Слайд 1Chapter 8
The Home and Automobile Decision
Слайд 2Learning Objectives
Make good buying decisions.
Choose a vehicle that suits your
needs and budget.
Choose housing that meets your needs.
Decide whether to
rent or buy housing.
Calculate the costs of buying a home.
Get the most out of your mortgage.
Слайд 3Smart Buying
Step 1: Differentiate Want From Need
Smart buying requires
separating wants from needs.
“Want” purchases require a trade-off.
Before
buying a “want,” determine whether the purchase will interfere with your ability to pay for your future needs.
Слайд 4Smart Buying
Step 2: Do Your Homework
After deciding to make
a purchase, comparison shop.
Start your research with publications that
provide unbiased ratings and recommendations such as:
Consumer Reports at www.consumerreports.org
Consumer’s Resource Handbook from the U.S. Office of Consumer Affairs at www.pueblo.gsa.gov
Слайд 5Smart Buying
Step 3: Make Your Purchase
Getting the best price might
involve negotiations.
Conduct research before haggling.
Know what the product’s mark-up is.
This
is the price dealers add on above what they paid for the product.
Consider what fits your monthly budget.
Слайд 6Smart Buying
Step 4: Maintain Your Purchase
Maintain your purchase after
the deal is complete.
Resolve complaints or issues.
First contact the seller,
then the company headquarters that made or sold the product.
Work with the Better Business Bureau and other local, state, and federal organizations.
Слайд 7Smart Buying
Checklist 8.1 Before You Buy
Decide in advance what
you need and can afford.
Take advantage of sales but compare
prices.
Be aware of extra charges that increase the total price.
Ask about refund or exchange policy.
Read and understand the contract before signing.
Learn about your cancellation rights.
Don’t succumb to high pressure tactics or do business over the phone with unknown companies.
Get everything in writing.
Слайд 8Smart Buying
Checklist 8.2 Making a Complaint
Keep a record of
your efforts to resolve the problem.
Contact the seller, then go
to the manufacturer.
Type letters, keep copies, and send letters with return receipt requested.
Allow time for the company to resolve the problem, then file a complaint with your local consumer protection office or Better Business Bureau.
Don’t give up until you are satisfied.
Слайд 9Smart Buying in Action:
Buying a Vehicle
Vehicles are your largest purchase,
next to buying a house.
Choices to consider:
Buy new
Buy used
Lease
the vehicle
Leasing is renting for an extended period with a small down payment and low monthly rates.
Слайд 10Smart Buying in Action:
Buying a Vehicle
Step 1: Differentiate Want From
Need
Determine which features you need.
Make a list of the
features you want.
Consider your employment, family, lifestyle.
Слайд 11Smart Buying in Action:
Buying a Vehicle
Step 2: Do Your Homework
How
much can you afford?
Typical family spends 4-6 months of annual
income on a new car.
Determine size of down payment.
Determine an affordable monthly payment.
Which vehicle is right for you?
Comparison shop, looking at choices and trade-offs.
Consider operating and insurance costs, and warranty.
Слайд 12Smart Buying in Action:
Buying a Vehicle
Step 3: Make Your Purchase
Be
sure to get a fair price.
Know the dealer cost or
invoice price.
Research using Edmund’s Car Buying Guide at www.edmund.com or AutoSite at their web site www.autosite.com/content/home.
Most car dealers receive a “holdback,” amounting to
2-3% of the price, when selling a car.
Слайд 13Smart Buying in Action:
Buying a Vehicle
Step 3: Make Your Purchase
Financing
Alternatives:
Cheapest way to buy a car is with cash, but
investigate all financing options before buying.
Keep financing out of the negotiations.
The shorter the term, the higher the monthly payments.
Слайд 14Smart Buying in Action:
Buying a Vehicle
Step 3: Make Your Purchase
Leasing:
Appeals
to those who are financially stable, like a new car
every few years, drive less than 15,000 miles annually, and don’t want hassle of trading in car.
Popular with those with good credit but not enough up-front money to buy.
1/3 of all new vehicles are leased.
Слайд 15Smart Buying in Action:
Buying a Vehicle
Step 4: Maintain Your Purchase
Keep
vehicle in best running condition.
Read owner’s manual and follow regular
maintenance.
Don’t ignore signs of trouble.
Listen for unusual sounds, drips, or warning lights.
Your first line of protection is the warranty.
Know your rights under the Lemon laws.
Слайд 16Smart Buying in Action: Housing
Many people equate home ownership with
financial success.
Housing costs can take up over 25% of
after-tax income.
Home ownership is also an investment – likely the biggest investment you will ever make.
Consider lifestyle, wants and needs, and budget constraints when making choices.
Слайд 17Your Housing Options
A House:
Popular choice for most individuals.
Offers space and
privacy.
Offers greater control over style decoration and home improvement.
Requires more
work than the other choices, including maintenance, repair, and renovations.
Most potential for capital appreciation.
Слайд 18Your Housing Options
A Cooperative (Co-op) is a building owned by
a corporation in which residents are stockholders.
Residents buy stock, giving
them the right to occupy a unit in the building.
The larger the space and the more desirable the location, the more shares you have to buy.
Difficult to get a mortgage.
Pay monthly homeowner’s fee for taxes and maintenance.
Слайд 19Your Housing Options
A Condominium (Condo) is an apartment complex that
allows individual ownership of the unit and joint ownership of
land, common areas, and facilities.
Allows direct ownership of the unit with a proportionate ownership in land and common areas.
Pay monthly fee for interest, taxes, utilities, and groundskeeping.
Слайд 20Your Housing Options
Apartments and other rental housing offer:
Affordability
Low maintenance situations
Little
financial commitment
Chosen by young, single people.
May be a lifestyle
decision.
Limited upkeep and no long-term commitment.
Offers lack of choice regarding pets or remodeling.
Слайд 21Smart Buying in Action: Housing
Step 1: Differentiate Want From Need
Determine
what you need versus what you want.
Decide what is important
to you:
Consider location – country, suburbs, or city
Consider the neighborhood – safety, convenience, schools
Слайд 22Smart Buying in Action: Housing
Step 2: Do Your Homework
Investigate the
potential home and all that goes along with it:
Neighborhood, community
lifestyle, satisfy needs.
www.homes.com/Content/NeighborhoodSearchMain.cfm
www.homefair.com
Understand how much you can afford to pay.
Слайд 23Smart Buying in Action: Housing
One-time Costs
Down payment
Closing/settlement costs
Points
Loan origination
fee
Application fee
Appraisal fee
Title search
Recurring Costs
Mortgage payments
PITI includes principal,
interest, taxes, insurance
Maintenance and Operating Costs
Repairs and maintenance items
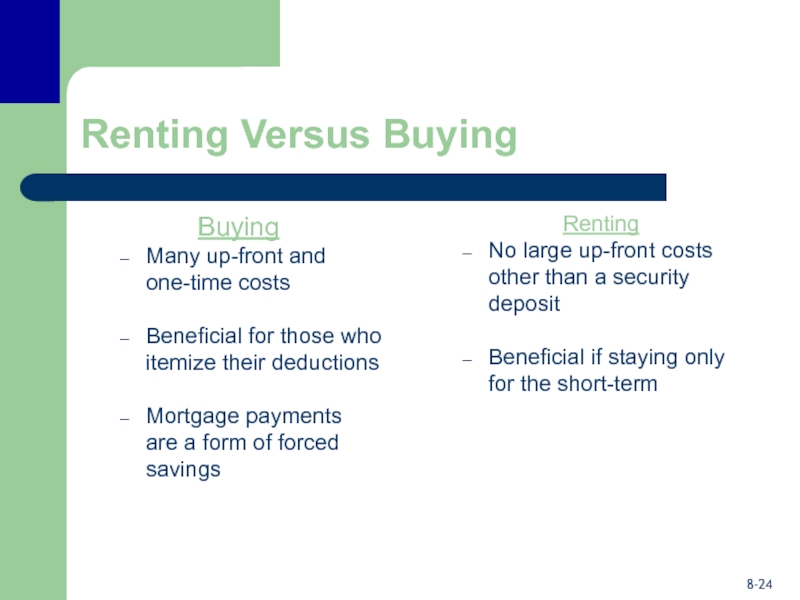
Слайд 24Renting Versus Buying
Buying
Many up-front and
one-time costs
Beneficial for those who
itemize their deductions
Mortgage payments
are a form of forced savings
Renting
No large
up-front costs other than a security deposit
Beneficial if staying only for the short-term
Слайд 25Determining What You
Can Afford
Before house hunting, ask yourself:
What is the
maximum amount the bank will lend me?
Should I borrow up
to this maximum?
How big a down payment can I afford?
Слайд 26What is the Maximum Amount the Bank Will Lend Me?
Lenders look at:
Your financial history – steadiness of income,
credit report, and FICO score
Your ability to pay – lenders use ratio of a maximum 28% PITI: monthly gross income
Appraised value of home – limit mortgage loan to 80%.
Слайд 27How Much Should You Borrow?
A mortgage is a large financial
commitment of future earnings.
Look at your overall financial plan
before deciding on how much to borrow.
Prequalifying – lender confirms the loan size based on ability to pay and down payment.
Слайд 28Financing the Purchase:
The Mortgage
Sources of mortgages:
S&Ls and commercial banks are
the primary sources of mortgage loans.
Mortgage bankers originate loans, sell
them to banks or pension funds, have fixed rate mortgages.
Mortgage brokers are middlemen who place loans with lenders for a fee but do not originate those loans. They do the comparison shopping.
Слайд 29Conventional and Government-Backed Mortgages
Conventional loans - from a bank or
S&L and secured by the property.
If default - lender
seizes property, sells it to recover funds owed.
Слайд 30Conventional and Government-Backed Mortgages
Government-backed loans – lender makes loan and
government insures it. VA and FHA account for 25% of
all mortgage loans.
Advantages:
Lower interest rate
Smaller down payment
Less strict financial requirements
Disadvantages:
Increased paperwork
Higher closing costs
Limits amount borrowed
Слайд 31Fixed-Rate Mortgages
Monthly payment doesn’t change regardless of changes in market
interest rates.
If rates are low, a fixed rate mortgage
locks in the low rates for the life of the loan.
An assumable loan can be transferred to a new buyer.
Prepayment privilege allows early cash payments to be applied to principal.
Слайд 32Adjustable-Rate Mortgages
With an ARM, the interest rate fluctuates based on
current market interest rates within limits at specified intervals.
Borrowers are
better off with an ARM if interest rates drop.
Initial Rate - “teaser rate” can be deceptively low and available for only a short time period.
Слайд 33Adjustable-Rate Mortgages
Interest Rate Index – rates on ARMs are tied
to an index not controlled by the lender, such as
6- or 12-month U.S. Treasuries.
Margin – the amount over the index rate that the ARM is set.
Adjustment Interval – how frequently the rate can be reset.
Слайд 34Adjustable-Rate Mortgages
Payment Cap – sets dollar limit on how much
the monthly payment can increase during any adjustment period.
If
interest rates go up, the monthly payment may be too small to cover the interest due.
This results in negative amortization. The unpaid interest is added to the unpaid loan balance, increasing its size.
Слайд 35Adjustable-Rate Mortgages
ARM Innovations:
Convertible ARM – convert traditional ARM to a
fixed rate loan during 2nd – 5th years.
Reduction-option ARM –
one-time optional interest rate adjustment to market interest during 2nd – 6th years.
Two-step ARM – interest rate is adjusted at end of 7th year, then constant for life.
Price level adjusted mortgage – low initial rate, payments and interest change with inflation.
Слайд 36Other Mortgage Loan Options
Balloon Payment Loan – small monthly payments
for 5-7 years, then entire loan due.
Graduated Payment Mortgage –
payments set in advance, rising for 5-10 years, then level off.
Growing Equity Mortgage – designed to let homebuyer pay off mortgage early.
Слайд 37Other Mortgage Loan Options
Shared Appreciation Mortgage – borrower receives below-market
interest rate and lender receives a portion of future appreciation.
Interest
Only Mortgage – combination of interest only payment at beginning, then pay both interest and principal for remainder of loan.
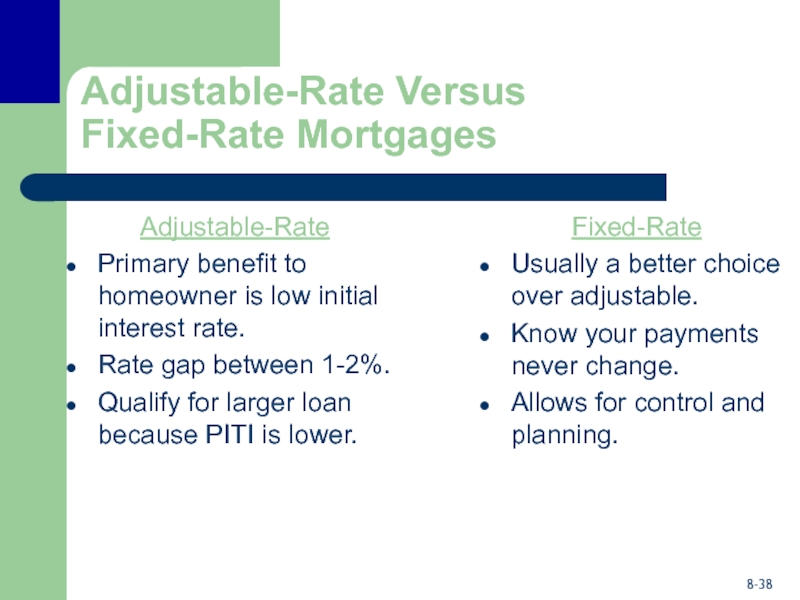
Слайд 38Adjustable-Rate Versus
Fixed-Rate Mortgages
Adjustable-Rate
Primary benefit to homeowner is low initial interest
rate.
Rate gap between 1-2%.
Qualify for larger loan because PITI is
lower.
Fixed-Rate
Usually a better choice over adjustable.
Know your payments never change.
Allows for control and planning.