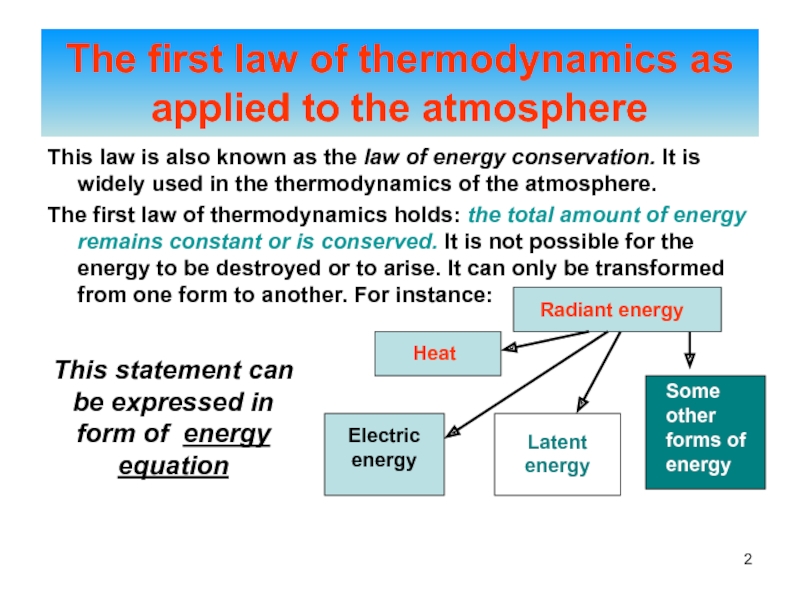
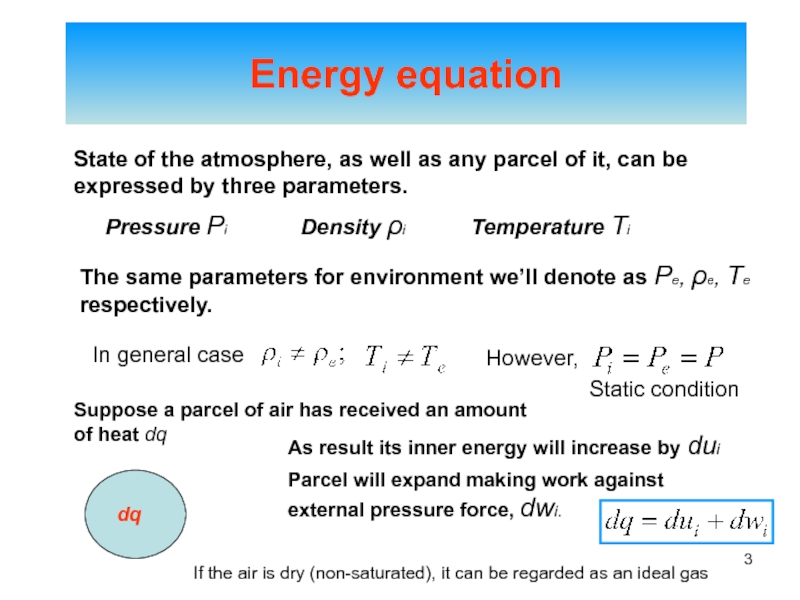
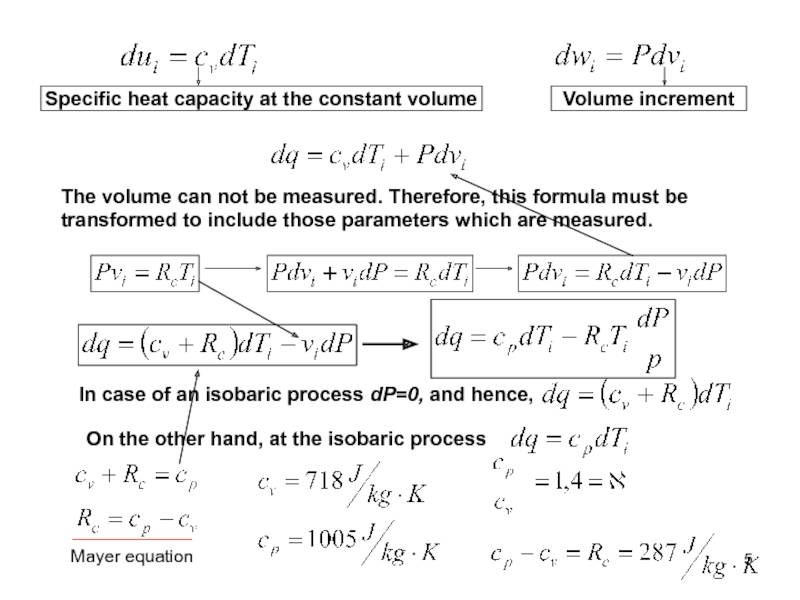
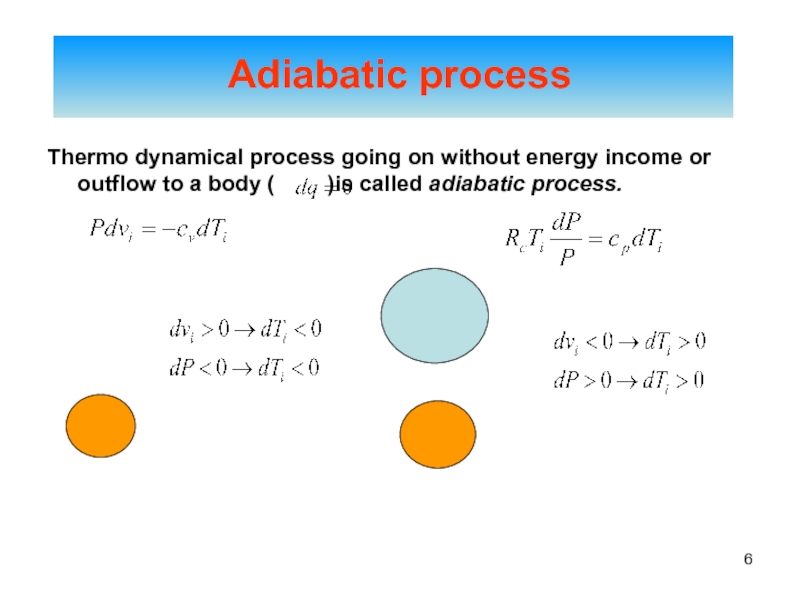
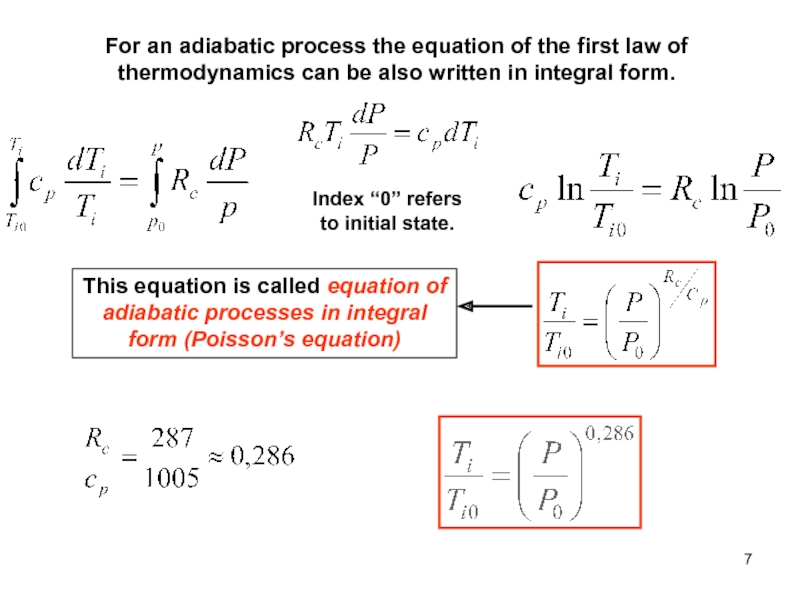
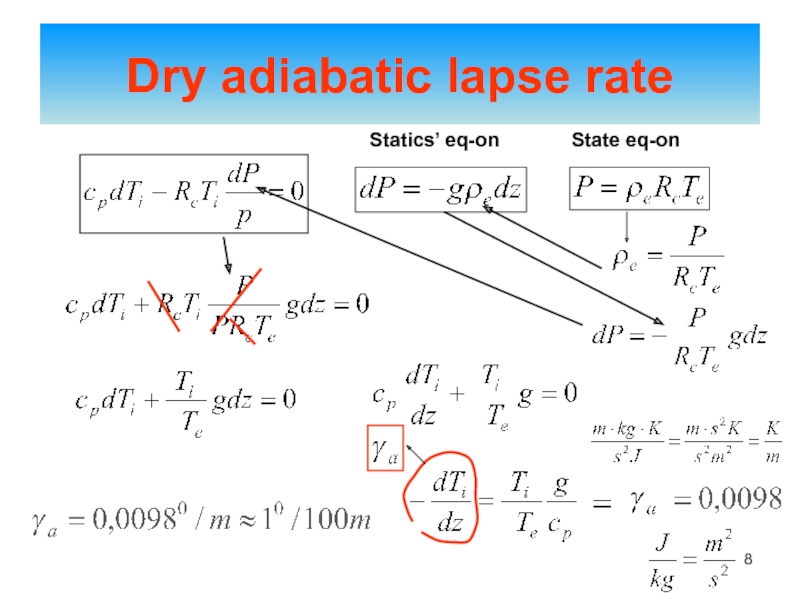
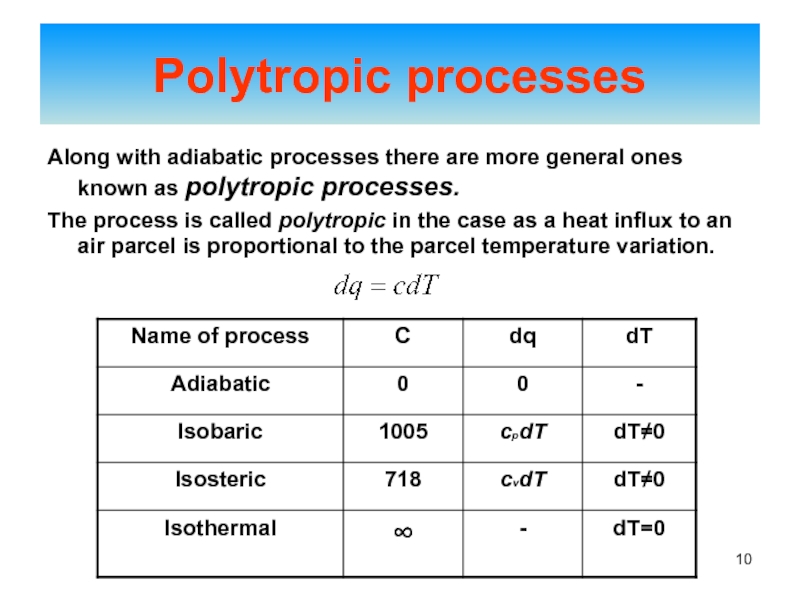
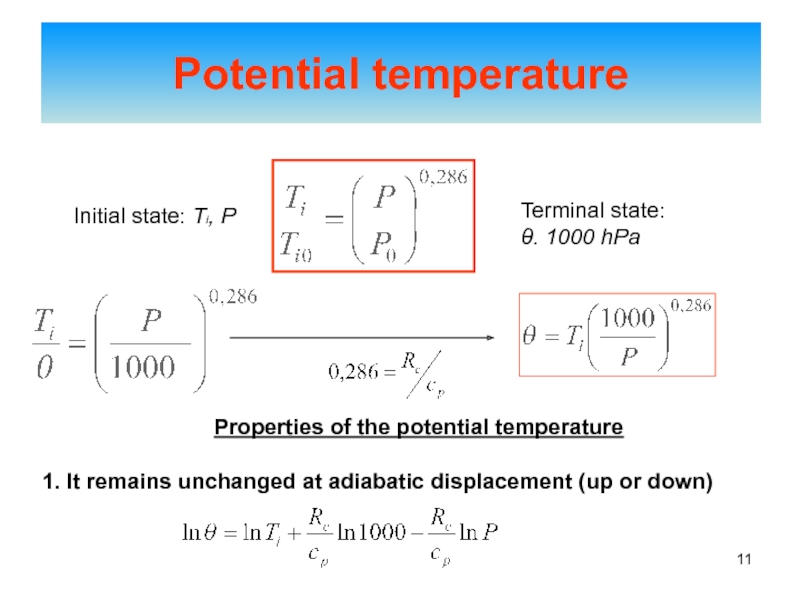
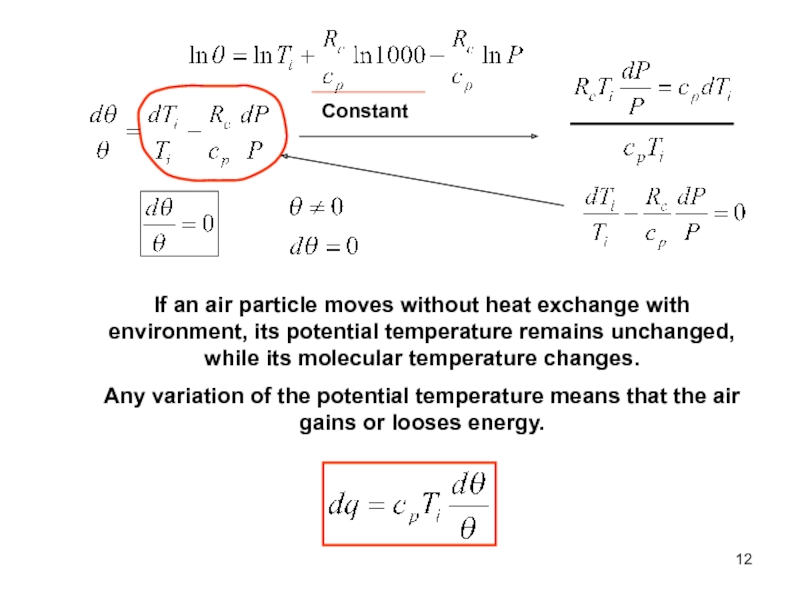
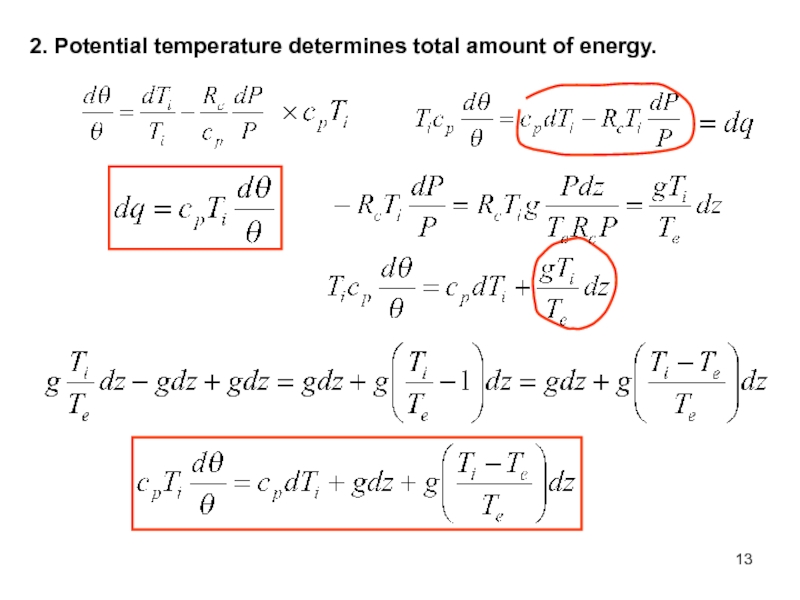
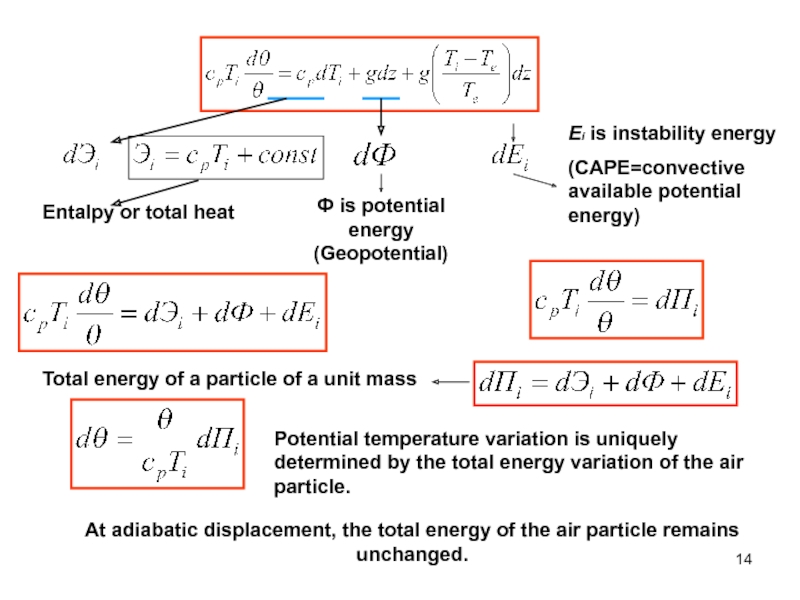
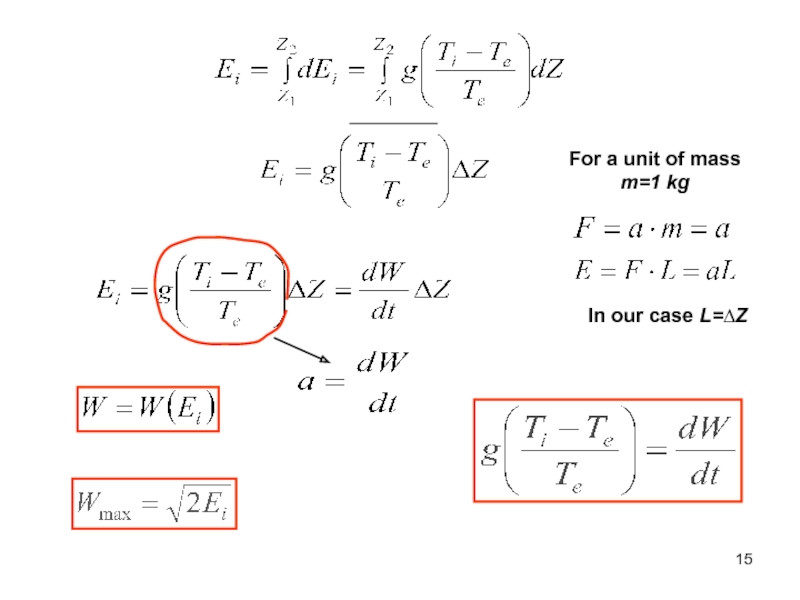
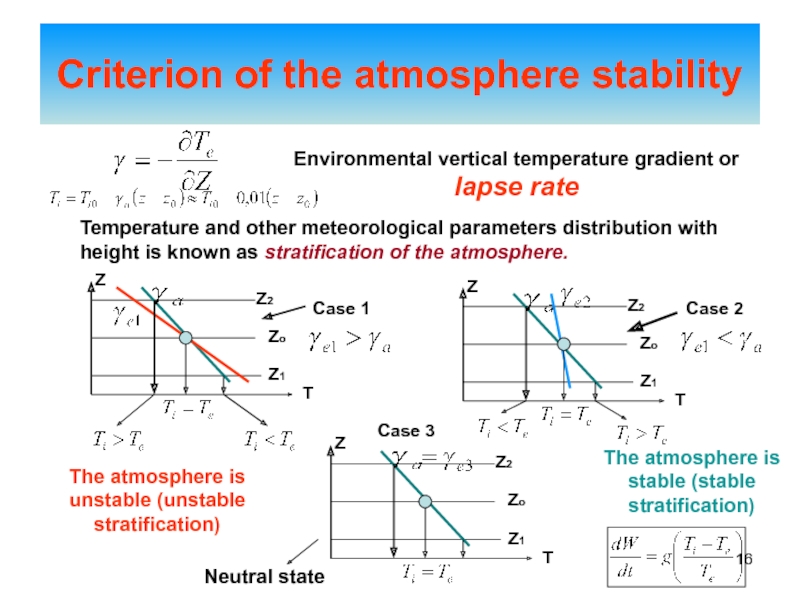
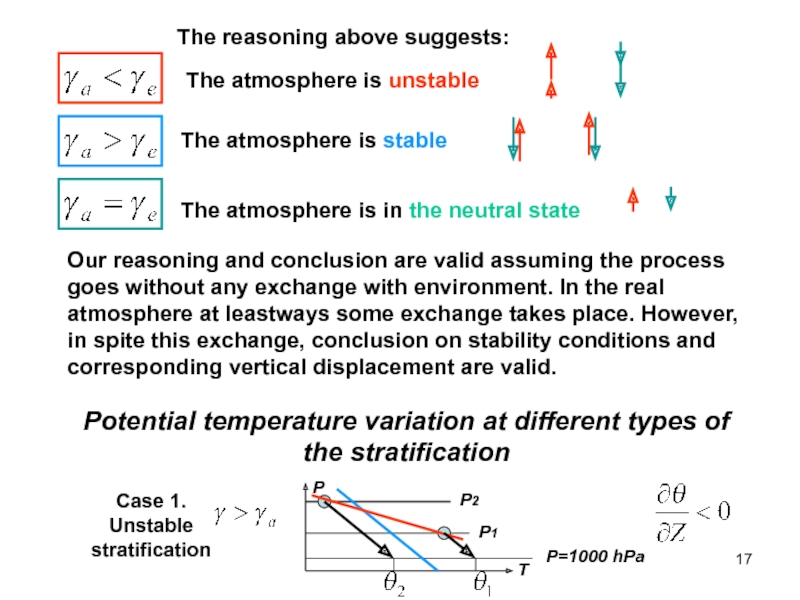
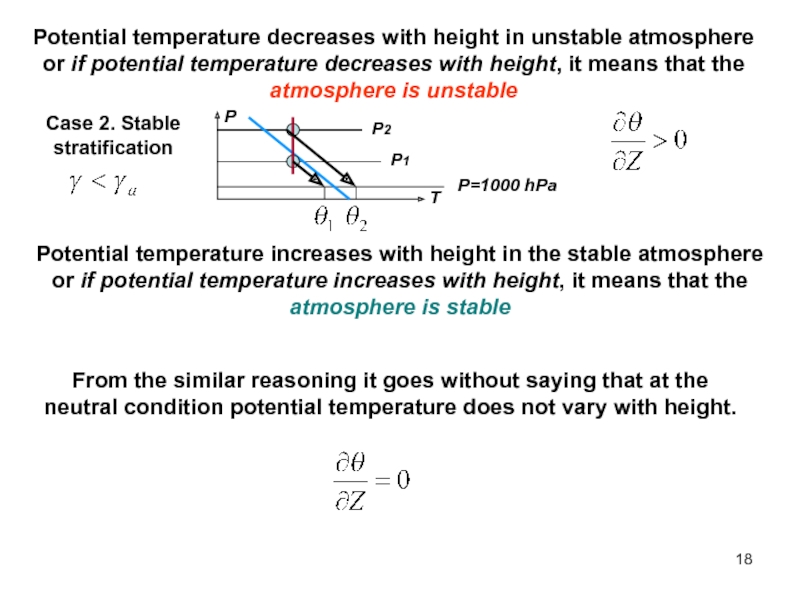
of energy from one form to another constantly occurs.
The branch
of meteorology dealing with the general regularities of energy transformation and variation of the state of the atmosphere under influence of heat influxes is calledTHERMODYNAMICS OF THE ATMOSPHERE