Internal growth strategies
Carlson Companies is one of the largest
private corporations in the United States. Its annual sales volume
is $ 42.0 billion. USA. The corporation has 1300 hotels in 100 countries, 920 restaurants in 598 countries and about 1200 tourist agencies in 150 countries. The corporation employs 175 thousand people.
The total revenue of the corporation for all its brands (Radisson Blu, Radisson®, Park Plaza®, Park Inn by Radisson, Country Inns & Suites By CarlsonSM, Hotel Missoni, TGI Friday's® and Carlson Wagonlit Travel (CWT)) in 2012 amounted to 42 billion US dollars.
Слайд 45Strategies for external growth
External growth is inorganic growth. It is
realized through the merger of two or more firms. A
firm can acquire another firm, or firms can come together to improve their competitiveness.
External growth is usually achieved through the implementation of the following strategies: 1) merger / acquisition; 2) establishment of joint ventures; 3) strategy of franchising; 4) globalization.
Слайд 46Strategies for external growth
There are two types of mergers /
acquisitions:
the firm merges with another firm in the same industry
that provides similar or related services;
the firm merges with another firm in a different direction of business, which has little in common with the existing one. Such a merger is called a conglomerate union.
Inorganic growth is rapid and allows you to quickly acquire assets. With such growth, there is no risk of overproduction, as the volume of services provided remains unchanged.
Слайд 47Strategies for external growth
We distinguish the following advantages from mergers:
the
merger of firms provides economies of scale in the production
and marketing of hospitality services;
more efficient use of productive assets makes it possible to increase profits;
there is the possibility of diversification;
the efficiency of resource use can be significantly increased;
it is often cheaper to acquire an existing firm than to establish a new one;
provides an opportunity to get a quick exit to new areas of business;
access to scarce raw materials, distribution network and management experience is provided.
Слайд 48Strategies for external growth
An example of the implementation of this
strategy is the strategic development of the German corporation Prussag,
which is the leading European tour operator, although until 1997 it was completely absent from the travel market.
Having reoriented itself from shipbuilding and mining activities, Prussag has made large investments in the tourist industry over the past few years. The structure of its organization is shown in Fig.
Слайд 50Strategies for external growth
A joint venture is the combination of
two or more enterprises to achieve mutually beneficial goals.
Unlike a
merger or acquisition, a joint venture should not be permanent, because it allows participants to retain their independence and individuality, and in some cases to compensate for the shortcomings of one company at the expense of the strengths of the other company.
A strategic joint venture can be developed to a strategic partnership.
Fig.
Слайд 52Characteristics of Moscow hotel market and strategy of leading hotels
Слайд 53Market of hotel services in Moscow
Moscow attracts two main categories
of customers, which is of great importance for hotel companies:
foreign
businessmen and tourists;
Russian businessmen and wealthy tourists.
Other segments of the tourist market allow hotels to exist if they found and servicing a specific market niche.
Local tourists coming to Moscow with cultural and educational purposes are not yet a sufficient market in order to increase significantly the download of hotels.
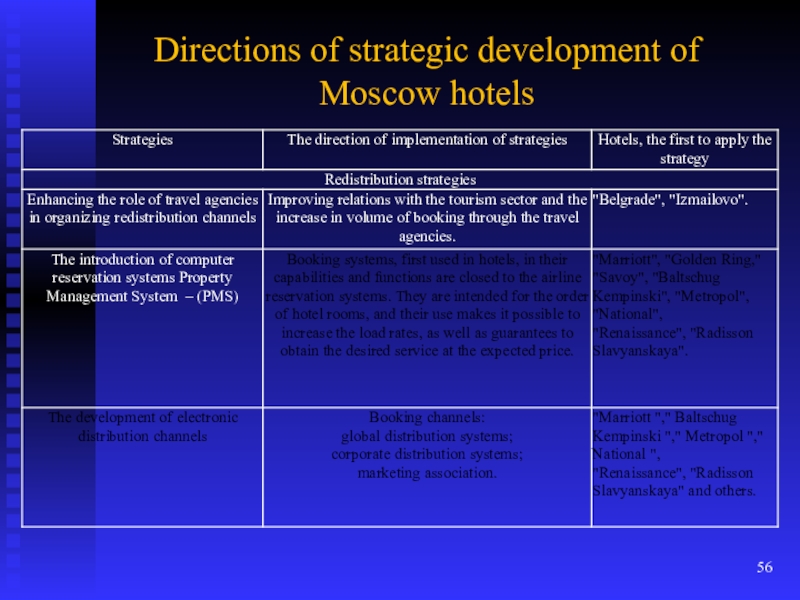
Слайд 54Directions of strategic development of Moscow hotels
Слайд 55Directions of strategic development of Moscow hotels
Слайд 56Directions of strategic development of Moscow hotels
Слайд 57Directions of strategic development of Moscow hotels
Слайд 58Directions of strategic development of Moscow hotels
Слайд 59Conclusions:
The success of the strategy in emerging markets depends on
the speed and determination of management decisions.
Hotel companies that are
able to promptly develop, produce and distribute its services to the tourist market, to respond to changes in consumer demand have more efficient management.