Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
The air humidity
Содержание
- 1. The air humidity
- 2. Memory flash ;)Please, give definitions to the following terms:Absolute humiditySpecific humiditySurface layerBoundary layer
- 3. Non stop rotation of water in the
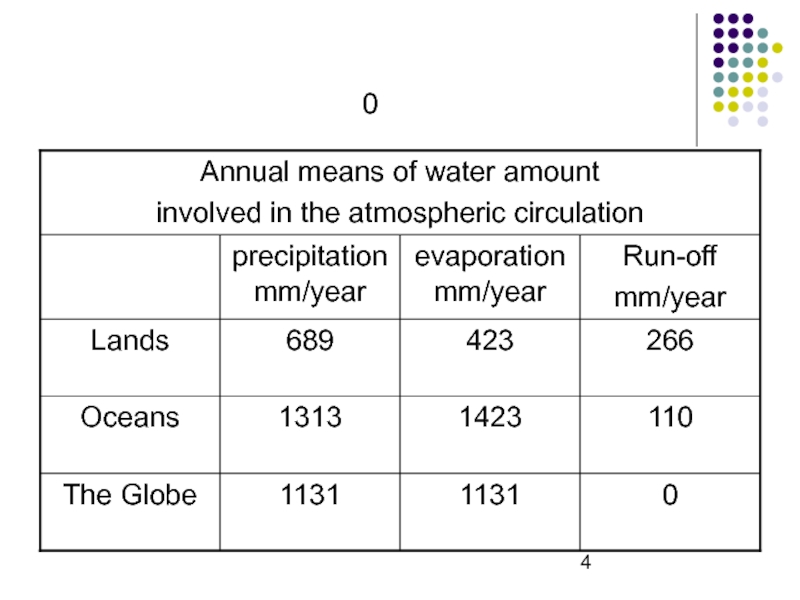
- 4. Слайд 4
- 5. 1 m21 m21 m2 = 10 000
- 6. Annual amount of precipitationSpb 680 mm, Wien 300 mm, Amsterdam 1200 mmTropics 680 mm/ day !
- 7. 1131 / 25.5=45 times or every 8
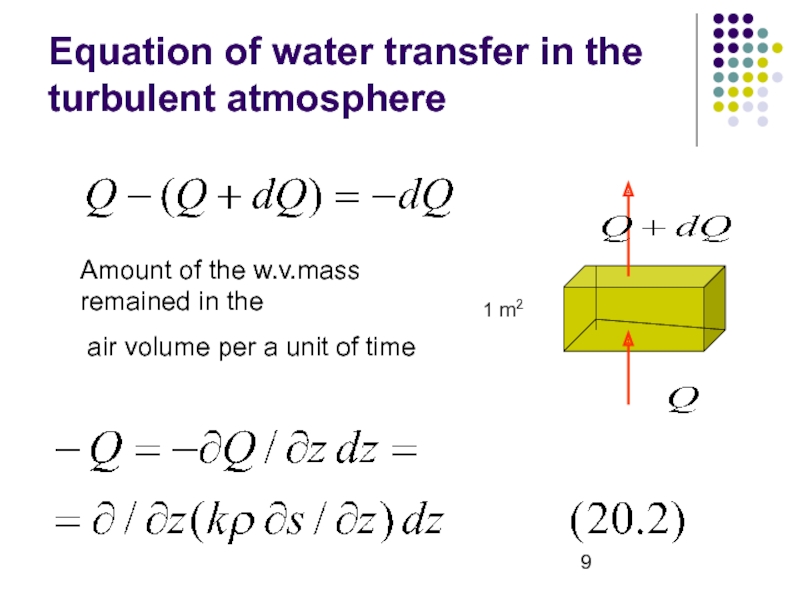
- 8. Equation of water transfer in the turbulent
- 9. Equation of water transfer in the turbulent
- 10. Advective terms could be neglected (too small)Advective terms could be neglected (too small)
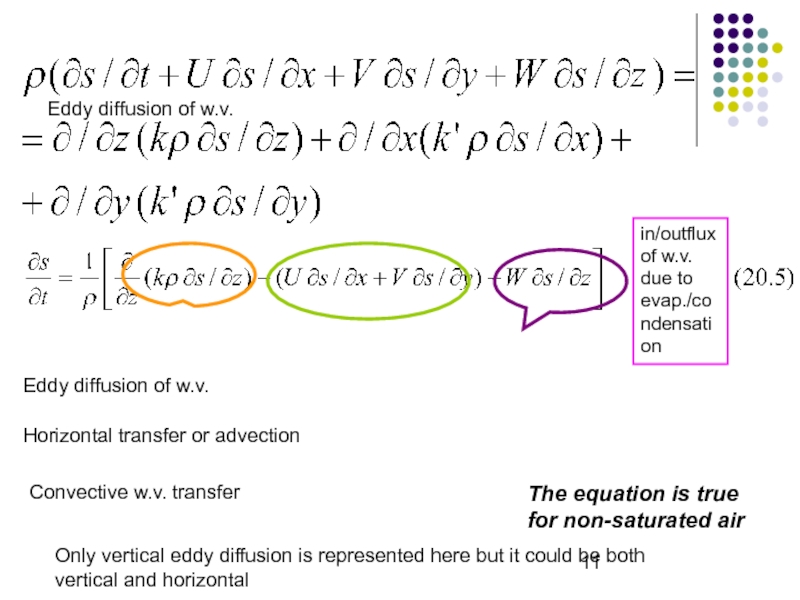
- 11. Eddy diffusion of w.v.Eddy diffusion of w.v.Horizontal
- 12. Distribution of the humidity characteristics with height
- 13. (20.8) shows that the w.v. eddy flux
- 14. Humidity distribution above the surface layerComparision of
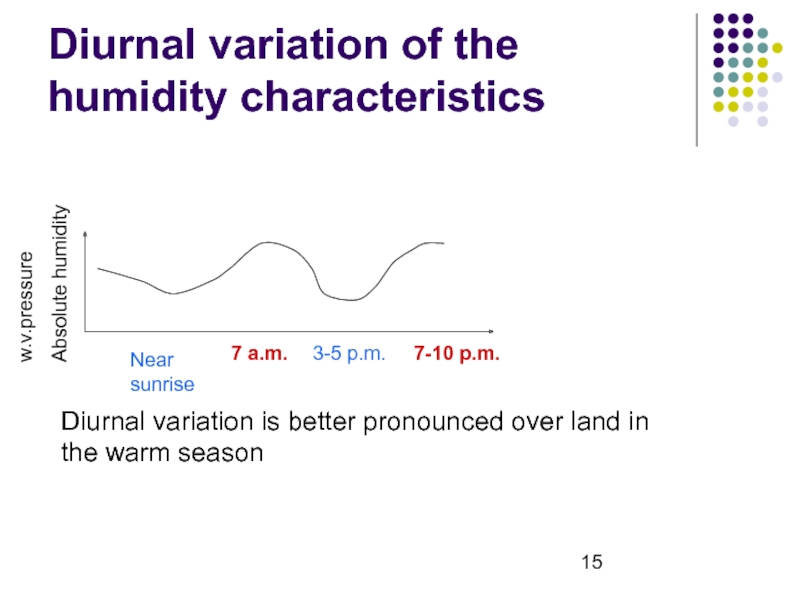
- 15. Diurnal variation of the humidity characteristicsNear sunrise7
- 16. Diurnal variation of the humidity characteristicsIn the
- 17. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Memory flash ;)
Please, give definitions to the following terms:
Absolute humidity
Specific
humidity
Слайд 3Non stop rotation of water in the atmosphere
http://www.meted.ucar.edu/mesoprim/mesodefn/index.htm
How much
is the amount of water
taking part in this rotation?
Слайд 51 m2
1 m2
1 m2 = 10 000 cm2
Water density
= 1 g/ cm3
What is thickness of water layer?
1
000 g : 1 g/cm3 = =1 000 cm3
1 000 cm3 : 10 000 cm2 =
=0.1 cm = 1 mm
1 kg of water per 1 m2 ? 1 mm of precipitated water
Слайд 6Annual amount of precipitation
Spb 680 mm, Wien 300 mm, Amsterdam
1200 mm
Tropics 680 mm/ day !
Слайд 71131 / 25.5=45 times or every 8 days
1.29 *10 13
t of water in the atmosphere (3 phases all together)
Equivalent
to 25.5 mmAnnual amount of precipitation is 1131 mm
How often is the water replaced in the atmosphere?
To evaporate 1131 mm of water we need
2.82* 10 5 J or 30% of solar radiation absorbed by the planet
1131 / 25.5=45 times or every 8 days
Слайд 8Equation of water transfer in the turbulent atmosphere
Only specific humidity
could be considered as a conservative characteristic of w.v.content of
a moving particle (no absolute or relative humidity, dew point, w.v.pressureСлайд 9Equation of water transfer in the turbulent atmosphere
1 m2
Amount of
the w.v.mass remained in the
air volume per a unit
of timeСлайд 10Advective terms could be neglected (too small)
Advective terms could be
neglected (too small)
Слайд 11Eddy diffusion of w.v.
Eddy diffusion of w.v.
Horizontal transfer or advection
Convective
w.v. transfer
Only vertical eddy diffusion is represented here but it
could be both vertical and horizontalThe equation is true for non-saturated air
in/outflux of w.v. due to evap./condensation
Слайд 12Distribution of the humidity characteristics with height in the surface
layer
Let’s find S=S(z) in the surface layer ? integrate (20.5)
from 0 to ZWith the accuracy 10 % :
Is the w.v.flux at z=0, i.e. the rate of evaporation from the Earth’s surface:
Слайд 13(20.8) shows that the w.v. eddy flux in the surface
layer
can be regarded as approximately unchangeable
with height (
as well as a heat flux).Similarly to the heat flux :
(20.8) shows that the w.v. eddy flux in the surface layer
can be regarded as approximately unchangeable
with height ( as well as a heat flux).
Similarly to the heat flux :
“S” decreases at Q’0 < 0 with height proportionally to ln z
Слайд 14Humidity distribution above the surface layer
Comparision of calculated and observed
w.v. pressure values shows that the observed values decrease with
height much more rapidly than calculated ones.Suring’s formula
( empirical)
Z in km
True within the boundary layer above the surface layer
Слайд 15Diurnal variation of the humidity characteristics
Near sunrise
7 a.m.
3-5 p.m.
7-10 p.m.
Diurnal
variation is better pronounced over land in the warm season
w.v.pressure
Absolute
humidityСлайд 16Diurnal variation of the humidity characteristics
In the night
when T air
drops
3 p.m.
RH=100% *e/E
e decreases near noon (summer)
E sharply increases (account
for T rise)relative humidity
In winter/over water surfaces:
One min, usually before sunrise.
Weak max, supposed before noon.
Reasons:
Eddy exchange is weak
Eddy transfer of the w.v. is compensated by evaporation