Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Европейская интеграция и Европейский Союз (ЕС)
Содержание
- 1. Европейская интеграция и Европейский Союз (ЕС)
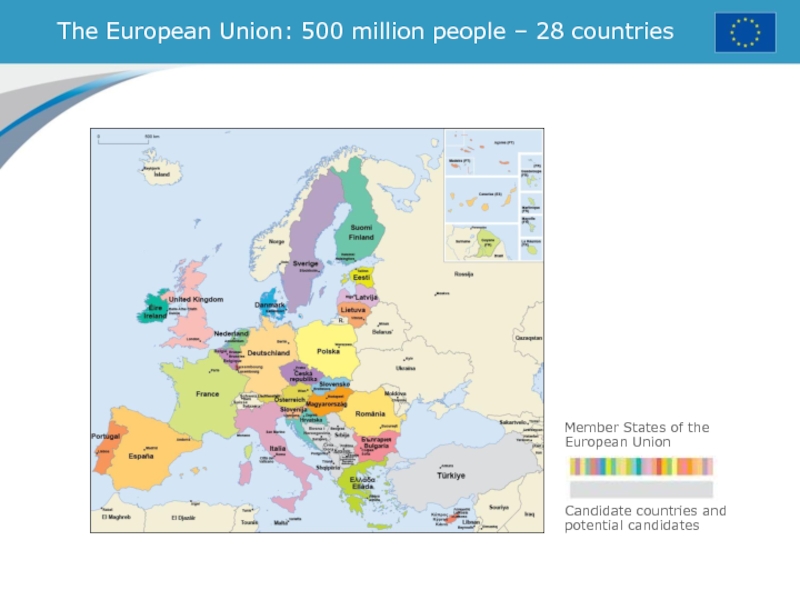
- 2. The European Union: 500 million people –
- 3. 24 official languages БългарскиČeštinadanskDeutscheesti keelΕλληνικάEnglishespañolfrançaisGaeilgehrvatskiItalianolatviešu valodalietuvių kalbamagyarMaltiNederlandspolskiportuguêsRomânăslovenčinaslovenščinasuomisvenska
- 4. The EU symbolsThe European flagThe European anthemThe euroEurope Day, 9 MayThe motto: United in diversity
- 5. Konrad AdenauerRobert SchumanWinston ChurchillAlcide De GasperiJean MonnetNew ideas for lasting peace and prosperity…Founders
- 6. Этапы европейской интеграции9 мая 1950г. - Декларация
- 7. Этапы европейской интеграцииПлан Шумана и ЕОУСИнститутыАвгуст 1952г.
- 8. «Каждый человек накапливает свой опыт самостоятельно с
- 9. Европейский Союз9 мая 1950г. - Декларация Шумана1951г.
- 10. Европейский СоюзЕвропейские сообщества - этапы интеграции 1.
- 11. Европейский СоюзЕвропейские сообщества - этапы интеграции4. Экономический
- 12. Европейский Союз1997г. Амстердамский договор2001г. Ниццкий договор2004г. Европейский
- 13. The treaties – basis for democratic cooperation
- 14. The EU Charter of Fundamental RightsBinding for
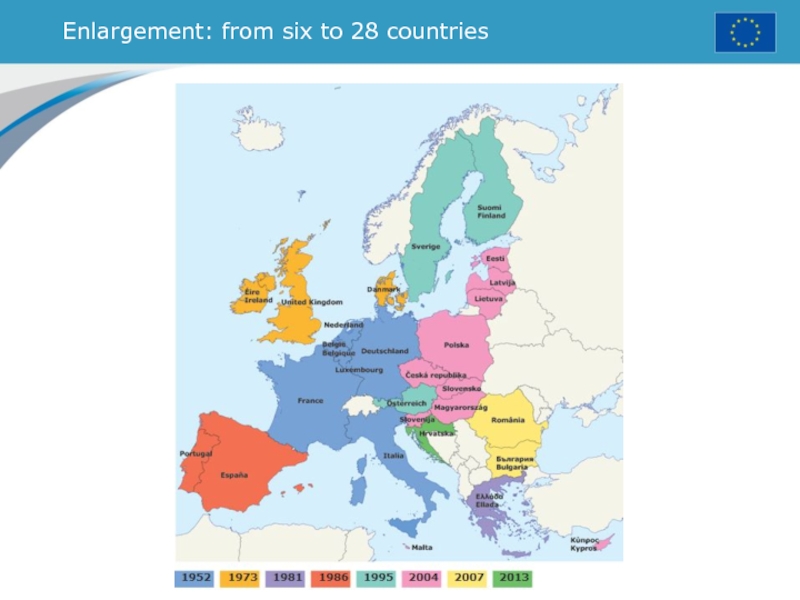
- 15. Enlargement: from six to 28 countries
- 16. Европейский СоюзРасширения ЕС. ЕС сегодня -
- 17. The big enlargement: uniting east and westFall
- 18. Candidate countries and potential candidates
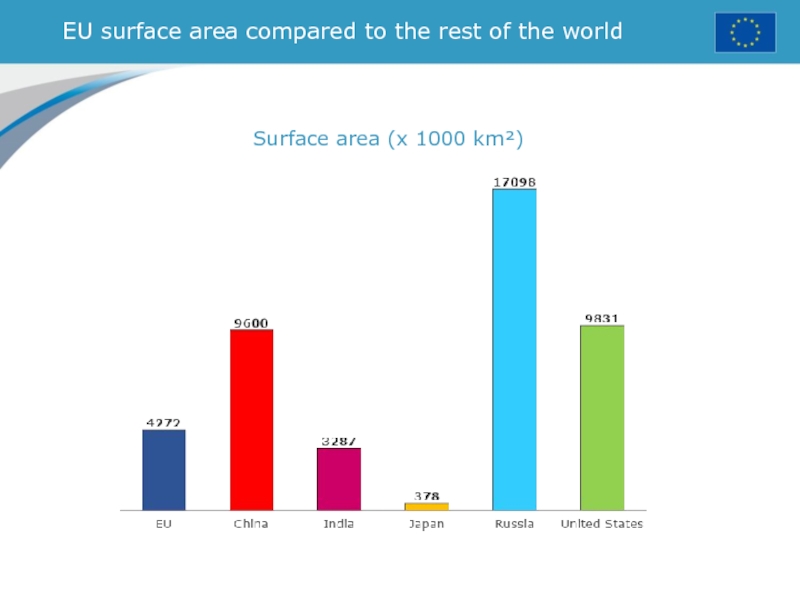
- 19. EU surface area compared to the rest of the worldSurface area (x 1000 km²)
- 20. EU population compared to the rest of the worldPopulation in millions (2015)
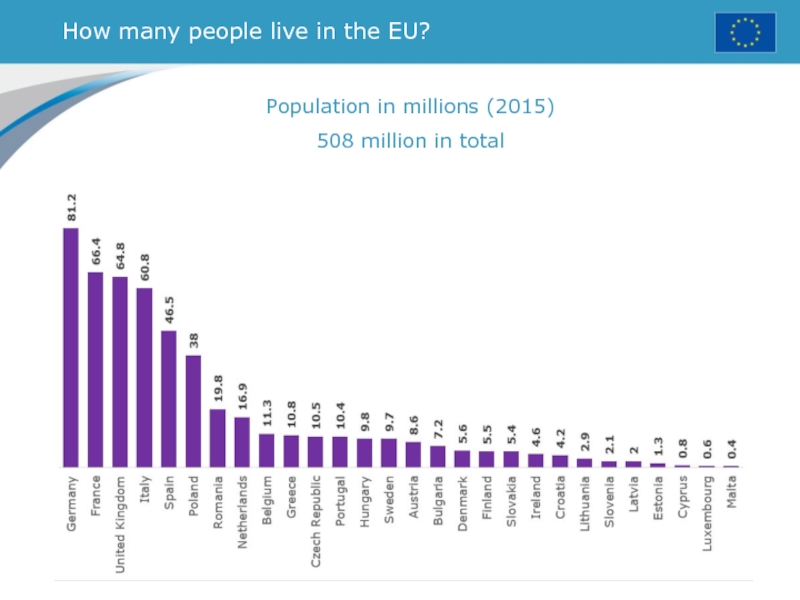
- 21. How many people live in the EU? Population in millions (2015)508 million in total
- 22. How rich is the EU compared to
- 23. GDP per inhabitant: the spread of wealthGDP
- 24. Solidarity in practice: the EU cohesion policy
- 25. The single market: freedom of choice (since
- 26. The euro – a single currency for
- 27. Free to move‘Schengen’No police or customs checks
- 28. An area of freedom, security and justiceEU
- 29. Energy sources in a changing worldFuel used
- 30. Research - investing in the knowledge societySpending on research and development in 2012 (% of GDP)
- 31. Going abroad to learnErasmus+Every year, more than
- 32. The EU is the biggest provider of
- 33. Three key playersThe European Parliament- voice of
- 34. The EU institutionsEuropean ParliamentCourt of JusticeCourt of
- 35. How EU laws are madeCitizens, interest groups,
- 36. The European Parliament – voice of the
- 37. The European political partiesNumber of seats in
- 38. Council of Ministers – voice of the
- 39. Council of Ministers – how they voteMost
- 40. Summit at the European CouncilHeld at least
- 41. A high representative for foreign affairs and
- 42. The European Commission – promoting the common
- 43. The Court of Justice – upholding the
- 44. The European OmbudsmanEmily O’ReillyThe European OmbudsmanInvestigates complaints
- 45. Спасибо за внимание !
- 46. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 324 official languages
Български
Čeština
dansk
Deutsch
eesti keel
Ελληνικά
English
español
français
Gaeilge
hrvatski
Italiano
latviešu valoda
lietuvių kalba
magyar
Malti
Nederlands
polski
português
Română
slovenčina
slovenščina
suomi
svenska
Слайд 4The EU symbols
The European flag
The European anthem
The euro
Europe Day, 9
May
The motto:
United in diversity
Слайд 5Konrad Adenauer
Robert Schuman
Winston Churchill
Alcide De Gasperi
Jean Monnet
New ideas for lasting
peace and prosperity…
Founders
Слайд 6Этапы европейской интеграции
9 мая 1950г. - Декларация Шумана
Баланс политических, экономических
и социальных мотивов
Политическое спонсорство США в деле улучшения отношений между
Францией и Западной Германией18 апреля 1951г. – Парижский договор и создание Европейского объединения угля и стали (ЕОУС)
Франция, ФРГ, Бельгия, Нидерланды, Люксембург, Италия
Наднациональность
Правосубъектность сообщества
Договор заключен на 50 лет. Срок действия истек в 2002г. После 2002г. функции ЕОУС перешли к ЕЭС
Отраслевая цель – создание общего рынка угля и стали (создан в 1953г.)
Слайд 7Этапы европейской интеграции
План Шумана и ЕОУС
Институты
Август 1952г. – начало работы
Высшего руководящего органа
Право инициативы
Совет министров
Отказ от принципа единогласия
Суд
Парламентская Ассамблея
Принципы
Превосходство институтов
Независимость
органов СообществаМежинституциональное сотрудничество в рамках единой системы принятия решений
Равенство государств
Слайд 8«Каждый человек накапливает свой опыт самостоятельно с самого начала. Одни
лишь институты становятся мудрее: они накапливают коллективный опыт. Благодаря этому
опыту и этой мудрости люди, действующие в рамках одних и тех же правил, не увидят изменений в их собственной натуре, но вместе с тем их поведение будет постепенно меняться»Жан Монне
Слайд 9Европейский Союз
9 мая 1950г. - Декларация Шумана
1951г. - Европейское объединение
угля и стали (ЕОУС)
Франция, ФРГ, Бельгия, Нидерланды, Люксембург, Италия
Наднациональность
Планы создания
Европейского оборонительного сообщества (ЕОС) и их провал (1954)1955г. Конференция в Мессине. Решение сконцентрироваться на экономических вопросах при развитии планов интеграции
1957г. - создание двух новых сообществ
Европейское экономическое сообщество (ЕЭС)
Европейское сообщество по атомной энергии (Евратом)
Центром интеграционных процессов стало ЕЭС
1965г. Договор о слиянии институтов трех Сообществ
Слайд 10Европейский Союз
Европейские сообщества - этапы интеграции
1. Зона свободной торговли
(1957-1968)
отмена таможенных пошлин, квот и других ограничений в торговле
между государствами-участниками сохранении автономии государств в таможенной и торговой политике по отношению к третьим странам
2. Таможенный союз (1968-1987)
введение вместо автономных средств торговой и таможенной политики общего таможенного тарифа и перехода к единой торговой политике в отношении третьих стран
3. Единый внутренний рынок (1987-1992)
свободное движение услуг, капиталов и рабочей силы
Слайд 11Европейский Союз
Европейские сообщества - этапы интеграции
4. Экономический и валютный союз
(1992–2002)
введение единой валютной и денежной политики ЕС с заменой
национальных валют единой валютой – Евро1986г. - Единый европейский акт – план перехода к Единому внутреннему рынку
1993г. Маастрихтский договор
Появление Европейского Союза
Европейский Союз
Первая опора - 3 Сообщества (ЕЭС, Евратом, ЕОУС)
Вторая опора - Общая внешняя политика и политика в области безопасности (ОВППБ)
Третья опора - Сотрудничество в области юстиции и внутренних дел
Слайд 12Европейский Союз
1997г. Амстердамский договор
2001г. Ниццкий договор
2004г. Европейский конституционный договор (Европейская
конституция)
2005г. - на референдумах во Франции и Нидерландах Европейский конституционный
договор отвергнут2007г. Лиссабонский договор (Договор о реформе)
1 декабря 2009г. - Лиссабонский договор вступил в силу
Упраздение «опорной» конструкции ЕС
Правосубъектность ЕС
Постоянный председатель Европейского Совета (избирается главами государств и правительств стран-членов ЕС на срок в два с половиной года)
Верховный представитель Союза по иностранным делам и политике безопасности
European External Action Service (Европейская служба внешнеполитических действий)
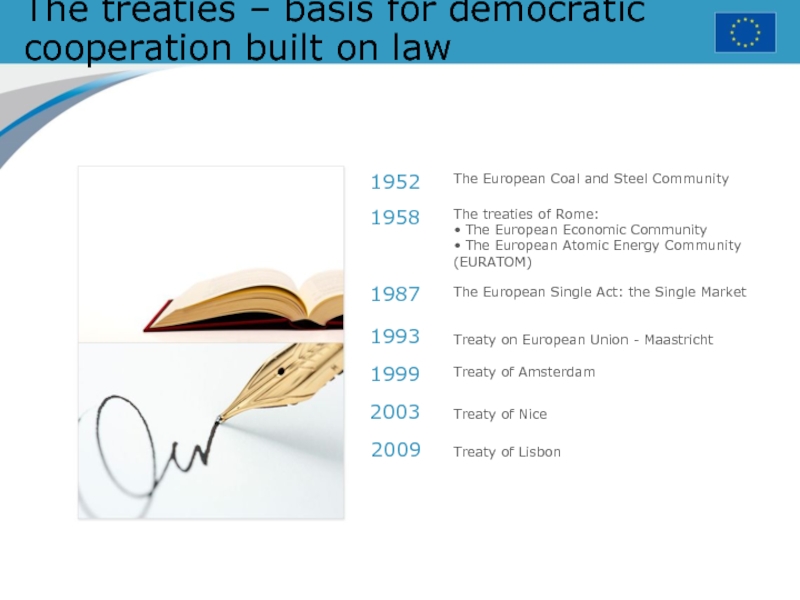
Слайд 13The treaties – basis for democratic cooperation built on law
The
European Coal and Steel Community
The treaties of Rome:
• The European
Economic Community• The European Atomic Energy Community
(EURATOM)
The European Single Act: the Single Market
Treaty on European Union - Maastricht
Treaty of Amsterdam
1952
1958
1987
1993
1999
2003
Treaty of Nice
2009
Treaty of Lisbon
Слайд 14The EU Charter of Fundamental Rights
Binding for all the EU's
activities
54 articles under 6 titles:
Freedoms
Equality
Solidarity
Citizens’ rights
Justice
Dignity
Слайд 16Европейский Союз
Расширения ЕС. ЕС сегодня - это 28 стран-членов
Страны-учредители:
Франция, ФРГ, Бельгия, Нидерланды, Люксембург, Италия
1973г. - Великобритания, Дания, Ирландия
1981г.
- Греция1986г. - Испания, Португалия
1995г. Швеция, Финляндия, Австрия
2004г. Эстония, Латвия, Литва, Польша, Чехия, Словакия, Венгрия, Словения, Кипр, Мальта
2007г. - Болгария, Румыния
2013г. - Хорватия
На сегодняшний день ЕС рассматривает как кандидатов на вступление Македонию, Черногорию, Сербию, Албанию и Турцию
ЕС также рассматривает как потенциальных кандидатов на вступление Боснию и Косово (частично признанное государство )
Слайд 17The big enlargement: uniting east and west
Fall of Berlin Wall
– end of Communism
EU economic help begins: Phare programme
Criteria set
for a country to join the EU:• democracy and rule of law
• functioning market economy
• ability to implement EU laws
Formal negotiations on enlargement begin
Copenhagen summit agrees to a big enlargement of 10 new countries
Ten new EU members: Cyprus, Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Slovakia, Slovenia
1989
1992
1998
2002
2004
2007
Bulgaria and Romania join the EU
2013
Croatia joins on 1 July
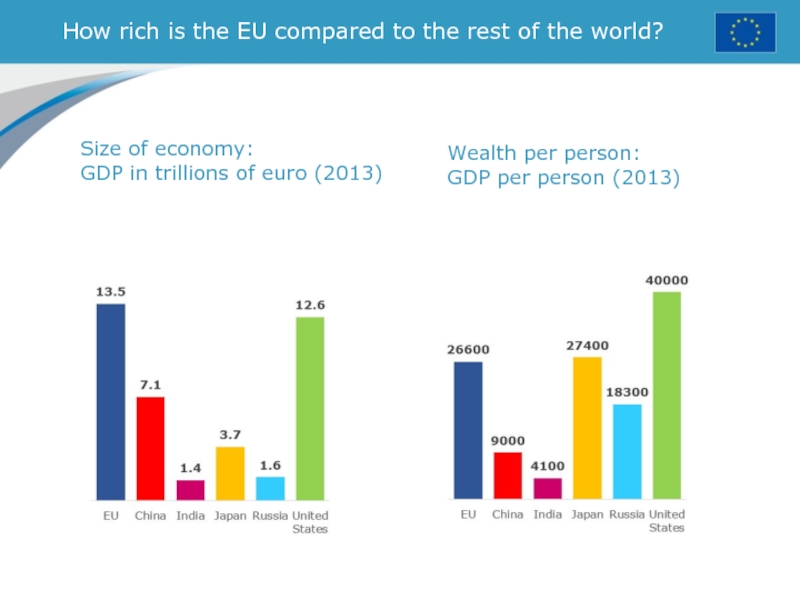
Слайд 22How rich is the EU compared to the rest of
the world?
Size of economy:
GDP in trillions of euro (2013)
Wealth
per person: GDP per person (2013)
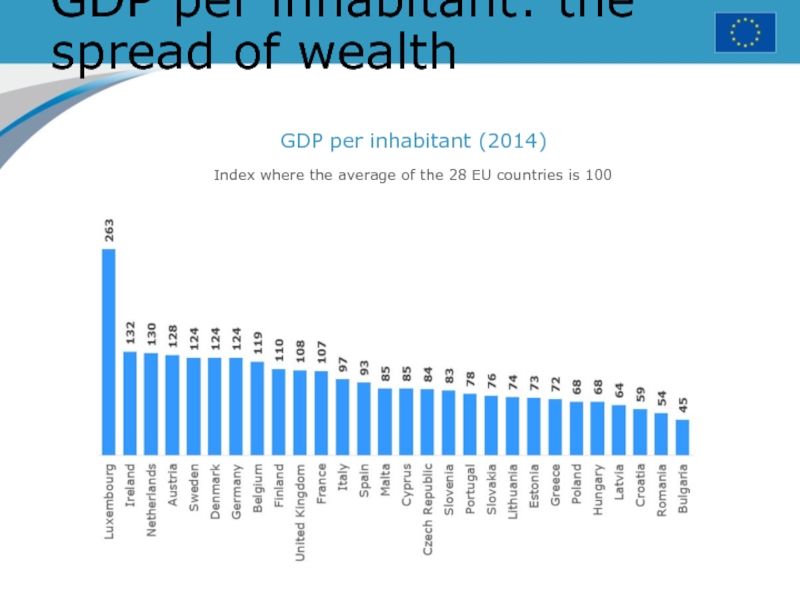
Слайд 23GDP per inhabitant: the spread of wealth
GDP per inhabitant (2014)
Index
where the average of the 28 EU countries is 100
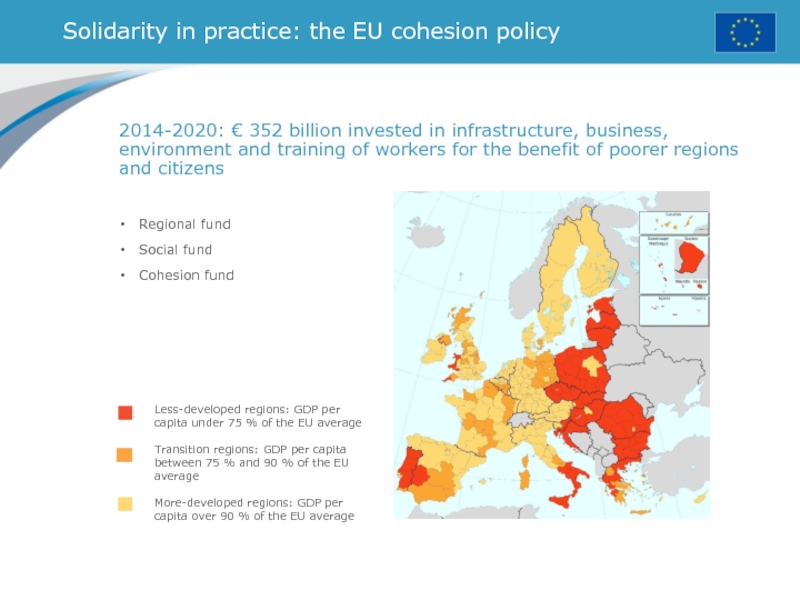
Слайд 24Solidarity in practice: the EU cohesion policy
Regional fund
Social fund
Cohesion
fund
Less-developed regions: GDP per capita under 75 % of the
EU averageTransition regions: GDP per capita between 75 % and 90 % of the EU average
More-developed regions: GDP per capita over 90 % of the EU average
2014-2020: € 352 billion invested in infrastructure, business, environment and training of workers for the benefit of poorer regions and citizens
Слайд 25The single market: freedom of choice (since 1993)
The single market
has led to:
significant reductions in the price of many products
and services, including airfares and phone callsmore choice for consumers
2.8 million new jobs
Four freedoms of movement:
goods
services
people
capital
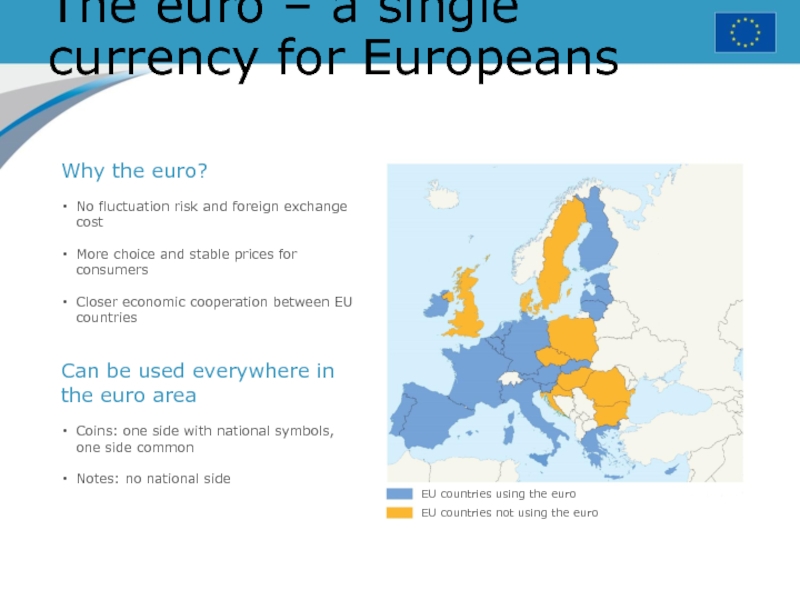
Слайд 26The euro – a single currency for Europeans
EU countries
using the euro
EU countries not using the euro
Why the euro?
No
fluctuation risk and foreign exchange costMore choice and stable prices for consumers
Closer economic cooperation between EU countries
Can be used everywhere in the euro area
Coins: one side with national symbols, one side common
Notes: no national side
Слайд 27Free to move
‘Schengen’
No police or customs checks at borders between
most EU countries
Controls strengthened at the EU’s external borders
More
cooperation between police from different EU countriesBuy and bring back any goods for personal use when you travel between EU countries
Слайд 28An area of freedom, security and justice
EU Charter of Fundamental
Rights
Joint fight against terrorism
Cooperation between police and law-enforcers in
different EU countriesCoordinated asylum and immigration policies
Civil law cooperation
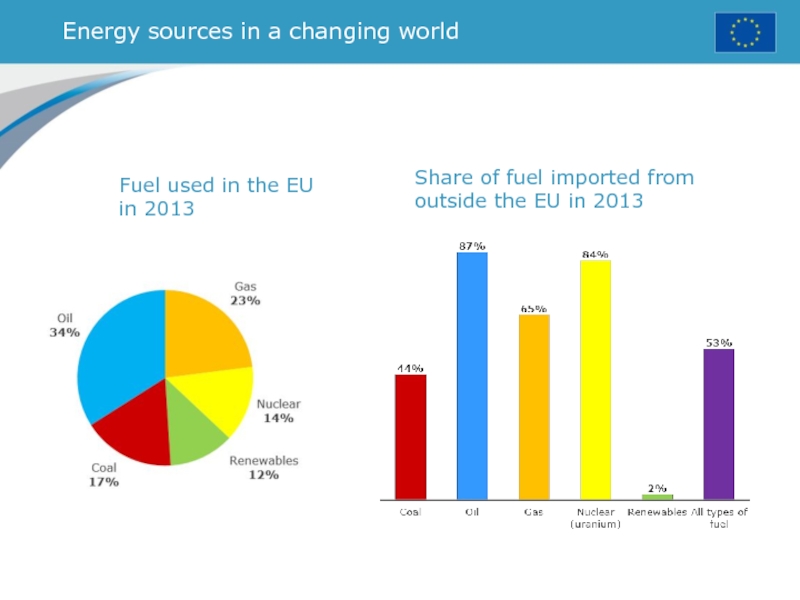
Слайд 29Energy sources in a changing world
Fuel used in the EU
in 2013
Share of fuel imported from outside the EU in
2013Слайд 30Research - investing in the knowledge society
Spending on research and
development in 2012 (% of GDP)
Слайд 31Going abroad to learn
Erasmus+
Every year, more than 400 000 young
people study or pursue personal development in other European countries
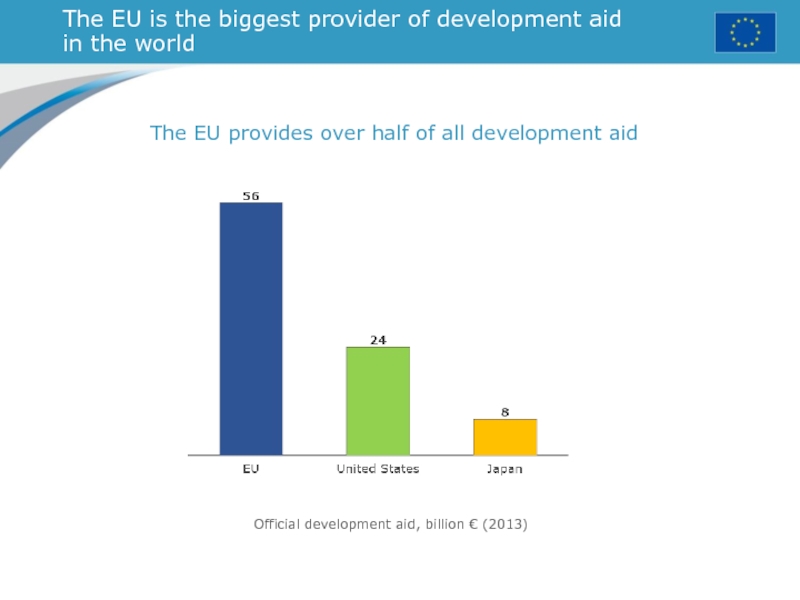
with the support of the EU’s Erasmus+ programme for education, training, youth and sport.Слайд 32The EU is the biggest provider of development aid in
the world
The EU provides over half of all development aid
Official
development aid, billion € (2013)Слайд 33Three key players
The European Parliament
- voice of the people
Martin Schulz,
President of the European Parliament
The European Council and the Council
-
voice of the Member StatesDonald Tusk, President of the European Council
The European Commission
- promoting the common interest
Jean-Claude Juncker, President of the European Commission
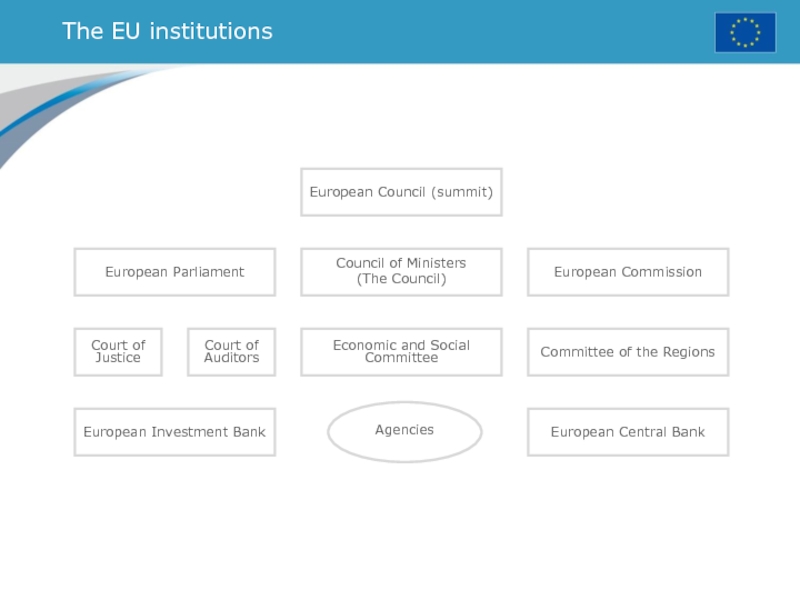
Слайд 34The EU institutions
European Parliament
Court of Justice
Court of Auditors
Economic and Social
Committee
Committee of the Regions
Council of Ministers
(The Council)
European Commission
European Investment Bank
European
Central BankAgencies
European Council (summit)
Слайд 35How EU laws are made
Citizens, interest groups, experts: discuss, consult
Commission:
makes formal proposal
Parliament and Council of Ministers: decide jointly
National or local authorities: implement
Commission and Court of Justice: monitor implementation
Слайд 36The European Parliament – voice of the people
Number of members
elected in each country
Decides EU laws and budget together
with the Council of MinistersDemocratic supervision of all the EU’s work
Austria - 18
Belgium - 21
Bulgaria - 17
Croatia - 11
Cyprus - 6
Czech Republic - 21
Denmark - 13
Estonia - 6
Finland - 13
France - 74
Germany - 96
Greece - 21
Hungary - 21
Ireland - 11
Italy - 73
Latvia - 8
Lithuania - 11
Luxembourg - 6
Malta - 6
Total - 751
Netherlands - 26
Poland - 51
Portugal - 21
Romania - 32
Slovakia - 13
Slovenia - 8
Spain - 54
Sweden - 20
United Kingdom - 73
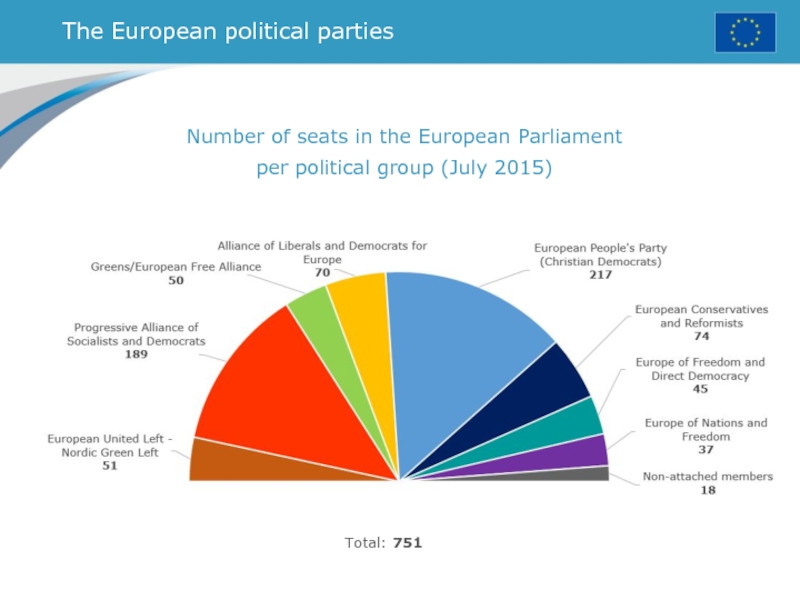
Слайд 37The European political parties
Number of seats in the European Parliament
per political group (July 2015)
Total: 751
Слайд 38Council of Ministers – voice of the Member States
One minister
from each EU country
Presidency: rotates every six months
Decides EU laws
and budget together with ParliamentManages the common foreign and security policy
Слайд 39Council of Ministers – how they vote
Most decisions in the
Council are taken by ‘double majority’.
A decision must have
the support of at least: • 55 % of Member States (16 countries)
• Member States that represent 65 % of the EU’s population
Слайд 40Summit at the European Council
Held at least 4 times a
year
Sets the overall guidelines for EU policies
President: Donald Tusk
Summit of
heads of state and government of all EU countries
Слайд 41A high representative for foreign affairs and security
Double role:
chairs
meetings of the Foreign Affairs Council
Vice-President of the European Commission
Manages
the common foreign affairs and security policyHead of the European External Action Service
Federica Mogherini
Слайд 42The European Commission – promoting the common interest
28 independent members,
one from each EU country
Proposes new legislation
Executive organ
Guardian of the
treatiesRepresents the EU on the international stage
Слайд 43The Court of Justice – upholding the law
28 independent judges,
one from each EU country
Rules on how to interpret EU
lawEnsures EU countries apply EU laws in the same way
Слайд 44The European Ombudsman
Emily O’Reilly
The European Ombudsman
Investigates complaints about poor or
failed administration by the EU institutions
For example: unfairness, discrimination, abuse
of power, unnecessary delay, failure to reply or incorrect proceduresAnyone in the EU can make a complaint