Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Audit risks
Содержание
- 1. Audit risks
- 2. Audit riskRisk of material misstatementDetection riskInherent riskControl risk
- 3. Audit riskAudit risk is the risk that the auditor expresses an inappropriate audit opinion
- 4. RiskAuditors accept some level of risk in
- 5. Risk and EvidenceAuditors gain an understanding of
- 6. ISA 315ISA 315 (Revised) Identifying and Assessing
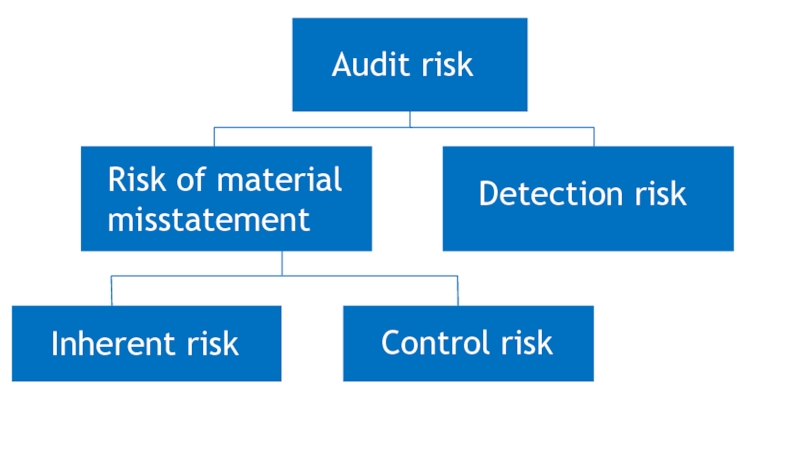
- 7. RoMMRisk of material misstatement is the risk
- 8. Components of RoMMRoMM = Inherent risk x Control risk
- 9. Inherent riskInherent risk is the susceptibility of
- 10. Examples?Complex accounting treatment (eg. Estimates); Nature of the company or the industry;
- 11. Examples of inherent risksExamples of inherent risks
- 12. Companies such as Zara and H&M operate
- 13. Components of RoMMRoMM = Inherent risk x Control risk
- 14. Control riskControl risk is the risk that
- 15. Audit riskRisk of material misstatementDetection riskInherent riskControl risk
- 16. Detection risk Detection risk is the risk
- 17. How to manage the risk?assigning more experienced
- 18. Managing the risk exampleSerikAga Ltd is from
- 19. As inherent risk and control risk are
- 20. As inherent and control risk are low
- 21. What is a misstatement?ISA 450: 'A difference
- 22. Risk assessment proceduresObservation and inspectionEnquiries Analytical procedures
- 23. Risk assessment proceduresUnderstanding the entity and its
- 24. Risk assessment proceduresThe information used to obtain
- 25. Risk assessment proceduresAnalytical procedures are defined in
- 26. Risk assessment proceduresKey ratios
- 27. Audit riskRisk of material misstatementDetection riskInherent riskControl risk
- 28. Слайд 28
- 29. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 4Risk
Auditors accept some level of risk
in performing the audit.
An
effective auditor recognizes that risks exist, are difficult to measure,
and require careful thought to respond.Responding to risks properly is critical to achieving a high-quality audit.
Слайд 5Risk and Evidence
Auditors gain an understanding of the client’s business
and industry and assess client business risk.
Auditors use the audit
risk model to further identify the potential for misstatements and where they are most likely to occur.Слайд 6ISA 315
ISA 315 (Revised) Identifying and Assessing the Risks of
Material
Misstatement Through Understanding the Entity and its Environment
states:
'The objective of
the auditor is to identify and assess the risk ofmaterial misstatement, whether due to fraud or error, at the financial
statement and assertion levels, through understanding the entity and
its environment, including the entity's internal control, thereby
providing a basis for designing and implementing responses to the
assessed risks of material misstatement.'
Слайд 7RoMM
Risk of material misstatement is the risk that the financial
statements are materially misstated prior to audit and consists of
two components, inherent risk and control risk.Слайд 9Inherent risk
Inherent risk is the susceptibility of an assertion about
a class of transaction, account balance or disclosure to misstatement
that could be material, before consideration of any related controls.Слайд 10Examples?
Complex accounting treatment (eg. Estimates);
Nature of the company or
the industry;
Слайд 11Examples of inherent risks
Examples of inherent risks for companies are
limitless, however, here are a few examples:
The car industry is
one of the first industries to suffer during an economic downturn due to the reluctance of the population to spend money or take out loans that they may struggle to pay back. For this reason, we could say that the car industry is inherently risky.Financial institutions deal with complex financial instruments such as derivatives. These instruments can be incredibly difficult to account for and value and so are inherently risky.
Слайд 12Companies such as Zara and H&M operate in the fashion
industry where trends and tastes change rapidly. For companies such
as these, sales and inventory balances are inherently risky.A company is heavily financed by debt. This is inherently risky as missed interest payments and repayments may lead to insolvency.
A company operates a profit related bonus scheme. Its profit figures are inherently risky as there is the incentive to management to manipulate them to achieve the bonus targets.
Examples of inherent risks
Слайд 14Control risk
Control risk is the risk that a misstatement that
could occur and that could be material will not be
prevented, or detected and corrected on a timely basis by the entity's internal controls.Could be higher or lower
Слайд 16Detection risk
Detection risk is the risk that the procedures
performed by the auditor to reduce audit risk to an
acceptably low level will not detect a misstatement that exists and that could be material.Detection risk comprises:
Sampling risk
Non-sampling risk
Слайд 17How to manage the risk?
assigning more experienced staff to risk
areas
increasing supervision levels
increasing the element of unpredictability in sample selection
changing
the nature, timing and extent of proceduresincreasing the emphasis on substantive tests of detail
emphasising the need for professional scepticism.
Слайд 18Managing the risk example
SerikAga Ltd is from an industry that
is highly exposed to the economic climate, uses lots of
complex treasuryinstruments such as interest rate swaps and futures and has a very poor system of internal controls
BakeMake Inc operates in a low risk industry, has few complex transactions and a highly sophisticated system of internal
controls.
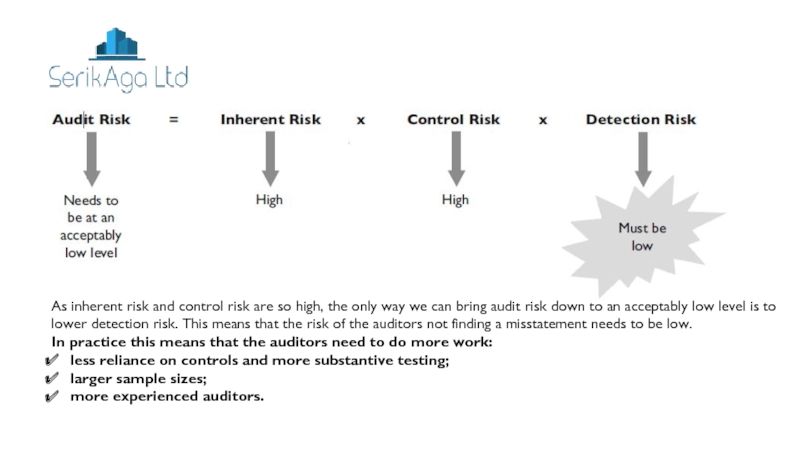
Слайд 19As inherent risk and control risk are so high, the
only way we can bring audit risk down to an
acceptably low level is to lower detection risk. This means that the risk of the auditors not finding a misstatement needs to be low.In practice this means that the auditors need to do more work:
less reliance on controls and more substantive testing;
larger sample sizes;
more experienced auditors.
Слайд 20As inherent and control risk are low then theoretically detection
risk can afford to be high. Be careful, however, as
this is a theoretical concept and under no circumstances will the auditors do no work! They can just do a different type of work:More reliance on the strong internal controls and less detailed substantive testing.
Слайд 21What is a misstatement?
ISA 450: 'A difference between the amount,
classification, presentation, or disclosure of a reported financial statement item
and the amount, classification, presentation, or disclosure that is required for the item to be in accordance with the applicable financial reporting framework. Misstatements can arise from error or fraud.'Слайд 23Risk assessment procedures
Understanding the entity and its environment
relevant industry, regulatory
and other external factors (including the financial reporting framework)
the nature
of the entity, including:– its operations
– its ownership and governance structures
– the types of investment it makes
– the way it is structured and financed
the entity's selection and application of accounting policies
the entity's objectives, strategies and related business risks
the internal controls relevant to the audit.
Слайд 24Risk assessment procedures
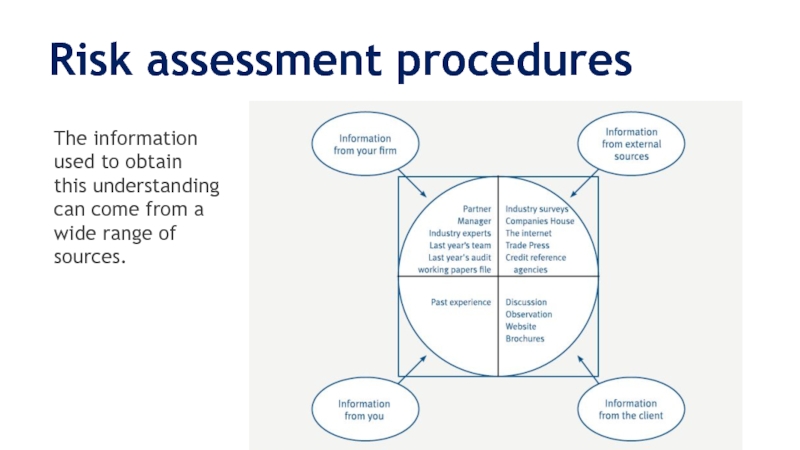
The information used to obtain this understanding can
come from a wide range of sources.
Слайд 25Risk assessment procedures
Analytical procedures are defined in ISA 520 Analytical
Procedures as:
'Evaluations of financial information through analysis of plausible relationships
among both financial and nonfinancial data' and investigation of identified fluctuations, inconsistent relationships or amounts that differ from expected values.Analytical procedures are fundamental to the auditing process.
Prior periods
Industry information
Financial ratios