Слайд 2
Query language
Query language is a written language used only to write
specific queries. This is a powerful tool as the user
can define precisely what is required in a database. SQL is a popular query language used with many databases.
Query languages are computer languages used to make queries in databases and information systems.
the Structured Query Language (SQL), has the form
select [field Fa, Fb, . . ., Fn]
from [database Da, Db, . . ., Dn]
where [field Fa = abc] and [field Fb = def].
Слайд 3Programming Language
A programming language is an artificial language that a computer understands.
The language is made up of series of statements that fit
together to form instructions. These instructions tell a computer what to do.
Among the most popular languages are:
Python
Java
C++
BASIC
Scratch
Слайд 4Types of program errors
We distinguish between the following types of
errors:
Syntax errors: errors due to the fact that the syntax
of the language is not respected.
Semantic errors: errors due to an improper use of program statements.
Logical errors: errors due to the fact that the specification is not respected.
From the point of view of when errors are detected, we distinguish:
Compile time errors: syntax errors and static semantic errors indicated by the compiler.
Runtime errors: dynamic semantic errors, and logical errors, that cannot be detected by the compiler (debugging).
Слайд 5Syntax errors
Example 1: Missing semicolon:
int a = 5 // semicolon is
missing
Compiler message:
Example.java:20: ';' expected
int a =
5
Example 2: Errors in expressions:
x = ( 3 + 5; // missing closing parenthesis ')' y = 3 + * 5; // missing argument between '+' and '*'
Слайд 6Semantic errors
Example 1: Use of a non-initialized variable:
int i; i++; //
the variable i is not initialized
Example 2: Type incompatibility:
int a
= "hello"; // the types String and int are not compatible
Example 3: Errors in expressions:
String s = "..."; int a = 5 - s; // the - operator does not support arguments of type String
Слайд 7Logical errors
Example 1: Errors in the performed computation:
public static int sum(int
a, int b) { return a - b ; }
// this method returns the wrong value wrt the specification that requires // to sum two integers
Example 2: Non termination:
String s = br.readLine(); while (s != null) { System.out.println(s); } // this loop does not terminate
Слайд 8Errors detected by the compiler and runtime errors
Example 1: Division by
zero:
int a, b, x; a = 10; b = Integer.parseInt(kb.readLine());
x = a / b; //ERROR if b = 0 This error occurs only for a certain configuration of the input (b = 0).
Example 2: File does not exist:
FileReader f = new FileReader("pippo.txt"); The error occurs only if the file pippo.txt does not exist on the harddisk.
Example 3: Dereferencing of a null reference:
String s, t; s = null; t = s.concat("a"); // The concat() method cannot be applied to a reference whose value is null.
Слайд 9Test data
valid - the most obvious or common data that should
work
valid extreme - unusual, extreme or unexpected data, eg the highest
and lowest (data that tests the limits but that should work)
invalid - data that should definitely fail
invalid extreme - data that is at the edge of failure and is nearly acceptable
erroneous - data that is the wrong data type
Слайд 10Invariant
Sometimes software developers use something called an invariantwhen they are testing
or fixing bugs. An invariant is a value or condition that can be
relied upon to be true when a program is being executed.
Using something that can be relied upon helps the developer to isolate the units that are working from the units that are not.
Слайд 114.2 CPU (Central
Processing Unit)
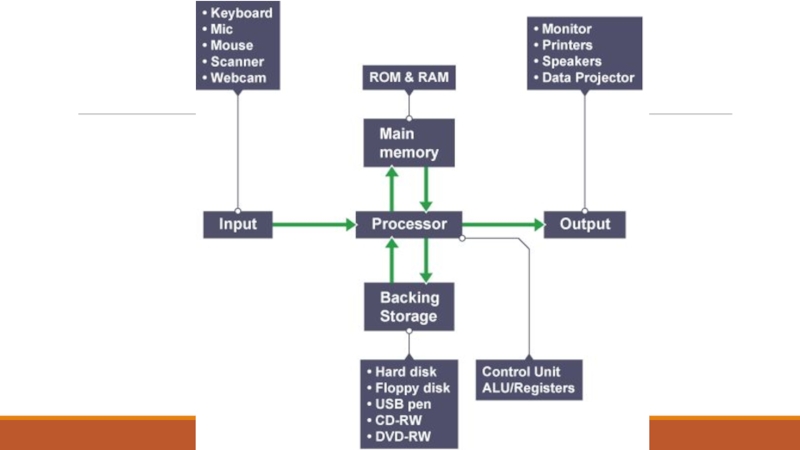
Слайд 12Introducing peripherals
Peripherals are devices that are not the computer's core architecture involved
in memory and processing. Peripherals include input hardware, output hardware and storage
devices.
A typical desktop computer could include:
inputs - mouse, keyboard, webcam, games controller
outputs - screen, printer, speakers, headphones
storage - hard drive
Слайд 15The CPU only performs a few basic functions:
performing mathematical operations
like addition and subtraction
moving data from one memory location to
another
making decisions and jumps to a new set of instructions based on those decisions
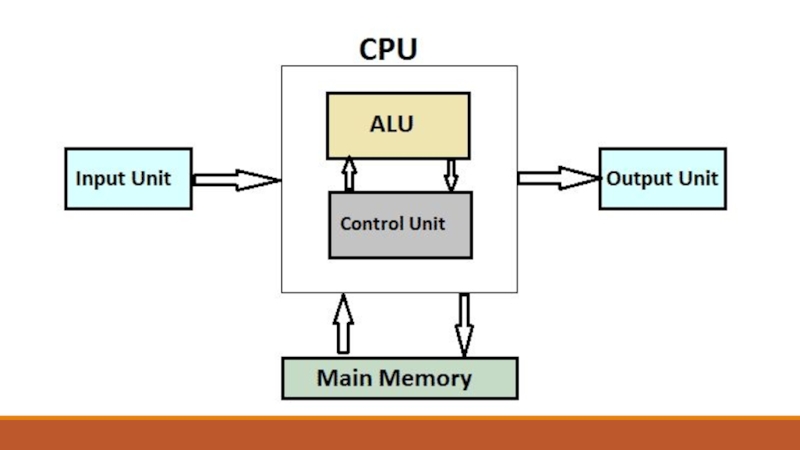
Слайд 16Arithmetic and logic unit
The arithmetic and logic unit (ALU) is where the
CPU performs the arithmetic and logic operations. Every task that your
computer carries out is completed here. Even typing into a word processor involves adding binary digits to the file, and then calculating which pixels on the screen should change so that you can see the characters. The ALU’s operations fall into two parts:
the arithmetic part, which deals with calculations, eg 1 + 2 = 3
the logic part, which deals with any logical comparisons, eg 2>1
Слайд 17Registers
Registers are also called internal memory or immediate access memory stores.
A register is a small amount of fast temporary memory
within the processor where the ALU or the CU can store and change values needed to execute instructions.
Different processors have different sets of registers. One important register is the program counter. This keeps track of the running order of the instructions and shows which instruction in the program is due to be executed next.
Слайд 18Control unit (CU)
The CU, which is also called the controller,
controls data moving through the processor, and controls the timing
of operations and the instructions sent to the processor and the peripheral devices. The CU directs the system to carry out program instructions. It does the fetching, decoding, and managing of instructions.
Слайд 19CPU speed
A computer’s speed is heavily influenced by the CPU it uses.
There are three main factors that affect how quickly a
CPU can carry out instructions:
clock speed
cores
cache
Слайд 20Clock speed
CPUs can only carry out one instruction at a
time.
The speed at which the CPU can carry out instructions
is called the clock speed. This is controlled by a clock. With every tick of the clock, the CPU fetches and executes one instruction. The clock speed is measured in cycles per second, and one cycle per second is known as 1 hertz. This means that a CPU with a clock speed of 2 gigahertz (GHz) can carry out two thousand million (or two billion) cycles per second.
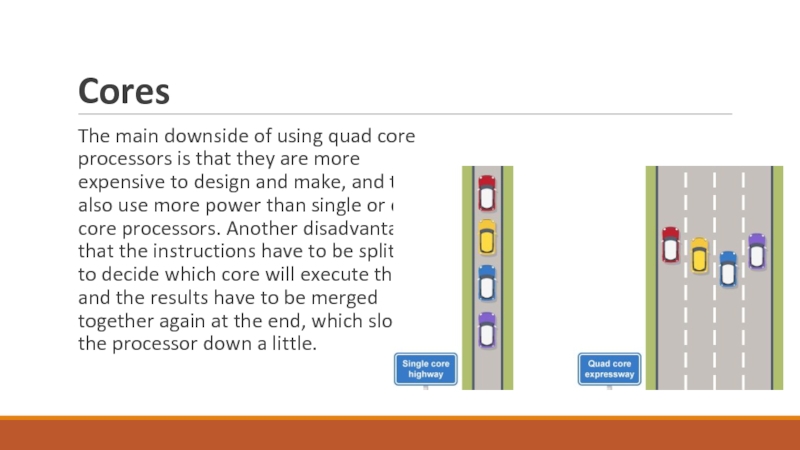
Слайд 21Cores
The main downside of using quad core processors is that
they are more expensive to design and make, and they
also use more power than single or dual core processors. Another disadvantage is that the instructions have to be split up to decide which core will execute them and the results have to be merged together again at the end, which slows the processor down a little.
Слайд 22Cache
A cache (pronounced ‘cash’) is a tiny block of memory built right
onto the processor. The most commonly used instructions and dataare stored
in the cache so that they are close at hand. The bigger the cache is, the more quickly the commonly used instructions and data can be brought into the processor and used.
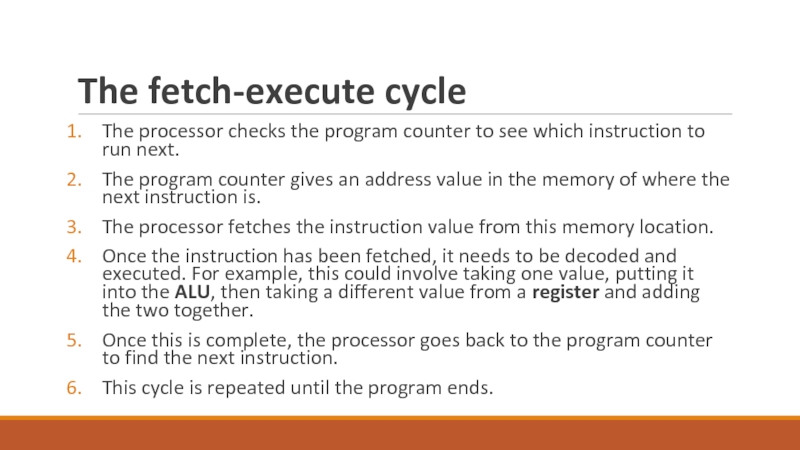
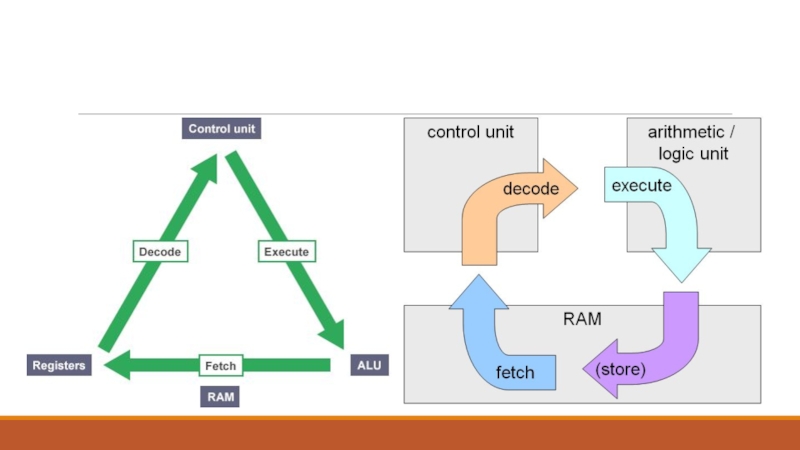
Слайд 23The fetch-execute cycle
The processor checks the program counter to see
which instruction to run next.
The program counter gives an address
value in the memory of where the next instruction is.
The processor fetches the instruction value from this memory location.
Once the instruction has been fetched, it needs to be decoded and executed. For example, this could involve taking one value, putting it into the ALU, then taking a different value from a register and adding the two together.
Once this is complete, the processor goes back to the program counter to find the next instruction.
This cycle is repeated until the program ends.