Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Risk Management PROJECT MANAGEMENT
Содержание
- 1. Risk Management PROJECT MANAGEMENT
- 2. Key TopicsWhat risk isTypes of RisksThe process of Risk ManagementRisk review
- 3. What Risk is The Project Management Institute defines
- 4. What Risk is Some risk managers define risk
- 5. Risk Management Companies need risk management to analyze
- 6. Risk Management The task of the risk manager
- 7. Risk classification Depending on the nature of appearance:
- 8. Risk classification Depending on the influence on the
- 9. Risk classification
- 10. Risk management process Project
- 11. Risk management process Project
- 12. Risk management process The
- 13. Risk management processIdentify: This is the process
- 14. Risk management process
- 15. Risk management process 1.
- 16. Risk Description: How to describe Risk. Main
- 17. Risk review How to perform a
- 18. Risk review.Example.Lets assume that, as a team,
- 19. Risk review.Example.We may have a shortage of
- 20. Risk review.Probability/ImpactNote that we have a combination
- 21. Risk review.Probability/Impact
- 22. Risk review. Last step – developing strategy.
- 23. Risk review. Last step – developing mitigation strategy.
- 24. Risk review.Qualitative and quantitative review Note that Risk
- 25. Risk review. When we should use it? Risk
- 26. Risk review. How could we use the
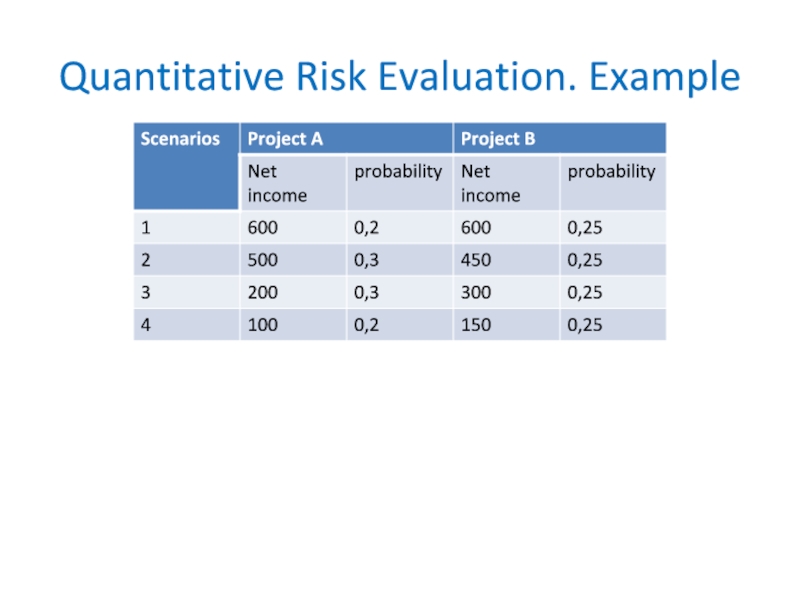
- 27. Quantitative Risk Evaluation1) the expected value (or
- 28. Quantitative Risk Evaluation. Example
- 29. Thank you for your attention!
- 30. Скачать презентанцию
Key TopicsWhat risk isTypes of RisksThe process of Risk ManagementRisk review
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Risk Management
PROJECT MANAGEMENT
Developed by Elizaveta Markovskaya, associate professor, Phd (Economics)
Слайд 3What Risk is
The Project Management Institute defines project risk as:
A risk is a possible future event that may affect
your project either positively or negatively. Слайд 4What Risk is
Some risk managers define risk as the possibility
that a future occurrence may cause harm or losses, while
noting that risk also may provide possible opportunities.Слайд 5Risk Management
Companies need risk management to analyze possible risks in
order to balance potential gains against potential losses and avoid
expensive mistakes.Risk management is best used as a preventive measure rather than as a reactive measure.
Слайд 6Risk Management
The task of the risk manager is to predict,
and enact measures to control or prevent, losses within a
company.The risk-management process involves identifying exposures to potential losses, measuring these exposures, and deciding how to protect the company from harm given the nature of the risks and the company's goals and resources.
While companies face a host of different risks, some are more important than others. Risk managers determine their importance and ability to be affected while identifying and measuring exposures.
Слайд 7Risk classification
Depending on the nature of appearance: political and economical;
Depending
on the character of effects: dynamic (pure) and (static) speculative;
Depending
on the sphere: industrial, commercial, financial, insurance, trade ;Other: country, currency, tax, credit, portfolio, organizational…
Another classification: external risk (political, ecological, currency, macroeconomic) and internal (project risk)
Слайд 8Risk classification
Depending on the influence on the management’s cost: single,
portfolio;
Depending on the possibility of the diversification: diversified, non-diversified;
Depending on
the influence on the price: essential, inessential;Depending on the possibility of the insurance: insured, non-insured;
Depending on the possibility to manage them: uncontrollable and controllable.
Слайд 10Risk management process
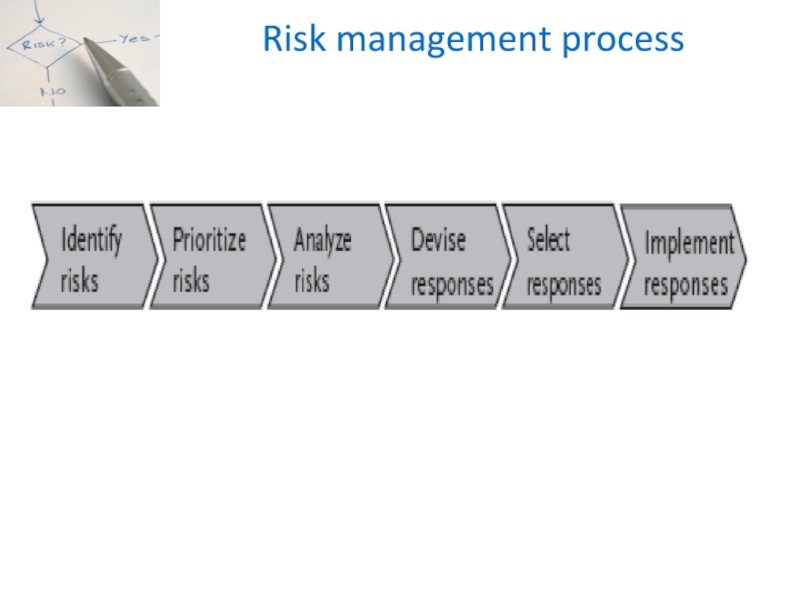
Project risk management is the
systematic design, implementation and monitoring of actions to identify, prioritize
and analyze project risks and to devise, select and implement responses to optimize these risks.Слайд 11Risk management process
Project risk management is the
systematic design, implementation and monitoring of actions to identify, prioritize
and analyze project risks and to devise, select and implement responses to optimize these risks.Слайд 12Risk management process
The key concepts from the
definition are explained below:
• Systematic: project risk management is a
structured method to deal with risks, including clear responsibilities, priorities and tasks. This contrasts with an ad hoc approach that relies on luck to succeed.• Action: performing tasks is central to risk management. In essence, it is about head, hands and eyes: to think up tasks, carry them out and monitor if they materialize .
Слайд 13Risk management process
Identify: This is the process to discover the
project risks that may be present. What risks form an
opportunity or threat to the project?Prioritize: Sorting the risks in order of importance. This enables the project team to deal with the largest risks first
Analyze: an understanding of risks is a precondition for taking effective measures. Analysis looks at the characteristics of individual risks and the relationship that exist between risks. Analysis can be qualitative or quantitative
Responses: a perfect analysis is beautiful, but it only adds value if it results in workable responses that change a project’s risk profile.
Слайд 15Risk management process
1. Setting the goals of
the risk management.
2. Risks identification.
3. Evaluation and analysis.
4. Risk elimination.
5.
Risk monitoring.Слайд 16Risk Description: How to describe Risk. Main characteristics.
1. Sphere where the risks appeared.
2. Type of the risks.
3.
Interested parts and its expectations.4. Quantitative risk characteristics.
5. Risk management, control.
6. Recommendations.
7. Strategic changes.
Слайд 17
Risk review
How to perform a risk review
First, a risk
review is a project team effort. While you may be
a very good team/project leader, it is always better to have three or four heads working together. Here is a simple process to follow:1. Generate a list of risks/problems that can impact your project
2. Assign a probability and impact rating
3. Prioritize the risks with those most serious at the beginning of your list
4. Develop strategies to minimize or eliminate the risks
Слайд 18Risk review.Example.
Lets assume that, as a team, our project is
to change-out a plant process control system. As a team,
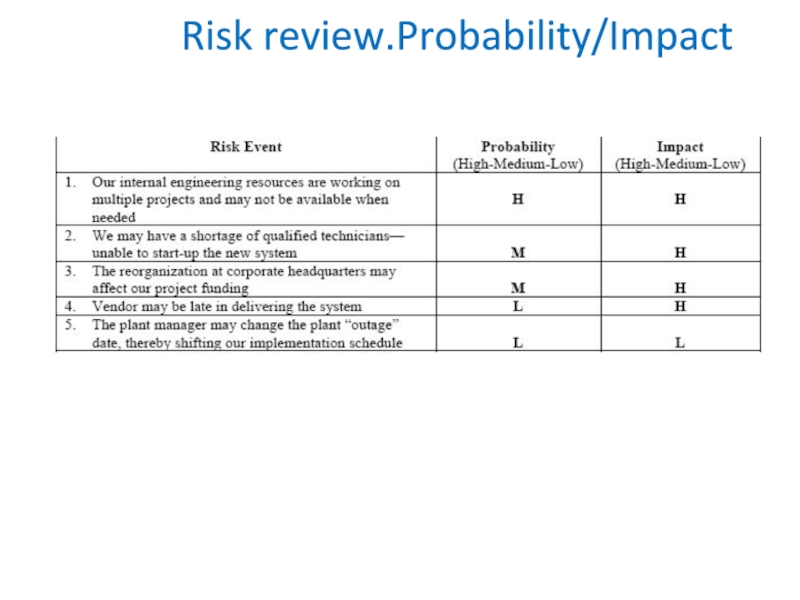
and by brainstorming, we have generated the following potential problems: (Note that these are not yet prioritized)Слайд 19Risk review.Example.
We may have a shortage of qualified technicians—unable to
start-up the new system
Vendor may be late in delivering
the system The plant manager may change the plant “outage” date, thereby shifting our implementation schedule
Our internal engineering resources are working on multiple projects and may not be available when needed
The reorganization at corporate headquarters may affect our project funding
Слайд 20Risk review.Probability/Impact
Note that we have a combination of internal and
external problems to deal with. With our list now generated,
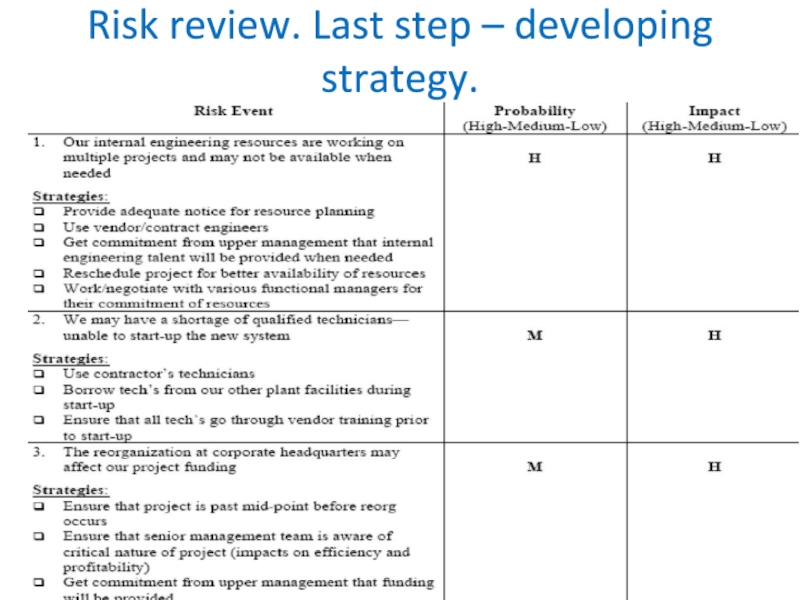
it is necessary to assign probabilities and impacts. In this case we want to determine the probability that the event may occur (High, Medium or Low); and, if so, the impact (High, Medium or Low). We have taken the above list and put into a table format as follows: (Note that these have now been prioritized based on risk probabilities/impacts)Слайд 24Risk review.Qualitative and quantitative review
Note that Risk No. 5 was
eliminated because it was a Low-Low. There is no point
in developing strategies for risks that have a low probability of occurring and a low impact even if they do. We have chosen to accept this risk. Always develop more than one strategy for each risk.Also, this type of risk review is a qualitative review because we have not developed a cost impact for each risk. A quantitative risk review would require the project team to have a strong grasp of cost impacts and also takes much longer to conduct.
Слайд 25Risk review. When we should use it?
Risk reviews should be
done on a continuous basis throughout a project. This is
because new risks will evolve as your project unfolds.Typically, you should perform a risk review at the following times:
? At the beginning of a project
? When the project goes through a shift from concept to planning to implementation to close
? Anytime you have a “gate” review scheduled
? Anytime a major risks event that you have identified is triggered
Слайд 26Risk review. How could we use the results?
Based on the
strategies developed for the above hypothetical project, it may be
necessary to adjust the schedule or increase the contingency funding.It may be that one should add schedule “milestones” to reflect vendor progress or to be more proactive in resource planning.
Remember, the purpose of a risk review is to provide insight about potential project problems and direct where you should spend extra time and effort in preventing them.