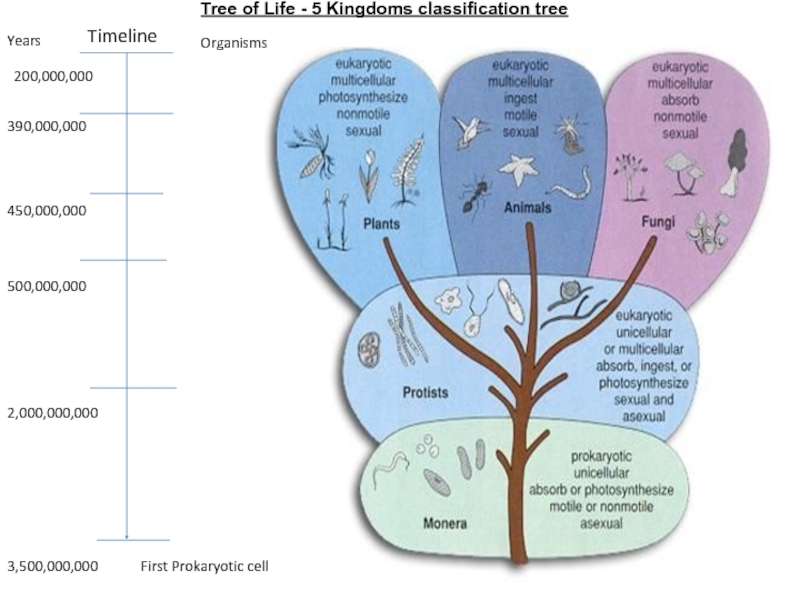
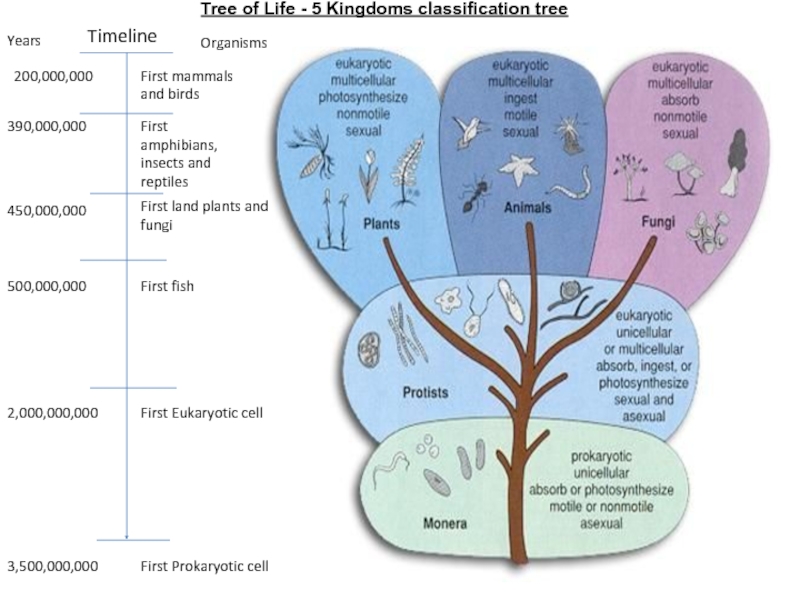
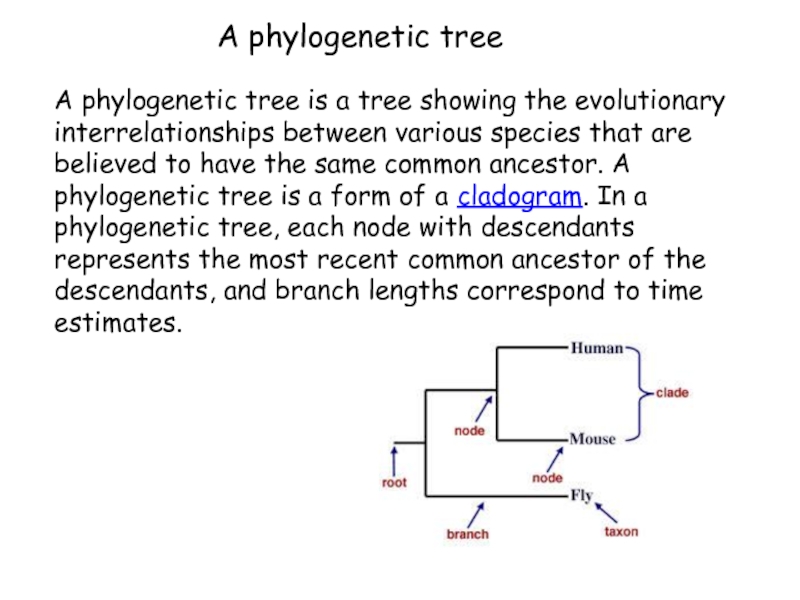
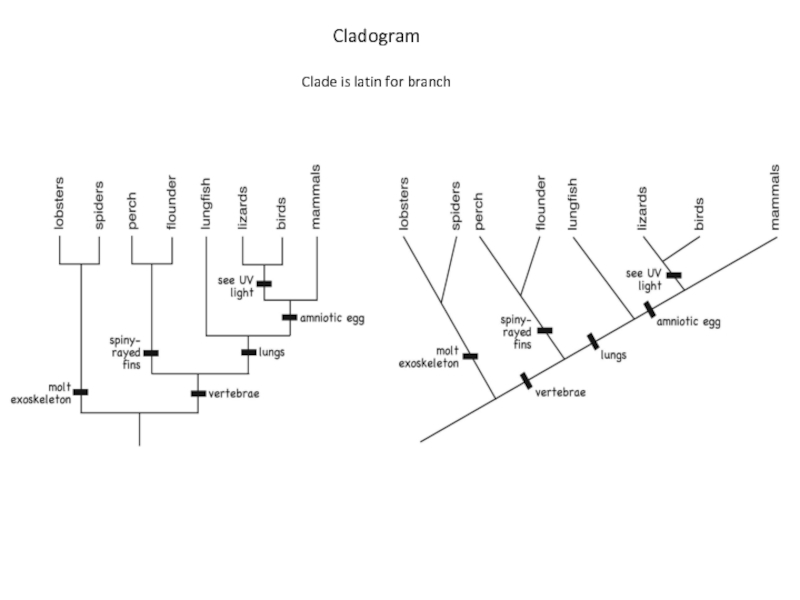
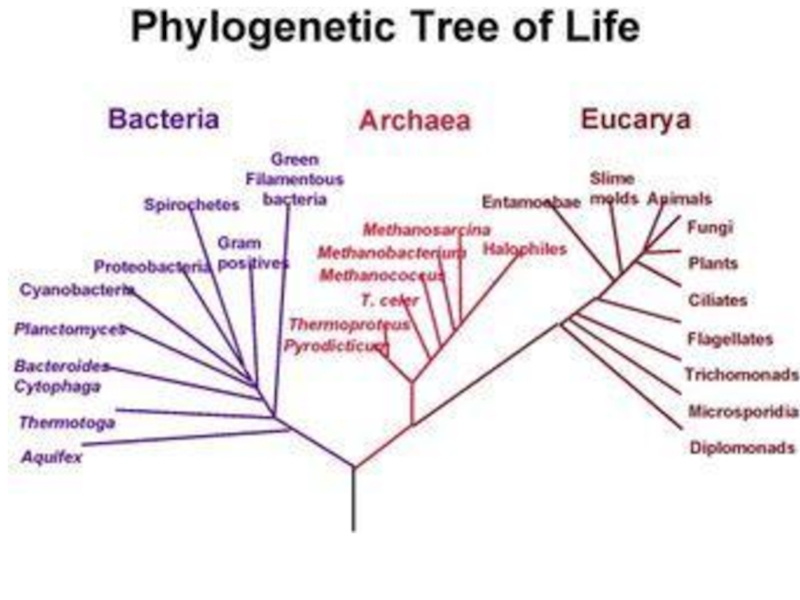
so that they can be studied more easily. The largest
groups in theclassification system for living things are called kingdoms.
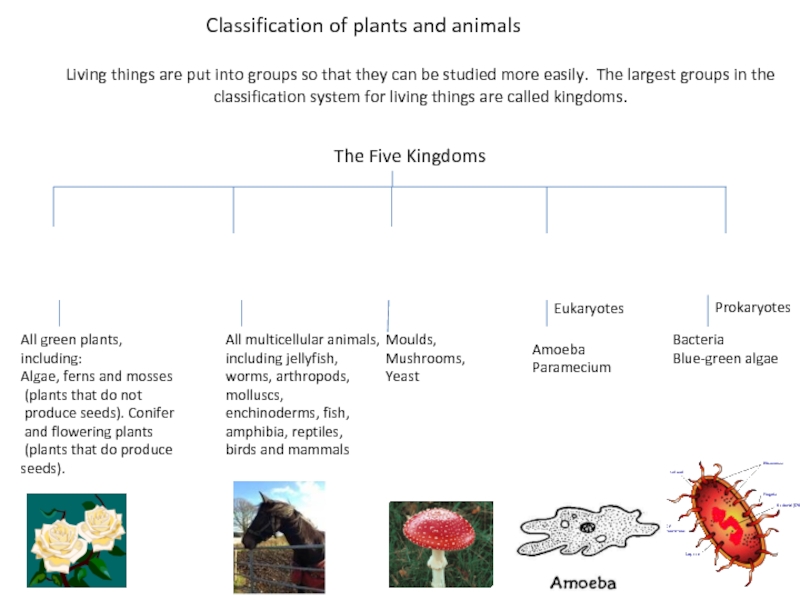
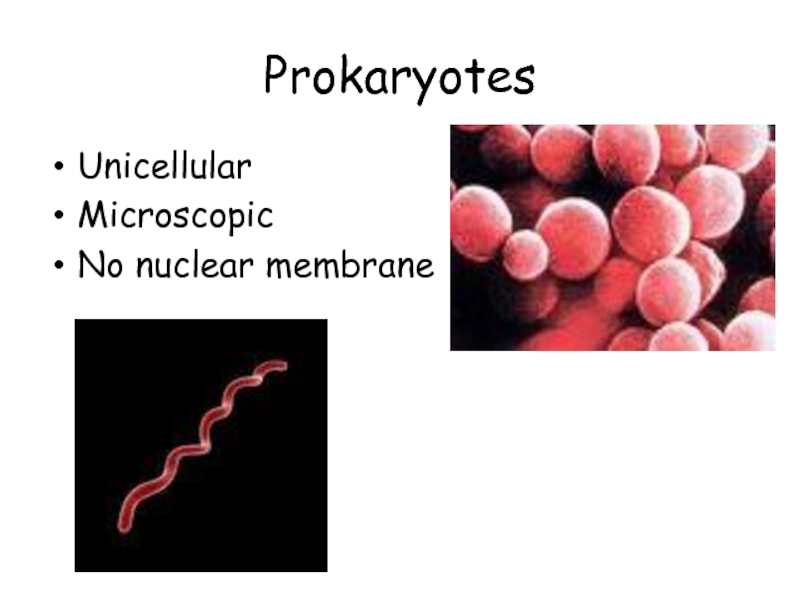
Prokaryotes
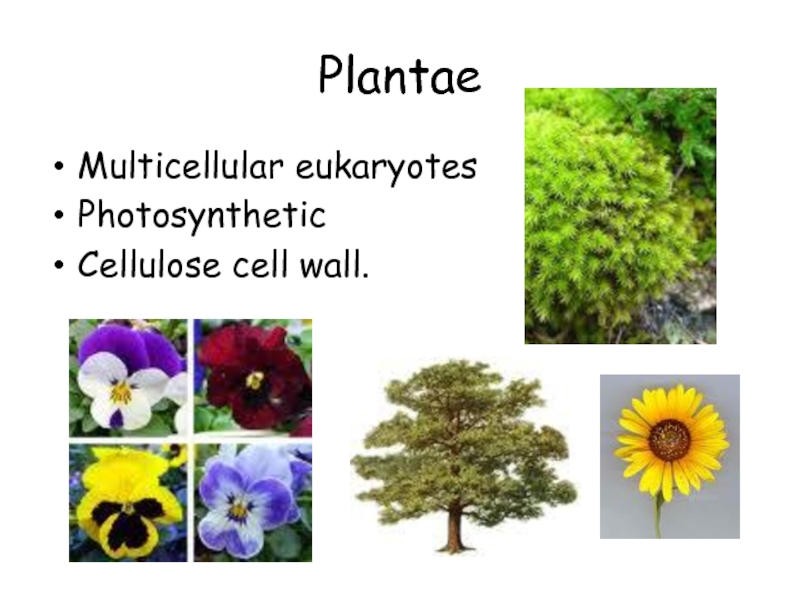
All green plants,
including:
Algae, ferns and mosses
(plants that do not
produce seeds). Conifer
and flowering plants
(plants that do produce
seeds).
All multicellular animals,
including jellyfish, worms, arthropods, molluscs, enchinoderms, fish,
amphibia, reptiles,
birds and mammals
Moulds,
Mushrooms,
Yeast
Bacteria
Blue-green algae
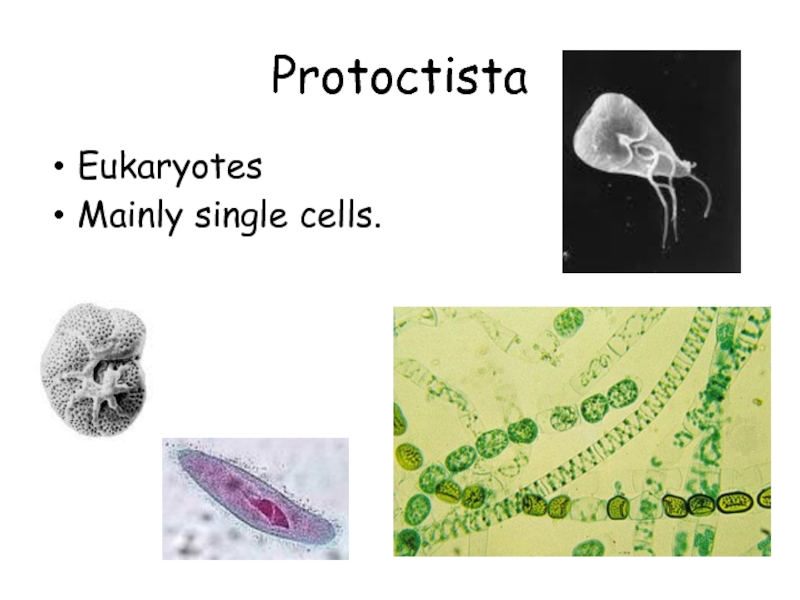
Amoeba
Paramecium
The Five Kingdoms
Eukaryotes