Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
ASEPSIS
Содержание
- 1. ASEPSIS
- 2. General principles of asepsis were accepted after
- 3. DEFINITIONSCLEANING - It is a process
- 4. DISINFECTION - it is a process which
- 5. To achieve sterilization of any instrument three
- 6. PRESTERILIZATION CLEANING Removal of the organic matters, blood
- 7. MANUAL CLEANINGSimplest and the cheapest method, but
- 8. ULTRASONIC CLEANINGPrinciple- conversion of electrical energy into
- 9. MECHANICAL WASHINGPrinciple- High-pressure jets of water with
- 10. Classification of the method of sterilizationA.
- 11. A. DRY HEAT Killing is due
- 12. Hot air oven :It is used to
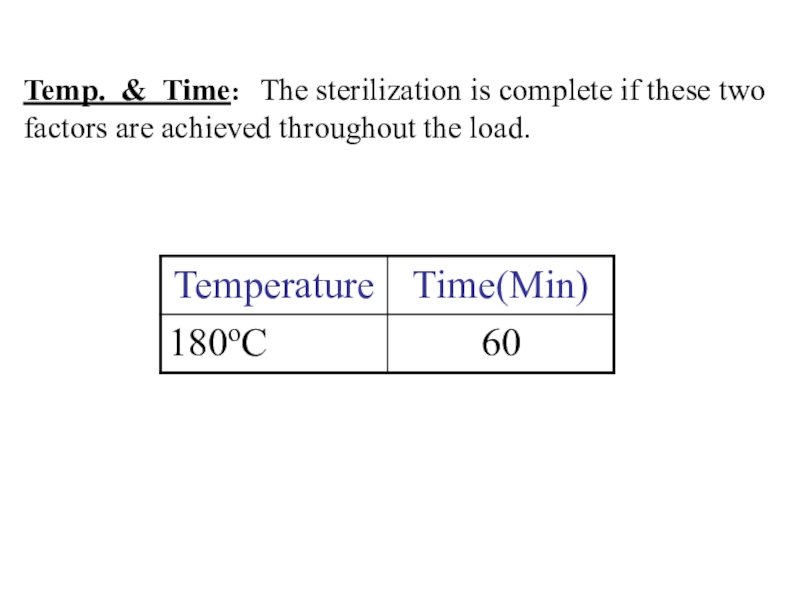
- 13. Temp. & Time: The sterilization is
- 14. Moist heat Causes denaturation and coagulation of
- 15. Sterilization control of the moist heat Physical
- 16. IRRADIATION Radiation used of two types Ionizing
- 17. Ionizing Radiation X-rays, gamma rays are highly
- 18. 2. Non-ionizing radiation Two types of non-ionizing
- 19. ETHYLENE OXIDE STERILIZATION (ETO)Used almost exclusively to
- 20. B. CHEMICAL Phenol Derivatives: Phenol, Cresol,
- 21. Mechanism of action of chemical disinfectants : Mechanism
- 22. Скачать презентанцию
General principles of asepsis were accepted after Joseph Lister (Father of antiseptic surgery) studied prevention of wound infection(1865-1891).
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2General principles of asepsis were accepted after Joseph Lister (Father
of antiseptic surgery) studied prevention of wound infection(1865-1891).
Слайд 3 DEFINITIONS
CLEANING - It is a process which removes visible
contamination but does not necessarily destroy micro organisms. It is
necessary prerequisite for effective disinfection or sterilization.ASEPSIS -Term used to describe methods which prevent contamination of wounds and other sites, by ensuring that only sterile object and fluids come into contact with them.
Слайд 4DISINFECTION - it is a process which reduces the number
of viable microorganisms to an acceptable level but may not
inactive some viruses and bacterial spores.STERLIZATION - it is the process of destruction or removal of all microorganisms from article, surface or medium, including spores.
Слайд 5 To achieve sterilization of any instrument three definite stages are
to be completed-
Pre sterilization cleaning
Sterilization process
Aseptic storage
Слайд 6PRESTERILIZATION CLEANING
Removal of the organic matters, blood and saliva which
provide protective barrier for microorganisms and prevents its destruction.
There are
three methods for cleaning-Manual
-Ultrasonic
-Mechanical washing
Слайд 7MANUAL CLEANING
Simplest and the cheapest method, but time consuming and
difficult to achieve.
Heavy duty gloves and glasses must be worn
to protect needle stick injury and to protect eye.Material used for manual cleaning
-Soaps
-Detergents
Слайд 8ULTRASONIC CLEANING
Principle- conversion of electrical energy into vibratory sound waves
which pass through a soap solution containing the instrument.
Used mainly for burs, bone files, bone cutter, artery forceps, saw etc. Слайд 9MECHANICAL WASHING
Principle- High-pressure jets of water with or without a
detergent which removes debris from instrument.
Small instrument like burs,
blade are not suitable for this type of cleaning.Слайд 10Classification of the method of sterilization
A. PHYSICAL
Heat
a)
Dry
b) Moist
Irradiation
CHEMICAL
a) Gas
b) Liquid antiseptics
Слайд 11A. DRY HEAT
Killing is due to :
- Dehydration and oxidation of organisms
- Protein denaturation
-
Toxic effects of elevated levels of electrolytes Слайд 12Hot air oven :
It is used to sterilize items, which
do not get damaged by high temp. such as laboratory
glass, instruments with sharp cutting edges, scissors, clampsСлайд 13Temp. & Time: The sterilization is complete if these
two factors are achieved throughout the load.
Слайд 14Moist heat
Causes denaturation and coagulation of proteins.
AUTOCLAVE :
Steam is
the effective means of sterilization, because of its
1. High penetrating
capacity.2. It gives of large amount of heat to surface with which it comes in contact.
3. To achieve sterility, a holding time of at least 30 minutes at 120 °C or 20 minutes at 132 °C at 1,1 above atmospheric pressure is required.
Слайд 15Sterilization control of the moist heat
Physical Indicator- an alloy
designed to melt only after being subjected to relevant holding
time.Chemical indicator- Strips or tapes that change color once the correct conditions have been met.
Bacteriological test – detection of bacterial clumps on the instrument after its streilization
Слайд 16IRRADIATION
Radiation used of two types
Ionizing radiation, e.g., X-rays,
gamma rays, and high speed electrons .
Non-ionizing radiation, e.g. ultraviolet
light, and infrared light. These forms of radiation can be used to kill or inactivate microorganisms.
Слайд 17Ionizing Radiation
X-rays, gamma rays are highly lethal to DNA
and other vital constituents.
They have high penetration power.
There is no
appreciable increase in temperature, thus referred to as cold sterilization.Commercial plants use gamma radiation for sterilizing plastics, syringes, swabs, catheters etc.
Слайд 182. Non-ionizing radiation
Two types of non-ionizing radiations are used
for sterilization:-
A. Ultraviolet -
Short range UV(UVC) is considered “germicidal UV”.
UV
will destroy micro-organismal DNA.Used mainly for air purification and water purification in hospitals.
B. Infrared –
It is most commonly used to purify air, such as in the operating room. Infrared is effective, however, it has no penetrating ability.
Слайд 19ETHYLENE OXIDE STERILIZATION (ETO)
Used almost exclusively to sterilize medical products
that cannot be steam sterilized or sensitive to radiation.
Mechanism
of action: It destroys micro-organisms by alkylation and cause denaturation of nucleic acids of micro-organisms.Plastics, rubber & photographic equipments can be sterilized by this method.
Also used for mass sterilization of disposable items, plastic syringes,needles,catheters,blades etc..
Слайд 20B. CHEMICAL
Phenol Derivatives: Phenol, Cresol, Resorcinol, Chloroxylenol
Oxidizing
agents :Pot.Permanganate, Hydrogen Peroxide, Benzoyol Peroxide
Halogens : Iodine, Chlorine
Biguanide : Chlorhexidine
Alcohols : Ethanol, Isopropanol.
Aldehydes : Formaldehyde
Acids : Boric acid, acetic acid
Metallic salts ; Silver Nitrate, Zince Sulfate,