Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Business Planning
Содержание
- 1. Business Planning
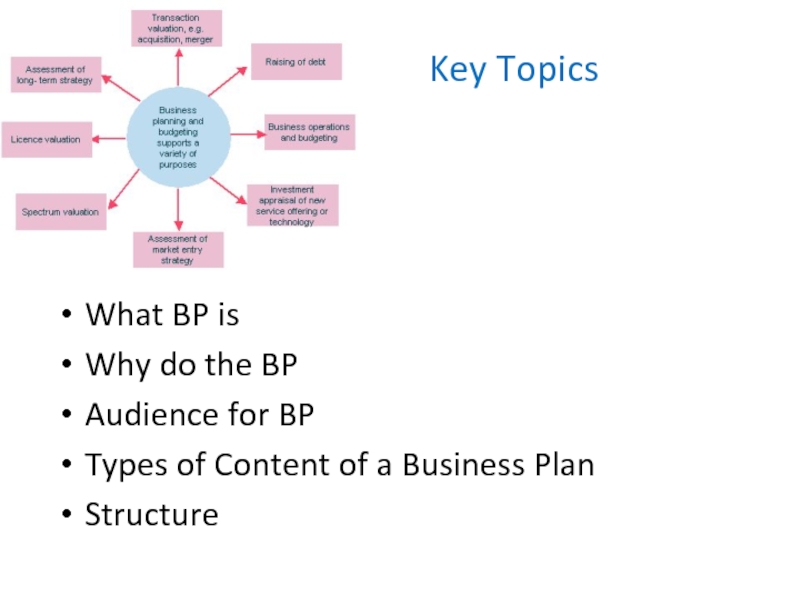
- 2. Key TopicsWhat BP isWhy do the BPAudience for BPTypes of Content of a Business PlanStructure
- 3. What BP isA business plan is a
- 4. What BP isBusiness plans may also target
- 5. Why do BPA business plan is often
- 6. Audience for BP. Externally or internally focused
- 7. Audience for BP. Externally focused plans. External
- 8. Audience for BP. Internally focused plans. Internal
- 9. Audience for BP. Internally focused plans. Internal
- 10. Audience for BP. Internally focused plans. Types
- 11. Benefits of doing BPTo identify an problems
- 12. Types of Content of a Business Plan
- 13. cover page and table of contents executive
- 14. Contents1 Executive summary 2 Organizational background 2.1
- 15. 4 Operational plan 4.1 Manufacturing/de4.1 Manufacturing/development4.1 Manufacturing/development
- 16. Business Plan. Typical Structure.Executive summary.Company Description2.1. History.2.2.
- 17. Business Plan. Typical Structure. 3.3. Investments.3.4. Schedule
- 18. Business Plan. Typical Structure.4.2.5. Company’s Market Strategy-Promotion
- 19. Business Plan. Typical Structure.6. Evaluation of efficiency of investment projects. 7. Risk analysis.
- 20. Executive Summary The executive summary specifies the key
- 21. Executive SummaryA loan request executive summary might
- 22. Executive SummaryFor a new venture, the executive
- 23. Executive SummaryFor an internal project plan, the
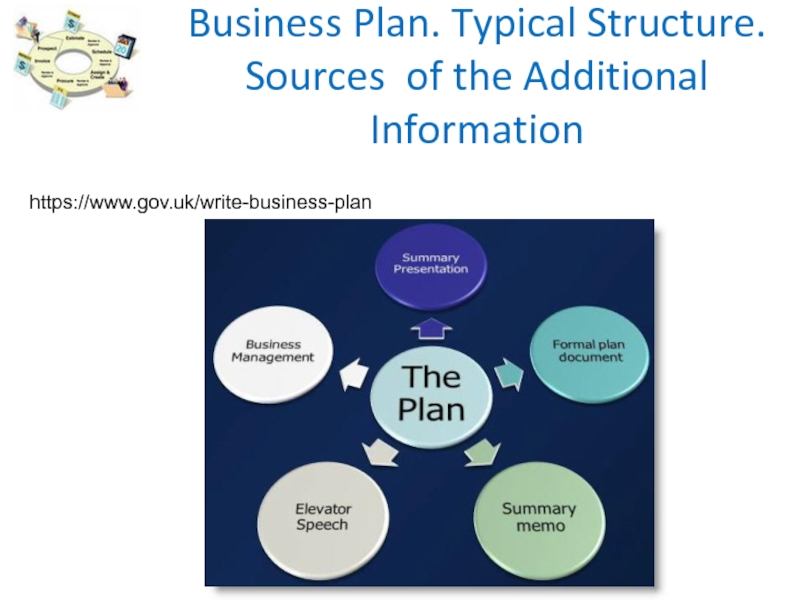
- 24. Business Plan. Typical Structure. Sources of the Additional Informationhttps://www.gov.uk/write-business-plan
- 25. Thank you for your attention!
- 26. Скачать презентанцию
Key TopicsWhat BP isWhy do the BPAudience for BPTypes of Content of a Business PlanStructure
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Business Planning
PROJECT MANAGEMENT
Developed by Elizaveta Markovskaya, associate professor, Phd (Economics)
Слайд 3What BP is
A business plan is a formal statement of
a set of business goals, the reasons they are believed
attainable, and the plan for reaching those goals. It may also contain background information about the organization or team attempting to reach those goals.Слайд 4What BP is
Business plans may also target changes in perception
and branding by the customer, client, taxpayer, or larger community.
When the existing business is to assume a major change or when planning a new venture, a 3 to 5 year business plan is required, since investors will look for their annual return in that timeframe.Слайд 5Why do BP
A business plan is often prepared when:
Starting a
new organization, business venture, or product (service) or
Expanding, acquiring
or improving any of the above. Слайд 6Audience for BP. Externally or internally focused plans.
Business plans
may be internally or externally focused. Externally focused plans target
goals that are important to external stakeholders, particularly financial stakeholders. They typically have detailed information about the organization or team attempting to reach the goals.Слайд 7Audience for BP. Externally focused plans. External stakeholders.
For –profit
entities: investors and customers;
Non-profits include: donors and the clients of
the non-profit's services;For government agencies tax-payers, higher-level government agencies, and international lending bodies such as the International Monetary Fund, the World Bank, various economic agencies of the United Nations, and development banks.
Слайд 8Audience for BP. Internally focused plans. Internal goals and stakeholders.
Goals:
the development of a new product, a new service,
a
new IT system; a restructuring of finance;
the refurbishing of a factory;
a restructuring of the organization.
Слайд 9Audience for BP. Internally focused plans. Internal goals and stakeholders.
An internal business plan is often developed in conjunction with
a balanced scorecard or a list of critical success factors. This allows success of the plan to be measured using non-financial measures. Слайд 10Audience for BP. Internally focused plans. Types of plans
Business plans
that identify and target internal goals, but provide only general
guidance on how they will be met are called strategic plans.Operational plans describe the goals of an internal organization, working group or department.
Project plans, sometimes known as project frameworks, describe the goals of a particular project. They may also address the project's place within the organization's larger strategic goals.
Слайд 11Benefits of doing BP
To identify an problems in your plans
before you implement those plans.
To get the commitment and
participation of those who will implement the plans, which leads to better results. To establish a roadmap to compare results as the venture proceeds from paper to reality.
To achieve greater profitability in your organization, products and services -- all with less work.
To obtain financing from investors and funders.
To minimize your risk of failure.
To update your plans and operations in a changing world.
To clarify and synchronize your goals and strategies.
Слайд 12Types of Content of a Business Plan
Business plans appear in
many different formats, depending on the audience for the plan
and complexity of the business.Though business plans have many different presentation formats, business plans typically cover five major content areas:
Background information
A marketing plan
An operational plan
A financial plan
A discussion of the decision making criteria that should be used to approve the plan.
There is no fixed content for a business plan.
Rather the content and format of the business plan is determined by the goals and audience. A business plan should contain whatever information is needed to decide whether or not to pursue a goal.
Слайд 13cover page and table of contents
executive summary
business description
business environment analysis
industry background
competitor analysis
market analysis
marketing plan
operations plan
management summary
financial plan
attachments and milestones
Typical structures for a business plan for a start up venture.
Слайд 14Contents
1 Executive summary
2 Organizational background
2.1 Current status
2.2
History
2.3 Management team
3 Marketing plan
3.1 Pricing
3.2
Demand management 3.3 Distribution/Positioning
3.4 Promotion and brand development
Typical structures for a business plan for a start up venture.
Слайд 154 Operational plan
4.1 Manufacturing/de4.1 Manufacturing/development4.1 Manufacturing/development plan
4.2 Information
and communications technology plan
4.2.1 Staffing needs
4.2.2 Training requirements
4.2.3 Intellectual property plan
4.2.4 Acquisition plan
4.2.5 Organizational learning plan
4.3 Cost allocation model
5 Financial plan
5.1 Current financing
5.2 Funding plan
5.3 Financial forecasts
6 Risk analysis
6.1 Risk evaluation
6.2 Risk management plan
7 Decision making criteria
Слайд 16Business Plan. Typical Structure.
Executive summary.
Company Description
2.1. History.
2.2. Company’s structure
2.3. Management
2.4.
Personnel.
3. Project Description.
3.1. General description.
3.2. State of project’s affairs.
Слайд 17Business Plan. Typical Structure.
3.3. Investments.
3.4. Schedule of financing.
3.5.
Schedule of investment project.
4. Market Analysis.
4.1. Industry description.
4.2. Company
position on the market.4.2.1. Description of the product and services.
4.2.2. Consumers.
4.2.3. Competition.
4.2.4. SWOT analysis
Слайд 18Business Plan. Typical Structure.
4.2.5. Company’s Market Strategy
-Promotion Plan
Marketing Plan
4.2.6. Pricing.
5.
Financial plan.
5.1. Conditions and assumptions.
5.2. Plan of incomes.
5.3. Plan of
expenditures.5.4. Financial strategy.
5.5. Prognostic financial reports (P&L, CF, Balance Sheet)
Слайд 19Business Plan. Typical Structure.
6. Evaluation of efficiency of investment projects.
7. Risk analysis.
Слайд 20Executive Summary
The executive summary specifies the key points of the
business plan.
It should define the decision to be made
and the reasons for approval. The specific content will be highly dependent on the core purpose and target audience. To get a sense of the difference the purpose and target audience can make, here are three different sets of key points for an executive summary - one for a loan request, one for a start-up seeking venture finance, and one for an internal plan.
Слайд 21Executive Summary
A loan request executive summary might contain the following
information:
Company information: name of company, years in business, legal structure,
minority and majority owners Brief description of project
Amount and length of loan
Objective reasons why the bank should be confident that the loan will be paid back. This likely will include
Financial track record
The future revenue stream
Any contracts in place that might guarantee the revenue stream is more than just a forecast.
Слайд 22Executive Summary
For a new venture, the executive summary might contain:
Company
information: name of company, proposed legal structure, current legal structure,
minority and majority investors.Amount of investment requested
Expected terminal value
Description of market opportunity
Objective reasons why the market opportunity can be exploited by this particular team
Слайд 23Executive Summary
For an internal project plan, the executive summary might
look like this:
Company information: not applicable
Description of project
Project
mandate: who requested the proposal, who is being assigned to carry it out Strategic, tactical and financial justifications
Summary of resources needed: staff, funds, facilities