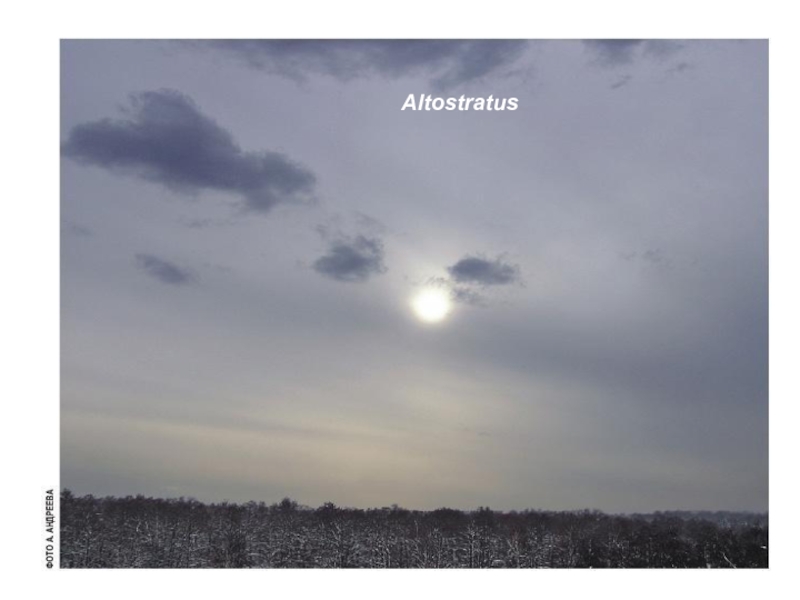
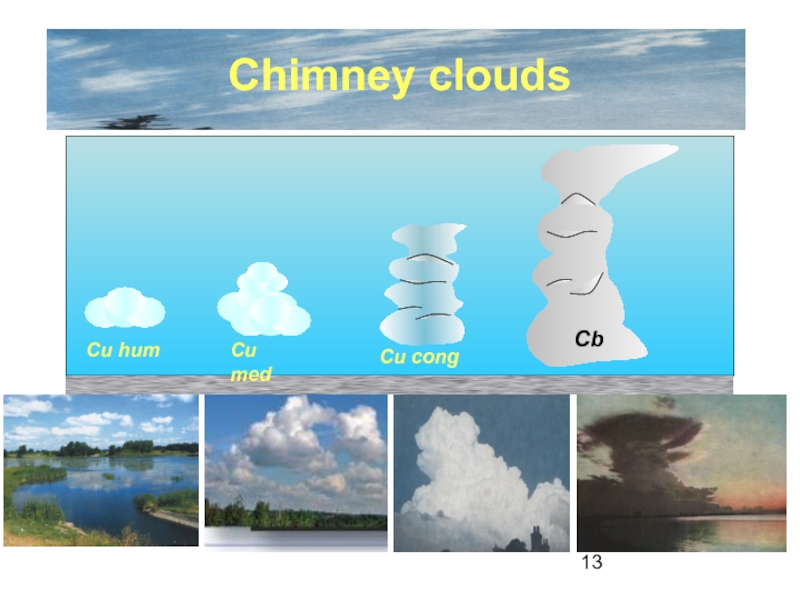
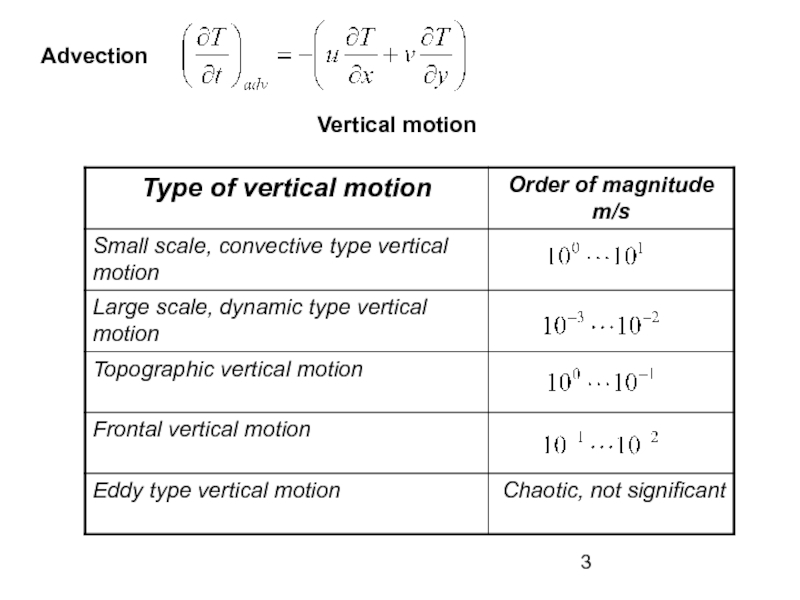
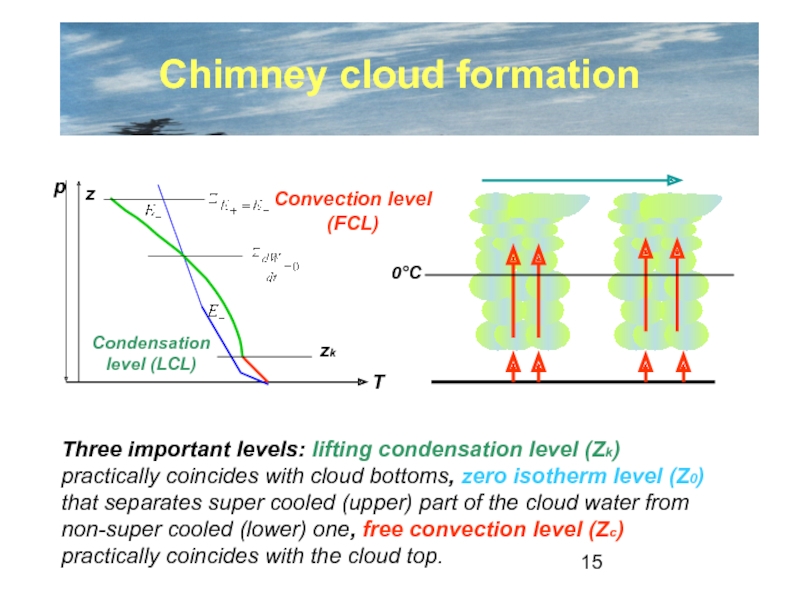
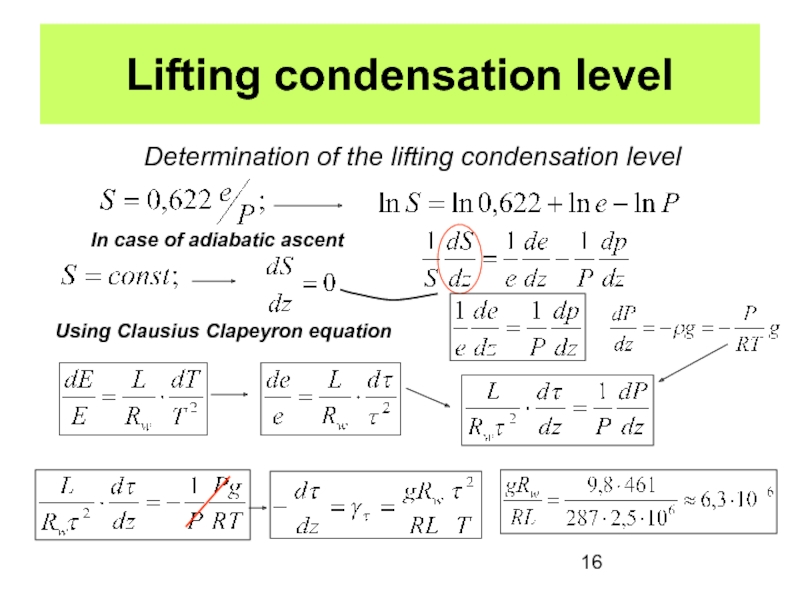
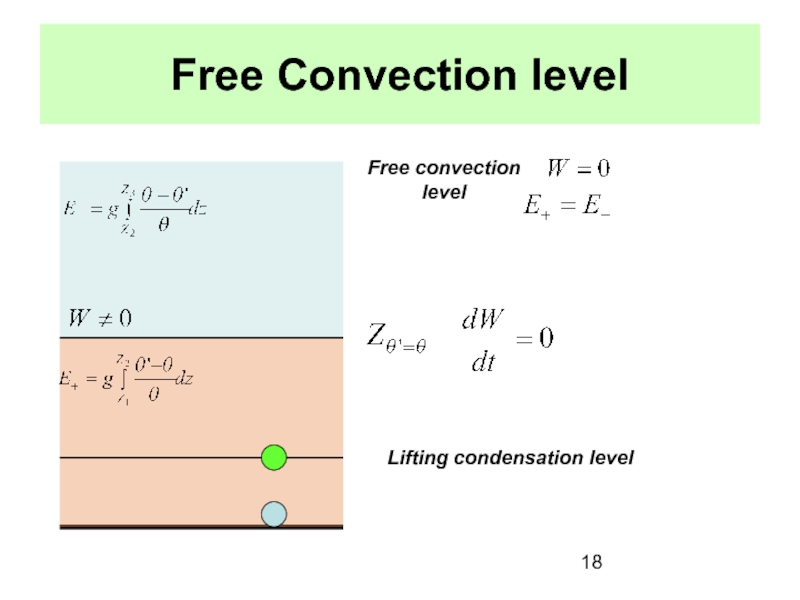
the Earth’s surface is called
CLOUD
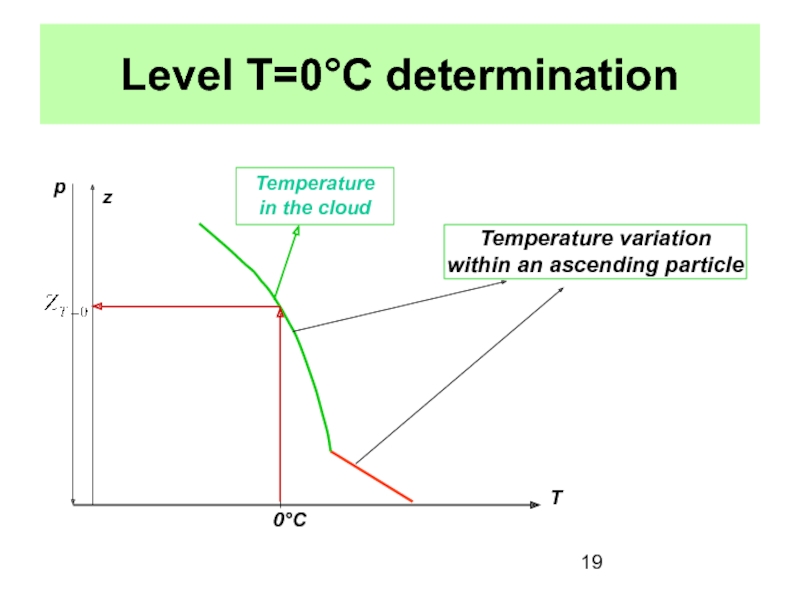
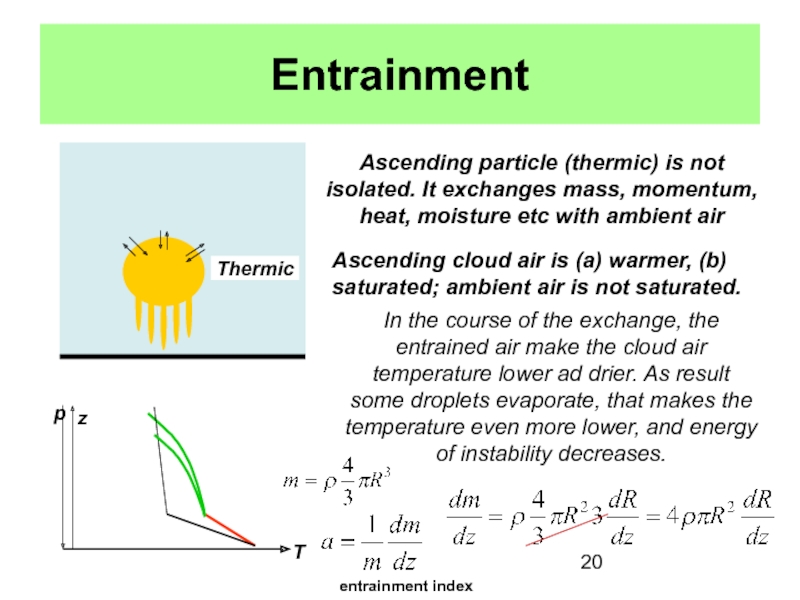
Cloud formation occurs as result of
water vapor condensation.Condensation takes place due to air temperature decrease and amount of water vapor increase.