Слайд 2Learning outcomes
Summarise the strategy of an organisation in a ‘strategy
statement’.
Identify key issues for an organisation’s strategy according to the
Exploring Strategy model.
Distinguish between corporate, business and operational strategies.
Understand how different people contribute to strategy at work.
Appreciate the contributions of different academic disciplines and theoretical lenses to practical strategy analysis.
Слайд 3Definitions of strategy (1)
‘..the determination of the long-run goals and
objectives of an enterprise and the adoption of courses of
action and the allocation of resource necessary for carrying out these goals’
Alfred Chandler
‘Competitive strategy is about being different. It means deliberately choosing a different set of activities to deliver a unique mix of value’
Michael Porter
Sources:
A.D. Chandler, Strategy and Structure: Chapters in the History of American Enterprise, MIT Press, 1963, p. 13
M.E. Porter, ‘What is strategy?’, Harvard Business Review, 1996, November–December,
p. 60
Слайд 4Definitions of strategy (2)
‘..a pattern in a stream of decisions’
Henry
Mintzberg
‘..the long-term direction of an organisation’
Exploring Strategy
Sources:
H. Mintzberg, Tracking Strategy:
Toward a General Theory, Oxford University Press, 2007, p. 3
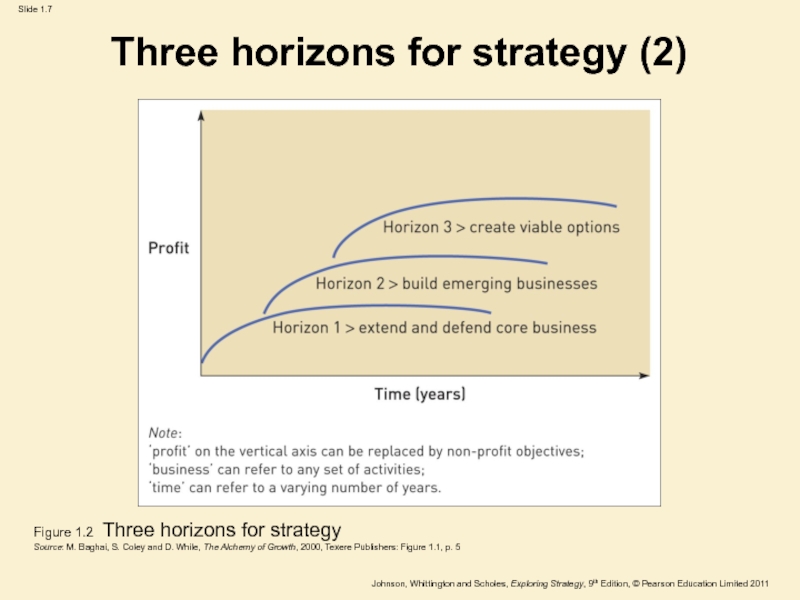
Слайд 6Three horizons for strategy (1)
Horizon 1 :
Extend and defend
core business.
Horizon 2 :
Build emerging businesses.
Horizon 3 :
Create
viable options.
Слайд 7Three horizons for strategy (2)
Figure 1.2 Three horizons for strategy
Source:
M. Baghai, S. Coley and D. While, The Alchemy of
Growth, 2000, Texere Publishers: Figure 1.1, p. 5
Слайд 8Stakeholders
Stakeholders are those individuals or groups that depend on an
organisation to fulfil their own goals and on whom, in
turn, the organisation depends.
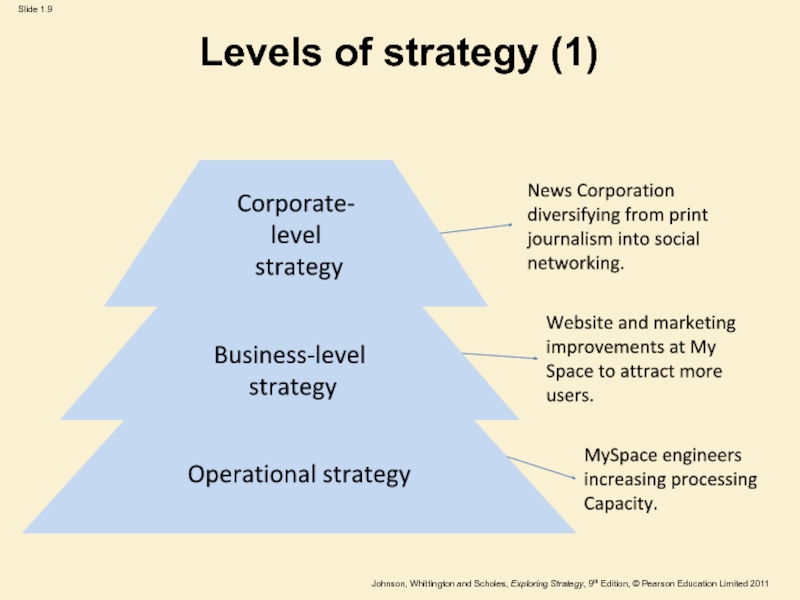
Слайд 9Levels of strategy (1)
Operational strategy
Business-level
strategy
Corporate-
level
strategy
News Corporation diversifying from
print journalism into social networking.
Website and marketing improvements at My
Space to attract more users.
MySpace engineers increasing processing
Capacity.
Слайд 10Levels of strategy (2)
Corporate-Level Strategy is concerned with the overall
purpose and scope of an organisation and how to add
value to business units.
Business-Level Strategy is concerned with the way a business seeks to compete successfully in its particular market.
Operational Level Strategy is concerned with how different parts of the organisation deliver the strategy in terms of managing resources, processes and people.
Слайд 11Strategy statements
Strategy statements should have three main themes:
the fundamental
goals that the organisation seeks, which draw on the stated
mission, vision and objectives
the scope or domain of the organisation’s activities
and the particular advantages or capabilities it has to deliver all these.
Слайд 12Working with strategy (1)
All managers are concerned with strategy:
Top managers
frequently formulate and control strategy but may also involve others
in the process.
Middle and lower level managers have to meet strategic objectives and deal with constraints.
All managers have to communicate strategy to their teams.
All managers can contribute to the formation of strategy through ideas and feedback.
Слайд 13Working with strategy (2)
Organisations may also use strategy specialists:
Many large
organisations have in-house strategic planning or analyst roles.
Strategy consultants can
be engaged from one of many general management consulting firms (e.g. Accenture, IBM Consulting, PwC).
There are a growing number of specialist strategy consulting firms (e.g. McKinsey &Co, The Boston Consulting Group).
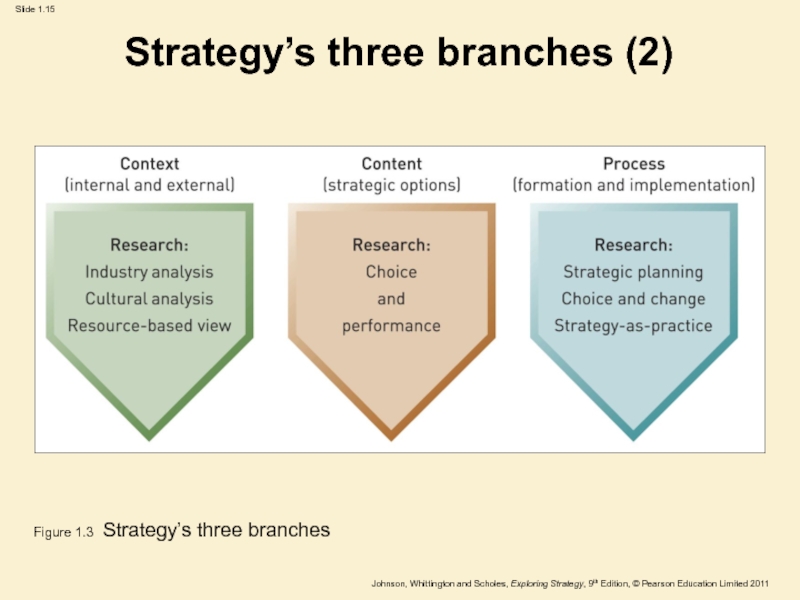
Слайд 14Strategy’s three branches (1)
CONTEXT – internal and external.
CONTENT – strategic
options.
PROCESS – formation and implementation.
Слайд 15Strategy’s three branches (2)
Figure 1.3 Strategy’s three branches
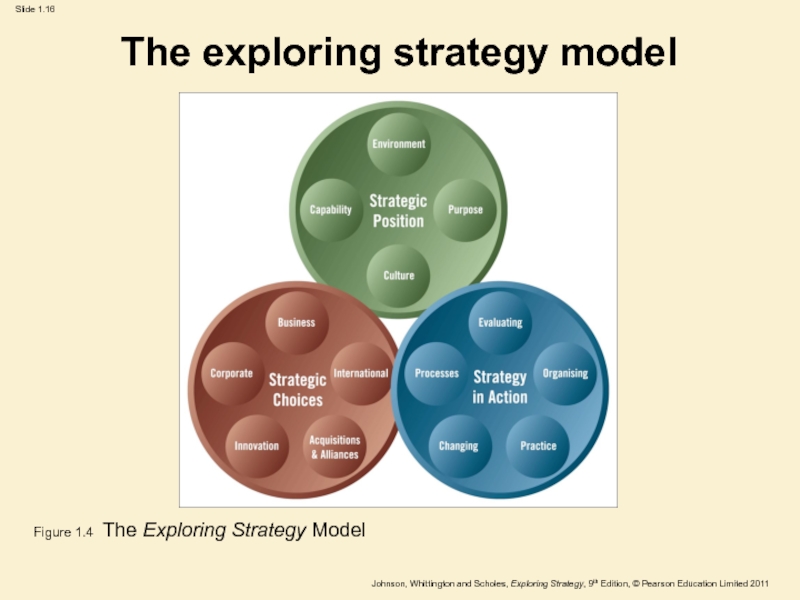
Слайд 16The exploring strategy model
Figure 1.4 The Exploring Strategy Model
Слайд 17Strategic position (1)
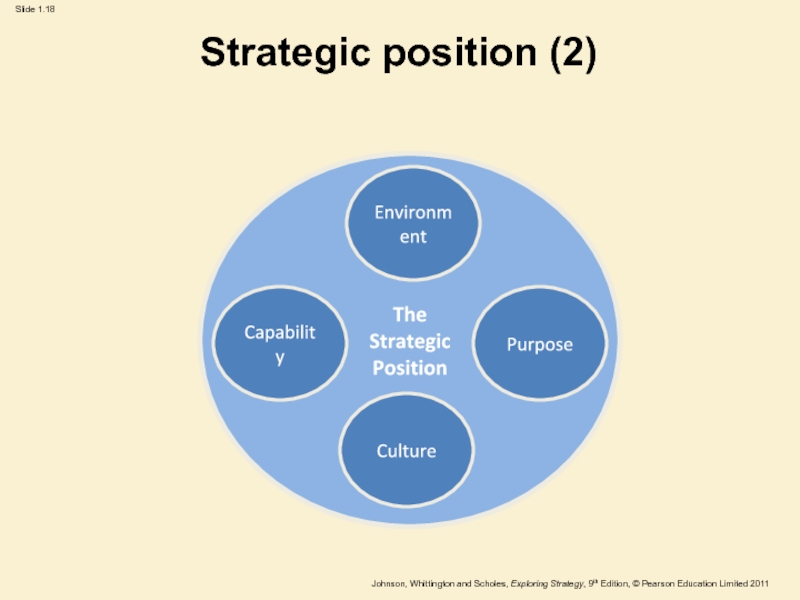
The strategic position is concerned with the impact
on strategy of the external environment, the organisation’s strategic capability
(resources and competences), the organisation’s goals and the organisation’s culture.
Слайд 18Strategic position (2)
The
Strategic
Position
Environment
Culture
Purpose
Capability
Слайд 19Strategic position (3)
Fundamental questions for Strategic Position:
• What are the
environmental opportunities and threats?
• What are the organisation’s strengths and
weaknesses?
• What is the basic purpose of the organisation?
• How does culture shape strategy?
Слайд 20Strategic choices (1)
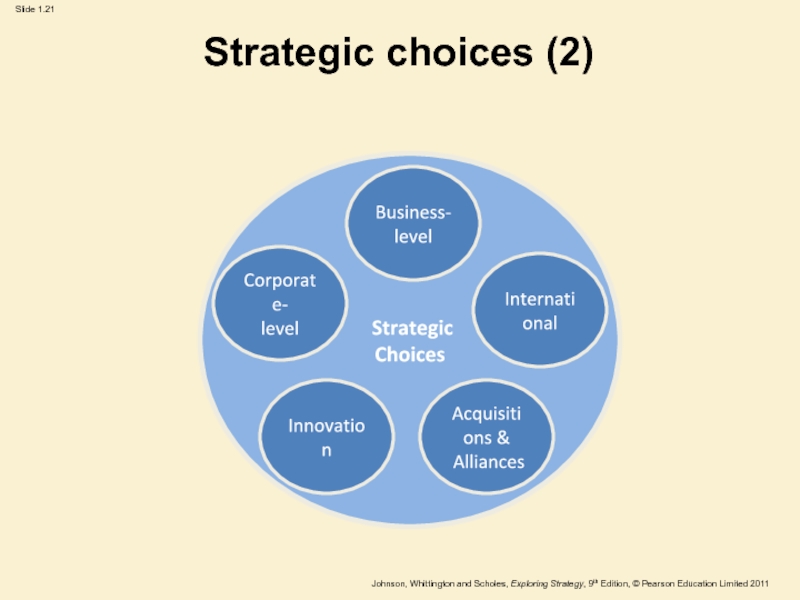
Strategic choices involve the options for strategy in
terms of both the directions in which strategy might move
and the methods by which strategy might be pursued.
Слайд 21Strategic choices (2)
Strategic
Choices
Business-
level
Innovation
International
Corporate-
level
Acquisitions &
Alliances
Слайд 22Strategic choices (3)
Fundamental questions for Strategic Choice:
• How should business
units compete?
• Which businesses to include in the portfolio?
• Where
should the organisation compete
internationally?
• Is the organisation innovating appropriately?
• Should the organisation buy other companies, form alliances or go it alone?
Слайд 23Strategy in action (1)
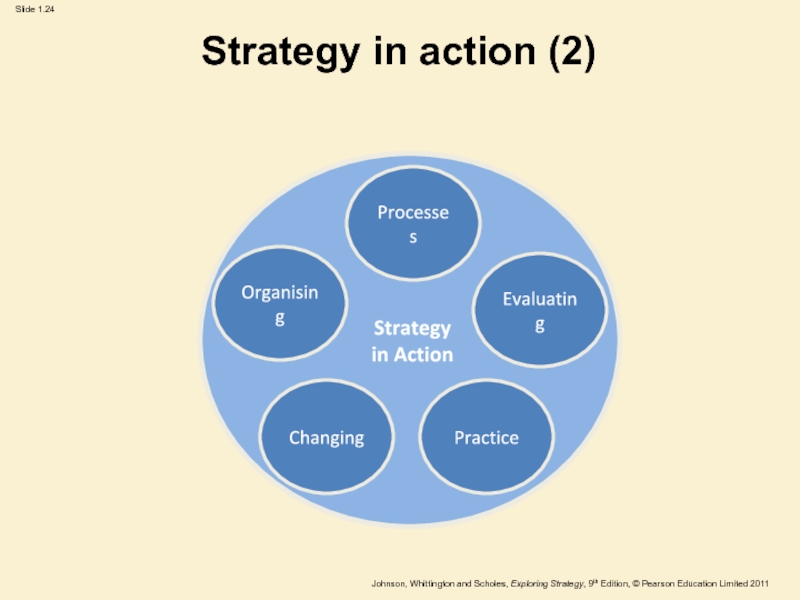
Strategy in action is about how strategies
are formed and how they are implemented.
The emphasis is on
the practicalities of managing.
Слайд 24Strategy in action (2)
Strategy
in Action
Processes
Changing
Evaluating
Organising
Practice
Слайд 25Strategy in action (3)
Fundamental questions for Strategy in Action
• Which
strategies are suitable, acceptable and feasible?
• What kind of strategy-making
process is needed?
• What are the required organisation structures and systems?
• How should the organisation manage necessary changes?
• Who should do what in the strategy process?
Слайд 26Exploring strategy in
different contexts
The Exploring Strategy Model can be
applied in many contexts.
In each context the balance of strategic
issues differs:
Small Businesses (e.g. Purpose and Growth issues)
Multinational Corporations (e.g. Geographical Scope and Structure/Control issues)
Public Sector Organisations (e.g. Service/Quality and Managing Change issues)
Not For Profit Organisations (e.g. Purpose and Funding issues)
Слайд 27The strategy lenses (1)
The strategy lenses are ways of looking
at strategy issues differently in order to generate many insights.
Looking at problems in different ways will raise new issues and new solutions.
Слайд 28The strategy lenses (2)
Strategy can be seen as:
Design
Experience
Variety (Ideas)
Discourse
Слайд 29Strategy as design
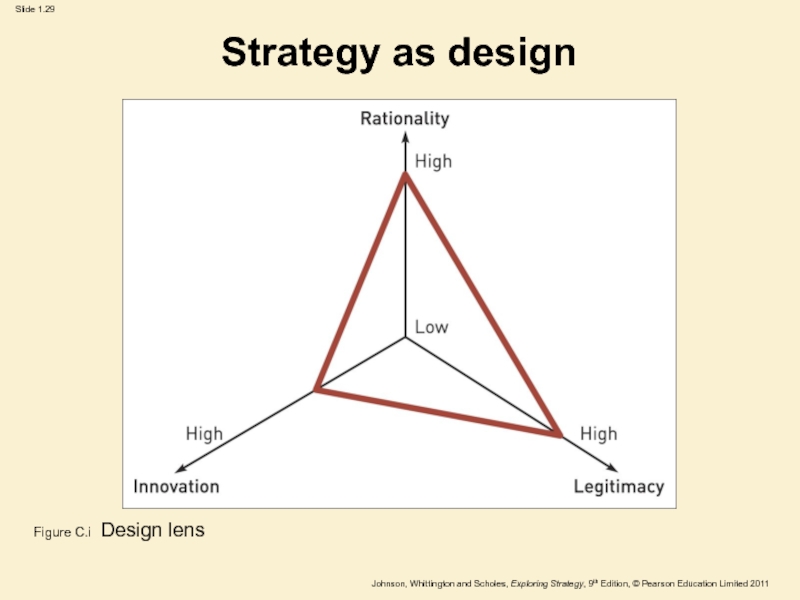
Figure C.i Design lens
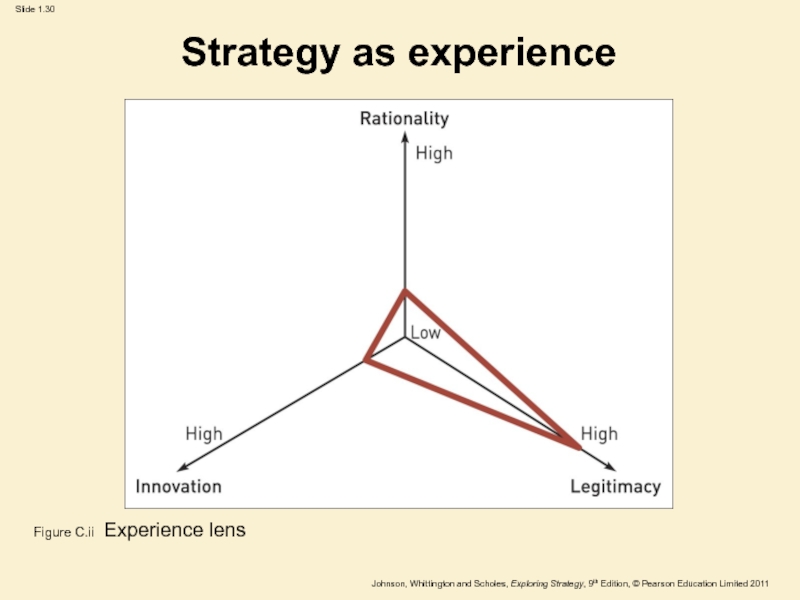
Слайд 30Strategy as experience
Figure C.ii Experience lens
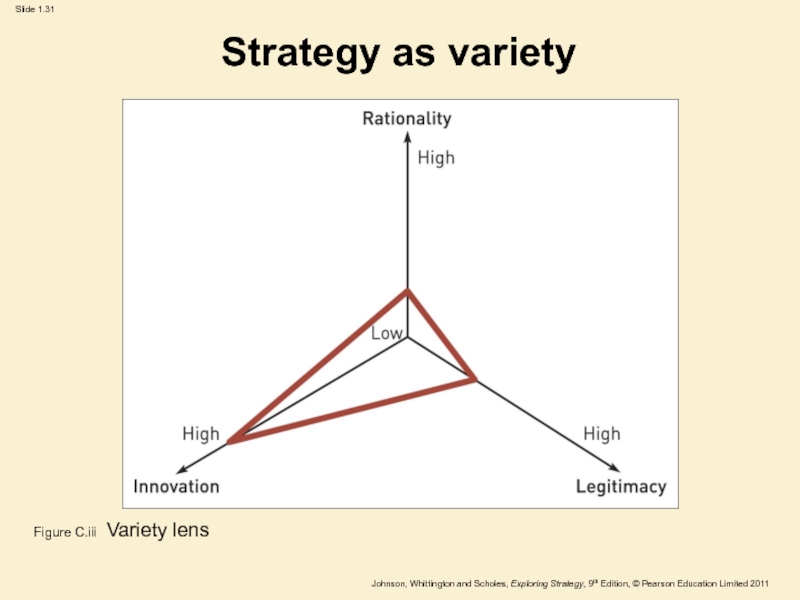
Слайд 31Strategy as variety
Figure C.iii Variety lens
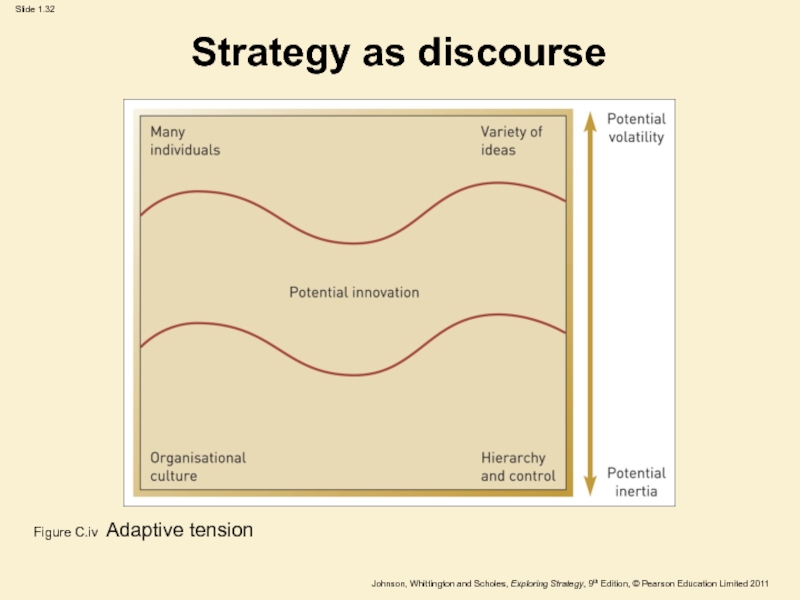
Слайд 32Strategy as discourse
Figure C.iv Adaptive tension
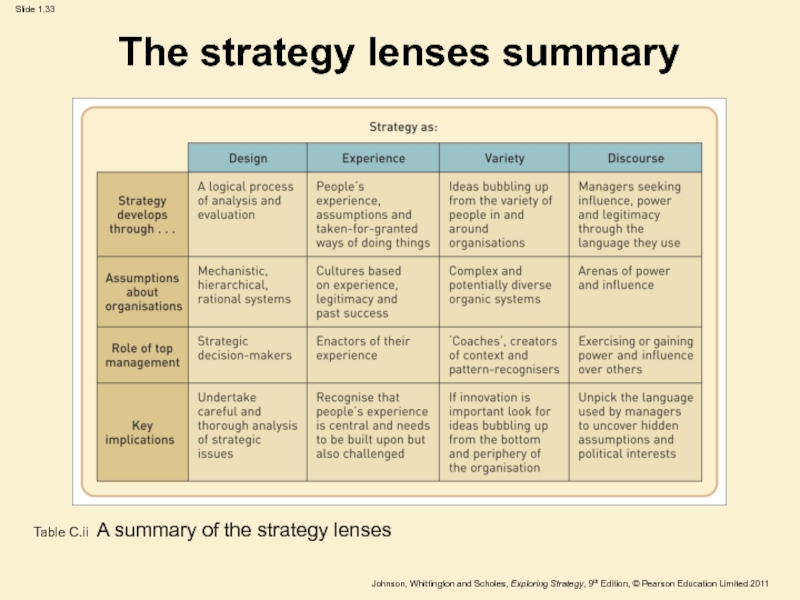
Слайд 33The strategy lenses summary
Table C.ii A summary of the strategy
lenses
Слайд 34Chapter summary (1)
Strategy is the long-term direction of an organisation.
A ‘strategy statement’ should cover the goals of an organisation,
the scope of the organisation’s activities and the advantages or capabilities the organisation brings to these goals and activities.
Corporate-level strategy is concerned with an organisation’s overall scope; business-level strategy is concerned with how to compete; and operational strategy is concerned with how resources, processes and people deliver corporate- and business-level strategy.
Strategy work is done by managers throughout an organisation, as well as specialist strategic planners and strategy consultants.
Слайд 35Chapter summary (2)
Research on strategy context, content and process shows
how the analytical perspectives of economics, sociology and psychology can
all provide practical insights for approaching strategy issues
The Exploring Strategy Model has three major elements: understanding the strategic position, making strategic choices for the future and managing strategy-in-action.
Strategic issues are best seen from a variety of perspectives, as exemplified by the four strategy lenses of design, experience, variety and discourse.