Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Comparative Politics
Содержание
- 1. Comparative Politics
- 2. Ways to classify states Democratic or non-democratic? Also
- 3. DemocraciesTremendous growth in numbers in 20th c.
- 4. Democracies not uniformKey Differences:* Presidential vs. Parliamentary
- 5. Democracies Share:A government based on the decisions
- 6. Ideas of Pericles (495-429 BC)
- 7. People & government connectedThrough free & fair
- 8. People & government connectedDemocracy means both: PROCEDURES –
- 9. U.S. Framers & DemocracyFear of majority tyranny
- 10. Five Dimensions to Examine1.) Participation: how people
- 11. Five Dimensions to Examine1.) Participation: how people
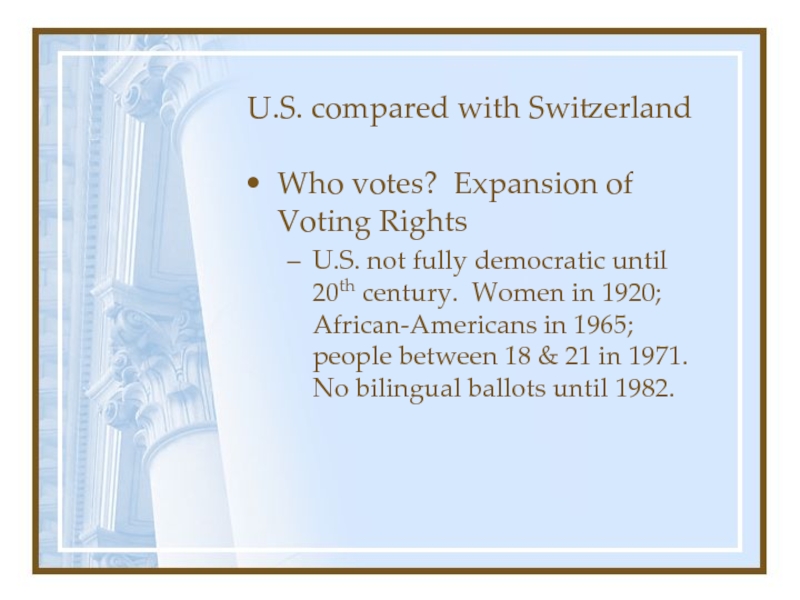
- 12. U.S. compared with SwitzerlandWho votes? Expansion of
- 13. U.S. compared with USSRWho votes? Expansion of
- 14. U.S. voting turnout Low turnout of electorate
- 15. U.S. compared with modern RussiaEffect of voting
- 16. 2.) PluralismHow does government advance tolerance for
- 17. Religious toleration In U.S., both Constitution & 1st
- 18. Religious toleration In Germany, Basic Law guarantees religious
- 19. 3.) DevelopmentalismHow does government ensure people can
- 20. U.S. compared with ArgentinaIn U.S., explicit socialization
- 21. 4.) Protection How does a government ensure democratic
- 22. U.S. and Britain comparedU.S. has written constitution
- 23. Challenges for democraciesDemocracies never guarantee provide absolute
- 24. U.S. rights during wartimeEspionage Act of 1917.Japanese-Americans’
- 25. British protections Britain relies on long-time practices
- 26. U.S. and Britain comparedDoes one type of
- 27. 5.) PerformanceHow well does government serve its
- 28. U.S. compared with India Factors include technological
- 29. U.S. compared with India Per capita incomeU.S. $40,100India $
- 30. U.S. compared with India Infant mortality rateU.S. 6.5 deaths
- 31. U.S. compared with India In fact, other measures
- 32. U.S. compared with India Also both countries have
- 33. Indian economic changesSince independence, a government-centered approach
- 34. Why the spread of democracy?Fatigue with authoritarian
- 35. In comparing democracies, remember that:Any discussion is
- 36. Скачать презентанцию
Ways to classify states Democratic or non-democratic? Also can study a state’s internal organization, since democracies vary greatly, as do non-democratic regimes
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 3Democracies
Tremendous growth in numbers in 20th c. Three waves of
growth:
End of WWI
End of WWII
1970s through 1990s
Now 121 electoral democracies
out of about 190 nation-states & 18 territories, according to Freedom House.Слайд 4Democracies not uniform
Key Differences:
* Presidential vs. Parliamentary government
* Ideologies (classical
liberalism vs. democratic socialism)
* Economic systems (capitalist vs. socialist)
* Types
of rights protected* Types of electoral systems
Слайд 5Democracies Share:
A government based on the decisions of the majority,
either directly or indirectly.
The people and government are connected both
thru the process (how decisions are made) and the outcome (what decisions are made).Слайд 6
Ideas of Pericles (495-429 BC)
Characteristics of democracies:
* Rule by
the people
* Equality under the law
* Pluralism: respect for diverse
viewpoints* Idea of a private domain
* High enough standard of living to secure people’s happiness
Слайд 7People & government connected
Through free & fair elections
Through access to
government officials
Through the types of policies enacted.
Слайд 8People & government connected
Democracy means both:
PROCEDURES – how decisions are
made, and
SUBSTANCE – what decisions are made (that is,
a check on what even a majority can do).Слайд 9U.S. Framers & Democracy
Fear of majority tyranny led to certain
choices to limit democracy:
Representative and not direct
Constitutional limits on
majority choices*Written constitution & rule of law
*Civil liberties protected in Bill of Rights
*Judicial review of actions of Congress & President
Слайд 10Five Dimensions to Examine
1.) Participation: how people select their government
officials & express policy preferences.
Franchise: who votes?
Effect: what issues are
subject to popular vote?Слайд 11Five Dimensions to Examine
1.) Participation: how people select their government
officials & express policy preferences.
On these issues, how does U.S.
compare with Germany?Слайд 12U.S. compared with Switzerland
Who votes? Expansion of Voting Rights
U.S. not
fully democratic until 20th century. Women in 1920; African-Americans in
1965; people between 18 & 21 in 1971. No bilingual ballots until 1982.Слайд 13U.S. compared with USSR
Who votes? Expansion of Voting Rights
Totalitarian Russia?
Women in 1917; national minorities in 1917 an 1922.
Слайд 14U.S. voting turnout
Low turnout of electorate complicates our ability
to claim strong participation element.
Average turnout of 50% in presidential
& 40% in midterm.1996: 49%
2000: 54.3%
2004: 59.6% highest since 1968
Слайд 15U.S. compared with modern Russia
Effect of voting on important issues
U.S.
has no national referendum or initiatives
RF uses both. Citizens can
review statutes & treaties. Слайд 162.) Pluralism
How does government advance tolerance for different ideas? Democracies
are composed of people of diverse viewpoints & backgrounds. How
are they accommodated? How are their interests represented?Слайд 17Religious toleration
In U.S., both Constitution & 1st Amendment’s Establishment Clause
restrict government involvement in religion. Framers’ intended to permit diverse
religious views to coexist in a democratic framework.Слайд 18Religious toleration
In Germany, Basic Law guarantees religious liberty. Government imposes
“church tax” to support recognized religions.
Intent is to strengthen civil
society. Some faiths not recognized or subsidized (Islam); others refuse state aid (Baptists & Methodists); and others discriminated against (Church of Scientology).Слайд 193.) Developmentalism
How does government ensure people can develop their full
potential?
Political socialization: process by which citizens learn basic political
values & beliefs, which enables them to act in the political system. Occurs in every political society.Sources: family, friends, political leaders, schools, interest groups.
Слайд 20U.S. compared with Argentina
In U.S., explicit socialization through school programs
like Character Counts & student dress codes.
Do they increase democratic
awareness?Supporters argue they do because they stress positive values & reject gang values.
Слайд 214.) Protection
How does a government ensure democratic values are protected?
How does it balance the need for liberty with counter
pressures for order & security?Compare U.S. & Britain.
Слайд 22U.S. and Britain compared
U.S. has written constitution and Bill of
Rights, and judicial review to enforce them.
Britain has no written
constitution or judicial review but has long tradition of rights & legal practices.Слайд 23Challenges for democracies
Democracies never guarantee provide absolute protection from government
control. No rights are absolute.
Wartime fears may drive majorities to
pass laws that restrict – and even criminalize – unpopular minorities.Слайд 24U.S. rights during wartime
Espionage Act of 1917.
Japanese-Americans’ internment during WWII.
Patriot
Act & other post 9/11 antiterrorism measures.
Courts often defer to
executive & legislative branches during crises.Слайд 25British protections
Britain relies on long-time practices & norms to
protect rights, as well as documents dating to the Magna
Carta in 1215.Also relies on the House of Commons – the people – to protect rights.
Слайд 26U.S. and Britain compared
Does one type of system better protect
citizens’ rights during national crises, when popular passions and fears
tend to drive national policy?Слайд 275.) Performance
How well does government serve its citizens’ material needs?
We can compare democracies in terms of socio-economic factors.
Text compares
U.S. & India on performance measure.Слайд 28U.S. compared with India
Factors include technological & industrial development,
natural resources, population size & other variables.
Population
U.S. 295,734,134
India 1,080,264,388
U.S.
ahead on many measures.Слайд 29U.S. compared with India
Per capita income
U.S. $40,100
India $ 3,100
Literacy rate above
age 15
U.S. 97%
India 59.5%
Men: 70% & Women: 48%
Слайд 30U.S. compared with India
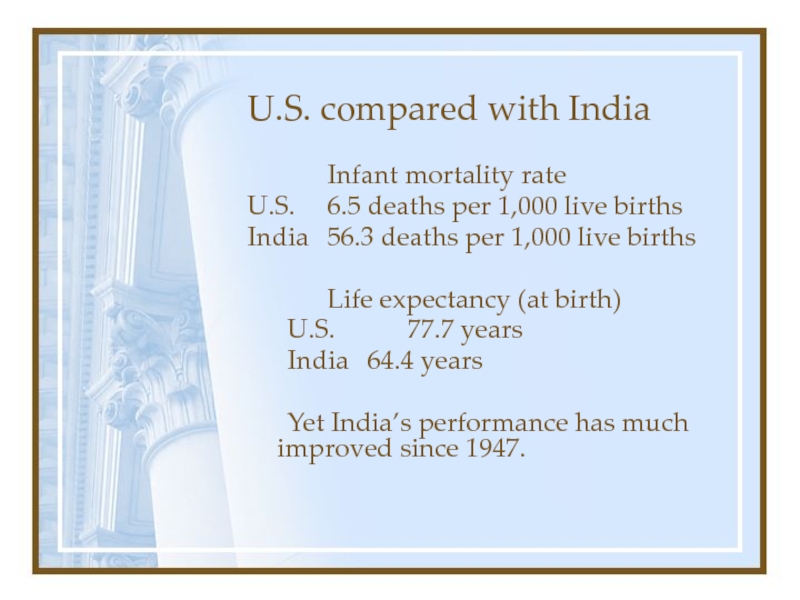
Infant mortality rate
U.S. 6.5 deaths per 1,000 live
births
India 56.3 deaths per 1,000 live births
Life expectancy (at birth)
U.S. 77.7 years
India 64.4
yearsYet India’s performance has much improved since 1947.
Слайд 31U.S. compared with India
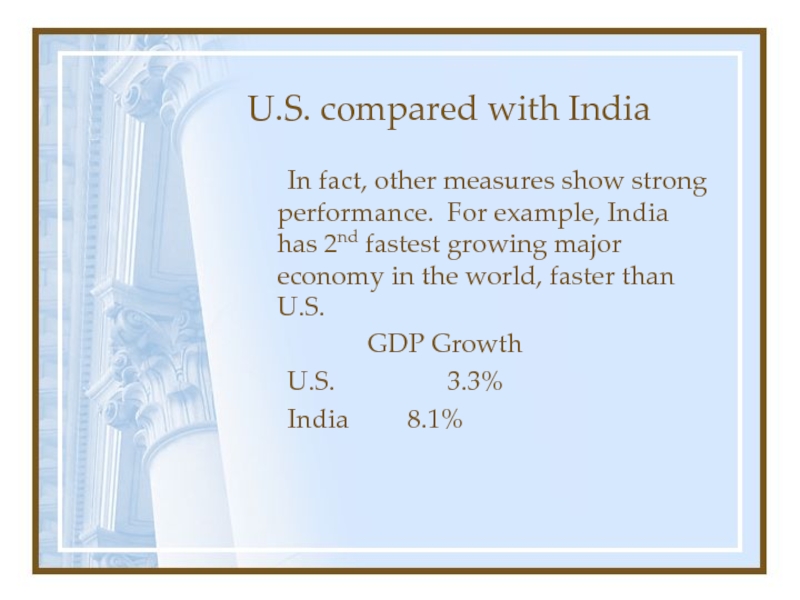
In fact, other measures show strong performance.
For example, India has 2nd fastest growing major economy in
the world, faster than U.S.GDP Growth
U.S. 3.3%
India 8.1%
Слайд 32U.S. compared with India
Also both countries have significant poor populations.
In U.S., top 1% of households own 38% of country’s
wealth, & top 20% own 83% of wealth.Population below poverty
U.S. 12%
India 25%
Слайд 33Indian economic changes
Since independence, a government-centered approach to economic policy
(railroads, aviation, energy, etc.).
Recently, however, some experiments with privatization &
foreign investment.Also family planning policies to control population growth.